History of Ottoman Empire
Cat: HIS
Pub:1992
#: 2211b
Tadashi Suzuki (鈴木董)
22525u
Résume
Remarks
>Top 0. Introduction:
- Ottoman Empire continued from 1299-1923 (624 years); called 'Soft Monopoly'.
- >Top Main battles of Ottoman Empire:
- 1071◎Battle of Malazgird; Saljuq won; Turmen inflowed actively in Anatoria.
- 1299◎occupied Sögüt; appear Muslim Turkish worrier (Ghazi)
- 1326◎occupied Bursa by 2nd Orphan; established Ottoman Empire
- 1331◎occupied Nicaea (=Iznik)
- 1363◎occupied Edirne (=Adrianople)
- 1389◎Battle of Kosovo; Mulad I defeated Serbian Army, and ruled Balkan Peninsula; But Murad I was assassinated by Serbian nobleman.
- 1396◎Nikopolis Crusade: defeated Eastern Euopean Allies
- 1402▲Battle of Ankara;defeated to Timur Army
- 1453◎Fall of Constantinople; controlled Crimean Khanate
- 1492▲Fall of Granada; Naşr Dynasty (Grtanada Kingdom 1232-) was defeated by Reconquista movement
- 1514△Battle of Chardoran; defeated Safavid Dynasty
- 1517◎defeated Mamuk Dynasty; occupied Syria-Egypt; protected Mecca & Medina
- 1523◎defeated Orde des Hospitaliers (Knights Hospitallers); occupied Rhodos Island; controlled eastern Medeterrean Sea
- 1526◎Battle of Hacs; occupied Hungarian territory
- 1529△First Siege of Vienna; withdrew due to winter
- 1538◎Sea Battle of Preveza; command of Mediterranean Sea
- 1571▲Sea Battle of Lepanto; was defeated by Spanish-Pope Allies
- 1683▲Second Siege of Vienna; defeated by European
- 1699▲Treaty of Karlowitz; loss of Hungary
- 1774▲Treaty of Küchuk・Kaynardzha; loss of Crimean Khanate
- 1821▲Greek War of Independence
- 1839▲Gulhane Edict; Tanzimat Westernization Reform
- 1877▲Russo-Turkish War
- 1878▲Treaty of Berlin; loss of most of Europ; Serious ill of Ottoman Empire
- 1908△Young Turk Revolution; Enver Pash
- 1912▲First Balkan War; loss of Macedonia
- 1920▲Treaty of Sèvres (defeat of WWI)
- 1922△Greek Army invaded Izmir; Mustafa Kemal repelled; abolished Sultan System.
- End 13C: Founded at Sögüt in Anatolia; Turkoman Beylik leader Osman I.
- 1354: Ottomans conquered Balkan.
- 1453: ended Byzantine Empire by 7th Mehmed II the Conqueror.
- 1520-66: Suleiman I the Magnificent; marked the peak of it power and prosperity.
- contained 32 provinces and numerous vassal states.
- the empire continued to maintain its strong economy, military throughout 17-18C.
- 1718-1730: Tulip period (Lâle Devri) ; relatively peaceful period under 23rd Sultan Ahmed III and Grand Vizier Nevesehirli Damat Ibrahim Pasha.; created Sadabad Palace, a new summer palace.
- >Top 1740-68: Its military system fell behind that of Habsburg and Russian empires.; suffered severe military defeats in late 18C and early 19C.
- 1768 Defeated in the Russian War, losing northern coast of the Black Sea, and in 1792 lost Crimean Peninsula.
- The former Yeniceri army sticked to the vested interest due to hereditary members and the military organization became obsolete.
- 1798: Egypt was separated after Napoleon expedition, and Greece became independent after the French Revolution.
- 19C: Balkan peoples required autonomy and independence from Ottoman, whose territory was limited to a small part of Balkans, Anatolia and part of Arab region.
- 1839-76: The Age of Tanzimat Reform (Westernization and Modernization Refoms), aiming at social reform compromising Shariah and Western modern law. But economically it became semi-colonized situation due to mono-culture of agriculture.
- 1908/7 Young Turk Revolution; restored the Ottoman Constitution and recall the parliament by multi party politics. (Second Constitutional Era)
- 1911: allied with Germany in response to the expansion of Pan-Slavism and participated in WWI on the Alley side.
- 1913 Coup d'état by CUP (Committee of Union and Progress); and joined the Central Powers at WWI.
- lost ME territories and were divided by UK and France.
- 1920: The Allies enforced the Treaty of Sèvres with 36th Mehmet VI and ceded most of the territory to the Allies.
- >Top 1919-1923: Backed by Turkish ethic opposition, Mustang Kemal (Atatürk) Pasha, defeated Greek troops near Ankara, and signed the new Treaty of Lausanne.
- 1923; Treaty of Lausanne; Ottoman monarchy abolished and declared the Republic of Turkey, expeled the Ottoman family abroad.
0. 序文:
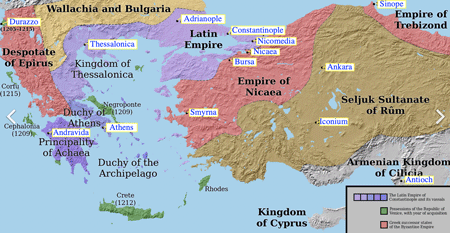
- Map of Anatolia (after 4th Crusade; 1202-04)
- 1299-1923: オスマン帝国は、624年間存続; 柔らかい専制制度
- アナトリアの小君侯国から発展したイスラム王朝から地中海の過半を有する世界帝国へ発展
- オスマン帝国の主な戦い:
- 1071◎マラーズキルドの戦い; セルジューク朝軍、ビザンティン軍に勝利。以後、アナトリアへのトルコ人流入が活発化
- 1299◎Sögüt占領; ムスリムトルコ系軍団 (ガーズィー)建国
- 1326◎ブルサ占領; 第2第オルファン; オスマン帝国設立
- 1331◎ニカエア (イズニク)占領
- 1363◎エディルネ(アドリアノープル)占領
- 1389◎コソヴォの戦い; バルカン半島を支配下
- 1396◎ニコポリス十字軍; 東欧連合軍に勝利
- 1402▲アンカラの戦い; ティムール軍に大敗
- 1453◎コンスタンチノープル陥落; クリミア汗国服従
- 1492▲グラナダ陥落; レコンキスタ運動
- 1514△チャルドランの戦い; サファヴィー朝撃退
- 1517 ◎マムルーク朝滅亡 シリア・エジプト領有; メッカメディア保護
- 1523◎ヨハネ騎士団撃退; ロードス島占領
- 1526◎モハーチの戦い; ハンガリー領有
- 1529△第1次ウィーン包囲戦
- 1538◎プレヴェザの海戦; 地中海制海権
- 1571 ▲レパントの海戦; 西・教皇連合艦隊に敗北
- 1683▲第2次ウィーン包囲戦
- 1699▲カルロヴィッツ条約; ハンガリー喪失
- 1774▲キュチュク・カイナルジャ条約; クリム汗国喪失
- 1821▲ギリシア独立戦争
- 1839▲ギュルハネ勅令;タンジマート西欧化改革
- 1877▲露土戦争
- 1878▲ベルリン条約; 欧州の大部分喪失; 瀕死の重病人
- 1908△青年トルコ革命; エンヴェル・パシャ
- 1912▲第1次バルカン戦争; マケドニア喪失
- 1920▲セーヴル条約(WWI敗戦)
- 1922△ギリシア軍イズミル侵入激地; ムスタファ・ケマル; スルタン制廃止
- 西欧キリスト教世界にとってはオスマンの衝撃。神聖ローマ帝国によるカトリック的世界帝国構築の夢の挫折
- 西欧は、ピョートルIのロマノフ朝を支援してオスマン帝国を圧迫
- WWIの敗戦後のセーブル条約で列挙クによるオスマン帝国解体に反対する勢力がトルコ共和国を樹立した。
- 1922 オスマン帝国はスルタン制度を廃止し、メフメトⅥは亡命、1924にはカリフ制度も廃止。
- 首都:
- 13C終: 始祖オスマンI がアナトリア西北部 (ソユット)に勢力確立 (Ghazi)
- 1326頃、オスマンの子第2代オルハンがブルサを占領
- 1453: 第7代メフムトII、コンスタンチノープル攻略、東ローマ帝国滅亡
- 1520-66: 第10代スレイマンI 荘厳者; オスマン帝国の最盛期
- 32州と多くの属国
- 17-18Cを通じて強固な経済・軍事体制を維持
- 1718-30: ツーリップ時代; 第23代アフメトIIIと大宰相 ネフシェヒルリ・ダマト・イブラヒム・パの時代、対外融和政策が取られ文化の円熟期
- 1722: サファヴィー朝が崩壊
- 1740-68: 軍事的には、ハプスブルク帝国とロシア帝国に押されて、18-19Cにかけて縮小傾向。
- 1768 露土戦争で敗北し、黒海北岸を、また1792にはクリミア半島を失う
- かつてのイェニチェリは隊員の世襲化により既得権に固執し、旧式化
- 1798のナポレオン遠征をきっかけにエジプトが分離し、またフランス革命後にギリシア王国が独立。
- 19C: またバルカンの諸民族は次々オスマンから自治・独立を進め、オスマン帝国はバルカンのごく一部とアナトリア、アラブ地域だけとなる。
- 1839-1876: タンジマート (西欧化・近代化改革)の時代: シャーリアと西洋近代法の折衷を目指した社会改革。経済的にも農業のモノカルチャー化で半植民地化していった。
- 1911: 伊土戦争により、リビアが帝国から離脱。
- 1914: 汎スラヴ主義拡大に対応してドイツと同盟してWWIに同盟国側で参戦
- 1920: 連合国は、第36代メフメトⅥとセーヴル条約を締結し、領土大半を連合国へ割譲した。
- 1922 : トルコ人の民族的な反発を受けてケマル・パシャは、アンカラに迫ったギリシア軍に勝利し、新たな講和条約ローザンヌ条約を締結した。
- 1923 トルコ共和国成立宣言し、オスマン家成因を国外に追放し、オスマン帝国は完全に滅亡した。
>Top 1. From a group of Warriors to a Nation:
- Until 11C, Anatoria was the easer half of Byzantine Empire; the land of Greek Orthodox.
- Turkish people (Turkestan):
- 6-8C: Turuk, 8-9C Uyghurs
- Central Asia was Turkish land (Turkestan)
- 751 Battle of Talas: Islamic forced advanced
- Turkish people became Islamic.
- Transfer of paper making technology
- >Top 1055 Great Seljuk Dynasty: Tughril Beg advanced to Baghdad, and exercised political power on behalf of Khalifa; called Sultan (<'power' or 'authority')
- Seljuk: a clan of Turk nomadic Ogs; Turkomans, who converted to Islam. later lad foundation for Seljuk Dynasty.
- 1063 Alp Arslan invaded Anatolia and defeated Byzantine Emperor Romanos IV.
- >Top 1077 Rum Seljuk founded:
- Its capital was originally Nikaia, but after being retaken by the 1st Crusade, it swept across Anatolia as the capital of Konya.; expanded Turkish language in Anatolia
- Three-cornered battles: among shrinking Byzantine world, expanding Islamic world, and southern European Catholic forces;
- 1204: Constantinople was occupied by 4th Crusade (mainly Venice)
- 1243: Mongolia invaded and made vassalization of Rum Seljuk Dynasty.
- >Top 1261: Byzantine Empire regained the capital; conflicted with Christian Akritai and Muslim Ghazi.
- 1326: After death of Ottoman Bey (Osman I), the successor occupied Bursa with hundred of soldiers, and made it its capital.; Beylik (<Bey)
- c1330: occupied Nikea
- 1337: occupied Nicomedia (between Bursa and Constantinople); thus occupied most of the Byzantine territory in Anatolia.
- this area was a land-traffic center, where technocrat bureaucrat such as Islamic laws scholars (Ulama) became Islamic lawyers (Judge, or Kadu) involved in trial and civil affairs as the center of Ottoman Empire.
- He opened his own Islamic law scholar training institution, the Islamic Academy (Madrasa)
- >Top Vizier (or Wazir <wazara, burden) (Chancellor) System: supported the general administration.
- Military organization is composed of, 1) Ottoman clan, 2) other Islamic Gazi groups, and 3) Byzantine Christians (partially converted to Islam)
- Sons of the Sultan were distributed as Beylerbey (Military commander).
