
'Imperial' Russian Geopolitics
Cat: HIS
Pub: 2019
#: 2206b
Yu Kozizumi (小泉 悠)
22306u
Titile
'Imperial' Russian Geopolitics
「帝国」ロシアの地政学
Index
Tag
; 2004 Presidential election; Baltic states; Belarus; CAASTSA; Color revolution; Crimea; CSTO; DNR; EaP; EEP; EEU; Far East; Geopolitics; Georgia; Georgy's ribbon; GPV; Inbetweens; LNR; Minsk protocol; NATO; Nuclear bastion; Orange revolution; R2P; Semi-sovereign; Sphere of influence; SSBN; Svaboda; Syria; Valdai; Vostochny;
Résume
Remarks
>Top 0. Introduction:
- On 2014/3/18 Russia annexed the Crimean Peninsula, and on 2022/2/24 invaded Ukraine; the world is about to enter the new Cold War situation.
- On the other hand, the situation of decoupling is getting more serious due to US-China trade war.
- It looks like a new era of the continental drift (the rift of political, economic and military divisions) causes wide-spreading; it is now required us how to keep cool mentality and to make medium and long0term viewpoint of analysis and action.
0. 序文:
- 2014/3/18のロシアによるクリミア半島併合、また2022/2/24 のウクライナ侵攻によって、世界は再び新冷戦を迎えようとしている。
- 一方で、米中貿易戦争からデカップリングの状況は一層深刻になりつつある。
- 正に、政治・経済・軍事的な大陸移動のような裂け目が広がりつつある。この時期に、いかに冷静さを保つと同時に、中長期的な視点での分析と行動が問われている。
>Top 1. How far is 'Russia?::
- In Russia, the term geopolitics (Геополитика) became common after the collapse of Soviet Union.
- originally, it is advocated in Nazi Germany as the right to life (Lebensraum) , which became the logic of aggression of Eastern Europe, and Soviet Union.
- Geopolitics is the impact of human division reflected on geography. (Kaplan)
- Ethnic composition of Russia: Ethnic diversity
- Russian 111M (78%); Tatar 5.3M (3.7%); Ukrainian 1.9M (1.4%); Bashkir 1.6M (1.1%); Chubashi 1.4M (1%)
- Diverse religions:
Russian Orthodox 41%;
Atheism 13%; (Western) Christian 6%; Islam 6.5%, Buddhism 0.5%; Judaism 0.1%
- >Top Soviet Constitution (Article 72) stipulates the right to withdraw:
- Awareness of national identity: fought together with Nazi in WWII.
- the symbol of 'Georgy's ribbon'; though Ukraine is negative.
- The collapse of Soviet Union: was '20C's greatest geopolitical tragedy" (Putin)
- Russian people (почти чаши) 26 lived outside the border of the Russian Federation.
- However, non-Russian live within it.
- Identity and geopolitics:
- 1) Western Europe-oriented:
- foreign minster Kozilev of Yeltsin administration pursued cooperative stance with Western countries.
- independent sovereign states form the former Soviet Union (Westphalia order)
- Dismantlement of Warsaw Pact, while Expansion of NATO (ignoring Russian's expectation); Russia's no hope of Western Europe orientation (1992/12)
- 2) Imperial-oriented:
- historical sovereignty by ethnic group; all Slavic people are Russian people.
- There are influential nationalist such as Zirinovsty (Chief of the LDP of Russia); Rogozin (President of the Space Authority & former Deputy Prime Minister); Luzhikov (former Mayor of Moscow); Dugin (philosopher); Solgenitzin (writer), etc.
- 3) Great power-oriented:
- Believer of great powers (Державники); such as President Putin.
- Former Soviet counties are the sphere of influence.
- Prevention of further expansion of NATO.
1. ロシアとはどこまでか:
- ロシアでは、特にソ連崩壊後、地政学 (Геополитика)という言葉はよく登場する。
- 元来は、ナチス・ドイツの生存権 (Lebensraum)を提唱。東欧侵略の論理とし、ソ連では、それをナチスのイデオロギーとした。
- 地政学=人間の分断が地理に及ぼす影響 (カプラン)
- ロシアの民族構成: 多様性
- ロシア人 111M (78%); タタール人 5.3M (3.7%); ウクライナ人 1.9M (1.4%); バシキール人 1.6M (1.1%); チュバシ人 1.4M (1%)
- 宗教も多様:
ロシア正教 41%; 無神論 13%; キリスト教諸派 6%; イスラム教 6.5%; 仏教 0.5%; ユダヤ教 0.1%
- ソ連憲法第72条には、脱退の権利が明記:
- National identity的意識: 共にナチスと戦った仲
- ゲオルギーのリボン [ウクライナは否定的]
- ソ連崩壊: "20C最大の地政学悲劇" (Putin)
- ロシア系(почти наши) 26M人が、ロシア連邦の国境外
- 一方、ロシア国境内には非ロシア的な民族もいる。
- アイデンティと地政学:
- 1) 西欧志向: アナーキー的
- エリツィン政権コズィレフ外相の西側協調路線
- 旧ソ連諸国からの独立した主権国家として扱う
(ウェストファリア的秩序)
- ワルシャワ条約解体とNATOの存続・拡大 (ロシアの期待無視)→1992/12 西欧志向の挫折
- 2) 帝国志向: 一極世界的
- エスニック集団による歴史的主権。スラヴ系諸民族=ロシアの民
- 民族主義者 (ジリノフスキー自由民主党党首、ロゴージン宇宙公社総裁、元副首相、ルシコフ元モスクワ市長、ドゥーギン哲学者、ソルジェニーツィン作家ど等が主張
- 3) 大国志向: オリガーキー的
- 大国主義者 (Державники) プーチン大統領が筆頭
- 帝国的秩序ではなく、旧ソ連諸国は影響圏
- NATO拡大阻止
>Top 2. 'Soverignty' and 'Sphere of Influence:
- 2017/12 US National Security Strategy (NSS) has positioned Russia as a power to change the status-quo, such as:
- 2008: intervention in Georgia (=Gruziya, Грузия)
- 2014/3-4: intervention in Ukraine; the Dopas region, and annexation of the Crimean Peninsula.
