World of Multi-Civilization
Cat: HIS
Pub: 1997
#: 1710b
Koichi Takaya (高谷好一)
17719u/18227r
Résumé
Remarks
>Top 0. Preface:
- Universalism vs. Multi-civilizations.
- Three fallacies of universalism:
- Supremacy of economic development
- Suppression of discrete logics
- Destruction of environment
- Root of universalism:
- Industrial Revolution in UK
- Darwin's theory of evolution
- Modern world system
- World Unit:
- National boundaries have be determined by the conveniences of the great powers.
- National boundaries should reflect unique world views; considering
- ecology, livelihood and society of the region.
- be called as 'Soical-cultural-eco-dynamic geography'.
- >Top Ecological regions:
- ① Desert region:
- ② Grassland region:
- ③ Farmland region:
- ④ Forest region:
- ⑤ Sea area:
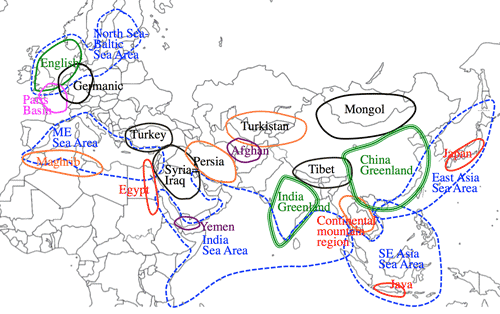
- Typical World Unit in Eurasia: <Fig.1>
- EA: East Asia Sea Area
- SE: South-East Asia Sea Area
- IN: Indian Ocean Area
- ME: Mediterranean Sea Area
- Eu: North Sea - Baltic Sea Area
- n: English Region
- p: Paris Basin Region
- g: Germanicic Region
0. 序文:
- 普遍主義 vs. 多文明主義
- 普遍主義の3つの誤り:
- 経済発展至上主義
- 個別論理の圧殺
- 環境破壊
- 普遍主義のルーツ:
- 英国の産業革命
- ダーウィンの進化論
- 近代世界システム
- 世界単位:
- 国境は列強の都合
- 本来は共通の世界観を共有する地理的範囲
- その地方の生態・生業・社会を重視
- Socio-cultural-eco-dynamic geography
- 生態地域区分:
- ①砂漠・②草原・③野(大農耕地)・④森・⑤海
- ユーラシアの代表的な世界単位:
- EA: 東アジア海域世界
- SE: 東南アジア海域世界
- IN: インド洋海域世界
- ME: 地中海海域世界
- Eu: 北海・バルト海世界
- n: イギリス世界
- p: パリ盆地世界
- g: ゲルマン世界
- <Fig.1> >Top Typical World Unit in Eurasia Continent:
>Top 1. World Regional Unit observed by on foot:
- Java World:
- Java Island is called 'Pearl in the Southern Sea'; rather dry volcanic island, which is suited to farming.
- Better hygienic environment with less harmful mosquitos.
- Indian styled single-storied house with earth floor, and fruits trees in the house.
- Development of irrigation and rice terraces enabling double (or even triple) cropping.
- Used to be an monarchy and court culture.
- Indian style meals: non-glutinous rice, steamed vegetables, and fried fish. (They don't east glutinous rice, raw vegetables, and boiled fish.)
- Continental Southeast Asia Mountainous Area (Forest world):
- Raw fish with fermented fish source.
- Shifting cultivation (slash & burn) of glutinous rice.
- Ten-several tens villages (mostly relatives)
- >Top Thai-Delta World:
- King is the operator of maritime commerce and port.
- Development of irrigation canals at the delta area (Chao Phraya river) by pressure of UK.
- Rama Ⅴ (Chulalongkorn, 1868-1910) reformed to be a modern nation, inducing a railway.
- Development of Chao Phraya river basin, as a successor of Ayutthaya kingdom (14-18C)converging Kingdom, southern theravada Buddhist, and Thai nation
- >Top Southeast Asia Sea World:
- Singapore, Jakarta, and Maraca as transit ports.
- Only port function, not expanding inland development.
- The function is distributed network; no center than the open sea.
- Port culture is open and migrating.
- >Top Chinese world:
- Chinese ecological unit:
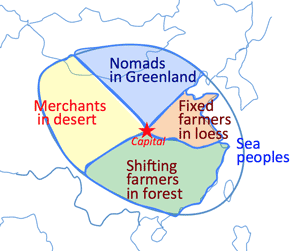
- Farmers in loess:
cultivating wheat in the Yellow River basin, and rice in the Yángzi River basin.
- Nomads in grassland:
grazing cattle according to seasons.
- Merchants in desert:
trading along oasis villages by trailing caravan by camels (now by trucks)
- Shifting farmers in forest:
farming by slash-and-burn in broadleaf evergreen and tropical rainy forests.
- Sea people in the East China Sea and the South China Sea:
Trading east-west coastal lines; formerly the basement of 'Wako' (Japanese pirates in 14-16C)
- the Imperial capital city: Chángān, Luòyáng
- located at the node of loess area, grassland, and oasis area.
- political logic of Confucianism; protecting farmers of loess area, excluding potential competitors.
- Kanji character is used as the common language for official documents and commerce.
- Recruitment of officials is not discriminated not by birth, but by Chinese higher officials examination (xiāngshì)
- Policy of governance of ethnic groups:
- Indirect governance by appointing the local head.
- Settlement by Han farmers; in Yúnnán, Chinese world extends in the valley area, and SE Asian mountainous world in hillslope area.
- Mixed blood child of Han father and minority mother tends to become minority group, due to minority preferential treatment in modern China.
1. 足で見つけた世界単位:
- ジャワ世界:
- "南海の真珠"。バリ島と並んでやや乾燥した火山島で隅々まで開墾
- 蚊が少なく衛生環境がよい
- インド風の平土間の家と屋敷林の果樹
- 潅漑・水田(棚田)の整備と二期作(時に三毛作)
- かつては王制と宮廷文化
- インド風食事: ウルチ米の水炊き・煮野菜・魚のフライ(
モチ米・生野菜・煮魚は食べない)
- 大陸東南アジア山地世界 (森の世界):
- 生野菜・魚醤をつけて食べる
- 焼畑でのモチ米栽培
- 集落は十数〜数十戸 (集落が家族的)
- タイ・デルタ世界:
- 王は海商・港の経営者
- 英国の圧力下でデルタ開拓 (潅漑水路網)
- ラーマ5世 (1868-1910): 近代国家へ。鉄道建設。
- チャオプラヤ流域開発 (アユタヤ王国 14-18C の後継)
- 王・南方上座部仏教・タイ族(民族の創造)の三位一体。
- 東南アジア海域世界:
- シンガポール、ジャカルタ、マラッカの中継港として発展 (港文化)
- 内陸には広がらず、散在する港群のみ
- 勢力は分散的、中心は公海
- 港文化は移動的・開放的
- 中華世界:
- 生態単位:
- 黄土の農民:
黄河流域のムギ作地帯。
但し、揚子江デルタ地帯は稲作水田地帯
- 草原の遊牧民:
草を求めて季節的移動。
- 砂漠の商人:
オアシスの鎖は交易路。ラクダのキャラバン。今はトラック
- 森の焼畑民:
揚子江以南の照葉樹林・熱帯多雨林
- 東シナ海・南シナ海の海民:
東西交易の基地。倭寇の活躍地。
- 都城 (長安・洛陽):
- 黄土の農民、草原の武人、オアシスの商人の結節点に位置。
- 儒教による政治論理。圧倒的多数は黄土の農民で、その潜在的競争相手を叩くのが仁政。
- 漢字は官庁用語・商人間の共通語。中華分は漢字の通じる範囲。
- 中華世界の民は出自とは関係ない。科挙制度による人材登用。
- 華夷秩序:
- 羈縻(きび)政策。少数民族には土司など完全な間接統治方式。
- 漢族農民の開拓入植。雲南では、谷筋は中華世界、斜面は大陸東南アジア山地世界。
- 父親が漢族、母親が少数民族の子供達は少数民族を選択 (少数民族優遇措置)
>Top 2. Japan as a world unit:
- Japan world:
- Sea World:
- Japan belongs to a fringe country of Chinese World.
- Tairano Kiyomori (12C): promoted Japan-Sòng trade
- Ashikaga Yoshimitsu (15C): promoted Japan-Míng trade; TàiTáng rice, Zen priests, Japanese pirates (Wako)
- Order of Land World:
- Nobunaga/Hideyoshi/Ieyasu established the centralized country, by sword confiscation, immobilized farmers to the land, and expanded rice cultivation by irrigation, as well as making the village as the common destiny.