- Tax management system (Divan, administered state property); poll tax (Jizya), and Land tax (Kharaj)
- >Top 1361: 3rd Sultan Murad I (1362-1389) conquered Adrianople (renamed Edirne), which became the second largest city of Ottoman Empire.
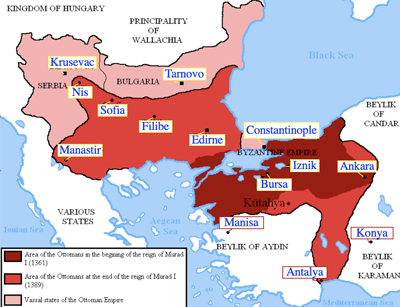
- firstly used the title of Sultan and increased the fame of the empire. (> config)
- He was the second son of Orhan Bey, the founder.
- acquired Edirne and mostly conquered the Balkan Peninsula; also made Bulgarian Emperor Ivan Shishman as a vassal at the battle of Samakov; he made the emperor's sister Maria a queen.
- >Top 1389: Ottoman troops defeated Hungary, Serbia, Bosnia, etc. at the Battle of Kosovo.; however Murad I was assassinated during the battle.
- Grand Vizier system (viziri azam, or vezirazam; head of government)
- Chandal Kara Haril, Grand Vizier organized the standing Army Yeniceri, which were raised and trained from pagan and foreign salves (which were different from production slaves); which constituted royal guards Mamluk and its core was called Kapikulu (meaning slaves of the gate)
- Such slave acquisition was called as Devşirme, which was an efficient compulsory recruitment & conversion system of teenage boys due to the pentic system (1/5 was allocated for Sultan0
- Excellent slaves were converted to Islam and hired as Sultan's pages; in addition some were selected as high-ranking military personnels, or assigned as even Viziers.
- In particular, Circassians (Cherkess or Adyghe) around the Black Sea in North Caucasus were employed throughout Islamic world.
- >Top 1396: 4th Sultan Bayazid I (1389-1402) defeated the Nicopolis Crusaders at Nicopolis near Donau River; who was awarded the title of Sultan by the Abbasid Caliphate. (became from traditional Bey to the Emperor Sultan), and also sieged Constantinople several times.
- 1396/9/25: Battle of Nicopolis: the battle between Ottoman Empire and European Union at Nicopolis near the banks of Donau river; European army was lead by Hungarian King Sigismund, Holy Roman Empire, France, Wallachia, Poland, England, Scotland, Switzerland, Venice, Genova, Malta Allied Force which was a large and the last crusade in the Middle Age. It ended with an overwhelming victory of Ottoman Empire.
- Catholic Pope was in the midst of a great division of the church, almost treated authority to convene the crusade.
- Since the Hundred Years War between English and France was in a lull, Richard II and Charles VI participated in the war, including financial assistance.
- Since this battle, European nations almost lost the will to fight against the Ottoman Empire.
- 1402: Bayazit I was taken prisoner and died in prison in the Battle of Ankara with Muslim Turkish conqueror Timur (1370-1405), causing 10 years of Sultan Interregnum.
- 1413: 5th Sultan Mehmed I (1413-21, called Celebi, noble-born or the Restorer) reunified Ottoman Empire. And the next 6th Sultan Murad II was enforced to recover the lost ground.
1. 戦士集団から国家へ:
- 11Cまでは、アナトリアはビザンツ帝国の東半分; ギリシャ正教徒の土地。
- トルコ系民族:
- 6-8C: 突厥 Turuk、8-9C ウイグル Uyghurs
- 中央アジアは、トルコ人の土地(トルキスタン)
- 751 タラス河畔の戦い; イスラム勢力の進出
- トルコ人も次第にイスラム化
- 紙の製法伝達
- 1055: 大セルジューク朝トゥグリル・ベグ Tughril Begがバクダードへ進出し、カリフ Khalifaに代わって政治権力を行使 (スルタン Sultanの称号 <権力・権威)
- セルジューク Seljuk: テュルク系遊牧民族オグズの一氏族。イスラムに改宗したトゥルクマーン Turkomansで、後にセルジューク朝の基礎を築く
- 1063 第2代アルプ・アルスラン Alp Arslanはアナトリアへ侵攻しビザンツ皇帝ロマノスⅣを破る。
- 1077 ルーム・セルジューク朝(Rum Seljuk)建国:
- 首都は、当初ニカイア Nikaiaだったが、第1回十字軍に奪還された後、コンヤ Konya 首都としてアナトリア全土を席捲; トルコ語の拡大
- 縮小するビザンツ世界、拡大するイスラム世界、南欧系カトリック勢力の三つ巴争い
- 1204; 第4次十字軍 (ベネチア)によってコンスタンチノープル占領される。
- 1243: モンゴル来襲し、ルーム・セルジュク朝を属国化
- 1261: ビザンツ帝国、首都奪回。キリスト教のアクリタイ Akritaiとムスリムのガーズィー Ghazi (<聖戦への参加者) との抗争
- 1326: オスマン・ベイ(オスマンI) 没後、後継者が数百人規模でブルサ占拠し、首都とする。
- ベイリク Beylik 君侯国 (<ベイ Bey, 君侯)
- c1330: ニケア占拠
- 1337: ニコメディア(ブルサとコンスタンチノープルの中間) を占拠。アナトリアのビザンツ帝国領をほとんど占拠; 陸上交通の集積地帯
- イスラム法学者 (ウラマー)が、イスラム法官 (カーディー; カドゥ)
<おなり、>となり
裁判と民政の関与し、テクノクラート官僚として、オスマン帝国組織の中心となる。
- また自前のイスラム法学者養成機関であるイスラム学院 (マドラサ Madrasa; メドレセ)を開設
- ヴェズィール Vizier (Wazir <wazara重荷) (宰相)制度; 行政全般を補佐
- 軍隊組織は、騎馬戦中心; 構成は 1)オスマン一族、2) 他イスラム系ガーズィー集団、3) ビザンツ系キリスト教徒(一部改宗者)
- 現君主の息子がベイレルベイ (軍司令官)
- 租税管理制度 (Divan or Diwan); 人頭税 jizya; 地租 kharaj の徴収
- 1361: 第3代皇帝ムラトI (Murad I, 1362-1389)、アドリノープル (エディルネ Edirneに改称)征服。オスマン帝国第2の都市。
- 初めてスルタンの称号を用い、オスマン帝国の名声を高めた。 (>左図)
- 君主オルハン・ベイの次男。
- エディルネの獲得し、バルカン半島征服事業。ブルガリア皇帝イヴァン・シシュマンをサマコフの戦いでブルガリアを臣従させた。その皇帝の妹マリアを后とした。
- 1389: オスマン軍は、ハンガリー、セルビア、ボスニアなどを撃破 (コソヴォの戦い, Battle of Kosovo); なお、ムラトI (Murad I) は戦いの最中に暗殺される。
- 大宰相制 (ヴェズィーリ・アーザム; or ヴェズィラザム)
- チャンダル・カラ・ハリル大宰相; 奴隷軍人制度・常備軍イェニチェリ(Yeniceri)創設
- 異教徒・異民族の家内奴隷として養育・訓練を受け、養子のような関係 (生産奴隷と異なる)
- 忠実な奴隷軍人は、マムルーク (or グラーム) となり、その中核はカプクル, Kapikulu (御門の奴隷の意) と呼ばれた。
- 奴隷入手は、ペンチック制度(1/5は君主の取り分)により効率の良いデウシルメ Deşirme (強制改宗) 制度 (10代の少年)
- 優秀な人材はイスラム教に改宗させてスルタンの小姓に採用。さらに高級軍人・宰相につく者も出てきた。
- 特に、北カフカース黒海周辺のチェルケス人はイスラム圏各地で採用された。
- 1396: 第4代バヤズィットI (Beyazit I, 1389-1402) は、ドナウ川近くのニコポリスで、ニコポリス十字軍を撃破; アッバース朝カリフからスルタンの称号を授与。(従来の君侯ベイから皇帝スルタンへ) ;数回に亘りコンスタンチノープルを包囲した。
- ニコポリス十字軍: ドナウ河畔ニコポリスでのオスマン帝国と欧州諸国連合 (ハンガリー王ジギスムント、神聖ローマ帝国、フランス、ワラキア、ポーラント、イングランド、スコットランド、スイス、ヴェネツィア、ジェノバ、マルタ連合軍; ニコポリス十字軍を呼ばれ中世最後の大規模な十字軍である。オスマン帝国の圧勝で終わった。)
- ローマ教皇は、教会大分裂中で、十字軍を招集する権威が後退
- 英仏は、百年戦争が小康状態だったので、リチャードIIとシャルルⅥは資金援助を含め参戦。
- この戦い以降、欧州諸国は連携してオスマン帝国と戦う意志を喪失した。
- 1402: ムスリムトルコ系の大征服者チィムール Timur (1370-1405)とのアンカラの戦いで、バヤズィットIは捕虜となり幽囚中に死亡 (10年に及ぶスルタン大空位時代 Ottoman Interregnum; Fetret Devri)
- 1413: 第5代メフメトI (Mehmed I, 1413-21) が、再統一した。その次の第6代スルタンのムラトIIもほとんどが失地回復に従事
>Top 2. Battle of Constantinople:
- Fall of Constantinople:
- >Top 1444-81: 7th Sultan Mehmed II (third enthronement; 1444-46, 51-81, called Fatih, the Conqueror); routined brotherhood ordinance, mentioning 'Murder would be preferable to disturbing the world order' (Kanun, or law of fratricide; new Sultan killed all his brothers upon ascending the throne); this practice had been done since Bayazit I era to prevent conflict about throning among brothers who have equal inheritance rights to heritage.
- Conquest of Constantinople: the last Emperor Constaine XI
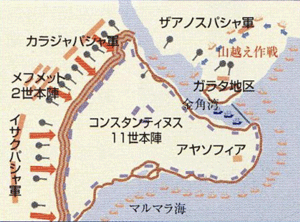
- Ottoman troops built Fort Rumeli on European side, following Fort Anadolu (Anatoria) on Asian side.
- also installed giant guns made by Hungarian Urban, with barrel 8.2m, caliber 76.2cm, stone bullet 550kg.
- prepared 300 warships and transport ships.
- Ottoman army: 100-120K (including 70K cavalry) vs. Byzantine 10K at most.
- West side of Constantinople: guarded by triple walls (Large Wall)
- South side: faced with Marmara Sea.
- North side: the bay entrance to the Golden Horn (Haliç) was blocked by a strong iron chain; the northern land of Galata lived by Genoa remained neutral (unlike Venice). Ottoman built a wooden path pained by oil on the north side of the Galata district, where they crossed 70 Ottoman fleets over the mountains.
- 1453/5/29 Ottoman all-out attacked; rushing into the city, being plundered for three days as the Pagan city.
- Dismissed and imprisoned peaceful Grand Vizier Haril Pasha. Since then, the Grand Viziers were selected from aides of slaves from different ethnic groups, and transferred to monarch tyranny.
- Such aides of slaves did not have a strong social background, only enslaved to the monarch regime, unlike influential Muslim-Turkish nobles.
2. コンスタンティノープルの攻防
- 第7代スルタンのメフメトII (三度目の即位, 1444-45, 51-81)
- 兄弟殺しの法令 (カヌーン); '世界の秩序が乱れるより、殺人の方が望ましい’; 遺産に対し平等の相続権を持つ兄弟間での皇位争いを防ぐという理由でバヤズィットI時代からの慣行
- コンスタンティノープル征服:
- 最後の皇帝: コンスタンティヌスⅪ
- オスマン軍は、アジア側岸のアナドル砦(Anadolu; Anatoria)に続き、欧州側岸のルメリ砦(Rumeli)を構築
- ハンガリー人ウルバンによる巨砲の製造; 砲身8.2m、口径76.2cm、石弾550kg
- 軍艦・輸送艦の建造 300隻
- オスマン軍: 10-12万 (内、騎兵7万)vs. ビザンツ軍1万
- 西側: 3重の城壁 (大城壁)
- 南側: マルマラ海
- 北側: 金角湾(ハリチュ, Haliç)の入り口は鎖で封鎖; 北側の大地ガラタ地区は、ビザンツを支持したヴェネティアとことなり、ジェノヴァは中立を維持。ガラタ地区の北側に木の道を作り、70隻ものオスマン艦隊を山越えさせた。<↓図>
- 1453/5/29 オスマン軍の総攻撃。市中へ突入
- 異教徒の都市は、3日間の略奪
- 和平派大宰相ハリル・パシャの罷免・投獄。以後大宰相は異民族出身の奴隷の側近が選ばれ、君主専制国家への移行
- 奴隷の側近は、ムスリム・トルコ系有力者と異なり、有力な社会的背景をもたず、君主に一身隷属。


>Top 3. Islam as Wisdom of Coexistence:
- Challenges of Ottoman Empire:
- To convert Constantinople into a Muslim-like city, including construction of Conqueror Mosque (Fartif Jermy) and Islamic Academy (Madrasa, or Medrese) in NW part of the old town.
