
The Dragons of Eden
Cat: Sci
Pub: 1977
#: 9703b
Carl Sagan
97131u/18220r
Title
THE DRAGONS OF EDEN
エデンの龍
Sub Title
Speculations on the evolution of human intelligence
人類の知能の進化に関する考察
Author
Carl Sagan
カール・セーガン
Published
1977
1977年
Why ?
- Astronomy and biology are the
most interesting fields to trace using the fruits of IT.
- 天文学と生物学はITの成果を使って追求すべき最も興味深い分野である。
Index
Tag
; Brain-machine; Colonization of land; Cosmic calendar; Drake's equation; Early reptile; Encephalization; Eukaryote 11.15; Falling-snake-dark; Fontanelle; Frontal lobe; Hippocampus; Hiss of attacking reptile; Limbic system 150ma; ; Neocortex tens ma; Occipital lobe; Our destiny; Pariental lobe; Reptilian complex; Solution exists; Temporal lobe; Waking-sleeping-dreaming; ; ;
>Top 1. The Cosmic Calendar:
- The world is very old, and human beings are very young. The most
instructive way to express the cosmic chronology is to imagine the
15 billion year lifetime of the universe compressed into the span
of a single year. Then every billion years of Earth history would
correspond to about 24 days of our cosmic year, and 1 second of that
year to 475 real revolutions of the Earth about the sun.
------------
- Jan 1: Big Bang
- May 1: Origin of the Milky Way Galaxy
- Sep 9: Origin of the solar system
- Sep 14: Formation of the Earth
- Sep 25: Origin of life on Earth
- Oct 2: Formation of the oldest rocks known on Earth
- Oct 9: Date of oldest fossils (bacteria/blue-green
algae)
- Nov 1: Invention of sex (by microorganisms)
- Nov 12: Oldest fossil photosynthesis plants
- Nov 15: Eukaryotes (first cell with nuclei) flourish
- Dec 1: Significant oxygen atmosphere begins to develop
on Earth.
- Dec 5: Extensive volcanism and channel formation on Mars.
- Dec 16: First worm
- Dec 17: Cambrian Period begins. Invertebrates flourish.
- Dec 18: First oceanic plankton. Trilobites flourish.
- Dec 19: Oldvician Period. First fish, first vertebrates.
- Dec 20: Silurian Period. First vascular plants. Plants
begin colonization of land.
- Dec 21: Devonian Period. First insects. Animals begin colonization
of land.
- Dec 22: First amphibians. First winged insects.
- Dec 23: Carboniferous Period. First trees. First reptiles.
- Dec 24: Permian Period. First dinosaurs.
- Dec 25: Mesozoic Era begins.
- Dec 26: Triassic Period. First mammals.
- Dec 27: Jurassic Period. First birds.
- Dec 28: Cretaceus Period. First flowers. Dinosaurs become
extinct.
- Dec 29: Tertiary Period. First cetaceans. First primates.
- Dec 30: Early evolution of frontal lobes in the brains
of primates. First hominid. Giant mammals flourish.
- Dec 31: Quarternary Period.
- 13:30 Origin of Proconsul & Ramapithecus
- 22:30 First humans
- 23:00 Widespread use of stone tools
- 23:46 Domestication of fire by Peking man
- 23:56 Beginning of most recent glacial period.
- 23:58 Seafarers settle Australia.
- 23:59 Extensive cave painting in Europe
- 23:59:20 Invention of agriculture
- 23:59:35 Neolithic civilization, first cities
- 23:59:50 First dynasties in Sumer, Ebla & Egypt
- 23:59:51 Invention of the alphabet, Akkadian Empire
- 23:59:52 Hammurabic legal codes in Babylon, Middle
Kingdom in Egypt
- 23:59:53 Bronze metallurgy, Trojan War, Invention of
the compass
- 23:59:54 Iron metallurgy, First Assyrian empire, founding
of Carthage by Phoenicia
- 23:59:55 Asokan India, Ch'in (Qin) dynasty China, Periclean
Athens, birth of Buddha
- 23:59:56 Euclidean geometry, Archimedean physics, Ptolemaic
astronomy, Roman Empire, birth of Christ
- 23:59:57 Zero and decimals invented, Rome falls, Moslem
conquests
- 23:59:58 Mayan civilization, Sung Dynasty, Byzantine
empire, Mongol invasion, Crusades
- 23:59:59 Renaissance in Europe, voyages of discovery
from Europe
- Now: Development of science & technology, first
steps in spacecraft planetary exploration
1. 宇宙カレンダー:
- 世界は非常に古く、人類は非常に若い。宇宙の年表を150億年と想定し、それを1年の時間に圧縮して表現してみたい。地球の各十億年の歴史は約24日に、また475年間が1秒に対応することになる。
------------