- In later Edo period, induced commercial crops such as cotton and mulberry. (Until then, Japan imported cotton and silk textiles from China paying by silver)
- Thereafter, realized National Isolation policy, backed by enhanced agricultural production.
- Japanese-Chinese World:
- Double centers of Japanese classical literature (Kokugaku) and Neo-Confuscianism developed by Zhū Xī in 12C (Shusi gaku)
- Since the end of Edo period;
'Reverence of the emperor, and expulsion of foreigners' policy changed to 'Reverence of the emperor, and opening of Japan' policy.
- After Meiji Restoration; 'Japanese spirit with the Western technology.'
- Sea people like Satsuma & Choshu won against Land people like Edo Shogunate. (Sea people were superior in information and arms.
- Modern Japan:
- Land people were based on farmers, while Sea people were industry and commerce.
- New type of people - residents in a modern apartment complex; no community sentiments with isolation and confidentiality
- Japanese tradition:
- self-sufficiency
- mutual aid
- Hollowing out of society:
- collapse of local community (security and mutual aid)
- increase of vicious crimes
2. 世界単位としての日本:
- 海の世界:
- 中華世界の縁辺。東夷の一つ。
- 平清盛 (12C): 日宋貿易
- 足利義満 (15C): 日明交流。貿易、太唐米、禅僧、倭寇
- 陸の世界の秩序:
- 信長・秀吉・家康による中央集権国家形成。刀狩り、農民の定着、潅漑稲作の拡充。村の運命共同体化。
- 江戸後期には江南の商品作物の導入。棉と桑の栽培 (それまでは綿製品・絹製品は輸入し、銀が流出)
- その後鎖国政策。農村を基盤に実力
- 日本型中華世界:
- 国学と朱子学の二焦点
- 幕末以降は、尊皇攘夷→尊皇開国
- 明治維新後は、和魂洋才。
- 薩長という海民が江戸幕府という農民型指導者に勝利 (海民は情報・武器で有利)
- 富国強兵。
- 現代日本
- 陸型日本は農業、海型日本は町工場と商店。
- さらにサラリーマン中心の団地族登場。共同体意識が希薄で孤立性・密閉性。
- 捨ててはならない伝統: (社会の空洞化)
- 自給自足の生き方
- 相互扶助の仕組み
- 社会の空洞化:
- 地域社会 (安全と相互扶助) の崩壊
- 凶悪犯罪の増加
>Top 3. Conceivable World Unit:
- Viewpoint of research of particular areas and distant view of wide area.
- Five categories of Eurasia:
Desert, Grassland, Field, Forest, and Sea area
- Desert area:
- Four Great Civilizations; Nile, Tigris-Euphrates, Indus, and Huàng Hé rivers.
- Chained oasis villages, trade centers, and walled cities; exchange of wealth and information
- Grassland area:
- located along the norther side of desert belt.
- unable cultivation due to lack of water; nomad people putting out cattle like sheep, goat, cow, horse, and camel.
- Cavalry corps with mobility and bow was strongest until the invention of firearms.
- Field area: expanded farmland
- Central part of China and India
- Mixed forest of deciduous trees and evergreen trees, developed about 2000 years ago.
- Better hygienic environment, and fertile soils.
- Enormous farmer population
- Forest area: area rejected human beings.
- Northern forest (Taiga) extending northern part of Eurasia, with coniferous trees and permafrost land.
- Tropical rainy forest extending Southeast Asia, with evergreen trees and harsh tropical disease, and man-eating animals
- Sea area: looks like a desert.
- convenient in transportation, enabling trading activities connecting sea ports.
- >Top Indian world - another Grassland world:
- Indian ecological unit: ① Deccan plateau, ②Indus dry valley, ③Ganges wet valley, ④East hills, ⑤West rainforest, ⑥North mountainous area
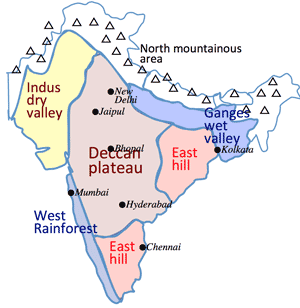
- Deccan plateau:
Vast basaltic plateau, suitable for millet cultivation other than rice due to small rainfall. Also producing area of cotton.
- Indus dry valley:
Less rainfall makes partly desert area.
Grazing of sheep and goats following poor grass.
- Ganges wet valley:
A large amount of rainfall, enabling rice cultivation (once a year).
- East hills:
Substantial rainfalls carried by wind from Bengal bay. Rice cultivation zone along valleys.
- West rainforest coast:
Steep mountainous area along Indian Ocean, belonging to tropical rain forest, producing forest products like pepper and cinnamon.
- North mountainous area: extending towards Himalaya mountains, producing finger millet (Eleusine coracana), wheat, and cattle breeding.
- Ethnic makeup:
- Northern: white Aryans
- Southern: black Dravidians
- North mountainous: Mongolians
- >Top Indian History:
- In Indus dry valley, since 5,000, particularly 2600-1600BC, Dravidian tribe cultivated wheat and grazed cows; Indus civilization started. (>Fig.1)
- In Ganges wet valley Munda tribe cultivated rice.
- Around 1800BC, equestrian Aryan tribe invaded the Indus dry valley, and controlled Dravidian cities, proliferating Brahmanism; Rigveda in Sanskrit, worship of nature gods.
- Features of Brahmanism is 'Varna' (caste); 1) Brahmins, priests, scholars, 2) Kshatriyas, rulers, warriors, 3) Vaishyas, merchants, 4) Sudras, laborers.
- Around 1000BC, Aryan tribe invaded Ganges wet valley, and controlled Munda tribe, who are near Southeast Asian, or Cambodian, and have a certain powers.
- 317-180BC Maurya Dynasty was established by Chandragupta, with peak period by Ashoka, who promoted Buddhism. The capital Pataliputra was located at the crossing point of Ganges wet valley and Indus dry valley, collecting population, arms and wealth.
- It was the age of hundred of schools and thoughts.
- Buddhism proliferated.
- Gupta Dynasty (320-550); established by Candragupta.
- Hinduism proliferated, particularly worshiped Shiva and Vishnu deities of Hinduism.
- Developed agriculture than Maurya Dynasty.
- Mughal Dynasty (1526-1858); Turkish-Islamic dynasty, with the capital at Delhi.
- Islam rulers prioritized to collect taxes than to covert people to Islam; thus most farmers remained Hindu.
- UK invaded in 18C and finally destructed Mughal Dynasty in 1858, tried to proliferate Christianity and British laws, which was repelled by Indian people.
- Typical Indian features:
- Order by Hinduism.
- Jati system; fixed occupation; blacksmith, laundryman, drummer, farmer, fisherman, worrier, monk, etc.
- Varna (caste) system: distinction of rank; Brahmin and Kshatriya as ruler, and Vaishya and Sudra (and also Dalit) as ruled.
- 'Jajmani system' (patron system); exchange of goods and services between higher castes and landless lower castes whose services are collectively ordered the village, which guarantees sustainable consideration for the lower castes.
- 'Bhakti faith'; worship particular gods (such as Shiva, or Vishnu) in Hindu.
- Even Christian is confined in a small box in Hindu world.
- >Top Islamic World:
- Islam unlike Buddhism or Christianity prescribes various guidelines in daily life; including taboos in food, or various rules in inheritance, and in commerce.
- >Top Syria-Iraq World:
- 'Fertile Crescent' is mountainous land with substantial rainfall and rich vegetation including apples, pears, wild wheat as well as wild sheep and goats, where agriculture and grazing started in the world for the first time.
- Sumer Civilization started after people shifted from rich mountainside to dried valley area; they dug wells and made irrigation system.
- About 4000BC Sumerian civilization started, collected wealth in lowland of Tigris and Euphrates rivers by trading; constructed walled cities, huge shrines, pyramids (ziggurat, stepped pyramid), made arms, and organized defense system
- Dug perennial wells in walled cities, having several ten meter vertical shaft and more than 100m inclined shaft, whose niches have lumps.
- The yield of wheat became several tens of seeds, due to irrigation system, fertilizer, and useful guidebook of farming. (Even medieval Europe's yield was about 4-5 times)
- The wave of civilization expanded from Mecca, Damascus, then to Bagdad; and the Early Modern age proliferated from Bagdad.
- In China, shifting the center from Chángān and Luòyáng, Early Modern age start from Jiāngnán, south of lower area of Yángzǐjiāng river.
- >Top Egyptian World:
- Since 5000BC agriculture along Nile river in Egypt had developed; now Cairo is a typical Islamic commerce city in Nile river delta area.
- Nile river is full of water due to whose origin is wet Africa.