- also built Safni Seman Islamic Academy as the highest school of the empire and was the center of Islamic law. The library collected many books written in Arabic, Persian and Turkish.
- also prepared other public facilities such as hospitals, restaurants for the poor, etc.
- Financial resources to support these facilities were arranged by religious donation property system (Waqf), as well as the incomes from public bath, bazaars, caravanserai, etc.
- Water supply for daily use was free.
- 1465-78: constructed Topkapu Palace on the hill at eastern end of the old town.
- Tried to recover the population drastically, setting up blocks (Mahalle) in the devastated city.
- in 1477 which could recover the population about 140K.
- the year after the conquest, ambassadors and merchants from various countries, including Venetian, regained to become an international city.
- >Top Religion rather than ethnicity:
- Millet system; each religious autonomy to coexist t Muslims and non-Muslims; the latter includes Greek Orthodox, Armenian churches, Judaism counted around 40%.
- Islam was far more tolerant than pre-modern Christianity; medieval and western Christianity remained undeveloped in coexistence system with pagans, causing murder of pagans by crusade movement.
- Islamic Jihad include not only war but persuasion to convert; having the concept of two domains such as Dal al-Islam (House of Islam; Realm of peace) and Dar al-harb (Realm of War); Islam prohibited forceful conversion, showing three choices of Koran, tribute or sword, and
- The city accepted and protected the people of the Book (Zinma) such as Manichaeism, Zoroastrianism, Hinduism, and Buddhism: the choice between Koran or sword was only applied for Arab idol worshipers.
- However, missionary works to Muslims were prohibited. Churches could be repaired but not allowed to newly build. (Coexistence under inequality)
- Ethnic Mosaic:
- Two large ethnic groups; Turks (conquerors) and Arabs who had Islamic culture and academic leaders, including Sunnis (mainstream), Shiites, and Dowles.
- Islamic minorities included Kurds, Klim Tatars, Amazighs (or Berber in West Africa), Bosnians, and Albanians (Balkans)
- Greek Orthodox included Greek (=Roman); Balkans are melting pots of Bulgarians, Serbs, Albanians, and Romanians, including Maronite, Copts, and Nestorians.
- To maintain the coexistence system, violent sanctions on Muslims occurred; Sultan standing forces suppressed some Muslim anti-Semitic riots, which were different from Jewish slaughter in Western Europe.
- Multilingual society: tolerant of printed matter publication and distribution.
- the official languages were Turkish, Persian and Arabic (Arabic was mostly used as high-class cultural language)
- and other Kurdish, Berber, Albanian, and Klim Tatar languages were used.
- Christians used Greek, Armenian, Serbian, Croatian, Romanian and Hungarian languages; Nestorians were native to Syriac and Arabic languages.
- Jews used Hebrew (literal), Arabic, Greek, Spanish (in Iberian peninsula), German, Yiddish (in Eastern Europe)
- Mehmet II himself understood Turkish (mother tongue), Arabic, Persian, and some Greek; who showed keen interest in Western culture.
- After the conquest of Constantinople:
- conquered almost entire Balkan Peninsula; gained land trade routes and improved economic power of the empire; also conquered Trebizond Empire in the Black Sea coast and made it a state of the Ottoman Empire.
- Defeated the influence of Genoa based in the Black Sea, and Venetia based in the northeaster Mediterranean coast.
- The princes' battle for the throne:
- After the death of Mehmet II, the battle between Bayazit and Jem.
- The Bayazit faction supported by Yeniceri took the initiative rather than brilliant Jem, and finally became 8th Sultan Bayazit II (1481-1512)
- Defeated prince Jem went into exile in Mamluk Dynasty; then went into exile in Rome after Hungary under the control of the Order of French.
- 1495/2/25 the death of the brilliant prince in the heathen land also meant the end of open atmosphere of Mehmet era.
- During Bayazill II era, Islamic laws became more authoritative and emphasized legitimacy of Sunni empire.
- >Top Safavid Dynasty in Iran:
- 1501 Shah Ismail conquered Azerbaijan and prevailed all Iran in the following ten years. He made the Shiites the state religion for the first time.
- Rather than being attracted to Shiite doctrine, he emphasized the sentiment of Turkish nomadic tribes.
- >Top 9th Sultan Selim I (1512-20, Yavuz, the Resolute):
- 1512 indecisive Bayazit II was abolished by his son Selim, who became Selim I.
- Selim I was a military genius; conducted great easer expedition, and purged domestic Shiites (against the influence of Safavid Dynasty)
- 1514 Ottoman artillery won the battle of Chaldiran, northwest of Tabriz, the capital of Safavid Dynasty; eventually various parts of Easter Anatolia became Ottoman-controlled areas.
- Tripolar structure of Islamic world; Ottoman Empire, Safavid Dynasty, and Sunni Mamluk Dynasty.
- 650-1258; changed from Umayyad Caliphate (Damascus) to Abbasid Caliphate (Baghdad).
- the Abbasid Caliphate granted equal rights to all Muslims realizing the golden age of Islam.
- Baghdad became a major commercial empire controlled trade routes of land and sea.
- It fused the cultures of Arabia, Peria, Greece, India, and China, achieving academic development and made a great influence on modern science.
- 1258: After Mongolia destroyed Abbasid Dynasty, the center of Islam shifted to Egypt.
- 1517/2/15: Selim I entered Cairo, the capital of Mamluk Dynasty; became the guardian of the Holy City of Mecca and Medina. At the same time, he inherited the Caliph as a religious authority, and established the Sultan-Caliph system.
3. イスラム=共存の智恵:
- オスマン帝国の課題
- コンスタンチノープルをムスリム的都市への改造
- 旧市街西北部に征服者モスク (ファーティフ・ジャーミー)、およびイスラム学院群(Madrasa, メドレセ)の建設
- サフニ・セマン・イスラム学院群はオスマン帝国最高学府とし、イスラム法学などの中心。図書館には、アラビア語、ペルシャ語、トルコ語の書籍所蔵
- その他公共施設 (病院、貧者食堂など)
- これらの財源は、宗教寄進財産 (ワクフ)制度の充実; 公共浴場、バザール、隊商宿等の収入を当てる
- 水道による生活用水は無料
- 1465-78:旧市街東端の丘にトプカプ宮殿の建設:
- 激変した人口の回復; 荒廃した街に街区 (マハッレ)設置
- 1477には、人口は約14万に回復
- 征服の翌年には、ヴェネティアを含め各国の大使、商人が集まり国際都市となったいった。
- 民族より宗教:
- ミレット(Millet)制度: ムスリム と非ムスリムの混在の保護と支配を兼ねる宗教自治体; ギリシャ正教、アルメニア教会、ユダヤ教で非ムスリムは40%位で共存
- イスラムは、前近代のキリスト教よりはるかに寛容; 中世西欧のキリスト教は異教徒との共存システムが未発達 (十字軍による異教徒殺戮)
- ジハード (Jihad)は、戦争だけでなく折伏を含め、ダール・アルハルブ (Dar al-harb, 戦争の家)をダール・アルイスラーム (Dar al-Islam, イスラムの家)への働きかけ; イスラムは、強制による改宗を禁止; コラーンか貢納か剣かの三択。
- 啓典の民の拡大: その後、マニ教、ゾロアスター教、ヒンドゥー教、仏教も被保護民 (ズィンマ)扱い; コラーンか剣かの選択は、アラブの偶像崇拝者のみ;
- 但し、ムスリムへの布教は禁止。教会も修理は可だが新築は不可 (不平等下での共存)
- 民族モザイク:
- 二大集団: トルコ人 (征服者)とアラビア人 (イスラム文化・学問の担い手)
- スンナ派(主流)、シーア派、ドウルーズ派
- イスラム少数派: クルド人、クリム・タタール、ベルベル人 (北アフリカ西部)、ボスニア人・アルバニア人 (バルカン)
- ギリシャ正教徒: ギリシア人 (=ローマ人);バルカンは人種のるつぼでブルガリア人、セルビア人、アルバニア人、ルーマニア人が割拠
- マロン派、コプト教徒、ネストリウス派
- 共存のシステム維持には、ムスリムにも暴力的制裁 (一部ムスリムによる反ユダヤ暴動にはスルタン常備軍が鎮圧); 西欧でのユダヤ人虐殺との違い
- 多言語社会; 印刷物の刊行と流通にも寛容
- 公用語はトルコ語。ペルシャ語やアラビア語は高級な文化言語;
- その他クルド語、ベルベル語、アルバニア語、クリム・タタール語
- キリスト教徒は、ギリシア語、アルメニア語、セルビア語、クロアチア語、ルーマニア語、ハンガリー語
- ネストリウス派はシリア語、アラビア語を母語とするキリスト教徒
- ユダヤ教徒は、ヘブライ語 (文語)、アラビア語、ギリシア語、スペイン語 (イベリア半島)、ドイツ語、イディッシュ (東欧ユダヤ教徒)
- メフメットII自身も、トルコ語 (母語)、アラビア語、ペルシャ語の他、ある程度のギリシア語を解した。
- メフメットIIは、西欧文化にも関心を示した。
- コンスタンチノープル征服後:
- バルカン半島ほぼ全土を征服; 陸上交易路を得て、オスマン帝国の経済力向上
- 黒海沿岸地域のトレビゾンド帝国を征服
- を占領し、オスマン帝国の一州とした。
- 黒海に拠点を持つジェノバ、地中海東北岸に拠点を持つヴェネティアの影響力を打破
- 王子の皇位争い
- メフメトII没後、バヤズイットとジェム王子間争い。
- 才気煥発なジェムよりも、イェニチェリ軍団を利用したバヤズィット派が主導権を握り、第8代バヤズイットII (1481-1512)として即位
- 破れたジェム王子は、マムルーク朝に亡命。その後ハンガリーを経てフランスの騎士団の管理下で、後ローマへ亡命した。
- 1495/2/25 ジェムは没し、英明な王子の異教徒の地での死は、メフメット時代の開明的な雰囲気の終焉でもあった。
- バヤズイットIIの時代は、イスラム法学がさらに権威化され、帝国のスンナ派の正統性が強調されるようになった。
- イランのサファヴィー朝:
- 1501 シャー・イスマーイルは、アゼルバイジャンを征服し、その後10年で全イランを制圧。初めてシーア派を国教とした。
- シーア派の教義に引かれたというより、トルコ系遊牧民諸部族の心情を重視した。
- 第9代スルタン セリムI (1512-20、ヤヴズ, 冷酷者):
- 1512: 優柔不断なバヤズイットIIを、子のセリムが廃して、第9代セリムIとなった。
- セリムIは軍事的天才。東方大遠征とともに、国内シーア派を大粛清 (サファヴィー朝への対抗)
- 1514 サファヴィー朝首都タブリーズ西北のチャルディランの戦いでは、オスマン軍の火砲で勝利; 東アナトリアの各地がオスマン支配下になった。
- イスラム世界の三極構造:
- オスマン帝国、サファヴィー朝と、スンナ派のマムルーク朝
- 650-1258: ウマイヤ朝 (首都ダマスクス)からアッバース朝 (首都バグダード)へ交代
- アッバース朝は全てのムスリムに平等な権利を認め、イスラム黄金時代を気づいた。
- バグダードは陸海路の交易路として大商業帝国となった。
- アラビア、ペルシア、ギリシア、インド、中国の諸文化を融合し、学問的に発展を遂げ、近代科学に多大な影響を与えた。
- 1258: モンゴルがアッバース朝を滅ぼして以降、イスラムの中心は、エジプトに移る。
- 1517/2/15 セリムI マムルーク朝首都カイロに入城; オスマン帝国は、聖都メッカ、メディナの守護者となる。同時に、宗教的権威者としてのカリフを加え、スルタン=カリフ制を確立した。
>Top 4. Road to the Islamic World Empire:
- Conquest of the entire Balkan:
- 7th Sultan Mehmed II (nicknamed Fatih, Conqueror) continued active conquest activities in the east and west even after the conquest of Constantinople.
