Magic Quadrant for Low Code Application
Cat: ICT
Pub: 2021
#: 2106b
Gartner
21313u/22817r
Title
Magic Quadrant for Low Code Application
ローコードアプリ4象限評価
Index
- Comment:
- Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Low-Code Application Platforms:
- AgilePoint:
- Appian:
- AuraQuantic:
- Betty Blocks:
- Creatio:
- Kintone:
- Mendix:
- Microsoft:
- Newgen:
- Oracle (APEX):
- Oracle (Visual Builder):
- OutSystems:
- Pega:
- Pront Forms:
- Quick Base:
- Salesforce:
- ServiceNow:
- TrackVia:
- Zoho:
- Vendors Added and Dropped:
- Glossary:
Résumé
Remarks
>Top 0. Comment:
- Gartner's Quadrant Analysis (2020) well describes competitive situation in the market, that is, who are the present winners and who produce attractive products.
- Low-code development of software has been challengers against high-code developers; but recently large conventional developers are participating in the battle for such advanced software development competition.
- This is probably because the role of software is expanding due to the centennial changes in the market such as IoT and AI, which require comprehensive strength of the developers.
- Careful reading of this quadrant analysis with reference to the keywords below reveals a new low code development market.
0. コメント:
- ガートナーの4象限の分析 (2020)は、市場の競争状況をうまく表している。即ち、誰が現在の勝ち組で、誰が魅力のある製品を作っているかを。
- ソフトウェアのローコード開発は、多コード開発者に対する挑戦者であった。しかし最近、従来の大手がこの先進的なソフトウェア開発競争に参画してきている。
- それはおそらくIoTやAIのような百年に一度の大変化によって、ソフトウェアの役割が拡大し、開発者の総合力が試されてきているからであろう。
- 下記のキーワードを参照しながら、この4象限分析を注意深く読むと、新たなローコード開発の市場が見えてくる。
>Top 1. Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Low-Code Application
Platforms, Gartner, Sept 30, 2020:
- Enterprise low-code application platforms deliver high-productivity and multi function capabilities across central, departmental and citizen IT functions. We evaluate 18 LCAP vendors to help guide you to the appropriate platforms for your needs.
- Strategic Planning Assumption:
- By 2023, over 50% of medium to large enterprises will have adopted an LCAP as one of their strategic application platforms.
- Market definition/Description:
- IT leaders are facing mounting challenges around application delivery. Developer shortages and skill-set challenges are impacting their ability to deliver increasing levels of business automation in a rapid and reliable fashion. In response, the vendors of low-code application platforms (LCAPs) have been improving the ease at which business applications can be delivered, providing broader capabilities requiring smaller and less specialized teams of developers.
- An LCAP is characterized by its use of model-driven* or visual development paradigms supported by expression languages and possibly scripting to address use cases such as citizen development, business unit IT, enterprise business processes, composable* applications and even SaaS applications. These platforms are offered by vendors that may be better known for their SaaS offerings, or their business process management (BPM) capabilities, as well as specialist vendors for rapid application development. The primary goal is increased application development productivity with reduced skill-set requirements for developers.
- Gartner formally defines an application platform as “a product or suite of products that offers development, deployment and execution capabilities for any of user experience, business process, business logic, and data.”
- An LCAP is an application platform that supports rapid application development, deployment, execution and management using declarative, high-level programming abstractions such as model-driven and metadata-based programming languages, and one-step deployments. LCAPs provide and support user interfaces (UIs), business processes and data services.
- Note that Gartner defines a no-code application platform as an LCAP that only requires text entry for formulae or simple expressions. The LCAP market therefore includes no-code platforms. Furthermore, “no code” is not a sufficient criterion for tasks like citizen development, as many complex tooling configuration tasks are “no code” but still require specialist skills.
- Magic Quadrant:
- Figure 1. Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Low-Code Application Platforms.