- cultivated the field by plowing by cows. Annual flood of Nile river overflows all fields; after the water was drawn, they sewed and pushed in the soil by pushing around by sheep or goats.
- Threshing was done by rotating cows or donkeys around the round threshing floor; the separated stems become feed for cattle.
- All land and water belong to the King; people worked just like in national firm.
- Marine factor was added after construction of Greek styled Alexandria in 332BC by Alexander the Great.
- Then conquered by Roman Empire and Byzantine Empire.
- >Top Fatimid Dynasty:
- Islam (Shiah sect) penetrated and established Fatimid Dynasty (Calliphate) (909-1171), operating agency commerce at Cairo, also producing commercial crops as sugar cane and rice.
(source: Wiki)
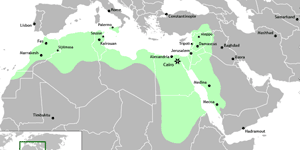
- >Top Aiyuubid Dynasty:
- Aiyuubid Dynasty (Sunni) (1169-1250) and Mamluk Sultanate (Sunni) (1250-1517) until Ottoman conquest in 1517.
- Mamluk Sultanate:
- Mamluk Sultanate bought eligible children from Turkey, Slav, and Europe and trained as Islamic military service men in typical merit system. Military general or even Sultanate (King) was selected among powerful Mamluk.
- Both Aiyuubid and Mamluk put emphasis on trading function in Indian Ocean and Mediterranean Sea.
- >Top Persian World:
- Persia is located at mountainous and hilly area about 1000m above sea level.
- Persia is Aryan tribe and Shiah sect in Islam.
- Unique Persian culture such as poet, picture, Zoroastrianism.
- In desert zone, there are different groups: 1)City residents (merchants), 2)Nomads, 3)Farmers.
- Farmers make small villages in mountainous area, cultivating wheat, etc using 'Qanat' (underground water channel). They settle down in village communities.
- Merchants and Nomads are migrating people between desert and grassland, maintaining a narrow strip of water relationship.
- >Top Turkish World:
- After decline of Seljuk Empire, and Seljuk Dynasty of Rum, In
13C Osman I invaded Anatoria peninsula, and established Bursa, NE of the peninsula in 1326 as the first capital, controlling east-west trade.
- The ancient city Bursa of the Ottoman Turks is called 'Yeşil Bursa' (Green Bursa), located in a steep valley covered by green trees, with surrounding green hills, contrasting with wide grey-brownish plain of Syria.
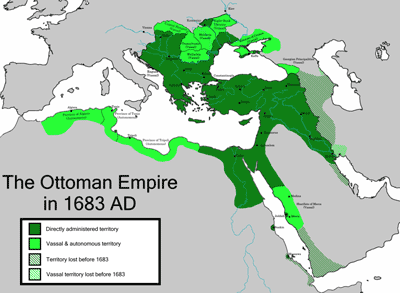
- In 1453, the Ottoman Turks conquered Constantinople, then the world largest city, changing its name to Istanbul. Since then the Ottoman Turks continued as the strongest empire for about 470 years.
- The Ottoman Empire is a flexible autocracy; allowing religious liberty, with Christians and Jews in the empire, who are recruited as the officials according to its merit system.
- But in the military sphere, they kept the centralized military organization which directly belonged to the Sultan.
- The title of the Ottoman Empire was called 'Shah-Han-Sultan, meaning King of Persia, Ruler of grassland, and Head of Islam
- Islamic World expanded twice; expanded from norther part of Africa up to Iran. And in 13-14C, Islam culture and commerce sphere expanded up to Southeast Asia, together with military expansion of Mongol and Turkish tribes. Turkish world was included in the Islamic culture in this second expansion.
- Turkey promoted modernization of Islamic culture, which is similar to those of Southeast countries.
- Other Desert and Grassland World Units:
- Maghrib World:
- The world of Berber tribe; settled down permanently, cultivating olive and wheat in farms of northern side of Atlas mountains, and also trading a frankincense.
- Yemen World:
- This country has exceptional substantial rainfall due to the wind from Indian Ocean and the high mountain at the tip of Arabian peninsula. This is another country called 'Happy Arabia' in the peninsula since the century of BC.
- Afghan World:
- The area is near Persia; people of this world has sufficient martial spirit.
- Pakistan is another world, which is different from this.
- Turkestan World:
- This comprises various oasis cities such as Samarkand or Tashkent, which function as core node connecting the commence road of the east and the west.
- Mongol World:
- This is a typical grassland world, which are nomads having strong cavalry corps. The strength was impaired by the development of firearms, but the martial spirit remains.
- Tibet World:
- This is a high-altitude Greenland world, adhering to Tibet Buddhism.
- Open communication with exterior worlds:
- Marco Polo (1254-1324): who wrote 'Devisement du monde', left Venetia, passing Turkey, Persia, Turkestan, arriving at the capital of Khubilai Khaan of Yuán Dynasty (1206-1368)
- Farmers return between summer field and winter field which are several km apart. Farmers have regular farming partners in remote area to do mutual support, or go to cities to work part-time in off-seasons.
- They like to go on a haji (pilgrimage) to Mecca or Karbala more than 1000km away. About 40-50 years ago, they traveled there by donkey or camel.
- Beduins feel that they don't want to continue stay long at the same place, which they feel gets dirty by such long staying.
- Islam could be said to be a system to secure travels; neither barriers, nor tax collection places in any travel route; conversely, there are mosques and lodges in many places for travellers.
- Sea World:
- As desert and grassland zone declined the route for travels in 16-17C, 'Age of Discovery' has come.
- >Top Indian Ocean World:
- Trade network beyond Indian Ocean, Arabian Sea, and Bengal Bay.
- Traded goods were silk and porcelain of China, food flavor of Southeast India, pepper of South India, ivory and gold of east coast of Africa.
- Islam merchants developed agent trading based on a small island (Eg. Zanzibar) of east coast of Africa, where less mosquitoes and better hygienic environment.
- At port cities, Islam culture prevailed; and mixture of not only race but also languages happened: Swahili was made as mixture of Arabic and local language of East Africa.
- Mombasa is located at southern coastal city of Kenya looks like that of Pakistan; and there were many people called Gujaraty, who came from Gujarat of West India.
- >Top Mediterranean Sea World:
- Mediterranean Sea World is smaller scale than Indian Ocean World. It functioned as a sea for the Orient.
- Around 3000BC, Phoenician had lived at Levant and Arvad located at the eastern end of the Mediterranean Sea, producing copper and glass product, being involved in various trading including their own products.
- Carthago and Greece appeared as a successor of Phoenicia.
- Carthago constructed triple layered walled city in a narrow peninsula of Tunis; the outer port is for commerce, and the inner one is for military base of about 200 galley warships.
- Galley Warship: (>Fig) has more than 100 oars of 2-3 layers for rowing. The bow was sharply covered by metal plate, intending to hurl itself to the enemy warship.
- The Mediterranean Sea had been a sea of industry, trade and war.
- After 10C Venezia became the main player of the sea.
- East and South of the Mediterranean Sea were occupied by the advanced Islam culture. North of the Sea was Europe, delayed area covered by forest. They traded metal and textile product from Islamic area, and timbers and slaves from Europe.
- Venezia initially functioned as hired soldiers for Byzantine Empire, involving to clean up the pirates. Thereafter, Venezia was involved to export timber (though the Pope embargoed timber to Islamic area), then started travel service (lodging and transport) particularly for the Crusades.
- 1204 expedition of the fourth Crusades; the target was changed to Constantinople of Byzantine Empire (Christian country) from Jerusalem.
- Venezia has no inland territory, having only small islands and ports of overseas settlements; mostly promoted trade and sometimes pirates activities using galley warships and sailing ships.
- Expansion of Inland Power:
- 1529 Paix de Cambrai (Paix des Dames)
- 1797 Napoleon occupied
- 1866 was annexed to Italy.
- >Top Viking Age 800-1050):
North Sea, Baltic Sea, & Norwegian Sea
- These are seas of Viking; in early modern age, it was the sea of Hanseatic League. Many rivers and lakes cause inland transportation inconvenient.
- 8-12C Age of Viking; Germanic farmers had settled at seashore and riverside, and expanded to do slash-&-burn agriculture, stock farming, fishery, hunting; also challenging trade and invasion with about 50 oarsmen and 20 sailors. Norsemen (Norse):
invaded Northern England and Sicily island, and battled with Venetia as hired soldier of Byzantine Empire.
- Baltic Viking: based on Gotland island in the Baltic Sea, and traded with Islamic merchants using Dnieper River and the Black Sea. (Lots of Arabic silver coins were unearthed from Gotland island.) Later, they built Kiev city.
