English |
Key |
Figure |
>Top 0. Introduction:
- This may be the last lecture at Tokyo Institute of Technology, so I made the best last message to the audience. The lecture was made in English, as several foreign students are included.
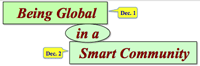
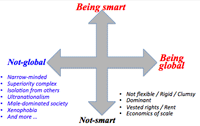
- Being global and being smart have similar background; to pursue smartness, people need to be global, conversely global mind needs to be smart.
|
 |
>Top 1. Changes of Decades:
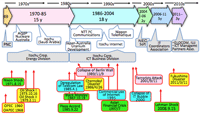
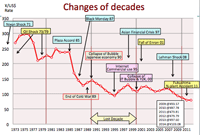
- Major changes occur in almost every decade: here is the world epoch-making events occurred in political, economical, and energy issues.
- The background is the changes of exchange rate Japanese ¥ per US$. After the WWII, the rate was fixed at ¥360/US$1 under the frame of Breton-Woods Agreement in 1944/7. (New Hampshire, US)
- Political events: Berlin wall, 9.11
- Economical events: Nixon shock, Black Monday, Plaza Accord, Asian Financial crisis, Lehman shock
- ICT events: Deregulation of telecom, Internet, IT bubble
- Energy events: OPEC/OAPEC, Oil shock, Chernobyl, Fukushima
|
|
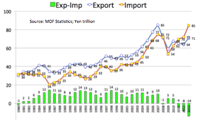
>Top 2. Trade structure: of Japan
- Constant trade surplus of Japan since 1980-2008:
- ¥7T/2001 →¥10T/2007→-¥14T/2013 (¥1T≒$10B)
- Export structure has changed since Lehman shock in 2008.
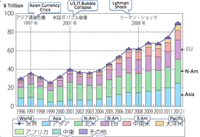
- Growth of Japanese direct investment since 2003; JDI in Asia.
- Growth of service industry
- Work force by industries: 2005
- Primary: 3.0M ( 5%)
- Secondary: 16.1M (27%)
- Tertiary: 41.3M (68%)
- Steady growth of knowledge industries: Knowledge & information, Medical & education, and Office services.
|
|
|
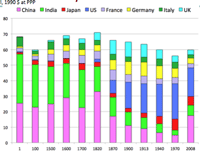
>Top 3. History of World GDP:
- Historical GDP by Angus Maddison, University of Groningen; The Economist (1-2008):
- based on 1990 US$ at ppp
- It should be said that China & India are recovering past glory of super power.
- Japan has been a substantial share in historical GDP; Edo, the feudalistic capital of Japan had been the biggest city worldwide.
|
 |
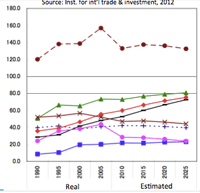
3a: World GDP & Export (2013):
- World GPD (ppp) and Export is changing: new reality of recent China and EU movement must be focussed.
- Establishing AIIB by 57 countries would play a new economic horizen:
- Japan is no more leading country in economic presence.
|
World GDP (ppp) 2013
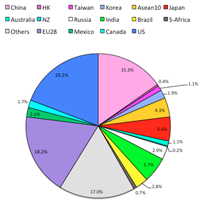
|
World Export (ppp) 2013
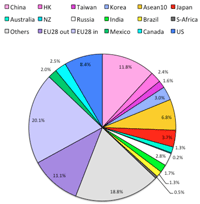
|
>Top
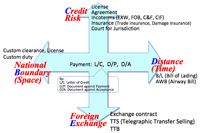
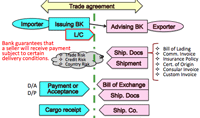
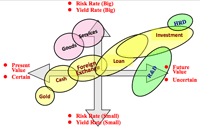
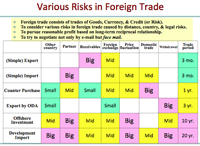
4. Why foreign trade?:
- Feature of foreign trade:
- Trading is not only goods, but currency and various risks.
- CDEF encirclement: Credit risk, Distance, Exchange, Boundary
- Risk/Yield vs. Present/Future risk:
- High risk high return trade vs. low risk low return trade.
- R&D seems most high risk & high return investment, but there is no alternative way; fostering human resources looks similar.
- Gold looks like the safest, but has negative interest.
- Letter of Credit is one of the established mechanisms to give creditability for both side of trade partners.