- Invaded Belgrade: Clashed powerful Hungary.
- 1456: conquered Athens controlled by Florence
- 1459: conquered Serbia
- 1461: conquered the Empire of Trebizond (collaborated with Turkish Aq Qoyunlu) on the Black Sea Cost, and also conquered Jandal Beylik.
- 1462: conquered principalities of Wallachia and Moldavia; defeating Vlad Tepes (Dracour Oulu) of Wallachia.
- 1463: conquered Bosnia.
- 1466: conquered Beylik of Karaman (capital Konya)
- 1478: conquered Albania.
- Balkan Peninsula was a region with higher agricultural productivity than Anatolia.
- Established Caravanserai network connecting basic cities of the land trade route in Anatoria.
- East-West Trade Route (Silk Road):
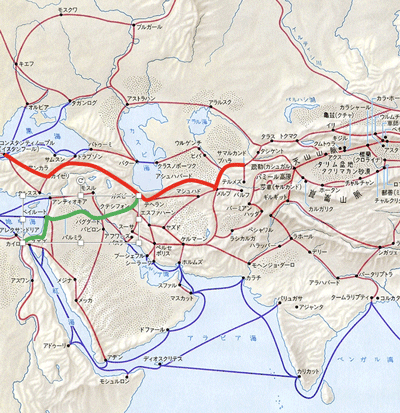
- Remote Trade Routes (the Silk Road)
- Route-1: Land road:
China - Central Asia - Iranian Plateau - Anatoria
- or go south from Iranian Plateau to Egypt.
- Carried Chinese ceramics and peppers from SE Asia.
- Route-2: Maritime road:
South China - Malacca Strait - Indian Ocean - Persian Gulf - Basra - Baghdad
- or sail to west to Red Sea - Egypt
- Route-3: North-South Trade Route:
Russian Plain - North Black Sea - Mediterranean Sea
- the Black Sea was the sea of Genoa
- 1475: Ottoman conquered Kaffa, the base of Genoa, made the Black Sea the Ottoman Sea.
- Imported fur, amber, honey, fish and grains.
- The Ottoman Sea:
- also Ottoman subordinated Crimean Khanate.
- Mehmet II showed keen interest in Italian culture
- he himself understood Italian language.
- invited Gentile Bellini, master painter in Renaissance period who stayed in Istanbul for 16 months (and painted portrait of Mehmet II)
- Mehmet II was almost only Sultan who had interest Western culture.
- 1480 ordered Gedik Ahmet Pasha to lead a large army to invade Southern Italy and temporarily occupied the Oran town.
- 1481 Mehmet II suddenly died during the expedition (49 years old); what would happen to the Renaissance culture if Italy were occupied by the Ottoman army?
- Succession battle between two prices:
- In Ottoman Empire, the farther-son inheritance system had been basically established, but the order of inheritance was uncertain. The ruled was decided when the one who received the vassal (Biat, Bahia) from the vassal group about the throne (Taft) at an early stage. The loser was executed.
- Bayazit faction got the support of Yeniceri military, and took the throne as Bayazit II, and strictly carried out orthodox Islamic policies.
- the defeated and brilliant price Jam went into exile in the Mamluk Dynasty and then to Western Europe, but could not recover the position.
- >Top End of 15C: Safavid Shah Ismail firstly established Shiite nation in the history.
- Ottoman Dynasty felt the crisis about the rise of Safavid Dynasty; abolished the indecisive Bayazit II and his son Selim became 9th Sultan Selim I.
- Selim I was a military genius and embarked a great eastern expedition.
- Meanwhile he purged 40K Shiites in the country; such a large-scale religious persecution was unprecedented, while the empire had promoted coexistence policy with heathens.
- 1514: defeated Shah Ismail in the battle of Chaldiran, north west of Tabriz, the capital of Safavid Dynasty. Although he won, he retreated due to the supply problem. But Safavid Dynasty was no longer able to attack Ottoman Dynasty. It showed the military significance of gun troops overwhelming the cavalry.
- >Top 1516: Selim I conquered Mamluk Dynasty
- attacked Aleppo, the key city of northern Syria and entered Damascus.
- 1517 attacked Cairo. Selim I succeeded detour operation and entered the capital city Cairo. The Mamluk Dynasty was defeated.
- Ottoman empire took control of most of the trading routes.
- Getting religious authority of Caliph (Khalifa), Selim I became the guardian of the two sacred cities of Mecca and Medina. (Sultan-Caliphate)
- also returned home with a large number of scholars, artist and craftsmen as well as a huge amount of loot.
4. イスラム的世界帝国への道:
- バルカン全土の征服
- メフメトIIは、コンスタンチノープル征服後も東西に活発な征服活動を続けた。(征服者, ファーティフと呼ばれた)
- ベオグラード攻略; 強国ハンガリーとの衝突:
- 1456: フィレンツェ支配のアテネ征服
- 1459: セルビア征服
- 1461 黒海沿岸のトレビゾンド君侯国 (トルコ系白羊朝と連携)征服とジャンダル君侯国を征服
- 1462: ワラキアとモルダヴィア両君侯国征服; ワラキアのヴラド・ツェペシュ (ドラクール・オウル)打倒
- 1463: ボスニア征服
- 1466 カラマン君侯国 (首都コンヤ)征服
- 1478: アルバニア攻略
- バルカン半島はアナトリアより農業生産力が高い地域
- アナトリアの陸上交易路の拠点都市にはキャラヴァン・サライ網を設置
- 遠隔交易路 (シルクロード):
(>左図)
- 第一ルート: 陸上の道
- 中国〜中央アジア〜イラン高原〜アナトリア
- イラン高原から南進してエジプト
- 陶磁器、胡椒
- 第二ルート:海上の道
- 南中国〜マラッカ海峡〜インド洋〜ペルシャ湾〜バスラ〜バクダード
- 西進して紅海〜エジプト
- 第三ルート: 南北交易路
- ロシア平原〜黒海北岸〜地中海
- 黒海は、ジェノヴァの海化
- 1475 ジェノバの拠点カッファ征服; 黒海をオスマンの海にした。
- 毛皮、琥珀、蜂蜜、魚、穀物を輸入
- 黒海が'オスマンの海'に:
- 1475 メフメットIIは、黒海北岸へ侵攻
- クリム・タタールのクリム汗国を属国化
- イタリア文化への関心:
- メフメットII 自身もイタリア語を解した
- ルネサンス絵画の巨匠ヴェネチアのジェンティーレ・ベッリーニをイスタンブルへ16ヶ月滞在 (肖像画も描かせる); 西欧文化への関心をもったほとんど唯一のオスマン君主
- 1480 ゲディク・アフメット・パシャが大軍を率いて南イタリアに侵攻し、オランの町を一時占領。
- 1481 メフメットII親征の途中で急死(49歳); イタリアがもしオスマン軍に席捲されたとしたらルネサンス文化はどうなったであろうか。
- 2王子の後継争い:
- 父子相続制が定着していたが、相続順位は不定。早期に玉座 (タフト)について群臣の臣従 (ビアット; バイア) を受けた者が支配者。敗者は処刑された。
- イェニチェリ軍団を味方につけてバヤズイット派が、バヤズイットIIとして即位。正統的なイスラム政治を遂行
- 敗れた英明なジャム王子は、マムルーク朝、さらには西欧に亡命したが再起ならず
- 15C末、サファヴィー家のシャー・イスマーイルが、初めてのシーア派国家を設立。
- サファヴィー朝の台頭に危機感を持ったオスマン朝は、優柔不断なバヤズイットIIを廃し、子のセリムがスルタンとなった (第7代セリムI)
- セリムIは、軍事的天才であり、東方大遠征に着手
- 国内では4万人のシーア派分子を粛清。異教徒との共存を進めてきたオスマン朝としては、大規模な宗教弾圧は空前絶後
- 1514: サファヴィー朝首都タブリーズ西北のチャルディラン Chaldiranの戦いで、シャー・イスマーイルを打破。勝利したものの補給問題もあり一旦退却。サファヴィー朝は以後オスマン朝に対して攻勢に出られなくなった。鉄砲隊が騎馬隊を撃破した軍事的意義。
- 1516: セリムI は、自らマムルーク朝親征:
- 北シリアの拠点アレッポを攻略し、ダマスクスに入城
- 1517: カイロ攻撃の開始。セリムの迂回作戦が成功してついに首都カイロに入城。マムルーク朝滅亡。
- 交易ルートのほとんどをオスマン帝国が掌握
- 宗教的権威者カリフの禅譲を受け、メッカ、メディナ二大聖都の守護者となった。
- 膨大な戦利品と共に多数にお学者、芸術家、職人を連れて帰国
>Top 5. Brilliance of Suleiman the magnificent:
- Suleiman the Magnificent, 'Kanuni, Lawgiver', who contributed to form Ottoman sultanic code.
- Territory of Ottoman Empire (1683); Wikipedia
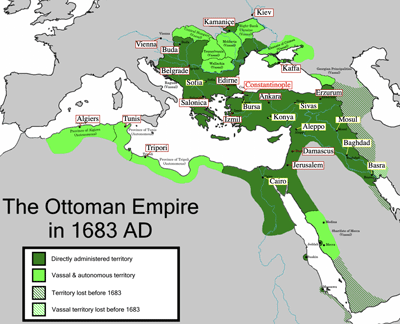
- 1520: Selim I died shortly after Mamluk conquest. Suleiman I was enthroned at 26 years old, who reigned 46 years, called a legislator.
- Suleiman I carried out the tradition of Ghazi, went off 13 direct expeditions during his reign.
- There ware many holy wars to the west. (called Kizil Elma, Country of Red Apples) (Red Apple is said to mean Rome)
- 1521: 1st battle: attacked Belgrade.
- 1522: 2nd battle: attacked Rhodes Island, southwester tip of Anatolia, the base for the maritime trade, where Knights of St. John defended and pirated the route.
- 1523: conquered Rhodes Island; the Knights moved to Malta Island.
- >Top Conquer of Egypt:
- 1523: Grand Vizier Pilly Mehmet Pasha remained since the former Sultan, but Suleiman appointed Ibrahim, a court slave & Sultan's secretary as the Grand Vizier.
- Pargali Ibrahim Pasha (Makbul Ibrahim Pasha, the 'Favorite'; lately changed to Maktul Ibrahim Pasha (the 'Executed'); 1493 born a Christian in Parga, a part of Venice and was enslaved during his youth. He first met Prince Suleiman near Edirne around in 1514 and became his servant.
- in 1523 Ibrahim was married to Muhsine Hatun (It is doubtful Ibrahim married Hatice Slutan, sister of Suleiman.)
- Ibrahim remain in office for 13 years. Ibrahim used various tactics to negotiate with Catholic powers. The Venetian diplomats regarded him as 'Ibrahim the Magnificent', a playful sobriquet.
- 1524 Ahmed Pasha, also a court slave, and was a candidate for Grand Vizier, was appointed Governor-general of Egypt. But he formed a rebellion tied with some Mamluk, but was suppressed and executed soon.
- Suleiman dispatched confident Grand Vizier Ibrahim Pasha to Egypt to regain Egyptian management, including investigating financial books; tax revenue from Egypt accounted about a quarter of all Ottoman revenues.
- In 1535 Ibrahim completed a monumental agreement with Francis I that gave France favorable trade rights within the Empire in exchange for joint action against Habsburg; enabling Franco-Ottoman naval maneuvers and basing of Ottoman fleet in southern France (in Toulon) in 1543-44.
- As Ibrahim's power and wealth grew, so did his arrogance, and behaved as if he were in charge. This deeply troubled Hurrem, or Roxelana, who plotted Ibrahim's downfall. In 1536 he was seized and killed.
- >Top 1541: as the 3rd battle, Suleiman conquered Hungarian Plains and Buda. The pagan lands are fascinating, unlike Islamic lands were conquered without looting.