- 13C Hanseatic League merchants:
based on Lübeck
port; trader of grain and timber from Russia, and salted fish meat and fish oil from Norwegian Sea.
- 16C Netherland grew, edging out Hanseatic League; thereafter English followed. Netherland imported raw wool from England and made woolen fabrics at Franders area (Bruges and Antwerp) and sold it all over Europe. Netherland was based in Amsterdam, which grasp the mastery of the sea rather than inland territory, becoming the world strongest maritime and naval country
- English imitates Netherland, emphasizing shipping industry, as well as developing textile industry and promoting the Industrial Revolution. They could transport enormous cargo and soldiers between distant places by power-driven vessels. The age shifted from Inland sea to Ocean.
- The developers of ocean were Islamic and Chinese merchants. Then, the main player changed to Spanish, Proteges, then Netherland, and English.
- >Top East Asian Sea World:
- At the coastline of East Asia Sea area, Japanese were main players. They lived by slush-and-burn farming, fishery, collection of aromatic incense, pearl collecting, and tortoise shell, as well as transported rice cultivated inland.
- In Sòng period, silk and porcelain were traded.
- In Míng period, tributary trade became main. In Míng and Qīng period, banned private overseas trade. Most activities in East Sea were promoted by Japanese pirates; most famous head was WángZhí (王直), having the base at Goto Islands of Nagasaki.
- 19C UK invaded this area; causing the Opium War (1840-42), the Arrow War, or the Second Opium War (1856-60); then Shànghái city was opened.
- After the collapse of Qīng Dynasty (1616-1912), Sea people increased based on Shanghai; the head was Jiǎng Jièshí of Zhèjiāng Province. While inland people, the head was Máo Zédōng, who established PRC in 1949.
- Since 1990s, Sea people recovered their influences in economy in costal zones such as Shànghái, Guǎngdōng, and Shēnzhèn.
- >Top Southeast Asian Sea World:
- This coastal zone of Malay language is called 'Sea Silk Road', usually excepting Thai, Vietnam, and Java. The population is rather dilute; involving slush-and-burn agriculture, collection of forest product, and fishery.
- 15-16C, Malacca Sultanate (1402-1511); composed of 1) Capital, 2) Malaysian villages, 3) Military port, 4) Sheik's dominated area (Arabic & Persian merchants), 5) vassal countries.
- When the first King Parmeswara, it became a vassal country of China. ZhèngHé visited here in his expedition. Many merchants from Ryukyu Islands to Egypt gathered here and communicated by over 80 different languages.
- The second King Iskandar converted to Islam.
- >Top Malaysian:
- have settled in Malay Peninsula (Malaysia), east coast of Sumatra Island (Indonesia) and coastal zone of Borneo Island (Indonesia); general term of mixture of southern proto-Mongoloid and Australoid people who speak Malay (or Melayu) language, and live widely from Indigenous Taiwanese, Malaysia, Singapore, Brunei, Indonesia, Philippines, south of Thai, part of Cambodia.
- >Top Ethnic Groups in Indonesia: (source: Wiki):
- Green painted areas are the places where Malaysian ethnic group live.
- Malaysian involved various works such as collection of forest products, fishery (shrimp, etc.), trade, pirates, shifting agriculture, coconut tree plantation.
- Population of Malaysia:
6.3M (Malaysian 50%, Chinese 37%, Indian 11%)
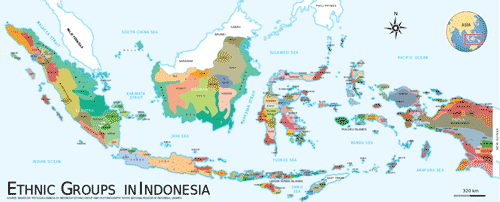
- Since middle of 19C UK promoted colonial economy (1874- 1957) ; appointing Malaysian as the king of port, using Indians as tappers of rubber plantation, and Chinese and for development of tin mining.
- City Kuala Lumpur was established during this time.
- After WWII, UK had withdrawn; Malaysian rejected Chinese, then who became Chinee-Malaysian.
- 1963 Malaysia was established (Federation of Malaya, Singapore, Sarawak, and Sabah)
- Tropical rain forest in the sea area was intensively developed by DDT and chainsaw.
3. 頭で考えた世界単位:
- 個別地域の探求と広域遠望の視点:
- ユーラシアの生態区分: 5つの生態型:
砂漠・草原・野・森・海
- ①砂漠:
- 例外的に水が得られるナイル、チグリス・ユーフラテス、インダス、黄河流域(四大古代文明)
- 砂漠には四大文明地を繋ぐ旅の宿場、交易拠点、城郭都市。富と情報が交叉。
- ②草原:
- 砂漠帯の北に平行 (トルコからモンゴル)
- 水不足ゆえに農耕には不適。羊・山羊・牛・馬・駱駝を引き連れた遊牧の民。
- 鉄砲登場までは騎馬軍団は最強。馬の機動力と強弓。
- ③野: 農地の広がり。
- 中国の中央部とインド。
- 落葉樹と常緑樹の混合林。2000年前に開拓。
- 衛生環境良好、肥沃な土壌。
- 巨大な農民人口。
- ④森: 人間を拒否した空間
- ユーラシア北方に広がる北方林 (タイガ)。針葉樹林、地面は永久凍土層。
- 東南アジアに広がる熱帯多雨林。広葉の常緑樹。猛烈な瘴癘の地。人食いの空間。
- ⑤海: 砂漠に似ている。
- 移動には便利。港を伝っての交易活動
- インド世界: もう一つの野の世界
- インドの生態区分:
①デカン台地、②インダス乾燥谷、③ガンジス湿潤谷、④東部丘陵地、⑤西岸多雨林帯、⑥北部山地
- デカン台地:
玄武岩台地の広大な部分が降雨量少ないので稲作ではなく雑穀栽培。棉の産地。
- インダス乾燥谷:
もっと雨が少なく一部は砂漠。多くの場所で貧弱な草を求めて羊や山羊の放牧
- ガンジス湿潤谷:
降雨量が多く、稲単作地帯。
- 東部丘陵地:
ベンガル湾からの風による降雨があり、山間部では稲作地帯。
- 西岸多雨林帯:
インド洋に面した急峻な山岳地帯。モンスーンを受けた熱帯多雨林。コショウやニッケイなど熱帯の森林産物を産出。
- 北部山地:
ヒマラヤへ続く山地。シコクビエやムギを作り、牧畜も盛ん。
- 人種構成:
- 北方: 白色のアーリアン系
- 南方: 黒色のドラヴィダ系
- 北部山地: モンゴル系
- 歴史的経緯:
- インダス乾燥谷中心にドラヴィダ系で、ムギ作と牛飼いの定住者で、インダス文明の担い手。(Fig.1)(source: Wiki)
