>Top 1. Those are all prepared by 19C:
- Basic Three-piece set prepared in 19C:
- Nation state, Corporation, and the Central Bank.
- established by the first 19C in western Europe.
- Japan is the earliest establishment of this three-piece set. (only 30-40 years after the western Europe
- Prologue to the modern age:
- Age of discovery:
- 1492: Christopher Columbus; reached the Caribbean Sea.
- 1497: Vasco da Gama: reached India via Cape of Good Hope
- made Westerb Europe and Asia into a single market (passing through the Islamic world)
- >Top Historical GDP: (>Fig.):
- a
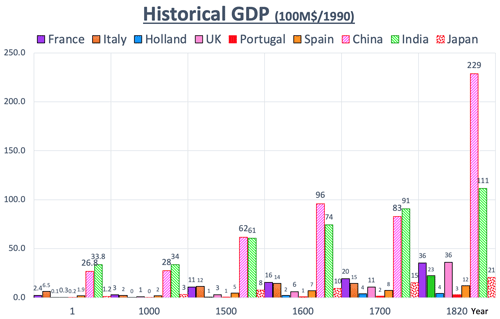
- Huge economic zone of Ming dynasty and Mughal empire;
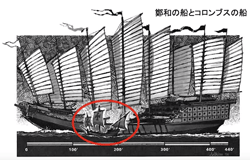
- >Top 1405-33: Zhèng Hé's (1371-1434) Grand Fleet: 7 times voyages.
- if Western European ships were encountered, there would be no oriental trade.
- Zhèng Hé's Bǎo Chúan; displacement 10 ,000 tons (no keel)
- Columbus's La Pinta vessel; displacement 80 tons
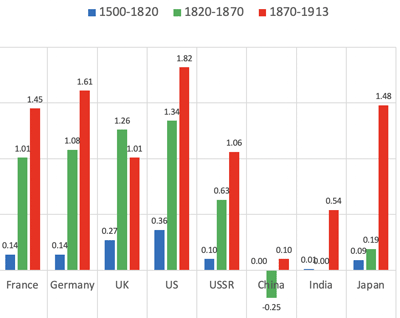
- Japan's GDP in 1500 almost equals UK+Spain+Portugal.
- per capita GDP is almost same between Wester Europe and Asia.
- In Italian middle ages, there were no tyrannical monarchs.
- , which was a cause of existence of City-State.
- British and French kingships were also limited,
- , which enabled growth of GDP per capita.
- Netherlands; woolen industry in the autonomous city was developed since 1000.
- Birth of civil property and ownership.
- as the birth of resistance to arbitrary tax collection rights.
- self-defense against the royal family of landowners.|
→16C: primary enclosure movement
- Netherlands is the factory and UK is the hinterland.
- In 17C, UK became prosperous by industry and trading.|
Navigation Act →Anglo-Dutch war.
- Netherlands was no longer a military power for Japan.
- >Top Formation of Nation-State:
- 16C was the century of prosperity in Western Europe, while 17C was a mini Ice Age.
- In Europe: 30-year War, Religious War, and plague pandemic caused declining population.
- Decline of Germany, while rise of France
- Migration to US; settles as Puritan self-employed farmers
- Second Anglo-Dutch War (1665-67); renamed to NY.
- 18C Japan: pollution stagnated, but literacy rate improved.
- Long 18C Europe: →Pax Britannica
- Anglo-French Hundred Years War (1685-1815)
- UK-French was almost draw; Austria Succession war, Spain Succession War.
- Seven Years' War (1754-63): UK+Proissen vs. France+Spain+Russian+Sweden;
- North America: UK overwhelmed the war; French and Indian War
- Southern India: Carnatic Wars; UK's Madras (now Chennai) vs. French Pondicherry
- the idea of Nation-State:
- Thomas Hobbs, 1588-1679: 'Social Contract"; Leviathan
- John Rocke, 1632-1704: 'Two Treatises of Government'; launched liberalism, separating the realms of Church and State.
- three greatest men: Bacon, Locke and Newton
- limitation of royal power; parliamentary democracy
- Adam Smith, 1723-90; liberal economics.
- Divine right of kings vs. tradition since Magna Carta
- Enlightened absolutists; appeared around UK and France.
- Austria; Maria Teresia 1740-80
- Prussia; Friedrich II 1740-86
- Russian; Екатерина (Catherine) II 1762-96
- After the French Revolution, the enlightened absolutists planned counter revolution.
- >Top Rise of Corporations:
- 17C Venice merchants: trade in Easter Mediterranean Sea.
- risk diversification of trade vessel by groups
- profit and loss settlement of each trade vessel
- General partnership: unlimited liability partnership
- difficult to assign freely
- Limited corporation:
- limited responsibility within the investment.