- 2015: intervention in Syria
- 2016: concerns about 2016 US presidential election
- 2018: NATO Secretary-General's Annual Report; Reduce in European Security and increase of unpredictability by Russian hybrid means.
- Russian intervention areas:
- the former Soviet Union countries (half domestic treatment):
- 2008: Georgian intervention
- 2014: Ukraine intervention
- >Top Outside Soviet Union countries (non-intervension; Wesfalia-like order)
- based on R2P (Responsibility to Protect)
- eg: 1999: NATO's intervention in Yugoslavia
- eg: 2003: Iraq War
- eg: 2001: US intervention in Afghanistan: Russia cooperated with US as the self-defense war.
- Concept of a sovereign state:
- a great power (Держава) like country;
- a country that can maintain a balance of power with other countries by its own power.
- the former Soviet Union countries are not 'sovereign states'
- Anarchy and Hierarchy:
- anarchy is a world of self-help; the hierarchy is altered by the interstate power balance.
- the sovereignty of lower countries is restricted to restricted to higher countries.
- >Top 2014: Valdai (Валдай) Conference: Russian-sponsored expert conference.
- 2018/10/18 @Sichi: the legitimacy of a nation is determined by the loyalty to US. (one-sided control of sovereignty)
- 2015: Russian National Security Strategy: 'to demonstrate its ability to provide sovereignty; independence, territorial integrity, and protect of compatriots in foreign countries.' (beginning of multipolar world)
- >Top Logic of 'sphere of influence':
- 2008: President Medvedev's five principles of diplomacy:
- International law, Multipolar world, Non-isolated, Protect of nationals, Special interest areas.
- special interest areas, where Russia has traditionally maintained special stakes
- when the relationship collapse, the interest is maintained by exercising influence, including military power.
- Sphere of influence: is range of the hierarchy of sovereign states.
- dominant relationship between the core of the empire and fringe countries.
- Gradation of sphere of influence:
- 1) Aggressive sphere of influence: generally in tandem with Russia:
- Kazakhstan, Belarus
- 2) Intermediate sphere of influence: slightly independent-oriented:
- Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, etc.
- 3) Negative sphere of influence: NATO and EU oriented:
- Ukraine, Georgia
- 4) Outside sphere of influence:
- NATO and EU member states
- Eastern Europe, Baltic countries
- however Russia opposes MD system deployment
- Russian Military presence: >Fig.
- Russia doesn't fold everything, focusing on air power, special forces, information gathering, and command & control, and doesn't dispatch large-scale ground troops, but cooperate with local cooperative military organization.
- >Top Color Revolution (Flower Revolution): US broke down of Russian's influential sphere.
- The multipolar world is still at stake.
- US is richly trying to maintain unilateral dominance. (Putin)
- overthrow the opposing systems that slams into the unipolar world by means of other than war. such as:
- 2003: Rose Revolution (Georgia)
- 2004: Orange Revolution (Ukraine)
- 2005: Tulip Revolution (Kyrgyzstan)
- 2000s: Arab spring
- 2014: Ukraine political change
- 2013: General Gerasimov (Валерий Герасимов) says inn the paper on the Arab Spring: "Non-military means, including political, economic, information, humanitarian and other protest potential of a wide range of inhabitants are applied. It appears in a form of peacekeeping or crisis management operations, combining formal or non-regular means with networked high-tech and high-mobility strategy; functions continuously a front in the enemy's domestic area."
2. '主権'と'勢力圏':
- 2017/12 米国国家安全保障戦略 (NSS, National Security Strategy) は、ロシアを現状変更勢力と位置づけた。
- 2008: グルジア介入
- 2014/3-4: ウクライナ介入; ドンパス地方への介入、クリミア半島併合; 2022/2/24全土侵攻
- 2015: シリアへの軍事介入
- 2016: 米国大統領選挙への懸念
- 2018: NATO事務総長の年次報告書;
- ロシアよる欧州へのハイブリッド手段活用による安全保障の減少と予測不能性の増大
- ロシアの介入地域:
- 旧ソ連諸国に集中している。(半ば国内扱い)
- 2008: グルジア介入
- 2014: ウクライナ危機
- 旧ソ連域外諸国では内政不干渉 (ウェストファリア的秩序)
- R2P=Responsibility to Protect (保護する責任)
- 例: 1999: NATOによるユーゴスラビア加入
- 例: 2003: イラク戦争
- 例: 2001: 米国のアフガニスタンへの介入; ロシアは、米国の自衛権の範囲内として米国に協力
- 主権国家とは
- 大国 (Держава) (=強国、列強)に近い概念
- 自力によって他国とのパワーバランスを維持できる国
- 旧ソ連諸国は「主権国家」ではない。
- アナーキーとヒエラルキー:
- アナーキーは自助の世界、ヒエラルキーは国家間Power balanceに応じて変質
- 下位国の主権は上位国に制限される。)
- 2014: Valdai (Валдай)会議 (ロシア後援の有識者会議)2018
- 2018/10/18 @Sichi プーチン演説の趣旨
- 米国に対する忠誠度が国家の正当性を決めるようになった。(主権の一極支配)