- 1519: Carlos I, King of Spain from Habsburg, also reigns as Karl V of the Holy roman Empire, who confronted Ottoman Empire.
- On the other hand, King François I of France who was defeated in a conflict with Karl V, determined to partner with Ottoman Empire. It is historically rare that Muslim and Christian monarchs collaborated; Suleiman's offensive against Habsburg was linked to François I. (Capitulation)
- >Top 1529/5/10: Vienna Siege Operation:
- Stronghold Vienna was dominated by Karl V's younger brother Ferdinand. Suleiman reached outside Vienna Castle on 9/20, started attack with 120 troops, and 300 cannons. The Vienna Defense Forces was a bit more than 50K.
- The siege operation took time and Suleiman was forced to withdraw due to harsh winter season in Vienna, which gave shocking event fro the Wester Christan world.
- Wester countries were forced to compromise with Protestants for the defense of Western Europe.
- >Top Suleiman's Era:
- Territory: occupied about 3/4 of the maximum territory of ancient Roman Empire.
- Suleiman was called the legislator (Kanuni), creating land registration books (Tafris), establishing the imperial dominated organization.
- Operation of the empire was performed by the organization, rather than relying on individual competence of the emperor.
- Gran Vizier as Chancellor, and majority of the local governors were mostly appointed from able court slaves who had no relative background.
- >Top The courts were consisted of the Old Palace and New Palace
, as well as an axillary palace of Galata Palace and Ibrahim Pasha Palace. The harem was moved from Old Palace to New Palace.
(supervised by Valide (Walida) Sultan, mother Sultan such as Hafsa Sultan is Suleiman's mother)
- >Top Two concubines:
- Until 8th Bayazit II; usually married a daughter of a neighboring monarch.
- After 9th Selim I, female slaves from pagans were hired in the back palace. Suleiman's mother Hafsa Sultan was such an example.
- Mahidevran; mother of the first born prince Mustafa.
- Hurrem; Russian-born daughter of Rthenian Orthodox priest, abducted by Crimean Tatars and sold to Istanbul as a female slave. She was known as Roxelana (Rushenian woman).
- She was favored by Suleiman I, and became mother of princes such as Mehmet, Selim, and Bayazit (the first mother of multiple princes).
- 1534: She broke the costume and became Empress form her slave status, creating de facto monogamy. Exiled her rival Mahidevran Sultan form the back palace. She also planed to fight for the successor to Suleiman I.
- >Top Battle with Safavid Dynasty:
- Rebellion of Kyzyl Tudge
- 1533: Expedition to Safavid Dynasty; entered the capital Tabriz.
- 1533/12: Submission of Algerian Navy, which intensified Ottoman Navy. Later Hayreddin Barbarossa (Redbeard) was appointed as Admiral of Ottoman Navy. (Kapudan Pasha, Grand admiral)
- 1534: The fleet of Barbaros occupied the town of Tunis.
- 1536: Suleiman executed Grand Vizier Ibrahim Pasha.
- 1538: Achieved a decisive victory over the Holy League at Preveza.
- 1541: Karl V lead a large army and raided Algeria, home of Barbaros, but it was defeated by Ottoman defense forces.
- 1543: At the request of France, Ottoman navy captured Nice which had been the side of Holy Roman Empire. Thus Mediterranean Sea effectively became the Sea of Suleiman.
- 1555: Concluded Ayasia Peace Treaty between Suleiman and Shah Tuffmarsp
- Battle for hegemony in Indian Ocean:
- Beginning 13C: Islamic forces infiltrated North India through Gazna Dynasty.
- in 16C, it extended to Central India
- 1526-1858: established Sunni Mughal Empire.
- 1498: Vasco da Gama developed a route to India around the Cape of Good Hope. Then Portuguese forces advanced into Indian Ocean to disrupt Muslim maritime routes. Ottoman Empire confronted Portuguese forces as a guardian of East-West trade and Mecca & Medina.
- 1538 At the request of Gujarat Sultan Dynasty, Suleiman dispatched a fleet to the Indian Ocean. And conquered Yemen, succeeding in defending the Red Sea route.
- Later years of Suleiman I:
- 1539: made marry her daughter Mihrimah Sultan to Rustem Pasha, a former court slave. Rustem later became Grand Vizier.
- 1940: Hurrem's firstborn Mehmed became crown prince, but soon he died young.
- 1553: Suleiman executed his eldest son Mustafa (whose mother Mahidevran) on charge of rebellion during an expedition to Iran.
- 1558: His beloved wife Hurrem died; intensifying succession battle between two princes.
- 1558: Suleiman's rival Karl V also died.
- 1561: Defeated Prince Bayazit tried rebellion, but went into exile in Iran and was executed there.
- 1565: dispatched expeditionary forces to Malta but in vain.
- 1566: Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian II broke the peace treaty and attacked Hungary. Old Suleiman, over 70 years old, lead a large army and carried out 13th and final conquest of Hungary.
- 1566/9/7 He died during the siege of Szigetvar at the age of 72. The death was treated secret, bringing victory of the battle.
- Suleiman's corpse was buried in the Sulemanie Mosque built by himself, where his beloved wife Hurrem sleeps.
- In addition to poetry, literature had also reached maturity after imitating stage of Arabs and Persia. Ottoman poetry master Barkey also appeared in this period. Suleiman's 46 years' era boasted a culture befitting a name of a magnificent person.
- Centering on Suleiman's reign, it is properly called that the early Ottoman Empire from end of 13C to end of 16C, and the late Empire from end of 16C to end of 18C.
5. 荘厳者スレイマンンの光輝:
- Suleiman the Magnificent and Hurrem Sultan:


- 1520: マムルーク朝征服後、ほどなくセリムI没。スレイマンI即位 26歳 (在位1520-66, 立法者と呼ばれる)
- スレイマンIは46年在位中13回親征実施。ガーズィーの伝統を継ぐ。
- 異教徒の土地である西方への聖戦が多かった。 (クズル・エルマ Kizil elma; 赤いりんごの国) 赤いリンゴとはローマを指すとも。
- 1521: 第1回親征: ベオグラードへ侵攻
- 1522: 第2回: アナトリアの西南端の海上交易路の拠点ロードス島; 聖ヨハネ騎士団が防御し、海賊行為を行っていた。
- 1523: 騎士団は、マルタ島へ移動。
- エジプト支配の確立:
- 1523: 当初、大宰相はピリー・メフメット・パシャが留任していたが、宮廷奴隷上がりのイブラヒムを小姓頭から大宰相に抜擢。
- パルガル・イブラヒム・パシャ ('お気に入り; 後に'処刑者'に) 1493: ヴェネティアの一部であるPargaで生まれのキリスト教徒。若い頃奴隷となる。1514頃、皇太子スレイマンとエディルネ近くで面識となり小姓となる。
- 1523: イブラヒムはムーシン・ハツンと結婚 (スレイマンの妹ハティス・スルタンと結婚したというのは疑わしい)
- イブラヒムは様々な権謀術数を用いてカトリック勢力と交渉した。ベネチアの外交団は彼を'荘重者イブラヒム'を呼んだ。
- 1524 大宰相候補だった宮廷奴隷出身のアフメット・パシャがエジプト総督へ就任した、一部のマムルークを組んで反乱を起こしたが、鎮圧され処刑される。
- スレイマンは、腹心の大宰相イブラヒム・パシャをエジプトに派遣し、帳簿の調査を含め、エジプト支配体制の確立を図る。エジプトの税収は、全オスマン収入の1/4を占めた。
- イブラヒムの権力と富が増えるにつれ傲慢となっていった。このことがヒューレムを悩まし、イブラヒムの失脚を画策した。1536に、彼は捕捉され殺された。
- 1541 第3回: ハンガリー平原を攻略し、ブダ征服。略奪なしのイスラム圏への征服と異なり異教徒の土地は魅力的。
- 1519 ハプスブルク家のスペイン王カルロスIは、神聖ローマ帝国カールⅤとして即位し、オスマン帝国と対峙
- フランス国王フランソワIは、カールⅤとの抗争に破れ、オスマン帝国を連携して対抗。ムスリムの君主とキリスト教徒の君主の連携は史上稀。(カピチュレーション Capitulation)以後、スレイマンによる対ハプスブルク攻勢はフランソワIと連動した。
- 1529/5/10 ウィーン包囲作戦出征:
- 牙城ウィーンは、カールⅤの弟フェルディナンドが支配。9/20にウィーン城外に到達。軍勢12万、大砲300門。ウィーン防衛軍は5万数千。
- 攻城に手間取り、ウィーンの厳しい冬季のため撤退を余儀なくされる。 西欧キリスト教世界に衝撃
- 西欧防衛のために、それまで対立してきたプロテスタント系諸公とも妥協せざるを得なくなった。
- スレイマン時代のオスマン帝国
- 版図: 古代ローマ帝国最大版図の約3/4を占めた。
- スレイマンは、立法者 (カヌーニー kanuni)と呼ばれ、検知帳 (タフリス)作成を始め、帝国支配の組織が確立した。
- 帝国運営は、皇帝個人の力量に頼るのでなく、組織による経常的な運営となった。
- 大宰相、宰相は全て、地方総督も大多数が、一身専属的な奴隷出身者で構成
- 宮廷組織は、旧宮殿、新宮殿と、ガラタ宮殿、イブラヒム・パシャ宮殿の補助宮殿があった。後宮 (ハレム)も旧宮殿から新宮殿へ移動。
- 2人の寵姫:
- 第8代バヤズィットIIまでは、近隣君主の娘と結婚
- セリムI 以降は異教徒出身の女奴隷を後宮に採用。スレイマンの母ハフサ・ハトゥンもその例
- マヒデヴラン; 長子ムスタファの生母
- ヒュッレム; ロシア出身でルテニア正教会司祭の娘で、クリミア・タタールに拉致され、女奴隷としてイスタンブールへ売られた。ロクセラーナ (ルーシの女)で知られる。
- スレイマンIの寵愛を受け、メフメット、セリム、バヤズィット王子の生母 (複数王子の生母も初)
- 1534 当時の慣習を破って奴隷身分から発起して皇后となり、事実上の一夫一婦制を築いた。ライバルのマヒデヴラン・スルタンを後宮から追放。スレイマンIの後継争いを策動。
- サファヴィー朝との攻防:
- 紅帽 (クズル・タッジ)の徒の反乱
- 1533: サファヴィー朝遠征。首都タブリーズへ入城。
- 1533/12: アルジェリア水軍の帰順。オスマン海軍の強大化; バルバロス・ハイレッディン (赤ひげ)は海洋州総督就任。
- 1534: バルバロス艦隊は、チュニスの町を占領
- 1536: 大宰相イブラヒム・パシャを処刑
- 1538: ローマ教皇と神聖ローマ皇帝連合艦隊をプレヴェザ海戦で撃破。
- 1541: カールVは、大軍を率いてバルバロスの本拠地アルジェリアを急襲したが、オスマンの防衛軍によって大敗を喫す。
- 1543: フランスの要請に応えて、神聖ローマ帝国側のニースを攻略; 地中海は実質的に'スレイマンの海'となった。
- 1555: スレイマンとシャー・タフマースプ間のアヤスィヤ講和条約
- インド洋の覇権争い:
- 13C初頭には、北インドにガズナ朝を通じてイスラム勢力が浸透
- 16Cには中部インドにまで及ぶ。
- 1526-1858 スンナ派のムガール帝国成立
- 1498: ヴァスコ・ダ・ガマが喜望峰周り航路開発。ポルトガル勢力がインド洋に展開し、ムスリムの海上ルートの寸断を図った。
- 東西貿易・メッカ守護者としてポルトガル勢力に対抗
- 1538 グジャラート・スルターン朝の要請で、インド洋に艦隊を派遣した。同時にイェメン征服し、紅海防衛に成功
- 晩年のスレイマンI:
- 1539 :娘ミフリマー・スルタンを宮廷奴隷出身のルステム・パシャに嫁がせる。ルステルは後に大宰相となる。
- 1540: ヒュッレムの長子メフメットが一時皇太子となるも、夭逝
- 1553: イラン遠征中に、長男ムスタファを謀反の罪で処刑
- 1558:愛妻ヒュッレム死去。2王子間での後継争い激化
- 1558: なおスレイマンのライバルのカールⅤも没
- 1561:反乱を起こした王子バヤズイットは、イランに亡命したが処刑された。
- 1565: マルタ島への遠征軍派遣したが失敗
- 1566: 神聖ローマ皇帝マクシミリアンIIが和睦を破りハンガリーを攻撃。70歳を越えた老スレイマンは大軍を率いて13回目の最後となるハンガリー親征を敢行。
- 1566/9/7: スィゲトヴァール包囲戦で陣中没(72歳)。その死は伏せられたまま勝利の勝鬨を挙げた。
- スレイマンの遺骸は、愛妻ヒュッレムが眠るスレイマン実親が建設したスレマニエ・モスク Süleymaniye Camii に葬られた。
- 詩を中心として文学もアラブ、ペルシャの模倣を脱し成熟期を迎え、オスマン詩の巨匠バーキーも登場。スレイマンの時代は、壮麗者にふさわしい文化を誇る。
- スレイマンの治世を中心に13C末〜16C末までを前期オスマン帝国、16C末〜18C末を後期オスマン帝国と呼 ばれる。
>Top 6. Legend of Organizational Empire:
- The Empire that Europeans fared its organization:
- Empire having strong and elaborated organization; with mighty standing regular army, having discipline of trained members, high technical standards supported by nation-wide taxation system.