- 1/1:ビッグバン
- 5/1:天の川の生成
- 9/9:太陽系の生成
- 9/14:地球の生成
- 9/25:地球上の生命誕生
- 10/2:地球最古の岩石の生成
- 10/9:最古の化石(バクテリア/藍藻)
- 11/1:性の発明(微生物)
- 11/12:最古の光合成植物の化石
- 11/15:真核生物(核をもつ細胞)繁栄
- 12/1:地球の大気中に相当量の酸素蓄積
- 12/5:火星での活発な火山活動および峡谷の生成
- 12/16:最初の蠕虫
- 12/17:古生代カンブリア紀始まる。無脊椎動物繁栄
- 12/18:最初の海洋プランクトン、三葉虫繁栄
- 12/19:古生代オルドビス紀。最初の魚類(最初の脊椎動物)
- 12/20:古生代シルリア紀。最初の導管植物、植物が陸上に進出
- 12/21:古生代デボン紀。最初の昆虫。動物が陸上に進出
- 12/22:最初の両生類。最初の有翅昆虫
- 12/23:古生代石炭紀。最初の樹木。最初の爬虫類
- 12/24:古生代二畳紀。最初の恐竜
- 12/25:中生代開始
- 12/26:中生代三畳紀。最初の哺乳類
- 12/27:中生代ジュラ紀。最初の鳥類
- 12/28:中生代白亜紀。最初の花。恐竜の絶滅
- 12/29:新生代第三紀。最初のクジラ目。最初の霊長目
- 12/30:霊長目の前頭葉の最初の発達。最初のヒト科。巨大哺乳類繁栄
- 12/31:新生代第四紀
- 13:30 類人猿プロコンスル、ラマピテクスの起源
- 22:30 最初の人類
- 23:00 石器の普及
- 23:46 北京原人による火の実用化
- 23:56 最後の氷河期開始
- 23:58 船乗り、豪州に植民
- 23:59 欧州での洞窟壁画
- 23:59:20 農業の発明
- 23:59:35 新石器時代、
最初の都市
- 23:59:50 シュメール、エブラ、エジプト国家の成立
- 23:59:51 アルファベットの発明、アッカド帝国
- 23:59:52 バビロニア帝国ハンムラビ法典、エジプト中王国
- 23:59:53 青銅器時代、トロイ戦争、磁石の発明
- 23:59:54 鉄器時代、最初のアッシリア帝国、フェニキアによるカルタゴ建設
- 23:59:55 アショカ王、秦王朝, アテネのペリクレス時代、ブッダ誕生
- 23:59:56 ユークリッド幾何学、アルギメデスの原理、プロレマイオスの天動説、ローマ帝国、キリスト誕生
- 23:59:57 ゼロ・十進法発明、西ローマ帝国滅亡、イスラムによる征服
- 23:59:58 マヤ文明、宗王朝、ビザンチン帝国、モンゴル侵入、十字軍
- 23:59:59 欧州ルネサンス、大航海時代
- 現在:科学技術の発展、最初の宇宙惑星探査
>Top 2. Genes and brains:
- The amount of genetic information in bacteria today is probably
not vastly greater than that in their ancient bacterial ancestors.
- In all organisms the hereditary molecules are nucleic acids (DNA)
- Viable but infertile matings of more widely separated species. Homo erectus and Homo habilis are classified as of
the same genus (Homo) but of different species.
- The book of life is very rich; a typical chromosomal DNA molecule
in a human being is composed of about 5 billion pairs of nucleotides.
The genetic instructions of all the other taxa on Earth are written
in the same language. This shared genetic language is one line of
evidence that all the organisms on Earth are descended from a single
ancestor, a single instance of the origin of life some 4 billion
years ago.
- Since there are four different kinds of nucleotides, the number
of bits of information is four time of 5 x 10^9 nucleotides, that
is, 2 x 10^10 bits of information.
- There was a striking improvement in the information content of
organisms on Earth some 3 billion years ago, and a slow increase
in the amount of genetic information thereafter.
- What is the information content of the brain?
Computer design suggests that the truth lies somewhere between the
following two extremes:
- the cerebral cortex is equipotent; any part of it may
substitute for any other part, and there is no localization
of function.
- or, the brain is completely hard-wired; specific cognitive
functions are localized in particular places in the brain.
- Some memories are funneled between the left and right cerebral
hemispheres by a conduit called corpus callosum.
- Penfield uncovered a remarkable localization of function in the motor cortex. Certain parts of the outer layers of our brain
are responsible for sending signals to or receiving signals from
specific parts of the body. The enormous amount of brain area committed
to the fingers - particularly the thumb - and to the mouth and the
organs of speech. Our learning and our culture would never have
developed without speech; our technology and our monuments would
never have evolved without hands.
- There are cells for horizontal, and cells for vertical, and cells
for diagonal, each of which is stimulated only if lines of the appropriate
orientation are perceived. At least some beginnings of abstract
thought have thereby been traced to the cells of the brain.
- Brain mass vs. body mass:
The evolution of mammals from reptiles over 200 million years ago
was accompanied by a major increase in relative brain size and intelligence;
and that the evolution of human beings from nonhuman primates a
few million years ago was accompanied by an even more striking development
of the brain.
