>Top 7. <Re:> Depopulating Japan
- Advent of marginal depopulating society; 896 communities could be extinct in Japan.
- ♥Depopulation=late marriage × birthrate
- Children born outside of marriage is quite exceptional in Japan; 22,402 babies, 2.29% in 2016;
- Chile 71%, Mexico 65%, Bulgaria 59%, France 57%, Norway 55%, Sweden 55%, Netherland 49%, UK 48%, Czech 47%, New Zealand 47%, Spain 43%, Austria 42%, US 40%, Germany 35%, Australia 34%, Canada 33%, Rumania 31%, Italy 29%,Poland 24%, Swiss 21%, Greece 8%, Israel 6%, Turkey 3%, and Korea 1.9%
- >Top ♦Birthrate:
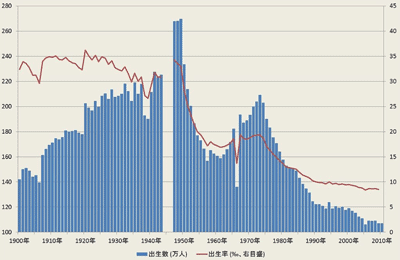
- 1st baby boom: 2.7M (1947-49); birthrate 4.32
- 2nd baby boom: 2.1M (1971-74); birthrate 2.14
- babies born: 1.03M in 2013; birthrate 1.43
- babies born: 0.98M in 2016: birthrate 1.44 (government target is 1.80)
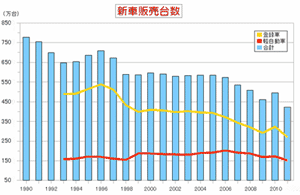
- marriage couple: 0.625M in 2016; male 31.1; female 29.4
- Birthrate of regional difference (2015): Av. 1.45
- Tokyo: 1.24
- Osaka: 1.39
- Okinawa: 1.96
- No braking of decreasing trend of the birthrate:
- ♠Population replacement level: sustainable birthrate: say 2.1
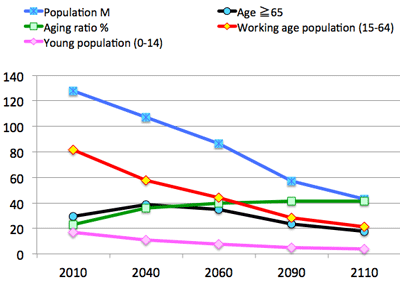
- If Japan recovers this level by 2030; then the populate stabilized at 99M around 2090 (after 60 years); law of inertia, or chronic disease
- Three stages of depopulation in Japan:
- First stage: Aging population increases, and working & young population decrease.
- Second stage: Aging population maintains, and working & young population decrease.
- Third stage: Aging, working & young populations decrease.
|
7.
参考: 人口減少の日本:
- ♥人口減少=晩婚化×出生率
- 日本は非嫡出子比率は2.29%/2016
- 仏57%, 英48%, 米40%, 独35%, 加33%
- ♦出生率:
|