- Sultan's Monarch Tyranny and centralized organization.
- >Top What constrained Sultan
- Title: Signature or seal (Tughra), Shah (Ancient Near Eastern King), and Han (Eurasian Great Conqueror)
- Justice: the political theory of Islamic world, saying; 'No King without soldiers, no soldiers without goods, no taxes without people, and no prosperity of people without Justice (Adalet)'
- Sultan: Guardian of the Islamic Holy Sharia, saying; 'Sultan, don't be proud of yourself. There exists Allah who is greater than you.'
- >Top Agent for Sultan:
- Grand Vizier (Zambezi) is the absolute agent for the Sultan (Kiri Amtrak)
- after 11th Selim II, the position became an absolute agent, since Sultan did not go to the front.
- Until middle of 17C, Grand Vizier works in his private mansion.
- 1654: Grand Vizier Elvish Mehmed Pasha founded Grand Vizier Office (Barb Asaphy)
- Competition between Grand Vizier and other Viziers. Viziers were a group of candidate of the Grand Vizier.
- Supremo Decision-Making Body: Conference in the presence of Sultan (Divani Humayun); Later Sultan only peeked into the meeting.
- During 16C, Conference in the presence of Sultan was held every day. But after that, 4 days only, i.e., Saturday, Sunday, Monday, and Tuesday.
- Basic members: 1) Grand Vizier, Viziers, 2) Military lawyers (Rumeli and Anadolu), 3) Secretary Keeper of Great Seal, and 4) Financial chief.
- Salary payment of the standing Army; on the same day of the conference; 4 times a year.
- Financial System:
- Unity and impartiality of Finance:
- Sultan's own finance; (internal account; Iç Hajine)
- National finance by Financier: (official account; Dush Hajine)
- Issuance of coins: copper/silver/gold coins
- >Top Taxes:
- Islamic tax: Kharaj (land tax) ; Ushr (1/10 tax on merchandise); Jizya (poll tax)
- Land tax:
- Custom duty:
- Method of tax collection:
- Local tax collectors dispatched from the center
- via direct tax collection or tax collection contract (Iltizam)
- >Top Court system:
- Fair and speedy trials (more universal method than Wester Europe in 16C.)
- Islamic court based on Sunni Islamic law (Sherri Mahkeme)
- Four major Sunni schools: Hanafi (main), Shafi'i, Maliki, and Hanbali
- Islamic lawyers (Qadi, قاظي)dispatched from the center
- Layers were involved not only trials, but some local administration.
- Legal documentation of Islamic Court: about 10K books
- Supreme Authority of Islamic law: Islamic Elders (doyen)
- 17C such elder was appointed by Sultan, but after appointment he is responsible for the legitimacy of the Sultan himself.
- Regarding mismanagement of 18th Sultan Ibrahim led to the demise the Sultan by such elders, saying; 'Is it legal to dethrone the Sultan who committed to give scholarly positions with bribes and confusion in the order of Empire? Yes, it is legal.'
- >Top Standing Army Organization:
- Yeniçeri Army (Infantry), and Cavalry Army (Six regiments)
- Auxiliary Armies: Artillery Brigade, Gun Carriage Brigade, Engineering Brigade
- Number:15K in 15C, increased to 66K in 17C
- Garrison: the main unit lives at the garrison in Istanbul (Kushra)
6. 組織の帝国の伝説:
- 西欧人が恐れた組織の帝国
- 強靭で精巧な'組織の帝国'; 強大な常備軍、組織構成員の規律、高い技術水準、全国レベルの徴税システム
- スルタンによる君主専制、中央集権組織
- スルタンを制約するもの
- 称号・花押(トゥグラ): シャー (古代オリエントの大王)とハン(ユーラシアの大征服者)
- 正義: イスラム世界の政治論 '兵なくして王なく、財なくして兵なく、民なくして税なく、正義 (アダレット)なくして民の繁栄なし'
- スルタン: イスラムの聖法シャーリアの守護者; 'スルタンよ、スルタンとて慢心するなかれ。汝より偉大なるアッラーがおわす'
- スルタンの代理人
- 大宰相 (ヴェズイラザム)はスルタンの絶対的代理人 (ヴェキリ・ムトラク)
- セリムII以降、親征に赴かなくなって以降、絶対的代理人化した。
- 17C中葉まで、大宰相は個人の邸宅で執務
- 1654: デルヴィッシュ・メフムト・パシャ大宰相が、大宰相府 (バーブ・アサフィー)を創設
- 大宰相と宰相の争い。宰相は大宰相候補の集団。
- 最高意思決定機関: 御前会議 (ディーヴァーヌ・ヒュマユーン); 後にスルタンは会議をのぞき見るだけとなった。
- 16C中には、御前会議は毎日開催→その後は土日月火の4日間のみ
- 基本構成員: 1)大宰相、宰相、2)軍人法官 (ルメリとアナドル)、3)国璽尚書 (ニシャンジュ); 文書を検討し花押を描く、4)財務長官 (デフテルダル)
- 常備軍の俸給支払も御前会議の日に実施。年4回支給
- 財政の仕組
- 財政の統一性と公平性;
- スルタン財政(内庫イチュ・ハジネ)
- 財務長官管理の国家財政 (外庫ドゥシュ・ハジネ)
- 貨幣発行: 銅貨・銀貨・金貨
- 租税:
- イスラム法租税: ハラチュ、ウシュル(1/10税)、ジズヤ
- 土地税: 国有地 (ミーリ)、自由処分地 (ミュルク)、宗教寄進土地 (ワクフ)
- 国有地は、スルタン直轄地、知行地、徴税管理下の土地
- 交通の要衝での関税
- 徴税方法:
- 地方財務官は、中央から派遣
- 徴税方法は、徴税官or徴税請負 (イルティザーム)
- 裁判制度
- 公正で迅速な裁判 (16Cの西欧より統一的)
- スンナ派イスラム法に基づくイスラム法廷 (シェリー・マフケメ)
- ハナフィー (主流)、シャーフィイー、マーリキー、ハンバリーの4大法学派
- イスラム法官 Kadi は、中央から派遣
- 裁判だけでなく、地方行政の一部機構も実行
- イスラム法廷文書 (シェリー・マフケメ・シジルレリ)の総数1万冊
- イスラム法学の最高権威; イスラムの長老, Kazasker
- 17cには、スルタンに任命されるが、任命後はスルタン自身の廃立を左右する存在
- 第18代スルタン・イブラヒムの失政に、イスラム法学者が決起し、スルタンを廃位した。
- '学問の諸職をふざわしい者に与えず、賄賂をもってふさわしからぬ者に与えて、秩序に混乱を生ぜしめた君主を廃位し除くことは適法となるか。適法である。'
- 常備軍組織
- イェニチェリ軍団 (歩兵)と騎兵軍団 (六連隊衆)
- 補助軍団: 砲兵軍団、砲車兵軍団、鎧師軍団 (修理・工兵)
- 総員: 15Cには1.5万、17Cには6.6万
- 駐屯: 本隊はイスタブル内駐屯地 (クシュラ)で生活
>Top 7. Human Resources Absorption & Training System:
- An Ideal Meritocracy:
- Even a shepherd can be a minister
- thus reported with envy by Habsburg ambassador; among Turks, their status or occupation depended on their abilities and achievements.
- In the case of Western Europe, all took into consideration of origin of birth to get high ranking positions.
- Тwo-tiered hierarchy in Ottoman Empire:
- >Top Askeri (military): tax-exempt ruling class, including men of the sword, men of the book, and men of the pen
- Islam was dominant religion, but only a few of Muslims are Askeri class, and majority were Reaya.
- On the contrary, very few of non-Muslims belonged Askeri class.
- Reaya (flock, mainly farmers): duty to produce and pay taxes.
- >Top School System:
- Primary education institute (Mektep, or Maktab); many attached to mosques.
- Higher education institute; Islamic Academy (Medrese); In addition to Islamic studies, also medicine was provided; in cases supplied dormitories and scholarships.
- to enter Medrese: necessary to obtain a license for required subjects.
- Islamic law scholars tended to put their children in the same position.
- there was a calling system to the center from rural areas, if good luck and connections.
- >Top Devsirme System:
- Continuous recruitment of standing army soldiers; unique system to incorporate teenage boys of Christian into Sultan slave army.
- Originally, Christians were protected people (Dhimmi) under Islamic law, but this didn't cause problems to collect such children and make them Sultan slaves.
- It can be said that Ottoman Empire was established at the frontier of the Islamic world.
- The target area was mainly Rumelia (Balkan) area; In Bosnia, Muslim Bosnians were also targeted. However, Jews were excluded.
- Candidate children: ages (8-20 years old), healthy; but excluded those who were an only child, know Turkish, and non-Muslim circumcisors.
- recorded birthplace, parent name, year of birth, and physical characteristics. After arriving at the center, were forced to convert to Muslim and given Muslim name. Those with good looking are particularly selected as pages in the court. Majority are allocated Yeniceri army members.
- As a training, sent to Turkish farmers in Anatolia for several years as agricultural labors force, to get used to Turkish life and Turkish language.
- After that, belonged reserve corps, with daily salary. Shift to Yeniceri Army was carried out as appropriate. Marriage was prohibited until becoming an officer. Those who had married by then were suspended from promotion and engaged in reserve role.
- After that, there were opportunities to promote to officer and captain. The corps secretary was usually selected from corps members, but since 15C, court slaves were frequently appointed instead.
- 1648 recruiting Christians effectively stopped.; in beginning 18C 23rd Ahmed II the practice of devshirme was abolished.
- >Top Gorgeous career path:
- Topkapu Palace: there are three sections; outer court (Billund), inner court (Endem, where white eunuch and pages (Ichoghlani; iç oglani), and back palace (Harem, where women and black eunuch)
- Sources of pages: bought slaves, prisoners of war, part of asset forfeiture, rebel slaves, hostages of neighboring princes. Constantly supplied based on Devshirme system, which sorted candidates by appearance, physical strength, intelligence, and future potential. Learned at court school (called Endern Mektebi). Pages were expected to be worriers, but later became bureaucrats.
- Selected pages became cavalry corps or court slaves. The best selected pages were assigned to Sultans's private room (Has Oda) through expedition room, food storage room, or treasure storage room. Lastly Sultan's private office manager (Has Oda Bash) was the most excellent page.
- Cases:
- 1) Pargali Ibrahim Pasha:
Pargali Ibrahim Pasha, born in Parga a part of Republic of Venice, becoming a slave, and first met Prince Suleiman near Edirne likely in 1514; appointed by Suleiman I from Has Oda Bash to the Grand Vizier (1523-36; 13 years; ); replacing Piri Mehmed Pasha appointed in 1518 by preceding Sultan 9th Selim I.
- 2) Rüstem Pasha:
he was taken as a child-slave to Constantinople, where well educated and built military and bureaucracy career. In 1539 married Mihrimah Sultan, daughter of Sultan Suleiman I and Hurrem Sultan. Became most successful Grand Vizier (1544-53 & 1555-1561, 15 years until his death); He became Grand Vizier 8 years after Ibrahim's death.