- 1602 Netherlands; East India Company; long distance voyage company
- by large dedicated sailing vessel; around the Cape of Good Hope to India
- stock exchange established; starting stock trade
- 1600 UK; East India Company; →1657 became limited responsibility organization.
- 18C the Industrial Revolution:
- developed light industries such as Jenny spinning machine; hydraulic spinning machine
- big capitals are not needed to invest light industries.
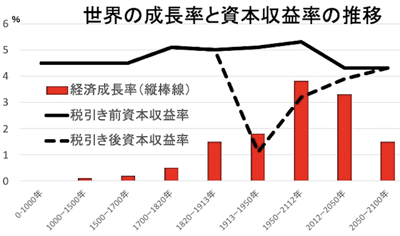
- 19C Economic development:
- mindset from 'uneasy wariness' to 'bold challenge'
- some failures can be covered by the growth trend.
- developed big industries such as railway transportation and steel manufacturing.
- large capital, and function of banks; promoted by the principle of limited responsibility.
- since 1930, the boom of railway construction mostly in US and Europe.
- Stock corporations law established;
- from particular license system to normative system (granted juridical personality without permission from the authority if it meets certain requirements set forth in the law.)
- 1856 UK Corporation Law; adopted normative system
- 1903 US Delaware state corporation; there was moral antipathy to the limited companies due to influence of Protestantism.
- 1930s: shareholder's double liability was abolished.
- Japan in Meiji era:
- 1866 Yukichi Fukuzawa's "Wester Circumstances"
- then best selling book of 200k copies
- introduced theory of merchant companies, including stock companies and bill payments.
- In Japan, there was no binding of Christian moral law.
- 1872 National Bank law;
- established private banks under license from the government.
- payment of capital in the form of government bonds distributed in lieu of feudal stipends.
- Railway companies:
- 1881 Japan Railway Co. established, then, Sanyo Railway Co., and Kyushu Railway Co. were established.
- No. 15 National Bank was established, supporting railway construction
- 1899; Normative system in establishing companies.
- 1906; Railway companies were nationalized after Japanese-Russo War (1904-05).
- >Top Central Bank:
- 1716: France, established Royal Bank
- issued banknotes convertible to gold.
- BS is:
(Asset) Purchaser's loan of the G-bond | (Debt) Royal banknotes
- but in 1720, the convertible note became inconvertible.
- 1803 France; sold French Louisiana to US at $15M (equivalent 24t of Au)
- 1694 UK, England Bank
- originally loan to the UK government £1.2M (equivalent 8.4t of Au);
in return for the loan, England Bank issued transferable certificate (3% pa);
which eventually evolved into an indefinite, interest-free banknote.
- 1697 England bank issued banknote as the limited corporation.
- 1821 returned to gold convertible banknote
- 1844 Robert Peel Act of 1844 (Bank Law); monopolized issuance of the banknotes.
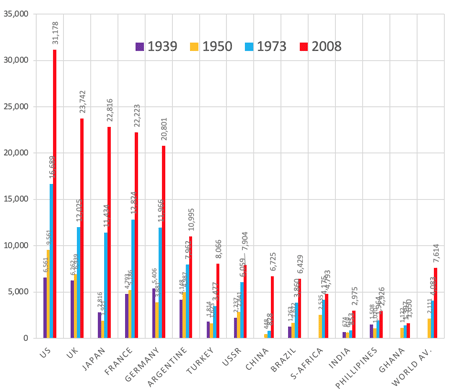
- 1869-94 William Gladstone, PM of UK, issued G-bond for Napoleon war (2.6 times GDP)→could decrease this debt to 1/4 by beginning of 20C.
- Meiji-Japan:
- 1871 New money act after the Meiji Resolution:
- 1 Ryo =4 Bu =16 Shu denominated into 1 yen (aiming gold standard equivalent 1.5g of Au)
- 1878: Gold and Silver combined standard system
- 1877: South-West War (Satsuma rebellion)→1881 political change by Matsukata finance.
- 1885: issued convertible banknote (Silver standard plus exchange management)
- 1897: New Currency Act, after the Sino-Japanese War (1894-95); returned Gold standard (1 yen=0.75g Au).
|
1.