- Vendor Strengths and Cautions
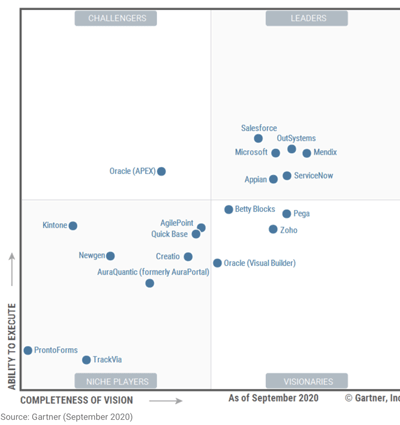
1. 4象限のローコード開発プラットフォーム:
- 企業のローコード・アプリ・プラットフォームは、全社IT部門、各部門、CitizenによるIT開発*において、高い生産性と多機能性を実現する。Gartnerは、LCAPベンダー18社を評価し、ニーズに合った適切なプラットフォームをガイドする。
- 戦略計画の想定:
- 2023年までに、中堅から大企業の50%以上が、戦略的アプリ・プラットフォームの1つとしてLCAPを採用する。
- 市場の定義/説明:
- IT部門のリーダは、アプリの導入(Delivery*)に関して深刻な課題に直面している。開発者不足やスキルセットの課題は、増加するビジネス自動化を迅速かつ信頼性の高い方法で提供する能力に支障をきたしている。これに対し、ローコードアプリ・プラットフォーム (LCAP*) のベンダは、ビジネスアプリの配信を容易にし、より小規模で専門性の低い開発者チームでも 開発できる幅広い機能を提供している。
- LCAPは、Citizen開発、現業部門のIT、全社のビジネスプロセス、Composable* Application、さらにはSaaSアプリなどのユースケース(use case*)に対応するために、表現言語やスクリプトでサポートされたモデル駆動型* またはビジュアル型の開発パラダイムを使用することが特徴。これらのプラットフォームは、SaaSやBPMの機能でよく知られているベンダや、迅速なアプリ開発のための専門ベンダによって提供されている。主な目的は、アプリ開発の生産性を向上させ、開発者のスキルセット要件を軽減することである。
- Gartnerは、アプリ・プラットフォームを"UX*、ビジネス・プロセス、ビジネス・ロジック、データのいずれかの開発、展開、実行機能を提供する製品または製品群"と定義している。
- LCAPは、アプリ・プラットフォームで、迅速アプリ開発、配備、実行、管理を、宣言型や高レベルの抽象化したProgramming、つまりモデル駆動型プログラミング言語* やMeta Database*ベースのプログラミング言語など、宣言型*の高レベルなプログラミング抽象化やOne-step deployments*を使って実施する。LCAPは、UI、ビジネスプロセス、データサービスを提供する。
- なお、Gartnerでは、フォームにテキスト入力のみを必要とするノーコード・アプリ・プラットフォームもLCAPと定義している。したがって、Citizen開発の場合位には、No-Codeは十分な基準ではない。複雑なツールの設定の多くは、No-Codeであっても専門スキルを必要とする。
- 4象限評価: (Fig.1 )
- リーダー: (M=Major Execution; S=Special Vision; )
- Salesforce (M1)
- OutSystems (S2, M2)
- Microsoft (M3)
- Mendix (M3, S1)
- ServiceNow (S3)
- Appian (M5, S4)
>Top 2. AgilePoint:
- AgilePoint is a Niche Player in this Magic Quadrant. Its LCAP product AgilePoint NX (version 7 was assessed here) is broadly focused on process-centric application development. Its operations are geographically diversified and its clients tend to be large and range across multiple sectors, with some emphasis on manufacturing, government and financial services. AgilePoint has added webhooks to allow external systems to subscribe to a wide range of events, eForm options for third parties like Microsoft SharePoint and Office 365, and AI-driven process routing for complex orchestration. Its 2020 roadmap includes distributed LCAP for edge computing, low-code integration of blockchain into existing apps, and further AI-driven application development.
- Strengths:
- Product: AgilePoint’s product offers a drag-and-drop graphical application designer, which includes a full stack of capabilities such as forms, processes, data models, portal pages and customized mobile apps. Additional automation options are available through partnerships with robotic process automation (RPA) vendors such as UiPath and Blue Prism.
- Platform ecosystem: To assist developers, AgilePoint offers prebuilt libraries such as popular process patterns, 70 predefined integrations and 700 process activities. AgilePoint also participates in other vendor ecosystems; it appears, for example, on the Salesforce AppExchange and Microsoft AppSource stores.