- An average neuron in a human brain has 1,000 - 10,000 synapses
or links with adjacent neurons. If each synapse responds by a single
yes-or-no answer to an elementary question,the maximum number of
bits of information is about 10^10 x 10^3 = 10^13 or 10 trillion
bits.
- Recently it becomes clear that there are electrical microcircuits
(sized μm) in the brain, whose neurons care capable of a much
wider range of responses than simple yes or no. This suggests
that intelligence may be the result not only of high brain-to-body
mass ratio but also of an abundance of specialized switching
elements in the brain.
- A rate of information processing by the brain:
5,000 bps.
- <Calculation:> the moon is 0.5 degrees in diameter.
- We can see 12 picture elements across: eye can resolve 0.5/12
= 0.04 degrees.
- The instantaneous field of view in our eye is 2 degrees on
a side.: (2/0.04)^2 = 2500 pixels
- each pixel requires 20 bit: 2,500 x 20 = 50,000 bit.
- the act of scanning the picture takes 10 sec.
- Therefore, our sensory data processing rate is about 50,000/10
= 5,000 bps
- (Cf: The Viking lander camera has 500 bps)
- But We are not recollecting visual images all our waking hours;
the average rate of data processing is about 5,000/50 = 100
bps
- Over 60 years, that corresponds to 2 x 10^11, or 200 billion
total bits. This is less than the number of synapses, since
the brain has more to do do than just remember.
- <Storage of information>
- Computer: 10^6 bits/cm3
- Brain: 10^13 bits/10^3 cm3 = 10^10 bits/cm3
- Ten thousand times more densely packed with information than
a computer.
- <Processing speed>
- Computer: 10^16 - 10^17 bps
- Brain: 10^4 bps
- The brain must be extraordinarily cleverly packaged and wired
, with such a small total information content and so low a processing
rate, to be able to do so many significant tasks so much better
than the best computer.
- >Top <Brain evolution>
Somewhere in the steaming jungles of the Carboniferous Period there
emerged an early reptile whose brain was a symbolic turning point
in the history of life. The two subsequent bursts of brain evolution,
accompanying the emergence of mammals and the advent of manlike
primates, were still more important advances in the evolution of
intelligence. Much of the history of life since the Carboniferous
Period can be described as the gradual (and certainly incomplete)
dominance of brains over genes.
2. 遺伝子と脳:
- 今日のバクテリアにおける遺伝子情報量は太古のバクテリアの祖先と比べても非常に大きくはない。
- すべての遺伝子分子は核酸(DNA)である。
- 生育可能だが不妊なのは種が異なる。ホモ・エレクトゥス(原人)とホモ・ハビルス(猿人)とは同じヒト属に区分されるが種は異なる。
- 生命の本は非常に豊富である。人間のDNA分子は約50億のヌクレオチドから成る。地球上のすべての種の遺伝情報は同じ言語で記述されている。この共通の遺伝言語は地球上のすべての生物が一つの共通祖先、40億年前に一つの生命の誕生の事件から由来することを示す証拠とされる。
- ヌクレオチドには4種類あるので、情報量としては50億個のヌクレオチドの4倍、即ち、200億ビットの情報量となる。
- 30億年前には、地球上の生物の情報量に目覚ましい改善があったが、その後は遺伝子情報量は緩やかな増加しかしていない。
- 大脳のどこに情報の中身が存在するのか?
コンピュータの設計で言えば、真実は以下の両極端の間にありそうである。
- 大脳皮質の各部分は等しい能力をもつ。どの部分も他の部分を代替でき、特別な機能の部位はない。
- 大脳は完全に機能分化している。特定の認識機能は大脳の特定の場所に局在している。
- ある記憶は、左右の大脳半球の間で脳梁と呼ばれる通路を通って伝達される。
- ペンフィールドは、大脳の運動皮質に著しい機能の偏在を発見した。大脳の外層のある部分は、体の特定部分に対し、信号を送ったり、受け取ったりする。大脳のかなりの領域は指、特に親指に、また口は話す器官に割り当てられている。我々の学習や文化は言語がなかれば発展しなかったし、技術や記念碑も手がなければ発展しなかったのだ。
- 水平、垂直、対角線を感知する細胞がある。それぞれの細胞は線が適切な方向の場合のみ感知する。少なくとも抽象的思考の初期はこのような大脳の細胞によって追跡されてきた。
- 大脳重量対体重:
過去2億年に亘る爬虫類から哺乳類への進化は、相対的に大脳のサイズと知能の増加を伴っている。また数百万年前のヒトでない霊長類からヒトへの進化は、更なる大脳の著しい発展を伴っている。
- ヒトの大脳のニューロンには、平均1,000 - 10,000ものシナプスがあり、隣接ニューロンと連絡している。このこの各シナプスが、基本的な質問に対し、Yes/Noで答えるとすれば、情報ビット数は、およそ10の10乗☓10の3乗、即ち、10の13乗となりこれは10兆ビットとなる。
- 最近の発見では、大脳の中に微小なμmサイズの電気回路があり、そのニューロンは単純なYes/Noだけでない広い反応を示すことができるという。これは、知性が単に体重比の大脳質量だけでなく、大脳の中の特殊なスイッチ要因の豊富さにも依ることを示唆する。
- 大脳の情報処理率:5,000 bps
- <計算> 月の直径は0.5度
- この直径内に12の画素視認可。目の分解能は0.5/12 = 0.04度
- 目の瞬間視野角は2度。
(2/0.04)の2乗=2,500画素
- 各画素の色調に20 bit必要
2,500 x 20 = 50,000 bit
- 画像スキャン時間:10秒
- 従って、視覚の処理スピードは
50,000/10 = 5,000 bps
- (参考:火星Viking探査機搭載カメラの能力は、500 bps)
- 但し、起きている間すべて画像再生している訳ではない。平均データ処理率は、およそ5,000/50 = 100 bpsと推定。
- 60年間続けば、2☓10の11乗、即ち2000億bitとなる。これはシナプスの数より少ない。ということで大脳には単なる記憶以上の処理能力がある!