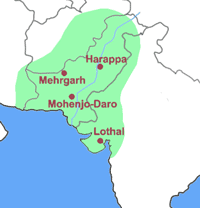
- ガンジス潤谷を中心にムンダ系で稲作
- 1800BC頃、中央アジアからインダス乾燥谷に騎馬民のアーリアンが侵入。ドラヴィダの都市群を支配し、バラモン教を布教。(リグ・ヴェーダ: 自然神に対する賛歌)
- バラモン教の最大の特徴は、ヴァルナの思想 (バラモン、クシャトリア、ヴァイシャ、スードラの4階級)
- 1000BC頃、アーリアンはガンジス湿潤谷に侵入し、ムンダ系を支配。ムンダ系は東南アジア、特にカンボジア人に近縁で実力があった。
- マウリア朝成立: 都はパータリプトラ (今のパトナ) で、ガンジス湿潤谷とインダス乾燥谷の人口・武力・富の結節点。
- 百家争鳴の時代。仏教が伸張。
- グプタ朝 (4-6C): インド的な文化が確立。マウリア朝よりも農業中心。ヒンドゥ教が浸透。
- イスラム勢力がインダス乾燥谷に侵入。16Cにムガール帝国建国し、デリー中心に亜大陸の大部分を支配。イスラム支配者は改宗より徴税優先。農民はヒンドゥのまま。
- 18Cには英国の影響増大。ムガール帝国滅亡。キリスト教の布教と英国流の法律を押しつけたが、むしろインド的な反発強まる。
- インド的なものとは:
- ヒンドゥ教による秩序
- ジャティー制度: 職業集団。鍛冶屋、洗濯屋、太鼓たたき、農民、漁民、軍人、僧侶等何百もの固定的な職業
- ヴァルナの制度: 貴賤の別。バラモン(僧侶)=クシャトリア(武士)によるヴァイジャ(農民)とスードラ(隷属民)の支配体制。
- なお差別のみならず、この制度(ジャジマニ制度)による職業の村抱えによる安定性もある。
- バクティ信仰: ヒンドゥの神々の中で特定の神だけを信仰すること。例えばヴィシュヌだけを全身全霊で頼る。
- キリスト教徒も、ヒンドゥ世界の中のキリスト教徒という小箱の位置づけ。
- イスラム教世界:
- 仏教やキリスト教と異なり、日常生活の指針を与えている。食の禁忌、相続、商法に至るまで価値観を共有。
- シリア・イラク世界:
- 肥沃な三日月世界は、山地で、降雨もあり植生も豊か。野生のリンゴやナシ類。野生のムギ、野生の羊や山羊が棲息。ここに世界初の農耕と牧畜が勃興。
- 文明発生は、豊かな山腹から乾燥した河谷に下ってから。井戸を掘り潅漑を行った。
- 4000BC。シュメール文明。低地に交易者が集住すると富の集積。城壁都市、巨大神殿、ピラミッド(ジグラト)、武器の制作、防衛組織の登場となる。(source: Wiki)
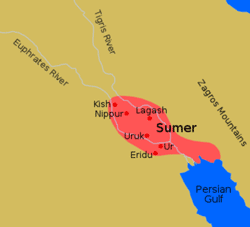
- 砂漠の城壁都市内に、枯れない井戸を掘削。縦坑数十m、斜坑100m以上。内部の壁龕にはランプ。
- ムギの収量は、1粒に対し数十倍の収穫。潅漑の整備、十分な施肥、立派な農書 (中世ヨーロッパでも4-5倍)
- メッカからダマスカスへ。さらにバクダッド。近世の波はバクダッドから四方へ拡散。
- 中国でも長安・洛陽から近世は江南へ移行)
- エジプト世界:
- 5000BC以来のナイル河沿いの農耕エジプトと、ナイル・デルタの商業イスラム的なカイロ。
- チグリス・ユーフラテス河に比べてナイル河は湿潤のアフリカに源があり、水量が豊富。
- 畑は牛に引かせた鋤で耕作。ナイル河の氾濫で畑は水没。湛水が消えた後、そこに播種し、羊や山羊を追い込んで歩き回らせ種子を土中の押し込む。
- 脱穀は円形の脱穀場に牛やロバによって穀粒と茎とを粉砕し分離し砕けた茎は家畜の飼料となる。
- 土地と水は王のもので、国営農場のような生産。
- アレキサンダー大王がアレキサンドリアの港町を建設したことで、エジプトに海の要素が追加。
- その後、ローマ、ビザンチンの支配。
- イスラーム(シーア派)が浸透し、10Cのファーティマ朝が成立。カイロを中心に仲介貿易。砂糖キビや稲など商品作物も生産。
- 12C後半にアイユーブ朝(スンニ派)、その後マムルーク朝が成立したが、すべてインド洋・地中海交易を重視。
- マムルーク朝は、トルコ、スラブ、ヨーロッパからの優秀な子供を購入し、イスラム教徒としての軍人を養成。平等で実力主義の運営で、将軍や王にもなれた。
- ペルシア世界:
- 平均高度1000mの山地と高原の地。
- アーリアンで、イスラームはシーア派。
- 詩・絵画・ゾロアスター教などアラブにないペルシャ文化
- 砂漠地帯には、①都市住民(商人)、②遊牧民、③農民の別集団がいる。
- 農民は、山間部に小さな集落を作り、カナート(地下水路)など活用し、ムギなど栽培。自立定住し、村落共同体的。
- 移動という点では、商人と遊牧民が砂漠と草原を移動し、一衣帯水性を維持。
- トルコ世界:
- 13Cにオスマンがアナトリア半島に侵入し、西のシルクロードの終点として、1326に都ブルサを建設し、東西貿易を牛耳る。
- オスマントルコの古都ブルサは、深い谷地で樹木に覆われ、町は緑色。周辺の丘陵地も草原。(シリアの灰褐色の広大な平坦地を対照的)
- 1453に当時世界最大の都市コンスタンチノープルを征服し、イスタンブールをした。以降オスマントルコは最強の帝国として470年間存在。
- オスマントルコは柔軟な専制制。非軍事部門では信教の自由。帝国内にはキリスト教徒、ユダヤ教徒が混在し、実力主義で役人に採用。
- 軍事面では、中央集権的な軍事組織で、スルタン直属の常備軍。
- オスマントルコの支配者は、シャー=ハン=スルタンの称号。ペルシャの大王+草原の覇者+イスラームの支配者。
- イスラーム世界は2回に亘って拡大。8C半ばまでにアフリカ北岸からイランに至るまで。13-14Cに、モンゴル・トルコ族の軍事的拡大と軌を一にして、イスラーム文化・商業圏を東南アジアにまで拡大。トルコ世界もこの第二次拡大時にイスラーム文化圏に組み込まれる。
- トルコ共和国と、東南アジアのイスラーム世界と同様に欧米風の近代化を消化。(source: Wiki)
- その他砂漠・草原帯の中の世界単位:
- マグレブ世界:
ベルベル人の世界。アトラス山脈の北面の農地にオリーブとムギを栽培。土着的。乳香貿易。
- イエメーン世界:
アラビア半島南端で高い山がインド洋からの湿潤な風を受けた多雨地帯。紀元前より"幸福なアラビア"でアラビアの中では別天地。
- アフガン世界:
ペルシアに近いが、実直で尚武の気風。パキスタンも別。
- トルキスタン世界:
サマルカンド、タシュケント中心に東西交易の要所としてオアシス交易都市。
- モンゴル世界:
典型的な草原の世界。遊牧と強い騎馬軍団。火器の進歩により強い騎馬軍団は消えたが、尚武の気風は残る。
- チベット世界:
高い標高だが、草原世界の一つ。過酷な自然環境の中で、チベット仏教を墨守。
- 外の世界とのオープンな交流:
- マルコポーロは、ヴェネツィアを出て、トルコ、ペルシア、トルキスタンを通過してフビライの都のお雇い外国人として居住。
- 農民もかなり夏営地と冬営地の間を移動 (数百km)。遠方の農民との相互手伝い、または町での雑業。
- 巡礼好き。聖地メッカ、カルバラへの巡礼は1000km以上。40-50年前はロバか駱駝で移動。
- ベドウィンは、同じ場所にしばらくいると汚れた感じがする。
- イスラムは旅を安全にするシステム。関所や徴税所がなく、至る所にモスクや宿泊所がある。
- 海の世界:
- 16-17Cに砂漠・草原帯がさびれていったのと対照的に大航海時代が到来。
- インド洋世界:
- インド洋+アラビア海+ベンガル湾を渡っての交易
- 中国の絹・磁器、東南アジアの香料、南インドのコショウ、アフリカ東岸の象牙・金
- イスラム商人は、アフリカ東岸の小島(ザンジバル島)を拠点に仲介貿易。蚊が少なく衛生環境良好。
- 港町ではイスラーム文化。混血。アラビア語と現地語とが混ざりスワヒリ語ができた。
- ケニアのモンバサはパキスタン風。グジャラティ(グジャラート州出身者)も多い。
- 地中海世界:
- インド洋に比べて小規模。地中海はオリエントのための海として機能。
- 3000BC頃、フェニキア人が地中海東端のレバント(Levant)やアルワド島中心に、銅製品・ガラス製品を製造。交易+工芸技術集団。
- フェニキアの後継者として、カルタゴとギリシアが登場。
- カルタゴは、チュニスの細い半島に三重の城壁都市を建設。外側が商港で、内側が軍港で200隻のガレー軍艦。
- 胴太の帆船で商品を輸送し、漕ぎ船(2-3段で100本超のオール)のガレー船が軍艦として護衛。船首は金属板で刀の刃状態で体当たり攻撃し、敵のガレー船のオールを破壊。(Source: Wiki)
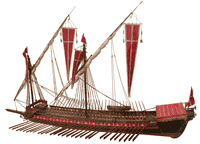
- 地中海は、工業・交易・戦争の海。
- 10C以降はヴェネツィアが活躍。
- 地中海の東・南はイスラームの先進文化。北側のヨーロッパは森に覆われた後進地。イスラム圏からは金属・織物の工芸品、コショウ。ヨーロッパ側からは木材・奴隷
- ヴェネツィアは当初はビザンチン帝国の傭兵として海賊退治。その後、交易としてはイスラーム圏への木材の輸出(ローマ教皇はイスラーム圏への木材禁輸だったが)。さらに十字軍相手の旅行業 (宿泊と輸送)
- 1204 第4次十字軍遠征。遠征先をエルサレムからコンスタンチノープルへ変更し、キリスト教国のビザンチンを攻略。
- ヴェネツィアは領土はなく、人口の小島と海外居留地の港のみで、ガレー船と帆船で交易+海賊活動。
- 陸の勢力拡大: 1529 カンブレー和約、1797 ナポレオン占領。1866 イタリアに併合された。
- 北海・バルト海・ノルウェー海世界:
- バイキングの海、近世にはハンザ商人活躍の海。川と湖が多く陸路は不便。
- 8-12C バイキングの時代。汀線と川筋で生活して海に展開したゲルマン的農民。焼畑農業、牧畜、漁労、狩猟。交易兼略奪の遠征を行う。50人位の漕ぎ手と20人位の戦士。(交・略・農・牧・漁の活動)
- ノース人:
イギリス北部やシチリアへ進出。ビザンチン傭兵のヴェネツィアはノルマンとよく戦闘。
- バルト海バイキング:
北海中央のゴトランド島が拠点。ドニエプル河から黒海を経てイスラーム商人と交流。(ゴトランド島から大量のアラブ銀貨出土) 後に、キエフを建設。
- 13C ハンザ同盟の商人達:
リューベックは港町の中心。ロシアから穀物・木材、ノルウェー海から塩漬け魚肉・魚油の運び屋。
- 16C オランダはこのハンザ同盟を押しのけて成長。(後にはイギリスが続く) フランドル地方の毛織物 (ブルージュ、アントワープ)がイギリスからの原毛を加工し、ヨーロッパ中に販売。オランダはアムステルダム拠点に領土ではなく制海権を握って世界最強の海運・海軍国となる。
- イギリスはオランダを真似て海運に注力。同時に織物工業も展開し、産業革命を主導。動力船によって大量の物資と兵員を長距離輸送。内海の時代から大洋の時代へ転換。
- 大洋の開拓者は、もともとはイスラーム商人と中国人。その後スペイン、ポルトガル、さらにはオランダからイギリスへの主役交代。
- 東アジア海域世界:
- 東アジア海域は汀線中心に倭人が活躍。焼畑農業、漁業、香薬、真珠、亀甲の収集運搬。また陸稲も運搬。
- 宋代の展開。江南の絹・磁器の交易。
- 明代になると朝貢貿易が前面。明・清時代は海禁政策。海民の活動は倭寇とされる。五島列島本拠地の王直は、東アジアで活発な交易活動。
- 19Cはイギリスがこの海域に進出。アヘン戦争、アロー号事件、上海開港。