- 2015: ロシア国家安全保障戦略: "ロシアは、主権、独立、領土の一体性、在外同胞の権利保護を行う能力を実証した。" (多極世界への以降の開始)
- 「勢力圏」の論理
- 2008: メドベージェフ大統領の外交5原則:
- 国際法、多極世界、非孤立、国民の保護、特別利害地域
- 特別利害地域は、ロシアが伝統的に特別の関係を結んできた国々
- その関係が破綻した時には、軍事力を含む影響力行使によって特別利害関係を維持する勢力圏である。
- 勢力圏とは、主権国家のヒエラルキーの及ぶ範囲
- 帝国という中核と周辺国の支配関係
- 勢力圏のグラデーション:
- 1) 積極的勢力圏: 概ねロシアと共同歩調:
- カザフスタン、ベラルーシ
- 2) 中間的勢力圏: やや独立志向:
- ウズベキスタン、トルクメニスタン等
- 3) 消極的勢力圏: NATOやEU加盟志向:
- ウクライナ、グルジア
- 4) 影響圏でなくなった地域:
- すでにNATOやEU加盟国
- 東欧、バルト諸国
- 但し、ロシアはMDシステム配備には反発
- ロシアの軍事プレゼンス:
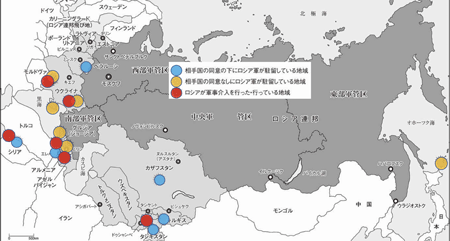
-
- ロシアはすべてを丸抱えにせず、空軍力、特殊部隊、情報収集、式統制が中心で、大規模な地上部隊の派遣はしないで、各派の軍事機構と連携して行う。
- カラー革命論: 米国によるロシア勢力圏の切り崩し
- 多極世界は、依然として危機に曝されている。
- 米国は成金的に、一極支配を維持しようとしている。(Putin)
- 一極世界に楯突く体制を、戦争以外の方法で転覆
- 2003: バラ革命 (グルジア)
- 2004: オレンジ革命 (ウクライナ)
- 2005: チューリップ革命 (キルギスタン)
- 2000年代: アラブの春
- 2014: ウクライナ政変
- 2013 ゲラシモフ参謀総長のアラブの春に関する論文:
- "非軍事的手段 (政治、経済、情報、人道、その他幅広い広い住民の抗議ポテンシャルに応じて適用される。軍事力は、平和維持各動及び危機管理という形態を装い、ネットワーク化されたハイテク・高機動戦略を、正規・非正規の手段を組み合わせ、敵国内部には継続的に機能する戦線が出現する。"
>Top 3. Landscape of 'the Occupation':
- Georgia and the Baltic States:
- 2008/8/7: Separated independent militias from Georgia and Geogian troops fight in South Ossetia. (South Ossetia conflict)
- Collision in Abkhazia on the Black Sea coast.
- Initilly, the Georgian army dominates Zihinbali, the capital of South Ossetia.
- Russian dispatched the Black Sea Fleet. (Five-day war)
- But Russia curbed to occupay Georgia's capital Tbilisi.
- Russia has an overwehlming military advantage over the former Soviet Union countries.
- Russia approved South Ossetia (3.9K㎢, 54K people) and Abkhazia (8.7K㎢, 242K) as independent states.
- 2007/2: Legality of the use of military force:
- Italian Defense Minister: said the use of military force is legal if approved by NATO, EU or UN.
- Putin critisized: 'the use of military force is only legal if approved by UN.'
- >Top 1990/5/11: NATO non-expansion policy:
- 'If Russia approves the unification of East and West Germany, NATO will not expand to the east by an inch.'
- Currently promoting NATO membership action plan (MAP).
- 2008/4 US President G. W. Bush: proposed to join Georgia and Ukraine to NATO membership.
- NATO's Bucharest Declaration: Joining to NATO on condition of demcratization and progress of domestic reforms.
- Russia considers the MAP as an irreversible point.
- US agreed to install MD (radar defense) in Czech Republic.
- 2008/8: The turning point of the 'sphere of influence' defense war:
- Intervention in Southern Ossetia: A militrary interverngtion to prevent Georgia from being incorporated into the sphere of other great powers.
- 'the Occupied 20%' becama a stake role to prevent Georgia to join NATO as long as keeping conflic with Russia.
- 2008/2: Kosovo autonomous province declared independence from Serbia; which US and EU approve.
- >Top Baltic States:
- 18C: were annexed to Russia.
- Estonia: Tallinn developed as a Hanseatic City.
- Latvia: Riga (Russia's Baltic center; Riga is famous for its railroad car factory.
- Lthuania: Vilnius, the capital.
- [Re: 1940/7: Chiune Sugihara, Deputy Consulate General of Japanese Consulate in Kaunas issued 1.500 'life visa' to Jews to Japan, agaist the intention of the ministry.]
- 1918: Declaration of Independece after the Russian Revoluton:
- 1920: Treaty of Tartu (Estonia); Treaty of Riga (Lativia); and Treaty of Moscow (Lithuania)
- 1917: During the Russian Revolution, Estonian and Latvian workers supported the Bolsheviks and had a civil ware against the counter-revolutionaries.
- 1922: The Baltic Staed didn't siigned in the Soviet Union Treaty.
- 1939: German-Soviet Secret Agreement: which was clarified by the glasnost (гласность);
- annexed to Soviet Union
- then, Nati German army occupied.
- after that, Soviel troops reoccupied and transferred to USSR
- 1945: at the Yalta Conference; US and UK connived the Soviet decision. But after the war, it was not approved.
- 1940: Japan approved Soviet's annexation of the Baltic States.
- 2004: Baltic Stated joined NATO and EU.
- 2007: Tallinn Incident; transfer of memorial monument bronze stature, emancipaction from Nati Germany. ('Bronze night')
- 2014: Russia ad Estonia demarcated the border.
- Population distribution:
- Estonia: Estonian 69%; Russina 25%
- Lativia: Latvian 64%; Russian 26%
- Lithuania: Lithuanian 6%; Russina 6%
- 2015: Baltic Stated: revived the Conscription.
- The importance of Kaliningrad:
- Russia's enclave surrounded by NATO countries.