- <情報の蓄積>
- コンピュータ:10の6乗 bits/cm3
- 大脳:10の13-14乗/1000cm3
= 10の10乗 bits/cm3
- 大脳はコンピュータより1万倍も蜜に情報を蓄積
- <処理スピード>
- コンピュータ:10の16-17乗bps
- 大脳:10の4乗 bps
- 大脳は小さな容量の中に、異常なほど賢く情報を詰め込み連携している反面、その処理スピードは遅いが、最良のコンピュータより遥かに多くの重要な仕事をこなすことができる。
- <大脳の進化>
古生代石炭紀の熱帯ジャングルのどこかで、生命の歴史にとって象徴的な転換点にあたる大脳をもった初期の爬虫類が登場する。その後2度に亘る大脳の進化があった。哺乳類とヒトに似た霊長類の登場はさらに知能の進化にとって重要だった。石炭紀以来の生命の歴史のほとんどはこのよう遺伝子に対する大脳の漸進的な支配というように記述され、それは今でも完了していない。
>Top 3. The triune brain:
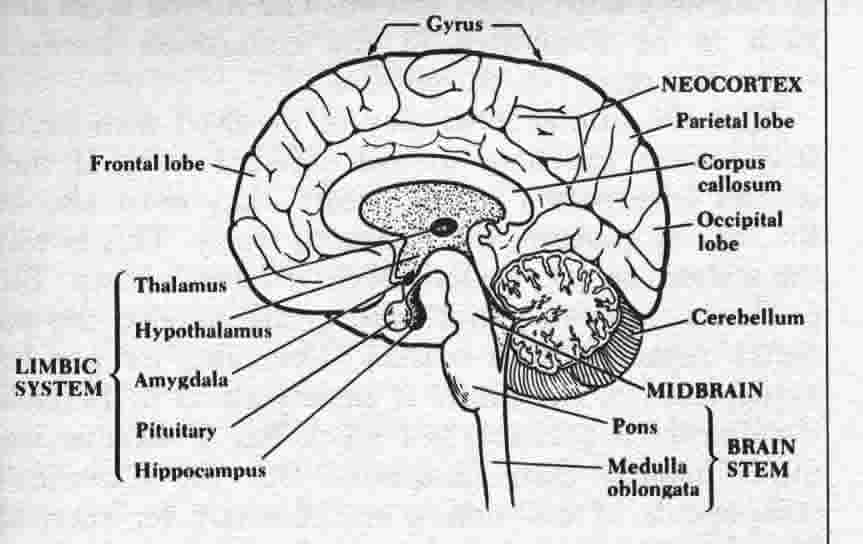
- We are obliged to look at ourselves and the world through the
eyes of three quite different mentalities.
- >Top Reptilian Complex (R-complex): evolved several hundred
million years ago.
The most ancient brain; lies the spinal cord, the hindbrain
and the midbrain. It contains the basic neural machinery for
reproduction and self-preservation, including regulation of
the heart, blood circulation and respiration.
R-complex plays an important role in aggressive behavior, territoriality,
ritual and the establishment of social hierarchies.
- >Top Limbic System: evolved 150 ma (million years ago). (Arms
and legs are called limbs because they are peripheral.) This
appears to generate strong or particularly vivid emotions. There
is a small almond-shaped inclusion in the limbic system called
the amygdala which is deeply involved in both aggression
and fear.
Mammals and birds are the only organisms to devote substantial
attention to the care of their young. Love seems to be an invention
of the mammals.
One segment of the old limbic system is devoted to oral and
gustatory functions; another, to sexual functions. The connection
of sex with smell is very ancient, and is highly developed in
insects.
Short-term memory of smell resides in the hippocampus.
- >Top Neocortex: evolved several tens ma (millions years ago).
Four major regions or lobes; the frontal, parietal, temporal
and occipital lobes.
- Frontal lobes: connected with deliberation, regulation
of action, anticipation for the future, and locale of worry.
- Parietal lobes: spatial perception and exchange
of information between the brain and the rest of the body
- Temporal lobes: complex perceptual tasks, connect
auditory with visual stimuli.
- Occipital lobes: vision, the dominant sense in
primates.