それらは19Cに出揃った:
- 現代の政治・経済の基本的な形: 3点セット
- 国民国家、株式会社、中央銀行
- 19C前半の西欧で確立
- 西欧以外では、日本が最速で成立 (30-40年遅れ)
- 近代へのプロローグ:
- 大航海時代
- 1492: Cristopher Columbus: カリブ海域に到達
- 1497: Basco da Gama: 喜望峰経由インドへ到達
- 西欧とアジアを単一の経済圏に
(イスラム圏を通過せずに)
- 近代までのGDPの変遷:
- 1405-33: 鄭和の大艦隊
- もし西欧の海鮮が遭遇していたら東洋貿易はなかった。
- 鄭和の宝船, 排水量10,000t
- コロンブス La Pinta号: 排水量 80 ton
- 日本のGDP/1500=英+スペイン+ポルトガル合計
- 一人あたりのGDPは、アジアと西欧でほぼ同じ
- 中世のイタリア: 専制的領主なし
→都市国家の反映の源
- 英仏の王権も限定的
→一人当たりGDPの成長可能
- 蘭の自治都市: 毛織物産業 (1000-)
- 市民的財産権・所有権の誕生:
- まだ恣意的徴税権への対抗力の誕生
- 地主的貴族の王家に対する自衛権
→16C: 第一次囲い込み運動
- 蘭が工場で、英国が後背地
- 17Cには、英国が産業と交易で興隆
→航海条例→英蘭戦争
- 日本にとっての蘭は、軍事強国でなくなったことは幸い
- 国民国家の形成:
- 16Cは、西欧繁栄の世紀; 17Cは小氷河期
- 欧州: 30年戦争・宗教戦争・ペスト大流行・人口減少
- 独の衰退、仏の強大化
- 米への移動 (自営農民としての入植者; 清教徒)
- 第二次英蘭戦争 (1665-67); NYへ改名
- 中国: 明王朝→清へ交代
- 18C日本; 人口停滞、識字率向上
- 18C欧州; 英仏引き分け; Austria継承戦争; Spain継承戦争
- 18C北米; 英の圧勝; French & Indian戦争
- 18Cインド; 英の勝利 Carnatic戦争
- 国民国家の思想:
- Thomas Hobbs 1588-1679; 社会契約説
- John Rock 1632-1704; 王権の制限・議会制民主主義
- Adam Smith 1723-90; 自由主義経済学
- 仏の王権神授説 vs. Magna Cartaの伝統
- 啓蒙専制君主:
欧州周辺に登場 (英仏以外)
- Austria; Maria Teresia 1740-80
- Prussia; Friedrich II 1740-86
- Russian; Екатерина II 1762-96
- 仏革命後は、啓蒙専制君主も反革命を画策
- 株式会社の勃興:
- 17C ベニスの商人; 東地中海貿易
- Groupによる貿易船のリスク分散
- 貿易船毎の損得精算方式
- 合名会社; 無限責任のPartnership
- 有限会社: 責任を出資金の範囲に限定
- 1602 蘭, 東インド会社; 遠距離航海会社
- 大型の専用帆船; 喜望峰回りのインド洋海域
- 証券取引所設立; 株式売買開始
- 1600 英, 東インド会社→1657 有限責任組織
- 18C, 産業革命
- Jenny紡績機、水力紡績機; 軽工業中心
- 大資本はまだ不必要
- 19C, 経済成長
- "不安な警戒心"→"大胆な挑戦心"
- 多少の失敗は、成長が癒やしてくれる
- 鉄道業や鉄鋼業勃興
- 巨大資本必要; 銀行の役割; 有限会社原理
- 1930以降; 欧米での鉄道ブーム
- 株式会社法
- 免許主義→準則主義へ
- 1856 英国会社法制; 準則主義へ移行
- 1903 米国Delaware州会社法制定 (米国Protenstantの精神風土の影響による有限会社への道徳的反感)
- 明治日本:
- 1866 福沢諭吉 "西洋事情"; 20万部発行
- 株式会社や手形制度の紹介; 商人会社論
- 日本には、キリスト教的道徳律の縛りなし
- 1872 国立銀行条例 (国の免許による民間銀行設立)
- 鉄道会社設立
- 1881; 日本鉄道設立; その後山陽鉄道、九州鉄道
- 第15国立銀行設立; 鉄道建設支援
- 1899; 株式会社設立の準則主義化
- 1906 日露戦争後に、鉄道会社の国有化
- 中央銀行:
- 1716 仏, 王立銀行設立;
- 金兌換券発行
- (債権) 国債購入者貸付金 | (負債) 王立銀行券
- 1803 仏領Lousianaを米国に売却 15Mドル(Au 24t)
- 1694 英国 Engliland銀行
- 政府への貸付 £1.2M (Au 8.4t)
- 貸付の見返り; 譲渡可能捺印手形 3%pa
→無期限・無利子の銀行券へ進化
- 1697 株式会社組織での銀行券発行
- 1821 金兌換再開
- 1844 Robert Peel銀行条例; 銀行券の独占発行権
- William Gradstone首相;
Napoleon戦争の戦費の公債発行; GDPの2.6倍
→20C初には1/4にまで減少
- 明治日本:
- 1871 新貨条例:
- 1両=4分=16朱→1円=Au 1.5g (金本位制志向)
- 1878: 金銀貨併用制
- 1877: 西南戦争→1881 明治14年政変 松方財政
- 1885: 兌換銀行券発行 (銀本位制+為替管理)
- 1897: 新貨条例, 日清戦争後; 1円=Au 0.75g 金本位制
|