3. '占領'の風景:
- グルジアとバルト三国
- 2008/8/7 グルジアからの分離独立派民兵とグルジア軍が、南オセチアで戦闘。
- 黒海沿岸のアブハジアでも衝突
- 当初は、グルジア軍が優勢。南オセチアの首都ツィヒンバリを包囲
- ロシア黒海艦隊投入; 五日間戦争
- ロシアは、グルジアの首都トビリシ占領を抑制
- ロシアは、旧ソ連諸国の軍隊に対しては圧倒的優位
- ロシアは、南オセチア (3.9K ㎢、54K人)とアブハジア (8.7K ㎢、242K人)を独立国家として承認
- 2007/2: 軍事力行使の合法性:
- イタリア国防省:' 軍事力の行使はNATO, EU, 国連で認められれば合法'
- それに対し、プーチン大統領: '軍事力の行使は、国連で承認された場合のみ合法'
- 1990/5/11: NATO不拡大方針 (1990/5/11)
- '東西ドイツを承認するならNATO軍は東方へ1インチも拡大しない。'
- 今は、NATO への加盟行動計画 (MAP=Membership Acgion Plan) 展開
- また、2008/4 米国ブッシュ大統領: グルジアとウクライナのNATO加盟提案
- ブカレスト宣言: 民主化、国内改革の進展を条件にNATOに加盟させる。
- ロシアは、MAPは引き返し不能地点と捉えている。
- 米国とチェコの間で、MDレーダー設置合意
- 2008/8: '勢力圏'防衛戦争の分岐点
- 南オセチアへの介入: グルジアが他の大国の勢力圏に組み込まれないための軍事介入。
- '占領された20%’は、グルジアをロシアの影響下に留めるための杭の役割→ロシアとの紛争を抱えている限りNATOへ加盟できない
- 2008/2: セルビアからコソボ自治州が独立宣言; 米国とEUが承認
- バルト三国:
- 18Cにロシアに併合
- エストニア: タリン (ハンザ同盟都市)
- ラトヴィア: リガ (ロシア帝国のバルト経営の中心地; リガは車両工場)
- リトアニア: ビルニュス;
- [注: かつてカナウス領事館あり。杉原千畝領事代理が本省の意向に反して命ビザ発給]
- 1918: ロシア革命後に独立宣言
- 1920: タルトゥ条約 (エストニア)、リガ条約 (ラトヴィア)、モスクワ条約 (リトアニア)
- ロシア革命では、エストニアやラトヴィアの労働者はボルシェヴィキを支持し、反革命派との内戦
- 1922: ソ連邦条約には、バルト三国は無署名
- 1939: 独ソ秘密合意: グラスノスチで秘密合意が明確化
- ソ連に併合
- その後、ドイツ軍の占領
- その後、ソ連軍の占領・編入
- 1945 ヤルタ会談で、米英はソ連の支配を黙認。戦後は、未承認とした。
- 1940 日本は、ソ連のバルト三国併合を承認
- 2004: バルト三国は、NATOとEUに加盟
- 2007: タリン事件; ドイツからの解放記念碑銅像移設 (ブロンズの夜)
- 2014: エストニアとロシアとの国境画定
- 人口分布:
- エストニア; エストニア人69%; ロシア人25%
- ラトヴィア; ラトヴィア人64%; ロシア人26%
- リトアニア: リトアニア人85%; ロシア人6%
- 2015:バルト三国; 徴兵制復活
- カリーニングラードの重要性
- NATO諸国に包囲されたロシアの飛び地
>Top 4. Russia's 'Sphere of Influence' and Ukraine crisis:
- 1991: Ukraine became independent from USSR
- 2004/5: East European eight countries joined EU.
- 2007: Romania and Bulgaria joined EU.
- Ukraine: area 600K ㎢, population 53M; one of major heavy industrial and agricultural areas in USSR.
- >Top In-Betweens: Belarus, Ukraine, Moldova, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Armenia.
- Total area of these countries 963K ㎢; Ukraine shares about 60% of the total area, and population of 63%.
- Ukraine is the core issue of staying within Russian influence.
- Kazakhstan shares 2.72M ㎢ and has population of 1.8M, but the land is mostly Islamic.
- Commonality of Russia, Belarus, and Ukraine: 'Almost Us'
- cat in Russian 'кот', in 'kit' in Ukrainian. But 'кит' means whale in Russian; so the anecdote says that Russian cat can return from whale to a cat (after the return of Crimean Peninsula).
- >Top From the Independence to Orange Revolution:
- Russian Natural Gas Pipeline; offered natural gas at a lower price than the market price.
- In addition, Ukraine received the toll revenue from the pipeline.
- Also, could export industrial and agricultural products to Russia.
- Active traffic of people, goods, and money.
- Munition production by the supply chain with Russia.
- >Top 2004: Presidential Election:
- Yanukovych candidate (pro-Russia) vs. Yushichenko (Pro-Western)
- Election in November: Yanukovych won, but the Supreme Court ordered re-election: (>voting Fig.)
- Yushichenko was elected at the re-election (Orange Revolution), and insisted to join NATO, and to leaved from EEP (Eurasian Economic Space; Russia-led common economic space).
- 2008/8 after the Georgia War, Yushichenko's administration suffered its internal conflict.
- >Top 2010: Presidential Election:
- Yanukovych was elected; withdrew to apply NATO membership, and agreed with Russia to extend Sevastopol navy base concession deadline further 25 years.
- 2012: Putin proclaimed EEU (Eurasian Economic Union) Initiative; based on the Russian, Kazakhstan and Belarus customs union.
- Russia intended a super-national coalition concept, not a reconstruction of the Soviet Union.
- >Top EU Policy:
- To promote ENP (European Neighborhood Policy):
- particularly, for the six former Soviet Union countries should be EaP (Eastern Partnership) concept; forming DCFTA (Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Area)
- "Making it safer for the EU' policy; eliminating intermediate options between Russia and EU.
- Require commitment to policy shifts in the politics, economy, trade and human rights of the partner countries.
- Support partial exemption from tariffs with EU, and financial and technical aid.
- Russian counters to Yanukovych's administration:
- Purchase o Ukrainian bonds.
- offered natural gas at 268.5 dollars per 1000 ㎥ (market price about 400 dollars; 67%)
- >Top 2013/11/21: Russian direct intervention.
- against 'Euro-maidan', calling for integration into Europe.
- clash between demonstrators and suppression forces.
- 2014/1: violet action of neo-Nazi group (Svaboda) and ultra-right party (the Right Sector); Azov regiment.
- Ukraine congress resolved to dismiss President Yanukovych (though it has no authority to dismiss)
- President Yanukovych fled to Russia.
- >Top 2014/3/16: Referendum at Crimea Peninsula.
- proclaimed independence from Ukraine; the Autonomous Republic of Crimea, and the Sevastopol Special City; signed with Russia on March 18.