- >Top Short-term and long-term memory reside mostly in different
parts of the brain. Human long-term memory is situated in the
neocortex. As we grow old, we sometimes forget what has just
been said to us while retaining vivid and accurate recollections
of events in our childhood. The problem is the connection between
our short-term and long-term memories; difficulty in accessing
new material into the long-term memory. This lost accessing
ability arises from an inadequate blood supply to the hippocampus in old age because of arteriosclerosis, etc.
- If I repeat the numbers out loud or write them down, I can
remember them quite well. This surely means that there is a
part of our brain which remembers sounds and images, but not
thoughts. I wonder if that sort of memory arose before we had
very many thoughts - when it was important to remember the hiss
of an attacking reptile or the shadow of a plummeting hawk,
but not our own occasional philosophical reflections.
- In the embryological development, an animal tends to repeat or
recapitulate the sequence that its ancestors followed during their
evolution. In human intrauterine development we run through stage
very much like fish, reptiles, and nonprimate mammals before we
become recognizably human.
3. 脳の三層構造:
- 我々は、自分自身および世界をまったく異なる視点から見つめている。
- 爬虫類的組織:数億年前に進化。
最も古い脳。脊髄、後脳、中脳に位置する。生殖および心臓、循環、呼吸を含む身体維持。
この組織はまた、攻撃的行動、縄張り、慣例、社会的階層の確立などに重要な役割を演じる。
- 大脳辺縁系:1.5億年前に進化(手や足は肢と呼ばれ周辺を意味する)。この機能は強烈あるいは活発な感情を表現する。大脳辺縁系の神経節にアーモンド状の扁桃核があり、これが攻撃や恐怖の深く関与している。哺乳類や鳥類は子供の保育に献身する唯一の生物である。愛情は哺乳類によって発明されたものらしい。
古い大脳辺縁系の一面は、口や味覚の機能に、また他の面では性的機能に関連している。嗅覚と性との結びつきは非常に古く、とりわけ昆虫に発達している。
嗅覚に関する短期記憶は海馬にある。
- 新皮質:数千万年前に進化。4つの部位・葉に分かれる。前頭葉、頭頂葉、側頭葉、後頭葉。
- 前頭葉:思索、行動管理、未来予測、および懸念
- 頭頂葉:空間認識、大脳と他の身体との情報交換
- 側頭葉:複雑な知覚、聴覚と視覚刺激の連携
- 後頭葉:霊長類の主な感覚器官である視覚
- 短期、長期の記憶は主に大脳の異なる部位に蓄えられる。人間の長期記憶は新皮質に位置する。年をとると我々は今言われたことを忘れる一方で子供の頃の出来事を生き生きと正確に覚えている。問題は我々の短期と長期の記憶の連結にある。即ち、新しいことを長期記憶にアクセスすることが難しくなる。これは動脈硬化などで年をとると海馬への血行不全が原因である。
- もし番号を大きな声で繰り返し、書いたりすれば、それをうまく覚えることができる。これは我々の大脳が考えではなく音やイメージを記憶する場所が確かにあることを意味している。このような記憶の種類は我々が多くを考えるようになる以前に生じていたと思われる。即ち攻撃しようとしている爬虫類のシューという音や急降下する鷹の影を記憶する方が、我々の哲学的な思索を記憶するより重要だったということだ。
- 発生学的な発展において、動物は祖先の進化の過程を繰り返したりする。人間も子宮の中の生育で、非常に魚のような段階から、爬虫類、哺乳類を経て、ヒトとして認識されるように育つ。
>Top 4. Encephalization:
- In the evolutionary line leading to man, when was the first large-scale
development of the neocortex? Paleontologists have deduced that "bipedalism
preceded encephalization," by which they mean that our ancestors
walked on two legs before they evolved big brains.
Species
Earliest
specimen
(million
years)
Endocranial
volume
(cc)
Height
(m)
Weight
(kg)
Brain
/Body
ratio
Australopithecus
robustus
3.5
500-550
1.5
40-60
90
Australopithecus
africanus
6
430-600
1-1.2
20-30
50
Homo habilis
3.7
500-800
1.2-1.4
30-50
60
Homo erectus
(Pithecanthoropus)
1.5
750-1250
1.4-1.8
40-80
65
Homo sapiens
0.2
1100-2200
1.4-2
40-100
45
- At the same epoch as Australopithecus robustus, there arouse Home habilis at a time when, for climatic reasons, the forests
were receding; African Savannah, an extremely challenging environment
filled with enormous variety of predators and prey.
- Since H. habilis and A. robustus emerged at the
same time, it is very unlikely that one was the ancestor of the
other. It is possible that both H. habilis, with a promising
evolutionary future, and A. robustus, an evolutionary dead
end, arouse from the gracile A. africanus, who survived long
enough to be their contemporary.
- The most striking aspect of the archaeological record concerning
tools is that as soon as they appear at all they appear in enormous
abundance. an inspired gracile Australopithecine discovered
for the first time the use of tools and immediately taught the toolmaking
skill to his relatives and friends.