- 3) Neveşehirli Damat Ibrahim Pasha:
Born in Nevşehir of a child of Muslim-Turkish influential person. Selected as secretary of the inner court from the outer court. Served as Grand Vizier for 23rd Sultan Ahmed III during Tulip period, when was unusual internal peace in the Empire.
Married to the daughter of the sultan, Fatma Sultan in 1717 at 14 years old and Ibrahim was 50. He was renowned for his scholars, poets, an artisans of his time. But he was murdered due to the mistake in his military action against Iran, and Ahmed II was also deposed.
- >Top Informal Intisab (relationship):
- Teacher-apprentice relationship in arts and tea practice
- a means for non-dominant layers to enter the dominant layer by making use of blood and territorial ties.
- Patronage: advancement due to the relationship of protector seeker client.
- Faction formation by the house of a leading officer
- Hereditary succession of Ottoman Society
- Originally, non-herediatary principle of Devshirme had been adopted as slave children, but de facto hereditary succession expanded.
- Influential families could only maintain and acquire governmental positions for their children, but which could easily be dismissed at the will of Sultan.
- Basically hereditary peers base on pedigree and family could not exist.
- In Ottoman society, there had been coexistence of both non-hereditary succession (openness, such as Devshirme) and de facto hereditary succession (closeness).
- This means the governing flexibility as the rule of Ottoman Empire. (called Soft Tyranny)
7. 人材吸収・育成のシステム:
- 理想的な能力主義社会
- 羊飼も大臣に
- ハプスブルク大使は羨望を込めて称賛: トルコ人の間では、地位も職種も能力と業績への報酬。
- 西欧の場合は、業績に関係なくすべて出自への配慮で高い官職につく。
- オスマン帝国の社会成層
- アスケリ(askeri, military): 免税・帯刀・騎乗等の特権身分: 軍人身分;
- イスラムが支配的宗教であったが、ムスリム中のごく少数がアスケリ身分で、大多数のムスリムはレアヤー身分
- 被ムスリムもごく少数はアスケリ身分に属した。
- レアヤー (reaya, flock):納税義務を負う被支配者身分: 主に農民
- 学校制度
- 初等教育機関: メクテプ; 多くはモスクに付属
- 高等教育機関: イスラム学院(メドレセ); イスラム諸学のほか、医学も
- メドレセには一部には寄宿舎・奨学金が支給
- 必要な科目の免許取得が必要。
- イスラム法学者達は、自分の子弟にも同職につかせる傾向があった。
- 幸運とコネがあれば、地方から中央へ吸い寄せるシステムがあった。
- デウシルメ制度:
- 常備軍兵士の継続的な人員補充
- 帝国内キリスト教徒の10歳台の少年を、スルタンの奴隷軍人へ組み込む制度
- 本来キリスト教徒は、イスラム法上は被保護民 (ズィンミー)。なのに、その子弟を徴収して奴隷とすることはイスラム法に反するはずだが、特に問題視されなかった。
- オスマン帝国がイスラム世界のフロンティアで成立した特殊事情とも言える。
- 対象地域は主にルメリ (バルカン)地域。ボスニアではムスリムのボスニア人も対象。但し、ユダヤ教徒は除外。
- 健康で欠点の内子供(8-20歳)が対象。一人っ子は除外、トルコ語を知っている者、非ムスリムの割礼者も除外。
- 出身地、父母名、生年、身体的特徴を記録。中央到着後はムスリムに改宗させ、ムスリム名を付与。容姿に優れた者は内廷の小姓に選抜。大多数はイェニチェリ軍団員
- トルコ式生活とトルコ語研修のため、アナトリアのトルコ系農民に農業労働力として数年間貸出
- その後は予備軍団である新兵軍団に所属。日給を支給。さらにイェニチェリ軍団への編入が適宜行われる。士官となるまでは結婚禁止。それまでに結婚した者は昇進停止させ予備役的雑務。
- その後、下士官、大隊長へ昇進。軍団長官, Beylerbey は、軍団員からの選抜が通例だったが、15C以降、宮廷奴隷が任命される例が増加。
- 1648には、キリスト教徒の採用は実質的に中止され、18C 第23代アフメトIIIはデヴシルメ制度を廃止
- 華やかな出世街道
- トプカプ宮殿は、外廷 (ビルン)、内廷 (エンデルン; 白人宦官と小姓イチュ・オウラン)、後宮 (ハレム; 黒人宦官と女人)
- 小姓の供給源: 購入者、捕虜、贈呈者、没収財産の一部、反乱者の子弟奴隷、近隣王侯の人質。恒常的供給はデウシルメ制度で、容姿・体力・知力・将来性で選別。宮廷学校 (エンデルン・メクテビと呼ばれた)。当初は武人重視から官人養成重視へ変化
- 小姓たちの配属も騎兵軍団や外廷へ転出する者。残った者も遠征室、食料貯蔵室、宝物室をへて最高のスルタンの私室 (ハス・オダ)へ配属。スルタン私室長 (ハス・オダ・バシュ)が筆頭。
- 事例:
- 1) スレイマンの寵臣の大抜擢
- イブラヒム・パシャの場合 (Parga出身の奴隷, 1514頃スレイマン王子のEdirne近辺で知遇); スレイマンによってスルタン私室長(ハス・オダ・バシュ)から大宰相 (1523-36; 13年間) へ抜擢された文人政治家で13年間大宰相を務める。1536年に反逆罪で処刑
- 2) 小姓出身の軍人宰相
- 16C中葉 ルステム・パシャもデウシルメにより内廷に配属。ハス・オダのNo.2のシラフタール (太刀持ち)から外廷のスルタン厩長に転出。その後アナドル州提督を経て宰相に抜擢。1539年にスレイマンとヒュッレムの王女ミフリ マーの女婿に抜擢。1544-53 & 1555-61年(15年間)死亡まで大宰相を務める。
- 3) 小姓出身の文人宰相
- 18C初: イブラヒム・パシャ: ムスリム・トルコ系地方有力者の子。外廷から内廷の書記に抜擢。当時王子だった第23代アフメトIIIの知遇を得る。1716大宰相代理を経てチューリップ時代の大宰相 (1718-30, 12年間)。文芸の良きパトロンだったが、イランへの軍事行動での対応を誤り、殺害され、アメフトIIIも廃位された。
- 非公式のインティサーブ (Intisab)
- 芸術・芸道分野での師弟関係で、入門や仕官に近い。
- 血縁・地縁を活かして非支配層が支配層に参入する手段。
- 庇護者パトロン〜被庇護者クライアントの関係による出世
- 有力大官の家を核とする派閥形成
- オスマン社会の世襲
- 本来はデウシルメという非世襲の原理が、部分的だが奴隷の子 (クル・オウル)として採用されるケースが増加し、事実上の世襲が拡大。
- 但し、有力な家系も、官職を維持獲得しただけで、スルタンの意志で解雇あり得た。
- 血統・家柄のみに基づく世襲貴族は存在できない構造
- オスマン社会は、デウシルメのような非世襲の原理 (開放性)と、事実上の世襲 (閉鎖性)が併存。
- これこそが、オスマン帝国支配の柔軟性の表れ。
>Top 8. Turning Corner of A Superpower:
- 1571: Battle of Lepanto: Combined fleet of Christians (Holy League; Spain and most of Italy, arranged by Pope Pius V, who died in 1573) defeated Ottoman fleet
- Strength of warships: Ottoman 224 vessels vs Christian 276. Of these 190 Ottoman's vessels were sunk or captured. Eventually Ottoman Admiral Ali Pasha was killed due to this result. Turkish deaths were 30K, while Christian side suffered 7.5K.
- Ottoman side was directed by Bertel Pasha, Vizier & Operations Commander, and Ulchu (Uluç) Ali Pasha, Algerian Governor who was in charge or Algerian Navy. The former insisted frontal operation, while the latter insisted on defense operation in he bay. Finally Ali Pasha, the Admiral who was an amateur derived from the court pages decided the frontal battle.
- The result was major defeat of the Ottoman Feet.
- Christians was superiority in guns and cannon aboard the ships. Christians 1814 guns vs, Turks 750
- After the defeat of battle, Grand Vizier Sokollu Mehmed Pasha (1565-79; 14 years) under 11th Selim II appointed Ulchu Ali Pasha as Grand Admiral, and started to rebuild the fleet.
- Eight months after the defeated battle, a large feet of 250 ships revived and deployed in the Mediterranean Sea. Christian side fleet was disbanded without taking advantage of the opportunity after the victory.
- Ottoman fleet captured Cyprus in the same year.
- Actually this Turkish defeat stooped Ottomans' expansion into the Mediterranean; eastern half under Ottoman control, and western half under Habsburgs and their Italian allies.
- >Top End 16C - beginning 17C: a large scale 'Jelali revolts' occurred in Anatolia. Ottoman Empire stood at a corner.
- This was caused by the incompetent rules continued after the death of Sultan Suleiman, as well as unappropriated persons were also appointed below the incompetent Grand Vizier.
- The frequency of Sultans who went to the battle fields were decreased. Prices also lived as a semi prisoners in the back palace without training as local governors. (lived in the golden cage) Women and eunuch officials in the back palace also gave adverse effects to the Empire. (Petticoat government)
- 14th Sultan Ahmed I's beloved princes Kösem Sultan ruled national affairs as the guardian of young 17th Murad IV. Her mother Kösem marries her slave Turhan to her own son 18th Sultan Ibrahim, and gave birth to Mehmed, later who became 19th Mehmed IV. But the power struggle between her mother Turhan and her ex-mother Kösem continued. Mehmed IV himself depended her mother in national affairs as co0rulers.
- Then followed by ineligible Sultans and short-term Grand Viziers caused political instability of the Empire; which was called Women governance, as the fish would be rotten from the head.
- Structural changes in Ottoman Society:
- the changes began with 12th Murad III (1574-95)
- Deterioration of Grand Vizier and Viziers; bribery rampant.
- farmers' distress due to harsh tax collection by the tax collection contractors.; the state-owned land was changed to private land by extending tax collection contract period, which meant landowners appeared.
- budget deficit due to expansion of Yeniceri Army (from 10K in 16C to 40K in 17C. (partly reflected the change of war tactics requiring more depending on artillery powers.)
- also the Empire had changed from military empire to bureaucratic empire
- number of bureaucratic officers; several tens in Suleiman's age to 800 in the end 18C.
- expansion of bureaucratic organization meant more increase of official documentation.
- the place of Decision-making shifted from the conferences by Sultan to those of Grand Vizier.
- increase of the function of Chief Secretary, who was the head of document administration, including roles as the Minister of Foreign Affairs to process documents with foreign countries.
- 1697 Ramie Mehmed Pasha was appointed Visier in 1702 from Secretary general, and then Grand Vizier in 1703 as appreciated to sign the Treaty of Karlowitz after the failure to siege the Second Vienna in 1699.
- Expansion of Technical Gap:
- In 16C the technology of Ottoman organization and military were at an outstanding level.
- even at 18C, which enabled to maintain the territory acquired in 16C.
- the continuous loss of Ottoman territory had occurred in relation with the technological gap with Western Europe.; most of Hungary was retaken by Habsburg Empire under the 1699 treaty of Karlowitz.
- In 18C, the territory of norther coast of the Black Sea was eroded by Russia, which successfully promoted Western-style reforms by Pyotr I, the Great. In the latter half of 18C, Ottoman Empire was defeated with Russian Ekaterina II at Russo-Turkish War, and lost the sovereignty of Crimean Khanate in Crimean Peninsula by 1774 Treaty of Küçuk Kaynarji.
- During 154 years between 1529 the first Siege of Vienna and 1683 the second Siege of Vienna, the military-technical power relationship with Western Europe had been decisively reversed.
- Awakening toward Nation State:
- In latter 18C, the Greeks in the Empire became aware of Greek nationalism as an ethnic group.
- 1789 the French Revolution influenced Ottoman Empire. From end 18C to beginning 19C, non-Muslim nationalists' consciousness emerged in the Balkan Peninsula.
- the religion-based Dhimmi system began to fluctuate; causing opposition to unequal coexistence under Muslim dominance.
- After that, the former Ottoman territory, particularly in Balkan Peninsula became a crucible of fierce ethic and religious conflicting areas even now.
- Ottoman Empire itself was forced to proceed Westernization; after WWI, the flow of dismantling of the empire could not be stopped.