- >Top Donetsk People's Republic (DNR), and Lugansk People's Republic (LNR):
- battle with Ukrainian troops; Ukrainian troops swelled from 120K to 200K.
- Russia dispatched volunteers to the Donpas region.
- Also, Russia deploys tens of thousands of Russian troops along the border.
- 2014/9/5 Minsk Protocol (1st)
- then 2015/2/12 2nd Minsk Protocol (mediated by France and Germany).
- 2022/2/21: Putin approved the independence of DNR and LNR.
- Ukraine could to join NATO as long as the war situation continues. Russia's goal seems to continue the war situation rather than win the war.
- Military balance:
- Russian troops are actually 900K (of which 250K are 12-month conscript; the combat missions operated by 200K officers plus 400K volunteers.
- while NATO troops counts 3.18M.
- 2022/2/24: Russian troops invaded Ukraine from three sides:
- Russia calls this the special military operation.
- >Top Russia's intervention in Syria:
- ME is not Russia's sphere of influence area
- from mid 2000s, Russia started to strengthen relations with ME, and also involved in Iran's nuclear development issue.
- from 2010s, Russia started to intervene in Syria.
- Purpose:
- Western Europe secures concessions since the colonial age.
- US secures oil concession and maintains hegemony in ME.
- Russia's ME policy:
- During the Soviet age, CENTO (Central Treaty Organization; 1959-1979) was organized against USSR.
- Russia's strategy seems to take non-idealistic actions in ME without solid strategy.
- Russia needs not to pursue further oil resources; Russia's energy self-sufficiency rate is 184%.
- Relationship between interventions in Syria and in Ukraine:
- which may function as a leverage against US.
- retreat of US direct involvement; but Russia could not substitute for the function of US in ME.
- destabilization of ME countries.; the value of stabilization through Russian intervention.
- Russia and Iran:
- 2016: temporal use of airbase; Russia
bombed western Syria from Hamadan airbase in Iran.
- Russia and Turkey:
- 2015/11: Turkish army shot down Russian military aircraft.
- 2016: both countries rapidly repaired the relationship.
4. ロシアの'勢力圏'とウクライナ危機:
- 1991: ウクライナ、ソ連から独立
- 2004/5: 東欧8ヶ国EU加盟
- 2007: ルーマニア、ブルガリアEU加盟
- ウクライナ: 600K ㎢、52M人、ソ連内での指折りの重工業地帯と農業地帯
- 狭間の国々 (In-Betweens): ベラルーシ、ウクライナ、モルドヴァ、グルジア、アゼルバイジャン、アルメニア
- これら6ヶ国 (963K ㎢) の中でウクライナは約60%、人口は63%
- ウクライナは、ロシア勢力圏内に留めるための本丸
- カザフスタンは、2.72M㎢、人口1.8M人だが、主はイスラム教徒
- ロシア、ベラルーシ (208K ㎢、 9.5M人)、ウクライナの言語・宗教・文化の共通性は大きい; ="ほとんど我々"
- 猫 (кот; ウクライナ語ではkit); なおロシア語で китは鯨 <'ロシア併合で猫も鯨から猫に戻れた。'
- 独立からオレンジ革命:
- ロシアの天然ガスパイプライン; 数分の1の価格で提供
- ウクライナは、パイプラインの通行料収入
- 工業製品、農産物をロシアへ輸出
- ヒト・モノ・カネの活発な往来
- 軍需品生産、ロシアとのサプライチェーン
- 2004: 大統領選挙
- ヤヌコーヴィッチ候補 (親露派)vs.ユシチェンコ候補 (親西欧派);
- 11月の選挙ではヤヌコーヴィッチ当選→最高裁で再選挙
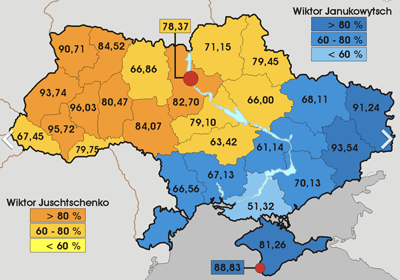
- ユシチェンコ当選 (オレンジ革命)し、NATO加盟、EEP (ロシア主導の共通経済空間)離脱主張。
- 2008/8 グルジア戦争後は、ユシチェンコ政権は内部対立
- 2010: 選挙; ヤヌコヴィッチ当選
- NATO加盟申請取り下げ、セヴァストーポリ基地の租借期限25年間延長
- 2012: プーチンにユーラシア経済連合(EEU)構想:
- ロシア、カザフスタン、ベラルーシの関税同盟を基礎としてEEU構想
- ソ連の再建ではなく、supernationalな連合体構想
- EU側の政策: ENP (European Neighbourhood Policy):
- 旧ソ連6カ国はEaP (Eastern Partnership); 包括的な自由貿易圏 (DCFTA); 'EUにとって安全にする'
- ロシアとEUとの中間オプションの排除
- 相手国の政治・経済・通商・人権についての政策転換の確約
- EUとの関税一部免除、財政・技術的支援
- ヤヌコーヴィッチ政権へのロシアの攻勢
- ウクライナ債の購入
- 天然ガス値引き 400→268.5ドル/1000㎥
- ロシアの直接介入
- 2013/11/21: ユーロマイダン; 欧州への統合を求めるデモ
- ネオナチ集団 (スヴァボーダ)、極右政党 (右派セクター)、アゾフ大隊などの行動隊の暴力的行動
- 2014/1: デモ隊と鎮圧部隊の衝突。
- ヤヌコーヴィッチ大統領解任決議 (本来は解任権限はない)
- ヤヌコーヴィッチ大統領は、ロシアへ逃亡
- クリミア自治共和国とセヴァストーポリ特別市は、クリミア共和国としてウクライナから独立。
- 2014/3/16に住民投票実施、3/18にロシアへの編入条約調印
- ドネツク人民共和国 (DNR)、ルガンスク人民共和 (LNR)
- ウクライナ軍との戦い; ウクライナ軍は12万→20万に増強
- ロシアは、ドンパス地域に義勇兵を派遣。
- ロシアは、国境沿いに、数万人規模のロシア軍を展開
- 2014/9: 第1次ミンスク協定
- 2015/2: 第2次ミンスク協定
- 2022/2/21: プーチンはDNRとLNRの独立を承認
- 戦争状況が継続すれば、当面はNATO加盟は不可能。
- 戦争に勝利することより、戦争状況を継続させることがロシアの目標
- 軍事バランス
- ロシア軍は実質90万 (内、25万は12ヶ月の徴兵; 戦闘任務は、将校20万+志願兵40万) vs. NATO軍は318万
- 2022/2/24: ロシア軍、三方よりウクライナ侵攻
- ロシアは、特別軍事作戦と呼ぶ。
- ロシアのシリアへの介入:
- 中東は、ロシアの影響圏ではない。
- 2000年代半ばから中東との関係強化に踏み出す。
- イランの核開発問題にも関与
- 2010代から、シリアへの介入に踏み切る。
- 目的:
- 西欧は、植民地時代以来の利権確保
- 米国は、石油確保と中東の覇権維持
- ロシアの中東政策
- ソ連時代は、CENTOでの対ソ包囲への対抗
- 非イデオロギー的・即物的
- 確たる戦略がない中東戦略
- ロシアのエネルギー自給率 184%
- シリアへの介入とウクライナへの介入の関係性
- 対米レバレッジ;
- 米国の直接関与の後退; 但し、米国に変わる存在ではない。
- 中東諸国の不安定化; ロシアの介入による安定化の価値
- ロシアとイランとの関係
- 2016 ロシア、イランのハマダーン空軍基地から発信して、シリア西部を爆撃
- ロシアとトルコとの関係
- 2015/11: トルコ軍によるロシア軍機撃墜事件
- 2016: 関係修復
>Top 5. Quadrangle relationship over the Northern Territories:
- Kuril Islands (Курильские острова) over 20 islands to Kamchatka Peninsula (Полуостров Камчатка)
- End period of World War II:
- by 1945/9/1: Occupation of three islands of Itrup, Kunashir, and Shitan.
- 1945/9/5: Occupation of Habomai Islands
- 1951: San Francisco Peace Treaty, Article-2, Pargraph-c; does not indicate 'to whom' the abandonment of the for norther island.
- then USSR insisted to insert the word of 'Soviet full sovereignty' in the paragraph-c; after all, USSR did not sign the treaty.
- 1956: Japan-USSR Joint Declaration, Article-9:
- 'After the conclusion of the peace treaty, Habomai and Shitan are handed over to Japan; the treatment of Itrup and Kunashir Islands remains ambiguous.
- 'both will agree to continue negotiations of the conclusion of a peace treaty including territorial disputes' (Letter of Matsumoto and Gromyko)
- 1991: Confirmation that the four norther islands are in dispute' (Gorbachev-Kaifu Japan-USSR Joint Statement)
- 1993: Declaration of Yeltsin-Hosokawa
- 1997: Declaration of Yeltsin-Hashimoto
- 2001: Statement of Putin-Mori
- thereafter: 'Peace treaty without preconditions'
- Abe suggested by Putin; inclined to substantial two-island negotiation.
- 2018/11/14: Putin-Abe talks:
- Putin mentions that 'USSR-Japan Joint Declaration does not specify the grounds for delivery or sovereign issue.' (Venice's merchant-like negotiation)
- 2019/1: Japan-Russia Foreign Ministers' Meeting:
- Foreign minister Lavrov mentions that the islands became Russian territory as a result of WWII.
- Recently, deterioration of US-Russia relations over the last a few years affects negative impact in Japan-Russia negotiations.
- Every September: Eastern Economic Forum at Vladivostok 2018:
- Putin proposed that earlier conclusion a Peace Treaty without preconditions.
- >Top Japan as a semi-sovereign state:
- Possibility of establishing a US military base in the norther territories after returning to Japan.
- Under the Japan-US Security treaty, US is entitled to set up military gases within Japanese territory by US notification.
- 2016/11: the same question to Taniuchi, Director National Security Bureau.
- 1983: release of the confidential documents of US-Japan Status of Forces Agreement (Ryukyu Newspaper disclosed the document in 2004)
- which states 'it is problematic considering the terms of the Security Treaty and Status of Forces Agreement to make a legal obligation with USSR to confirm not to establish facilities or areas in the northern territories after the returning to Japan.'
- There is still a possibility of a proposal to separate the administration and sovereignty; confirmation of freedom to travel and economic activities in the islands, subject to the Russian law (not covered by US-Japan Security Treaty)
- The difference of Russia's perspective and Japan's perspective.
- >Top Military presence in Far East:
- Russia 80K (total 900K); China 2,000K; North Korea 1,000K; South Korea 500K; Japan 240K
- Russia deployed SSBN (Submarine Ballistic missile Nuclear powered) on the Kamchatka Peninsula; a nuclear Bastion.
- Russian Far Eastern Federal District:
- area 6.95M ㎢, 6.2M population (decreased from 8M in USSR age)
- while Northeast China: lives 100M people; so-called Population pressure.
- 1968: Canadian premier Trudeau said; ' Canada is like sleeping next to an elephant.'; Russia's view of China would be the same. 'keep the neighbors as they are and don't make them enemies.'
- Russia's largest trading partner; Germany and Netherlands used to be; but in recent years China has been the top partner.
- 2018: Russia-China trade dollar 100B; actually Chinese money supports Russian energy industry under Western sanctions.
- The authoritarian system is indispensable to govern unstable and huge nation. Easy democratization may lead to the collapse of the nation. The attitude of US looks interference with domestic affairs.
- Russian reacts restraint to China's Belt and Roda Initiative.
- China does not cause a color revolution.
- 2015: Putin-Xi Meeting; confirmed coordinating Russian Eurasian Union Project and Chinese Belt and Road Initiative.
- Since the national interests between Russia and China are far apart, mutual deepening in sensitive issues tend to be avoided.
- The length of national border is about 4,000 km (Cf. 7,000 km with Kazakhstan); where USSR had 50 military divisions even in peacetime.
- Russia and China cannot be an alliance, nor an hostile relationship.