- An interesting number of fossils are found with holes and
fractures in their skulls. In Pliocene -Pleistocene times there
was almost certainly a vigorous competition among many manlike
forms, of which only one line survived- the tool experts, the
line that led to us.
- >Top Childbirth is painful because the evolution of the human skull
has been spectacularly fast and recent. The incomplete closure of
the skull at birth, the fontanelle, is very likely an imperfect
accommodation to this recent brain evolution.
- Evolution of the prefrontal lobes must accompanied the awareness
of death. Burial ceremonies go back at least to the time of
Neanderthal.
- The development of human culture and the evolution of those physiological
traits most likely proceeded hand in hand: the better our genetic
predispositions for running, communicating and manipulating, the
more likely we were to develop effective tools and hunting strategies.
- One can imagine gestural languages being gradually supplemented
and then supplanted by verbal languages, which originally may
have been onomatopoeic. We know enough about the hunting of
large animals to realize that some language is required for
cooperative stalking.
- The development of language, tools, and culture may have occurred
roughly simultaneously.
4. 脳の進化:
- 人類につながる進化の過程の中で、大脳新皮質がいつ大きく発展したのだろうか。古生物学者の推論では、"二足歩行が脳の発達より先行した"とされ、我々の祖先は大脳を発達させる以前から二足歩行をしていたことを意味する。(左図参照)
- アウストラロピテクス・ロバスツスと同じ時期にホモ・ハビルスが登場する。その時期は気候上の理由から森林が後退したアフリカ・サバンナであった。そこは捕食者と獲物の大勢いる非常に競合する環境だった。
- ホモ・ハビルスとA. ロバスツスがほぼ同時期に登場していることからして、一方が他方の祖先であるとは考えられない。ホモ・ハビルスが進化的な発展性も保ち、一方のA.
ロバスツスの方は進化が止まった状態で、いずれもその時点まで生き延びた繊細な体型のアウストラロピテクス・アフリカヌスから発生してきた可能性がある。
- 道具に関する考古学的な記録で特に驚くべきに、一旦、道具が登場するやその数が非常に多く発見されることである。アウストラロピテクス属が初めて道具を発明すると、すぐその作り方を親戚や友人に教えた。
- 穴や裂け目のある頭蓋骨が相当数見つかる。これは鮮新世や更新世の時代は、類人猿の間で激しい競争があり、その中の道具作りに優れた我々に続く一系統のみが生き残った。
- 人類の頭蓋骨の進化があまりにも急激で直近のことだったので出産には苦痛と伴う。出産時の頭蓋骨が完全に閉じられていない泉門はおそらく最近の大脳の進化がまだ十分に適合していない証拠と思われている。
- 前頭葉の進化にともない死の認識が始まった。埋葬の儀式は、少なくともネアンデルタール人まで遡る。
- 人類の文化と生理学的な特徴とは、相まって発展してきた。走り、交信し、操作することの遺伝的な素質が発揮されると我々はますます効果的な道具と狩猟方法を発展させることになった。
- 身振り言語は最後は擬音語だったが、徐々に言語に取って代わられたと推定される。大型動物を仕留めるために協力して忍び寄るためには何らかの言語必要としたことは想像に難くない。
- 言語と道具と文化とはおそらく同時に発展してきたものであろう。
>Top 5. States of mind:
- There are three principal states of mind in human beings; waking,
sleeping and dreaming. An electroencephalograph (EEG) records quite
distinct patterns of electrical activity in the brain during these
three states. Brain-wave frequencies are between 1-20 Hz.
- What is sleep good for? Our nocturnal vulnerability is very evident;
the Greeks recognized Morpheus and Thanatos, the gods of sleep and
death, as brothers.
- There is some recent evidence that the two types of sleep,
dreaming and dreamless, depend on the life-style of the animal.
Predators are statistically much more likely to dream than prey.
Deep dream sleep is rare among prey. In dream sleep, the animal
is powerfully immobilized and remarkably unresponsive to external
stimuli. Dreamless sleep is much shallower.
- In a late Mesozoic landscape the mammals sleep fitfully by
day and the reptiles by night.
- Visual-information processing in reptiles is done not in the brain
but in the retina; the optical processing apparatus in the neocortex
was largely a later evolutionary development.
- Dinosaurs were, compared to mammals, remarkable stupid. Body weight
and brain volume are:
- Tyrannosaurus rex's: 8 tons - 200 cc,
- Brachiosaurus: 87 tons - 150 cc,
- Triceratops: 7 tons - 70 cc,
- Diplodocus: 12 tons - 50 cc
- Stegosaurus: 2 tons - 30 cc (stupid than a rabbit)
- Saurornithoides: 50 kg - 50 cc (the most intelligent
dinosaurs)
- Carnivorous dinosaurs such as Tyrannosaurus were relatively
larger-brained than such herbivores as Diplodocus and Brachiosaurus. (Cf: Sharks are the largest-brained fish for
their body weight.)
- If the dinosaurs had not all been mysteriously extinguished some
65 million years ago. what would be the dominant life forms on Earth
today?