- Various risk of foreign trade: optimized portfolio of risk and prospect is most important.
|
|
|
>Top
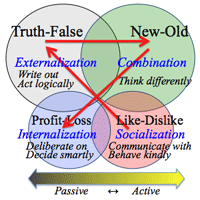
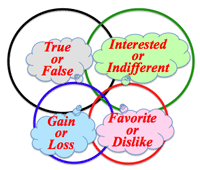
5. Herrmann model:
- Herrmann Model: "The Whole Brain Business Book, 1996"
- In the global world, we need to survive making full use of four parts of our brain;
- in making trade, in living well, in choosing our foods, in communicating with others, in solving the problems, & in mitigating troubles or anger.
- Each color comes from "Six Thinking Hats, 1986"
|
|
 |
>Top
6. Communication:
- Lingua franca:
- English is must, then Spanish because of easier pronunciation, then Chinese because of common use of characters for Japanese.
- Other foreign languages are also useful to learn a bit.
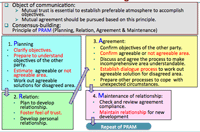
- Language is essential in negotiation: in particular PRAM (Planning, Relation, Agreement, & Maintenance) principle; the key is to:
- Confirm agreeable or not agreeable area.
- Establish dialogue process
- Maintain relationship for new development
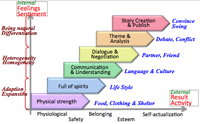
- Steps to global adaptability:
- Internal feelings or sentiment
- External result or activity
|
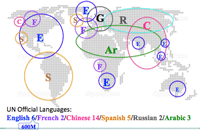
- Chinese: 1,400M
- English: 600M
- Spanish: 500M
- Arabic: 300M
- Russian: 200M
- French: 200M
|
|
>Top
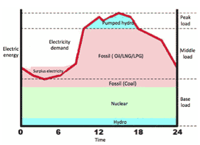
7. Energy issue in Japan:
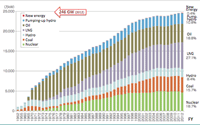
- Electric power plants capacity in Japan (952-2012):
- Actual power generation is different; e.g., nuclear after 3.11.
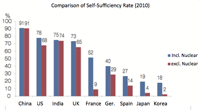
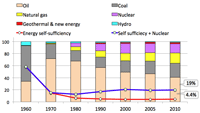
- Energy self-sufficiency rate:
- Japan only 4.4%, Germany 29%, US 91%
- Japan become 19% if nuclear is regard as domestic fuel from political viewpoint, though actually imported from overseas.
|
|
 |
>Top
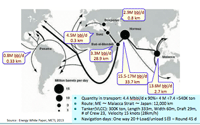
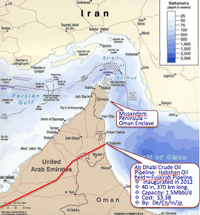
8. Choke point in the oil road:
- Located between Gulf of Oman and Persian Gulf.
- Route length: Me - Malacca strait - Japan: 12,000 km
- Navigation days: 20 days (one way) + 5 days (loading & unloading) = around 45 days.
- Import by Japan 4.4Mbbl/d x 90% = 4M /7.4 = 540 Kton
- Tanker (VLCC): 300Kton, 333 m length, 60 m width
- Passing Hormuz: 17 Mbbl/d, width of the strait 33.7 km; Av. 17 tankers/d; 80% of which to Japan.
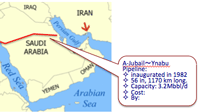
- Detour Pipelines: Al Jubail-Yanbu (Saudi); Habshan - Fujairah (UAE)
|
|
|
>Top
9. Smart Community:
- A smart community is a community where various next-generation technologies and advanced social systems are effectively integrated and utilized, including
- the efficient use if energy, utilization of heat and unused energy sources, improvement of local transportation systems and transformation of the everyday lives of citizens.
- Demand Response (DR): Impact of DR: by "Energy reform can relieve Japan" by Glocom FTM Forum, 2014 and "Reform of electric system" by
Norio Murakami report.
- Smart meter in 1M households: @¥10K x 1M = ¥10B
- Peak cut of 10A: 100V x 10A = 1kW
- Total Negawatt: 1kW x 1M = 1GW = 1 Nuclear Plant
- Compensation: @¥20/kWh x 1M =¥20M/h = ¥1.2B/60h
|

|
>Top
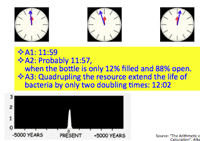
10. Tricky exponential growth:
- by "The Arithmettic of Growth: Methods of Calculationn " by Albert A. Bartlett"
- Bactria grow by division so that 1 bacterium becomes 2, the 2 divide to give 4, and so on.