- however, China's supply of arms to the influential countries jeopardizes Russia's sole position as the arms supplier.
- >Top Belarus position:
- a member of CSTO (Collective Security Treaty), which advocates a neutral nation because of caution with the three Baltic countries and Poland; also is reluctant to conduct military exercises.
- China's advance into former Soviet countries as a successor and trader of military technology heritage during the Soviet age.
5. 北方領土をめぐる日米中露の四角形:
- 千島列島: カムチャッカ半島までの20余の島々
- 第二次世界大戦末期:
- 1945/9/1までに: 択捉、国後、色丹3島占領
- 1945/9/5には、歯舞諸島占領
- 1951: サンフランシスコ講和条約第2条c項
- 北方4島の'誰に対する'放棄か明示なし
- ソ連はc 項に'ソ連の完全な主権'の文言主張→結局、条約に調印せず。
- 1956: 日ソ共同宣言第9条:
- 平和条約締結後に、歯舞、色丹を引き渡す。国後、択捉島の扱いは玉虫色
- '領土問題を含む平和条約締結に関する交渉を継続することに同意' (松本・グロムイコ書簡)
- 1991: 北方4島が係争地であることの確認' (ゴルバチョフ・海部日ソ共同声明
- 1993: エリツィン・細川宣言、1997: エリツィン・橋本宣言、2001: プーチン・森声明
- その後: '前提条件なしの平和条約締結'; 実質二島論
- 2018/11/14: プーチン・安倍会談; '日ソ共同宣言では、引き渡しの根拠や主権が明記されていない' (ベニスの商人的交渉)
- 2019/1: 日露外相会談; ラブロフ外相 '第二次大戦の結果としてロシア領となった。'
- 過去数年間の米ロ関係の悪化は、日ロ交渉の制約要因
- 毎年9月; 東方経済フォーラム@ウラジオストク
- 2018: プーチン提案 '前提条件なしに平和条約締結を'
- 半主権国家としての日本
- 返還後の北方領土に、米軍基地が設置される可能性
- 日米安保条約では、米国は通告によって日本の領域内に軍事基地を設定できる
- 2016/11 谷内国家安全保障局長に対しても同様質問
- 1983 日米地位協定の機密文書公開 (2004 琉球新報社)
'返還後の北方領土には施設・区域を設けないとの法的義務をソ連側と約することは、安保条約・地位協定上問題がある'、との注が記載。
- 施政権と主権の分離提案の可能性あり。渡航・経済活動自由、但し、ロシア法適用 (安保の適用外)
- ロシアの面的な視点、日本の点的な視点
- 極東における軍事力展開:
- ロシア80K (計: 900K)、中国2,000K、北朝鮮 1,000K;韓国500K、日本240K
- カムチャッカ半島に、SSBN (Submarine Ballistic missile Nuclear powered)を配備; 核要塞
- ロシアの極東連邦管区:
- 面積 6.95M ㎢、6.2M人 (ソ連時代は8M) 人口減少
- 中国東北部: 100M人; 人口圧力
- 1968: カナダは、'象の隣で眠るようなもの' (トルドー); ロシアの中国観も同様。隣人をそのまま留め、敵にしないこと。
- ロシアの最大貿易相手国: 従来はドイツ・オランダだったが、ここ数年は中国がトップ
- 2018: 中ロ貿易 100Bドル; 西側の制裁下で中国マネーはロシアのエネルギー産業を支えている。
- 権威主義体制は、不安定で巨大な国家を統治する上で不可欠な政体。安易な民主化は国家の崩壊を招く。米国の姿勢は、内政干渉。
- ロシアは、中国の一帯一路構想には抑制的反応
- 中国は、カラー革命を起こさない。
- 2015: プーティン・習会談: ロシアのユーラシア連合プロジェクトと一帯一路との連携させる。
- 中ロ間の国益の所在が離れているので、相互深入りは避ける傾向;
- 中ロ国境の長さは4,000km (カザフスタンとは7,000km); ソ連は、平時でも50個師団 (1-2万)を展開
- 中ロは、' 同盟にはなれないが敵にもならない'
- 但し、中国の武器供与によって、ロシアが唯一の武器供与国としての立場が危うくなる。
- ベラルーシは、ポーランド・バルト三国との警戒から、中立国家を標榜 (憲法第18上)
- CSTO (Collective Security Treaty)加盟国だが、軍事演習には消極的。
- 中国による旧ソ連諸国への進出; ソ連時代の軍事技術遺産の継承・貿易。
>Top 6. New geopolitical front - the Arctic:
- Geography: 1/5 of Russian territory belongs to the Arctic Circle:
- >Map of the Arctic >Fig.
- the Arctic circle is defines northern latitude more than N66.33.
- Geographical value of the Arctic circle: by Norwegian National Institute for Defense Studies.
- Arctic strategic significance:
- Discovery and exploration
- Scientific progress
- Confrontation and conflict
- Climate change
- >Top Key geography:
- GIUK (Greenland, Iceland, and UK) gap
- Russia's Presek Space Station (800km north of Moscow)
- Russia's Vostochny Cosmodrome (Amur)
- NSR (Norther Sea Route); Russia could become the center of global trade routes.
- 2013 Russia's Arctic Strategy:
- Cooperation and conflict in the Arctic region.
- Resource development (Arctic ocean shelf)
- Year-0round use of NSR, including connection to rivers, railroads and air networks.
- Nuclear icebreakers
- Strengthening border security
- >Top Military aspects of the Arctic:
- State Armament 10-year Plans (GPVs) 2018-2027
- Four contrites other than Russia are NATO member countries.
- Reduction of ice caps due to global warming; enables to use conventional weapons and vessels.
- Expanding the scope of operations in the Arctic.
- Improvement of A2 (Anti-access; prevent to enter into the area) and AD (Area Denial; prevent military operation in the area) capacity.
- Modernization of SSBN; will expand Northern Fleet (1→4) and Pacific Fleet (2→4)
- >Top Sweden and Finland approach NATO:
- change of the Nordic military balance
- US sanction (CAASTSA, Countering America's Adversaries Through Sanction Act)
- Significance of the Arctic to Russia:
- Awareness of great economic value as well as military threats.