- Descendants of Saurornithoides: think the base 8 arithmetic
was quite natural?
- The dinosaurs died because of a nearby supernova event. Nocturnal
mammals and deep-sea fish could have survived this higher ultraviolet
intensity.
- >Top Young primates appear to be born with only three inborn fears
- of falling, snakes and the dark.
- I wonder if the waking state of other mammals is very much like
the dream state of humans - where we can recognize signs, such as
the feeling of running water and the smell of honeysuckle, but have
an extremely limited repertoir of symbols such as words.
5. 心の状態:
- 人間の心には主に3つの状態がある。覚醒状態、睡眠状態、夢想状態である。脳波計によれば、これら3状態の大脳の脳波には際立った違いがある。脳波の周波数は1-20
Hzである。
- 睡眠には何か良いことがあるのか。我々は夜に襲われやすいというの明らかだ。ギリシャ神話でも眠りの神モルフェウスと死の神タナートスは兄弟として描かれている。
- 夢を見る睡眠と夢を見ない睡眠は動物のライフスタイルによる。補食者は被食者よりも統計的に多く夢をみる。被食者は深い夢を見る睡眠はしない。深い夢見る睡りでは動物は全く動かなくなり外部刺激に反応しない。夢のない眠りはもっと浅い。
- 中生代後期に風景では、哺乳類は昼間眠り、爬虫類は夜眠っていた。
- 爬虫類の視覚情報は、大脳ではなく網膜で処理されている。新皮質での視覚処理機構は、後で進化の発展によって獲得された。
- 恐竜は、哺乳類に比べて著しく愚かである。体重と脳の容量は、
- ティラノザウルス:
8トン-200cc
- ブラキオザウルス:
87トン−150cc
- トリケラトプス:
7トン−70cc
- ディプロドカス:
12トン−50cc
- ステゴザウルス:(兎以下)
2トン−30cc
- サウロニソイデス:
50kg - 50cc(最も賢い恐竜)
- ティラノザウルスのような肉食恐竜はブラキオザウルスのような草食恐竜に比べて、より大きな脳をもっていた。(なお鮫は魚の中では、体重比で最大の脳を持つ。)
- もし恐竜が突如として65百万年前に絶滅しなかったら、今日地球上の支配的な生命はどうなっただろうか。
- サウロニソイデスの子孫で、8進法の計算を当然と見なしたかも。
- 恐竜は近くの超新星爆発が原因とする説がある。夜行性の哺乳類と深海の魚だけが、強烈な紫外線から免れて生き延びた。
- 若い哺乳類はこの3つの恐怖を抱いて生まれてくる。それらは落下、ヘビそして暗闇である。
- 他の哺乳類の覚醒状態は人間の夢想状態によく似ている。そこでは合図、例えば水の流れる感じ、スイカズラの匂いなどである。但し言葉のような記号に対しては極端にレパートリが制限される。
>Top 6. Search for extraterrestrial intelligence:
- Communications with EI may employ:
- electro-magnetic spectrum, most likely the radio part of the
spectrum
- or gravity waves, neutrinos, tachyons (if they exist)
- new aspect of physics that will not be discovered for another
three centuries.
- The number of advanced civilization in the Milky Way galaxy depends
on many factors, ranging from the number of planets per star to
the likelihood of the origin of life. Once life has started in a
benign environment and billions of years of evolutionary time are
available, intelligent beings would develop.
- The evolutionary path would be different from us. There should
be many functionally equivalent pathways to a similar end result.
Smart organisms by and large survive better and leave more offspring
than stupid ones.
- Intelligent organisms evolving on another world may not be
like us biochemically; different adaptations - from enzymes
to organ systems - to deal with the different circumstances.
But they must still come to grips with the same laws of nature.
- >Top Their brains will have had different evolutionary histories
in different environments. But I think it highly probable that our brains and machines and their brains and machines will ultimately
understand one another very well.
- One consequence seems clear; the receipt of a message from an
advanced civilization will show that there are advanced civilizations,
that there are methods of avoiding the self-destruction that seems
so real a danger of our present technological adolescence.
- In mathematics is called the existence theorem. Finding a
solution to a problem is helped enormously by the certain knowledge
that a solution exists.
- >Top <Frank Drake's Equation> (from 'Cosmos')
N= Ns x fp x ne x fl x fi x fc x fL
where,
N : the number of advanced technical civilization
in the Galaxy.
Ns : the number of stars in the Milky Way Galaxy.
(estimated 4 x 10^11)
fp : the fraction of stars that have planetary systems.