- 清帝国崩壊後は、上海を拠点に海民の大膨張。勢力の中心は浙江財閥(蒋介石)。一方、陸側には毛沢東。1949 中華人民共和国成立。
- 1990年代以降、経済のグローバリゼーションの中で、再び海民勢力が興隆。上海・広東・深圳など沿海部の経済。
- 東南アジア海域世界:
- タイ、ベトナム、ジャワを除く東南アジアの海岸部でマレー語圏で海のシルクロード。人口はむしろ希薄で、焼畑農業、森林物産採取、漁労。
- 15Cから100年間、マラッカ王国。①王都、②マレー人集落、③軍港、④シェイクの支配地(アラブ・ペルシア商人)、⑤属国
(Source: Wiki)
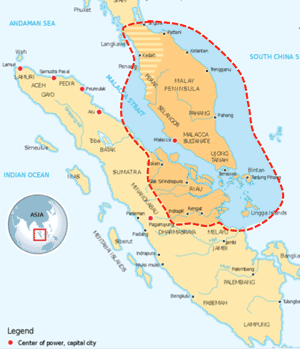
- 初代のパラメスワラ王の時、中国の属国。鄭和の遠征途中寄港。東は琉球、西はエジプトから商人が集積し、80を越す言語が交流。
- 第二代イスカンダールはイスラームに改宗。
- マレー人は森林物産採集、漁業(エビ漁)、交易、海賊、焼畑、ココヤシ園開拓など臨機応変の多様な生活。
- イギリスによる植民地経済。港の王はマレー人。開発は中国人・インド人を導入してイギリスが直営。プランテーション、錫鉱山開発(ヨーロッパのメッキ工業に対応)
- 19C半ばには、中国人を使用して道路・鉄道の建設によってさらに奥地の錫鉱山開発。ゴムのプランテーションは、インド人をタッパー(樹液採集者)をして使用。クアラランプールの町もこの過程で建設。
- 第二次大戦後はイギリスは撤退し、マレー人による中国人排斥運動が起こる。中国人も華人としてマレーシア国民化。
- 海域周辺の熱帯雨林は、DDTとチェーンソーによって開発が進展。
>Top 4. World Units in Europe:
- Europe is not one, but a collection of different regions:
- North of the Alps: Celt & Germanic world.
- Temperate mixed forest zone, slush-and-burn agriculture, grazing, and hunting. Youth were combatants under the head; were almost pantheists.
- South of the Alps:
- Mediterranean Sea World from Phoenicia, Carthago, Greece, then Rome.; were Christians, believing humanism and living city lives.
- Such high culture only penetrated the upper class; did not proliferate into the general public. People were divided into the one who speak Latin and the other local language.
- >Top Family Type in Europe:
- Family Type in Europe (Emmanuel Todd, 1993)
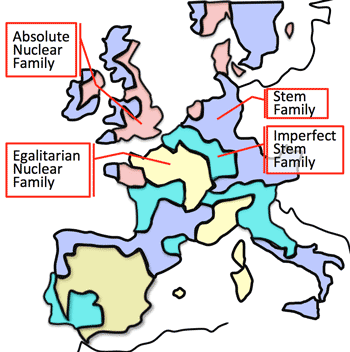
- >Top The Nation State:
- 'Naturalization of the king': As a result of integration of the territory, the scale of the country necessitated to assign jobs to bureaucrats, who can speak only local language. Thus the king needed to speak it, which is said naturalization of the king.
- >Top France:
- is very confident as the center of Europe; because most of European royal families spoke French, adopting humanism which lead to People's Revolution.
- 10C Paris Basin, which is open from the Alps directly connecting to the Mediterranean Sea.
- In other European areas, two-field system agriculture by 4-5 families. But in Paris Basin, the village scaled about 50 families, adopting three-field system
- 14-15C Europe had exhausted by Plague infection as well as Hundred Years' War (1337-1453)
- 16C Flourishing Culture of Bourbon absolute monarchism, introducing Renaissance in Italy.
- French Central World: causing the following new waves:
- Court culture, the Enlightenment such as Deism, Materialism, Empiricism, and finally People's Revolution.
- After the success of French Revolution, Napoleon defeating (Anti-France) Coalition.
- >Top Germanic World:
- Hilly area has wide forest and pasture land, where having less towns, as described 'Germania' (98) by Cornelius Tacitus (55c-120).
- Near their house, they cultivate barley and wheat at the common farm by slash-and-burn method. Around there they put out sheep, goat, horse, cow, and pig grazing in the common pasture. Agriculture was mostly done by women, while men were involved hunting or stayed at the fort as soldiers.
- The head of the tribe made decisions by consensus of men; provided there were layers of noblemen, ordinary men, and slaves.
- 4-5C Germanic Migration: (>Fig.)
- In 1648 at the time of Westphalia Peace Treaty after the 30-years War, there were still about 300 territoria (state in the Holy Roman Empire).
- In the middle 19C, there were still 40 territoria.
- Serious German; in 1517 Martin Luther promoted the religious reformation, protesting secular priests' governance. Luther publish 'The Ninety-Five theses', criticizing the sales of indulgences, which has no foundation in the gospel; also continued to translate translation of the Bible to German language.
- In Paris basin, there is sovereign power combined with wealthy merchants, contrastively in Germanic World, there are territoria supporting Catholic under the Holy Roman Empire; but the original pro-Catholic supporters fiercely protested against religious authority of Roman Catholic.
- In 19C Germany changed to Nation-state to counter the surrounding nation-states by Bismarck's blood and iron policy (1862).
- >Top England World:
- England was the pasture for sheep, which was far more backwoods than France.
- Henry Ⅷ promoted Religious Reform and economic policy; forfeiting wide territory owned by the Roman Catholic; breaking off the tie with Roman Catholic and established the Anglican Church.
- >Top Promoted mercantilism; imposing heavy export tax for raw wool, while relieving tax for wool fabrics to cultivate woolen textile industry.
- Executed enclosure policies twice; the first in 16C and the second in 18C; causing to create vast landowners and landless labors who work at the textile industry.
- The progress of the Industry Revolution also created new factory managers; which caused new type of conflicts arose but each time occurred compromising and shifting steadily to the industrial nation.