- A mixture of cooperation aspects (economic and environmental), and contradictory aspects (political and security)
- the strategic importance of the Arctic Ocean (as well as Okhotsk)
- maintenance of retaliatory nuclear attack capabilities.
6. 新たな地政学的正面-北極:
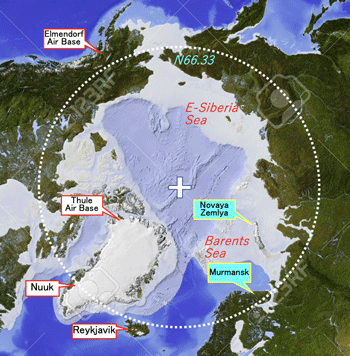
- ロシアの3.1M ㎢は北極圏に属する(1/5)
- 北極圏の地理的価値: ノルウェー防衛研究所
- 北極の戦略的意義
- 発見・探検
- 科学の進歩
- 対立・紛争
- 気候変動
- 地理的特徴:
- GIUKギャップ
- プレセツク宇宙基地: (モスクワの北方800 km)
- ボストチヌイ宇宙基地; (アムール州)
- 北極海航路 (NSR=Northen Sea Route): ロシアが世界的な通商ルートの中心になる可能性
- 2013 ロシアの北極戦略:
- 北極における協調と対立
- 資源開発 (北極海大陸棚)
- NSRの通年利用; 河川・鉄道・航空網との接続
- 原子力砕氷船
- 国境警備の強化
- 北極海の軍事的側面:
- 国家装備プログラム; GPV (2018-2027)
- ロシア以外の4ヶ国はNATO加盟国
- 地球温暖化により冠氷の減少で、通常型兵器の利用が可能
- 北極圏での作戦範囲の拡大
- A2 (Anti-Access)・AD (Area Denial)能力向上
- SSBNの近代化; 現在は北極艦隊1、太平洋艦隊2を各4隻に拡大
- SwedenとFinlandのNATOへの接近; ノルディックバランスの変化
- 米国の制裁 (CAASTSA=Countering America's Adversaries Through Sanctions Act)
- ロシアにとっての北極圏の重要性
- 大きな経済的価値と軍事的脅威の認識。
- 協力の側面(経済と環境)と対立する側面(政治と安全)の混合
- 北極海 (およびオホーツク)の戦略的重要性: 報復核攻撃能力の維持。
>Top 7. Russian related words:
- агитпункт: agitating point
- арктика: Arctic
- азчефть: <Азербайджан <нефть, oil
- акула: shark
- алмаз: diamond
- берёза: birch
- вепрь: Vepr, wild boar
- гепард: <G. Gepard, cheetah
- гопник; гопница; гопота: subculture <гоп–стоп
- гривна: unit of medieval Russina currency <necklace
- жигули: massif; mountaineous area
- заслон: barrier
- зенит: zenith
- калина: Carina; guelder rose
- КГБ, KGB: Комитет Государственной безопасности СССР
- кинжал: dagger; htpersupersonic missile
- коммиссар: commissioner
- Комсомолец Украины: Ukraine comsomol
- кремль: castle
- курил: Курильские острова, Kuril islands <cf. krill
- ласточка: swallow
- наука: science
- новичок: novice, beginner; >nerve gas
7. Russian related words::
- медбедь: bear
- мочить в сортире: kill at the loo.
- охотник: hunter
- открытое акционерное общестово, ОАО; public company
- острог: jail
- перестройка: perestroika
- погром: chaos
- публичное акционерное общестово, PAO; public company
- путь: way, path, track
- самиздат; samizdat, undergroud press
- салют: salyut, fireworks
- силовики: from KGB staff <сила, force
- стрела: аrrow
- точка: point
- цапфир: sapphire
- цариам: Czarism
- царебич; царевна: prince; princess
- шторм; <G. Sturm, storm
- янтарь: amber
Comment
- I think substantial part of the author's sources is based on information written in Russian language.
- In order to understand present international situation, Russian and Chinese are important along with English.
- From this decisive year when Ukraine crisis occurred, NHK will terminate TV language course in Russian, one of US official languages; this decision means to enforce us to close one eye to observe correctly what happens in the multi-polar world.
- 著者の情報源の相当部分は、ロシア語の情報収集が元になっていると思う。
- これからの国際情勢を理解するには、英語と並んでロシア語・中国語が重要になる。
- ウクライナ危機が生じているこの年から、NHKでは国連公用語の一つであるロシア語のTV語学講座を中止するという。この決定は、多極世界が起こっていることを理解するために、片目を閉じろを言うようなものである
 |
'Imperial' Russian Geopolitics |
Cat: HIS |
Yu Kozizumi (小泉 悠) |
22306u |
Titile |
'Imperial' Russian Geopolitics |
「帝国」ロシアの地政学 |
|---|---|---|
Index |
||
Tag |
; 2004 Presidential election; Baltic states; Belarus; CAASTSA; Color revolution; Crimea; CSTO; DNR; EaP; EEP; EEU; Far East; Geopolitics; Georgia; Georgy's ribbon; GPV; Inbetweens; LNR; Minsk protocol; NATO; Nuclear bastion; Orange revolution; R2P; Semi-sovereign; Sphere of influence; SSBN; Svaboda; Syria; Valdai; Vostochny; | |
Résume |
Remarks |
>Top 0. Introduction:
| 0. 序文:
|
>Top 1. How far is 'Russia?::
| 1. ロシアとはどこまでか:
|
>Top 2. 'Soverignty' and 'Sphere of Influence:
|
2. '主権'と'勢力圏':
|
>Top 3. Landscape of 'the Occupation':
|
3. '占領'の風景:
|
>Top 4. Russia's 'Sphere of Influence' and Ukraine crisis:
|
4. ロシアの'勢力圏'とウクライナ危機:
|
>Top 5. Quadrangle relationship over the Northern Territories:
|
5. 北方領土をめぐる日米中露の四角形:
|
>Top 6. New geopolitical front - the Arctic:
|
6. 新たな地政学的正面-北極:
|
>Top 7. Russian related words:
|
7. Russian related words::
|
Comment |
|
|