(roughly 1/3)
ne : the number of planets in a given system that are ecologically suitable for life. (conservatively 2)
fl : the fraction of otherwise suitable planets on which life actually arises. (roughly 1/3)
fi : the fraction of inhabited planets on which an intelligent from of life evolves. (say 1/10)
fc : the fraction of planets inhabited by intelligent being
on which a communicative technical civilization develops
(say 1/10)
fL : the fraction of a planetary lifetime graced by a
technical civilization. (less than 1/10^8)
- Therefore, N will be about 10
- But consider the alternative, the prospect that at least some
civilizations learn to live with high technology; that the contradictions
posed by the vagaries of past brain evolution are consciously resolved
and do not lead to self-destruction, of if 1% of civilizations can
survive technological adolescence:
then fL will be about 1/100, N will be 10^7 (=10 million)
6. 地球外知能探査:
- 地球外知性との交信の手段は
- 電磁波スペクトラム、特にラジオ波
- 重力波、ニュートリノ、タキオン(もしあれば)
- 新たな物理学(あと3世紀はかかるだろうが)
- 我々の銀河系にある先進文明の数は恒星にある惑星の数から生命発生の可能性までなどの多くの要因に依存する。一度生命が好ましい環境下で発生すると数十億年の進化の時間があれば知的生物に発展する。
- その進化の道筋は我々と異なるだろう。機能的には同じような多くの道筋をたどって同じような結果になり得る。賢い生物は愚かな生物に比べ、大体長く生き延び、多くの子孫を残す。
- 他の世界で進化した知的生命は我々と比べて生化学的に、酵素から器官システムに至るまで異なっているだろう。しかし同じ自然法則を活用しているに違いない。
- 彼らの脳は異なった環境下で異なった進化の歴史をもつ。しかし我々の脳と機械は彼らの脳と機械を究極的には相互にうまく理解し合える確立は非常に高いと思う。
- 他の先進文明からのメッセージを受信することの結果の意味することは明らかである。それは他に先進文明が存在しているという事実である。そして我々の現在の技術的青春期における現実となっている危険から自己破壊を防ぐ方法があることを示すことになる。
- これは数学的には存在定理と呼ばれるものである。問題の解を見つけるに当たっては、解が存在するという確かな知識によって非常に助けられるのである。
- <ドレイクの式>
N= Ns x fp x ne x fl x fi x fc x fL
ここで、
N : 銀河系にある先進技術文明の数
Ns : 銀河系にある恒星の数(約4 x 10の11乗)
fp : 惑星系をもつ比率(約1/3)
ne : 生命発生にふさわしい環境をもつ惑星の数(約2)
fl : 実際に生命が発生する比率(1/3)
fi : 知的文明に進化する比率(1/10)
fc : 通信技術文明を持つ比率(1/10)
fL : 技術文明が存続する比率(1/10の8乗)
- 上記想定では、N は約10個。
- 別の想定も可能。
すくなくとも幾つかの文明は高い技術文明を長らえることを学ぶし、過去の大脳の進化の気まぐれに毒されることの逆の場合として意識的に自己破壊を解決する場合、あるいは1%の文明が技術的黎明期を脱して生き延びる場合などという想定である。
この場合、fL は1/100となり、
N は10の7乗(=1000万)
Comment
>Top Knowledge is our destiny.
"It is only in the last day of the Cosmic Calendar that substantial
intellectual abilities have evolved on the planet Earth. We are unlikely
to survive if we do not make full and creative use of our human intelligence," Carl Sagan concludes.
知性は我々の運命なのだ。
「宇宙カレンダーの大晦日においてようやくこの地球惑星に実質的に知的可能性が進化した。我々人類の知性を全面的かつ創造的に活用しなければ、我々はおそらく生存できなくなる」と、カール・セーガンは結論づけている。
 |
The Dragons of Eden
|
Cat: Sci
|
Carl Sagan |
97131u/18220r |
Title |
THE DRAGONS OF EDEN |
エデンの龍 |
|---|---|---|
Sub Title |
|
|
Author |
|
|
Published |
|
|
Why ? |
|
|
|
||
Tag |
; Brain-machine; Colonization of land; Cosmic calendar; Drake's equation; Early reptile; Encephalization; Eukaryote 11.15; Falling-snake-dark; Fontanelle; Frontal lobe; Hippocampus; Hiss of attacking reptile; Limbic system 150ma; ; Neocortex tens ma; Occipital lobe; Our destiny; Pariental lobe; Reptilian complex; Solution exists; Temporal lobe; Waking-sleeping-dreaming; ; ; | |
>Top 1. The Cosmic Calendar:
|
1. 宇宙カレンダー:
|
>Top 2. Genes and brains:
|
2. 遺伝子と脳:
|
>Top 3. The triune brain:
|
3. 脳の三層構造:
|
>Top 4. Encephalization:
|
4. 脳の進化:
|
>Top 5. States of mind:
|
5. 心の状態:
|
>Top 6. Search for extraterrestrial intelligence:
|
6. 地球外知能探査:
|
Comment |
>Top Knowledge is our destiny."It is only in the last day of the Cosmic Calendar that substantial intellectual abilities have evolved on the planet Earth. We are unlikely to survive if we do not make full and creative use of our human intelligence," Carl Sagan concludes. |
知性は我々の運命なのだ。「宇宙カレンダーの大晦日においてようやくこの地球惑星に実質的に知的可能性が進化した。我々人類の知性を全面的かつ創造的に活用しなければ、我々はおそらく生存できなくなる」と、カール・セーガンは結論づけている。 |
|---|