- The number of grows exponentially with a doubling time of 1 minute.
- bacterium is put in a bottle at 11:00 and is is observed that the bottle is full of bacteria at 12:00.
- Q1: When was the bottle half-full?
- Q2: At what time would bacteria in the bottle first realize that they were running out of space?
- Q3: At 11:59, bacteria look offshore on the outer shelf and discovered three new empty bottle. The discovery quadruples the total space resource known to the bacteria. How long can the bacterial growth continue if the total space resources are quadrupled?
|
- Our dead and our unborn reside in the realm of chronos!
|
>Top
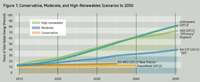
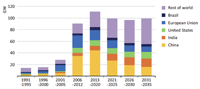
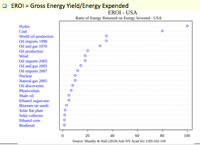
11. Sustainable energy:
- Forecast of sustainable energy: Long-term Forecast: by REN21 Report, 2014
- Positive prediction: by GEA (Global Energy Assessment), Greenpeace
- Moderate prediction: by IEA (International Energy Agency)
- Conservative prediction: by two major oil companies
- Power Generation ratio by sustainable energy: World 20%, EU 21%
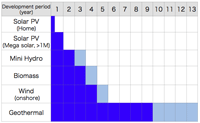
- Development period of sustainable energy:
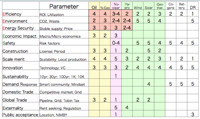
- Energy best mix:
|
|
|
>Top
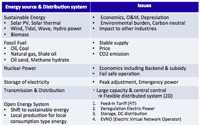
12. Open energy system:
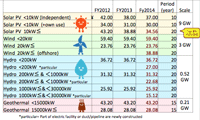
- Incentive of introduction of sustainable energy:
- Sustainable Energy had been about 10% before 3.11.
(9% of the above was Hydro. Solar/Wind/Geothermal/Biomass were only 1%).
- Sustainable Energy grows 13% annually since introduction of FIT in 2012;will grow 3.4 times of the present in ten years.
- To increase energy self-sufficiency rate (now 4%).
- To minimize import of fuel energy (about ¥3T) since 3.11
must be increased.
- To prevent the global warming:
- To curb CO2 emission by using more sustainable energy.
- To promote distributed power generation.
- To explore new energy source overseas.
- To activate regional economy; “Local production for local consumption”
- To accelerate innovation for smart community for international competitiveness.
- Feed-In Tariff system in Japan: since 2012/7
- by Agency of Natural Resources & Energy, METI
|
|
>Top
13. IOT and Demand response (DR):
- Internet of Things (IoT):
- New horizon of the Internet:
- PC: 1.9B (from iPad to mobile internet)
- Cellular phone: 5.3B (from mobile phone to smart phone)
- TV set (from AppleTV to smart TV)
- Smart Grit Terminal: smart house, smart meter, smart appliance, smart car (PHV, EV), smart parking
|
Development of IoT:
- 1G: visualization of electricity
- 2G: DR
- 3G: Watching service
- 4G: revolutionary applications expected.
|
>Top
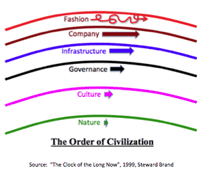
14. The order of civilization:
- "The Clock of the Long Now", 1999, by Steward Brand:
- All civilizations suffer shocks, yet only those that absorb the shocks survive.
- Components in a system that have different change rates and different scales of sizes.
- The combination of fast and slow components makes the system resilient.
- Fast is discontinuous, slow is continuous; (respond quickly or ignore the shock.)
|
 |
>Top
15. Heart-shaped solar field:
- Australian Solar Power Company (Conergy Australia) announced a plan to complete next year the world’s first heart-shaped solar field in the area of wild mangrove vegetation in New Caledonia.
- To produce enough energy to power 750 homes on the island, saving 2M tons of carbon dioxide in 25-year lifetime.
- Why the heart shape?
They wished to make a statement that solar project was friendly to the environment and a benefit to the island community.
|

- Only visible from the air: "The Heart of New Caledonia"
|