- The history of Ottoman Empire gives us valuable suggestions about the fate of an empire with vast territories and diverse ethnic groups, and the trials of coexistence with diverse elements in society.
8. 超大国の曲がり角:
- 1571: レパントの海戦: キリスト教徒の連合艦隊がオスマン艦隊に大勝
- キリスト教側276隻vs. オスマン側224隻。内、190隻が撃沈・拿捕された。オスマン側大提督アリ・パシャ戦死
- さらに宰相・作戦総司令官のベルテル・パシャとアルジェリア水軍叩き上げのアルジェリア総督ウルチュ・アリ・パシャ。前者は正面作戦を、後者は湾内での防衛作戦を主張した。大提督アリ・パシャは、宮廷小姓出身で海戦には素人。
- 結果は、正面作戦を採用し、オスマン艦隊は大敗を喫した。
- 第11代セリムIIの下での大宰相ソコルル・メフメット・パシャが、敗戦後、ウルチュ・アリ・パシャを大提督に任命し、艦艇再建に着手。
- 敗戦後8ヶ月で250隻の大艦隊が復活して地中海に展開。一方の連合艦隊は勝利後の好機を活かすことなく解散していた。
- 16C末〜17C初にかけてアナトリアでの大規模な'ジェラーリの反乱'が起きた。オスマン帝国は曲がり角に立っていた。
- スレイマン大帝没後、無能な支配者が相次ぐ。大宰相以下にも不適任者が任命された。
- 親征に赴くスルタンも減少。王子たちも知事としての訓練なく、後宮内での半幽囚生活。後宮の女人と宦官の悪影響 (女人の天下)
- 第14代アフメトI の愛姫キョセム・スルタンは、第17代ムラトIVの後見人として国政を支配。
- 母后キョセムは、自分の息子イブラヒムに奴隷トゥルハンを娶らせ、メフメト出産する。のちに第19代Mehmed IVとなったが、母后トゥルハンと前母皇后キョセムとの権力闘争が継続する。Mehmed IV自身は母を共同支配者として国政に関与させる。
- その後、不適格なスルタンと短期間の大宰相が続き、政治が不安定化;女人天下に加えて、 '魚は頭から腐る'状況
- オスマン社会の構造変化
- 変化は第12代ムラトIII (1574-95)から始まった
- 大宰相・宰相の劣化、賄賂の横行
- 徴税請負制による過酷な徴税による農民の窮迫
- 徴税請負期間の長期化にともない国有地が、私有地的に変化。大地主が登場
- イェニチェリ軍団拡大 (16C初の1万から17C初の4万)による財政赤字化 (但し、戦術が軍事革命で火砲中心になってこともある)
- 軍人帝国から官僚帝国へ
- 財政組織も、スレイマン時代の数十人から18C末には800人へ拡大
- 組織の拡大は、公文書の増加。
- 意思決定の場も、御前会議から大宰相府へ
- 文書行政の長である書記官長の重要性拡大。諸外国との文書処理を行う外務大臣的役割。
- 18Cになると、西欧との軍事力が逆転し、戦争より外交がより重要になる。
- 1697 書記官長出身のラーミー・メフメット・パシャは、1699第二次ウィーン包囲失敗後のカルロヴィッツ条約を締結した功績で、1702に宰相、1703に大宰相となる。
- 技術格差
- 16Cは、オスマン帝国の組織と軍事技術は卓絶したレベル
- 18Cでも16Cに獲得した領土を維持できた。
- 帝国の恒常的領土喪失は、対西欧関係で生じている。1699のカルロヴィッツ条約でハンガリーの大部分をハプスブルク帝国に奪還された。
- 18Cには、ピョートル大帝による西欧型改革を進めたロシアによって黒海北岸の領土侵食された。18C後半にはエカテリーナのロシアとの露土戦争に敗北し、1774キュチュク・カイナルジャ条約によってクリミア半島のクリム汗国の宗主権を放棄させられた。
- 1529年の第一次ウィーン包囲と1683年の第二次ウィーン包囲戦の154年間に、西欧との軍事・技術の力関係が逆転した。
- 国民国家への目覚め
- 18C後半、帝国内ギリシア人が民族としてのギリシア・ナショナリズムを意識。
- 1789のフランス革命の影響。18C末〜19C初にかけてバルカン半島で非ムスリムのナショナリズム意識が台頭。
- 宗教に基軸を置くズィンミー制度が揺らぎ始める。ムスリム優位の下での不平等な共存への反発
- その後、旧オスマン領が激しい民族紛争、宗教紛争のるつぼとなる現代の状況につなる。
- 結局、オスマン帝国は、西欧化を進めることになるが、WWI以降、帝国解体の流れを押し止めることができなかった。
- オスマン帝国の歴史は、広大な領域と多様な人間集団を有し、多様な要素による共存を志向してきた帝国の運命について貴重な示唆を与えてくれる。
>Top 9. Glossary (Turkish - English):
- adalet
- askeri
- Bey
- Beylik
- cami
- khalifa خليفة
- devşirme دوشيرمه
- Dhimmi ذمي
- divan; diwan
- elma
- five pillars of Islam;
- grand vizier
- harb حارْب
- hadim
- harem
- iç
- intisab انتساب
- jihad جهاد
- jizyaِ ِجزََْية
- kapiklu
- kervansaray
- kharaj خراج
- kizil
- kul; köle
- Lâle Devri
- medrese
- mektep
- paşa پاشا
- qadi
- qibla قبلة
- Quran القرآن
- Rumelia
- salah صلاة
- sefardi
- sharia شريعة
- Sultan ساطان
- Tanzimat
- tughra; tugra طغرا
- yeniçeri
- ichoghlani; iç oglani
- valide
- wqafَ وْقف ; vakif
- zakat زكاة
- justice
- military, martial
- Emir-i a'zam (Great Emir); lord, ruler
- Tevaif mülûk
- mosque
- Caliph
- Devşirme system; <gather; recruiting system; called 'blood tax', forcibly recruiting soldiers and bureaucrats; it counterbalance Turkish nobility, who sometimes opposed Sultan.
- protected people; state obligation under sharia to protect individual life, including freedom of religion, loyalty to the state, and payment of jizya tax (zakat is obligatorily paid by Muslim)
- high government ministry or chief official; <custom house, council chamber; or long cushioned seat
- apple; Kizil elma=red apple
- 1) Shahada (faith شهادة); 2) Salah (prayer صلاة); 3) Zakat (giving زكاة) ; 4) Sawm (fasting صوم); 5) Hajj (pilgrimage حج
- vaziri a'zam; sadri a'zam صدر اعظم ; chancellor
- war; Dal al-Harb=realm of war
- eunuch; castrated human male
- harem حريم; private part of Arab household
- inner, internal; close to the center
- relationship
- jihad; <effort for Islam; struggle on behalf of Islam
- jizya, per capita tax on dhimmis (non-Muslim), exempting women, children, elders, handicapped, ill, slaves.
- <kapi=gate, house; kulu=slave
- an inn having a central courtyard where caravans can rest
- Islamic tax on agricultural land and its produce.
- red; Ar. ahmar أحمر
- slave; Ar. عبد
- Tulip Era in Ottoman Empire; lale=tulip; devir=era
- Ar. Madrasah مدرسة; school for Islamic theology
- school; Ar. مدرسة
- General, minister
- qadi, قاظي; Islamic judge
- direction to Kaaba in Mecca
- religious text of Islam, revelation from God
- Balkans
- praying
- Jews in Iberia Peninsula
- Sharia; a body of Islamic law
- ruler; power; authority
- reorganization
- calligraphic monogram, seal of a Sultan affixed to officia documents.; characteristically 2 loops of the left and 3 vertical ines in the middl, stacked writing on the bottom and 2 textensions to the right.
- Janissaries;<yeni=new; çeri=soldier; Ar. إنكشارية
- Page; >page of honour, 式服の裾持ち
- mother; Ar. أم
- wqaf=stop; a part of Sadaqah صدقة, charity, benevolence
- almsgiving; Islamic religious obligation
- 正義
- 軍
- 君侯
- アナトリア半島に割拠した君侯国
- モスク; スレマニエ・モスク Süleymaniye Camii
- カリフ; ムハンマド後のイスラム最高権威者
- デヴシルメ制度
- イスラム法の下での保護政策 (宗教の自由、国家への中世、jizya税支払; イスラム教徒はzaka喜捨)
- オスマン帝国高官
- リンゴ
- イスラム五行; 告白、礼拝、喜捨、断食、巡礼
- 大宰相
- 戦争
- 宦官
- ハレム; アラブの私室
- イチュ; 内廷の
- インティサーブ、師弟関係
- ジハド; 自己犠牲して戦う(JHD)
- 非ムスリムへの人頭税
- 軍人奴隷; マムルークと同一起源; 近衛兵; キリスト教徒少年から徴収
- 隊商宿
- 農地やその生産物に対するイスラム税
- 赤い
- 奴隷
- チューリップ時代
- イスラム法学院
- メクテプ, 初等教育期間
- パシャ, 大臣
- イスラム法裁判官
- キルバ; メッカ・カーバ神殿の方向
- クルアーン
- ルメリア; バルカン半島
- 礼拝
- イベリア半島のユダヤ人
- シャーリア法
- スルタン
- タンジマート; 近代化改革運動
- スルタンの花押、公文書冒頭に記載
- オスマン帝国の常備歩兵軍団; spoonがシンボル
- 君主や貴族の小姓; 馬、テーブルマナー、チェス等研修
- 母后; ハレムの支配者
- 慈善事業 (モスクや学校等)への資金提供; 喜捨 Sadaqahの一種
- 喜捨
Comment
- In 2022 with the invasion of Ukraine by Russia, it is important to unravel history of the world, because it is as if a 21C Crusaders were formed.
- The world should be understood keeping an eye on not only Europe & US, and Russia, but also China, India, South America and Middle East. Why Turkey tries to mediate between Russia and Ukraine. Then, I recognized the historical role of the Ottoman Empire which had been a superpower between the West and the East for more than 600 years.
- Also, a Turkish drama "History of Ottoman Empire" was very inspiring. There existed until recently an international nation where Turkish, Arabic, Persian, Russian, and Italian languages were spoken.
- The Ancient Roman Empire had existed only in the memory of history. However, the tradition of Byzantine Empire was inherited by Ottoman Empire and neighboring countries and survived until recently, and still influences various current historical formations.
- 2022 ロシアによるウクライナ侵攻を契機に、世界史をさらに紐解くことにした。あたかも21Cの十字軍が編成されたかのような騒ぎである。
- 世界は、欧米やロシアだけでなく、中国やインド、南米や中東の動向には目を離せない。そしてなぜトルコがロシアとウクライナの仲介をしているのか。そして、西アジアで600年余に亘って超大国であった東西間に位置するオスマン帝国の歴史的役割を改めて認識することになったのである。
- またトルコ制作のドラマ"オスマン帝国外伝"には、大いに刺激を受けた。トルコ語とアラビア語・ペルシャ語・ロシア語・イタリア語が飛び交う国際的な国家が、確かに最近まで存在していたのだ。
- ローマ帝国は歴史の中にしか存在していなかった。だがその東ローマ帝国の伝統は、オスマン・トルコや周辺国に継承されてごく最近まで存続し、今も様々な歴史形成に影響を与えている。
 |
History of Ottoman Empire |
Cat: HIS |
Tadashi Suzuki (鈴木董) |
22525u |
Résume |
Remarks |
>Top 0. Introduction:
| 0. 序文:
|
>Top 1. From a group of Warriors to a Nation:
| 1. 戦士集団から国家へ:
|
>Top 2. Battle of Constantinople:
|
2. コンスタンティノープルの攻防
|
>Top 3. Islam as Wisdom of Coexistence:
|
3. イスラム=共存の智恵:
|
>Top 4. Road to the Islamic World Empire:
|
4. イスラム的世界帝国への道:
|
>Top 5. Brilliance of Suleiman the magnificent:
|
5. 荘厳者スレイマンンの光輝:
|
>Top 6. Legend of Organizational Empire:
|
6. 組織の帝国の伝説:
|
>Top 7. Human Resources Absorption & Training System:
|
7. 人材吸収・育成のシステム:
|
>Top 8. Turning Corner of A Superpower:
|
8. 超大国の曲がり角:
|
>Top 9. Glossary (Turkish - English):
|
Comment |
|
|