- Conquer of World Sea:
- In naval power, English was late starter; ordering Netherland to make English vessels, which then were authorized to pirate Spanish vessels carrying silver or other goods on the way from the new continent; the plundered goods were shared with the Royal family and the pirates.
- 1588 Phillip Ⅱ; English fleet destroyed Spanish 'Armada Invencible'.
- Then Netherland had already dominated spice trade from Southeast Asia.
- English inevitably invaded India and promoted the Triangular Trade; exporting cotton fabrics to India, procuring opium there and exporting it to China, from where importing tea for Europe.
- English also promoted another Triangular Trade; exporting cotton fabrics and arms to the West Coast of Africa, procuring Negro slaves there, transporting them to North America to work at cotton plantation, from where importing the cotton back to English to fabricate it.
- English became the world industrial center, and selling the products worldwide by gunboat diplomacy.
- While they tried to become 'gentlemen', who aimed to acquire: 1) certain assets, 2) decent life-style including suitable architecture with family emblem, and hunting as a hobby, etc., 3) sophisticated culture including understanding classic literature, and 4) political participation.
- >Top Disparity in English society expanded; concurrently pursuing to be respectable leaders according to the economic development as well as required Protestantism-like diligence and appropriate economy or virtue (pursue of honorable poverty)
4. ヨーロッパの世界単位:
- アルプス以北: ケルト・ゲルマン世界:
- 温帯混交林帯で、焼畑・牧畜・狩猟。若者は首長の下の戦闘員。森に適した汎神論者。
- アルプス以南:
- フェニキアからカルタゴ、ギリシア、ローマへ続く地中海世界。キリスト教、人文主義、都会生活。
- 高級文化は上層エリート層のみに浸透。一般民には広がらず、ラテン語を話す層と地方語を話す一般民衆との二層構造。
- Emmanuel Todd, 1933:
- 直系家族: (Stem family)
父親の絶対権威。長男のみが継承。
- 不完全直系家族 (Imperfect stem family):
父親の権威絶大。子供は平等。
- 絶対核家族 (Absolute nuclear family):
父親の権威は弱い。長男が特別扱い。遺産は遺言による。
- 平等主義核家族 (Egalitarian nuclear family):
父親の権威は弱い。子供は平等。遺産は兄弟で平等に分配
- 国民国家
- 王の帰化。領土統合の結果、国の規模が拡大し、官僚に業務分担させた。その業務は地方語で行い、王も地方語を話すようになり、国民国家が成立。
- フランス:
- ヨーロッパの中心という自負。ヨーロッパ中の王家はフランス語。人文主義、市民革命をリード。
- 10C パリ盆地。ここだけアルプスが分断されており地中海に直結。
- ヨーロッパの他では4-5戸の二圃式耕作だが、パリ盆地は50戸の大集落があり三圃制大農場が存在。
- 14-15C ペストや100年戦争で疲弊
- 16C ブルボン絶対王制の栄華期。イタリアでのルネサンス文化を導入。
- フランス型中華世界:
パリの宮廷文化、啓蒙主義(理神論、唯物論、経験論、自然科学)。
- 新興勢力の台頭と共に、宮廷文化、啓蒙主義、革命へとつながってヨーロッパに拡大。
- 1789 フランス革命の成功の後、ナポレオンによる対仏大同盟の撃破。
- ゲルマン世界:
- 丘陵地は、森と牧草地が広く、町は少ない。タキトゥスのゲルマニアの記述。
- 家の近くに共同耕地での焼畑農業で大麦・小麦を栽培。その周辺の森と放棄畑地に羊・山羊・馬・牛・豚を共同放牧。農作業は基本的には女の仕事。男は狩猟・砦の戦士。
- 部族長は男達の合議のまとめ役。但し、貴族・平民・奴隷の階層はある。
- 4-5C ゲルマンの大移動。東の草原からの騎馬民(騎馬と弓矢)に誘発。ゲルマン側も新たな戦闘技術と築城技術で対抗し、城郭都市をもつ領邦国家群へ移行。
- ゲルマン民族大移動: (Source: Wiki)
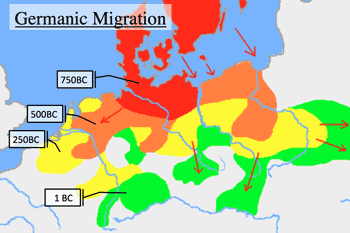
- 1648年 三十年戦争後ウエストファリア条約時点でも約300の領邦国家。19C中頃でも約40の領邦国家から成る。
- 真摯なドイツ人。1517 ルターの宗教改革。世俗的な司祭達の支配に反抗。ドイツ語訳の聖書重視。
- パリ盆地では、商人と結託した王権。一方ゲルマン世界はカトリックを擁護する領邦国家群である神聖ローマ帝国。そのカトリック擁護者がローマの宗教権威に強烈に反抗。
- 19C ビスマルクの鉄血政策によって国民国家を建設し、周辺の国民国家に対抗。
- イギリス世界:
- イギリスはフランスに比べ圧倒的な後進地(羊の牧場地帯)。
- ヘンリー8世(1509-47)による宗教改革と経済政策。イギリス内のローマ教会の広大の領地を没収し、ローマカトリックと断絶し、国教会を創設。
- 重商主義政策の推進。原毛に重い輸出税、毛織物に軽い輸出税をかけ毛織物工業を育成。
- 2度のエンクロージャー政策: 第一次16C、第二次は18C。この結果、大土地所有者の出現と土地なし機織工場の労働者の出現。
- 産業革命の進展で、新興の工場経営者層も登場。対立が起こるが妥協が図られ、着実に工業立国へ移行。
- 世界の海の制覇:
- 海軍力でも当初は後発。船自体もオランダから購入。新大陸から銀を運搬するスペイン船を、王家公認の私掠船(海賊船) で、略奪品は王家と山分け。
- 1588 スペインの無敵艦隊を撃破。
- 東南アジアの香料貿易はオランダが地歩を築いていた。
- イギリスはインドに着目。三角貿易の推進。綿布をインドに、インドでアヘン調達し中国で販売。中国からは茶の輸入。
- 大西洋でも三角貿易。綿布・武器をアフリカ西海岸に輸出し、黒人奴隷を獲得し、カリブ海に運び砂糖キビプランテーションを経営し、砂糖をヨーロッパに輸入。同様に黒人奴隷を北アメリカに運び、綿花を栽培し、イギリスで綿布に加工。
- イギリスは世界の工場ととあり、その製品を砲艦外交で世界中に販売。
- その反面、ジェントルマンの条件。①財産、②それらしい生活様式(家紋のついた場所、狩猟の趣味など)、③教養、古典に通じること、④政治参加。
- イギリス社会の階級格差拡大。経済発展に加えて尊敬に値する指導者像。プロテスタント的勤勉や節約の美徳の推奨 (清富の思想)
>Top 5. How to utilize world unit:
- Earth World with Structure:
- Ecologically-adapted World Unit:
- This type rises occupation for living according to the given ecology, and also confines the society and world view.
Eg. Java World, or Southeast Asia Mountainous World
- Networked World Unit:
- This type is created along the zone of desert and grassland. Though sea and desert are not suited for living, but create networked life-style moving between ports or oasis. Generally the population of this world is scarce, but surely connect between the nodes by networked relationship.
- Major Civilization-typed World Unit:
- This type enables high density agriculture population in wide area. Around this area, various people surround, such as merchants, nomads, shifting-farmers, and seamen. This is the World Unit including all these fringed people and life. To maintain unification of this vast world, particular ideology is essential; Chinese World with Confucianism, and Indian World with Hindu.
- >Top Automorphic vs. Xenomorphic:
- These are terms of mineralogy; automorphic or idiomorphic: the external form of mineral constituents is controlled only by the internal crystal structure, caused by temperature difference of crystallization'. Xenomorphic is antonym of automorphic.
- Major Civilization is usually automorphic, while Networked World is xenomorphic
- Europe originally developed by Ecologically-adapted World Units, but after modern age, they tend to show autmorphic by establishing nation-state.
- Regional-dependent vs. Personal-dependent:
- Ecologically-adapted type and Major Civilization type are regional-dependent; where farmers, in particular, are regional-dependent.
- Networked type depends on each constituent world view, or personal-dependent; where merchants, in particular, are personal-dependent.
- Early Modern vs. Modern:
- In Early Modern age, Networked World Units were activated.
- But in Modern age, those units tend to behave more like idiomorphic actions, apart from their original scenographic features.
- >Top Orient World:
- When people moved from wed hillside to dry valley of Tigris & Euphrates rivers, they invented to make irrigation and to build walled city to secure water and use safely irrigated agriculture.
- After the construction of cities, merchants in the walled cities, rainfed farmer in the hillside, and nomads in the desert live separately.
- As a total Eurasian continent, the Orient World is more city-like; and desert zone extends across Eurasia, connecting Chinese World at the east end and Indian World, and having Mediterranean Sea at the west; other places are mostly forest.
- According to the expansion of Islam, modern Islamic economy is promoted by typically personal-dependent and scenographic Islamic merchants.
- Europe had been delayed area of North-Western end, but by the cheap mass production of textile and improvement of firearms, they succeeded to sell the mass produced products worldwide using their military advantage.
- After gaining military advantage, Europe invaded Islamic trade network in most idiomorphic method backed by repulsion toward Islam.
- >Top Modern Capitalism is rooted in such Enforced Sales Network developed by Europe; originally promoted by England, thereafter shifted the role to US.
- The Enforced Sales Network is now changing Exploitative Network; the center is factory producing the goods and surrounding supply source of materials, and the target market of exporting the goods. The price and other terms are decided by the central function, which causes discretional exploitation.
- >Top Cf. Investor-State Dispute Settlement (ISD clause or ISDS (Settlement)); 'If an investor from one country (home state) invests in another country (host state), the host state violates the rights granted to the investor under public international law, public international law, then that investor may bring the matter before an arbitral tribunal.' (source: Wiki)
- >Top Casting Vote Area of modern age:
- Asia: wort most rapidly economic developing area; if they chose alternative strategy other than global competition, it would become big impact.
- China and India:
Both civilizations retain long tradition and history since 2000 years ago other than global market economy.
- Southeast Asia:
This area had retained symbiotic relationship with their forest; which can be ecologically categorized as Post-Modern.a
- >Top Authority of Europe vs. Authority of Southeast Asia:
- There are double canopies in Europe; Royal Family who speak French and Christianity.
- In Southeast Asian society is the world of Pantheism; authority may be 'Dewa-Raja' (theocracy, Dewa<God, Raja<King), or nobleman of white land, Shamanism or Animism, or sometimes highest peak or huge tree.
- Cf. Mt. Fuji < Mountain Immortal
- ASEAN was initiated by Malaysia, Philippines, and Thai, all of which are Sea World states. ASEAN is a supranational organization, which was not agreed through political speculations, but loosely connected supracommunity where member states smartly are expect to use the Sea World logic.
5. 世界単位をどう生かすか:
- 構造をもった地球世界:
- 生態適応型の世界単位:
- 与えられた生態に対応した生業・生活が生まれ、それに規制された社会・世界観が作られている。
例: ジャワ世界、東南アジア山地世界
- ネットワーク型の世界単位:
- 砂漠・草原帯にできた世界単位。海・砂漠は居住には適していなが、港やオアシスを拠点を伝わって移動する生活形態。全体として人口希薄地だが、拠点間をネットワークで結ぶ世界である。
- 大文明型の世界単位:
- 高密度の農民人口が広範囲に亘ってひろがっている。この密集帯の周辺には、商人、放牧民、焼畑農民、船乗りがいるが、それらを含めイデオロギーを共有する世界単位である。世界には儒教と中華世界とヒンドゥ教のインド世界がある。
- 自形と他形:
- 大文明型は自形に、ネットワーク型は他形になる。
- ヨーロッパは、生態適応型世界単位として発生したが、近代に入って国民国家という自形になった。
- 属地的と属人的:
- 生態適応型と大文明型は属地的。農民は典型的に属地的。
- ネットワーク型は、構成員一人一人の世界観に依るので属人的。商人は典型的に属人的。
- 近世(Early modern)と近代(Modern):
- 近世はネットワーク型世界単位群が活発な活動を展開
- 近代になると、本来の他形性をかなぐり捨てて自形的挙動をとるようになった。
- オリエント世界:
- 人々が湿潤が山腹から乾燥したチグリス・ユーフラテスの河谷に移動してから、水を得るために潅漑設備・城塞都市を構築した。
- 都市群が生まれた後、城郭都市の商人と山腹の天水農民と砂漠の遊牧民の住み分け。
- ユーラシア全体としては、オリエントは全体として都市的で、ユーラシアを横断して砂漠の帯が延び、東端には中国とインドの野の世界があり、西には地中海がある。その他のお所は森である。
- イスラームが広がって近世のイスラーム経済の担い手は、極めて属人的・他形的なイスラーム商人であった。
- ヨーロッパは、西北の後進地域であったが、安価な織物の量産と火器の改良で近代になって、武器を背景に世界中に量産した織物を販売した。
- ヨーロッパは、イスラームへの反発から武力を手に入れると自形的にイスラーム交易ネットワークに侵入した。
- 近代資本主義はヨーロッパが拡大した強制販売ネットワークのことである。最初はイギリス、後にアメリカに中心が移った。
- 強制販売ネットワークは、今や収奪ネットワークとなった。中心は工業製品を作り出す工場と、周辺の原料供給産地、さらに製品を輸入されられる市場である。価格は中心が決めるので収奪はし放題である。
- 現代のキャスティングボート地域:
- アジア: 世界最大の経済成長の地域だが、成長を手控える挙にでれば大きなインパクがある。
- 中華世界とインド世界:
経済市場主義ではなく、2000年来の哲学をもっている。
- 東南アジア:
森との共生を体現してきた地域で、生態史的にポストモダンを位置づける可能性がある。
- ヨーロッパの権威と東南アジアの権威
- ヨーロッパを天蓋状に覆うのは、フランス語を話す王家とキリスト教の権威の二重天蓋がある。
- 東南アジアの場合は、権威は、先端放電しているデワ・ラジャ(神主)、白い地の貴人、修行僧の呪術者、あるいは高峰や巨木など汎神論の世界である。
- 東南アジアは、ジャワ世界、ベトナム世界、タイ・デルタ世界があるものの突出した巨大勢力はなく、身軽な港町ネットワーク世界で独自の経済・文化圏である。
- ASEANはマレーシア、フィリピン、タイの海域的な国が主導した。ASEANは超国家組織だが、政治的取引で合意した機構ではない。海域世界の論理を各国がうまく利用して緩く結合した共同体である。
>Top 6. How to survive world unit:
- Dualism vs. Coexistence:
- Whether (Huntington's) Crash of Civilization, or coexistence of multi and miscellaneous life spheres.
- Darwin's Theory of Evolution vs. Kinji Imanishi's theory of natural science.
- Antithesis of rationality of science.
- Regional Philosophy:
- Present age tends to make hollow both individual and region. This philosophy give unique viewpoint focusing the value of region.
- Function of feeling a pain:
As a result of having pursued modern convenience and easiness by using modern enhanced or enlarged tools, facility, and organization, the trend of hollowing of human being is getting unavoidable.
- It is essential to fell the object by the sense of oneself without inserting intermediate media.
- The final judge should be done based on the ecological logic rather than rationality or efficiency.
6. 世界単位に生きる:
- 二元論 vs. 共存論:
- (ハンチントン流の)文明の衝突か、多様雑多のもの生活圏レベルの共存世界
- ダーウィンの進化論 vs. 今西錦司の自然学理論
- 科学の合理性に対するアンチテーゼ。
- 地域哲学:
- 個人も地域も空洞化しつつある現在、この地域哲学は必要。
- 痛みを感ずる機能: 現代の道具・装置・組織の巨大化・精密化により近代の便利さ・安楽さの追求の結果した結果、人間の空洞化が起こっている。
- 自分自身と対象の間に人工的な中間物を入れないで感じること。
- 最終判定者は、合理性や能率ではなく、生態論理であるべき。
Comment
- This is an antithesis to simple globalization.
- It is a hot issue whether the present information age has the structure of 'The World is Flat' or of segmented 'different worlds.'
- 本書は単純なグローバリゼーションに対するアンチテーゼである。
- 現在の情報化時代は、フラットな世界な世界構造なのか、あるいは異なる世界の集まりなのかの熱い議論がある。
World of Multi-Civilization
|
Cat: HIS |
|
Koichi Takaya (高谷好一) |
17719u/18227r |
Résumé |
Remarks |
>Top 0. Preface:
|
0. 序文:
|
|
|
>Top 1. World Regional Unit observed by on foot:
|
1. 足で見つけた世界単位:
|
>Top 2. Japan as a world unit:
|
2. 世界単位としての日本:
|
>Top 3. Conceivable World Unit:
|
3. 頭で考えた世界単位:
|
>Top 4. World Units in Europe:
|
4. ヨーロッパの世界単位:
|
>Top 5. How to utilize world unit:
|
5. 世界単位をどう生かすか:
|
>Top 6. How to survive world unit:
|
6. 世界単位に生きる:
|
Comment |
|
|