- Innovation: AgilePoint eForms provides a cross-platform alternative and replacement for Microsoft InfoPath, simplifying Microsoft data collection for those who don’t want to invest in Power Apps. In addition, it has added AI-driven process flows to provide dynamic workflows, and is starting its journey toward low-code edge computing and support for digital twins and the Internet of Things (IoT).
- Cautions
- Overall viability: AgilePoint is a relatively small and self-funded company with a successful legacy from the BPMS market area, but it will need to further invest in growth and brand recognition to compete against the much larger vendors in the LCAP market.
- Business model: AgilePoint’s participation in the Microsoft and Salesforce ecosystems for some of its business means it can also be competing against those ecosystems’ hosts in the LCAP market. Although AgilePoint adds some differentiation such as process-centric characteristics with these vendors, such advantages will likely reduce over time as these partners add their own business process capabilities.
- Marketing strategy: Although AgilePoint is growing well, and has an appropriate partnering strategy, it has less LCAP market visibility than many other vendors in this Magic Quadrant. While its strategy to extend to the IoT and edge could be successful as a move toward specialization, it also has the potential to compound its Niche Player status. AgilePoint is, however, ramping up its marketing in this area, with broader outreach via social media and direct/indirect partner channels.
2. AgilePoint:
- AgilePointは、この4象限評価ではニッチ・プレーヤーである。同社のLCAP製品であるAgilePoint NX (Version 7)は、プロセス中心のアプリ開発に広く注力している。同社の事業は地理的に分散しており、その顧客は大規模で、製造業、政府、金融サービスに重点を置いた複数のセクターに及ぶ。AgilePointは、外部システムがさまざまなイベントに参加できるようにするWebhooks*、Microsoft SharePointやOffice 365などのサードパーティー向けのeFormオプション、複雑なorchestration*のためのAIによるプロセス・ルーティングを追加した。その2020年のロードマップには、エッジコンピューティングのための分散型LCAP、ブロックチェーンを既存アプリへ組込むためのローコード開発、さらにAI主導のアプリ開発が含まれている。
- 強み:
- 製品: AgilePointの製品は、ドラッグ&ドロップ式のグラフィカルなアプリ・デザイナーを提供しており、フォーム、プロセス、データモデル、ポータルページ、カスタマイズされたモバイルアプリなどフルスタックの機能を備えている。また、UiPathやBlue PrismなどのRPAベンダとの連携により、追加の自動化オプションが利用できる。
- プラットフォーム・エコシステム: 開発者を支援するため、AgilePointは一般的なプロセスパターン、70の定義済統合化、700のプロセスアクティビティなどの構築済のライブラリを提供している。また、Salesforce AppExchangeやMicrosoft AppSourceなどの他ベンダのエコシステムにも参加している。
- イノベーション: AgilePoint eFormsは、Microsoft InfoPathに代わるクロスプラットフォームの代替と置き換えを提供し、Power Appsへの投資を望まない人のためにMicrosoftのデータ収集を簡素化する。さらに、ダイナミックなワークフローを提供するためにAI駆動のプロセスフローを追加し、ローコードのエッジコンピューティングや、Digital TwinやIoTのサポートに向けた取り組みを開始している。
- 留意点:
- 全般的な展望: AgilePointは、BPMS市場で成功した実績を持つ比較的小規模の私会社だが、LCAP市場ではるかに大きなベンダーと競争するためには、成長とブランド認知にさらなる投資が必要となる。
- ビジネスモデル: AgilePoint はビジネスの一部で Microsoft や Salesforce のエコシステムに参加しているため、LCAP 市場ではこれらのエコシステムのホストと競合する可能性がある。AgilePointはこれらのベンダとの間でプロセス中心の特性などの差別化を図っているが、このような優位性は、これらのパートナが独自のビジネスプロセス機能を追加していく中で減少していく可能性が高い。
- マーケティング戦略: AgilePointは順調に成長して適切なパートナー戦略を持っているが、この4象限評価の他の多くのベンダに比べて、LCAP市場での認知度は低い。IoTとエッジコンピューティングへの拡張戦略は、専門性を高める動きとしては成功する可能性があるが、ニッチプレーヤーとしての地位を悪化させる可能性もある。しかし、AgilePointはこの分野でのマーケティングを強化しており、SNSや直接/間接的なパートナーチャネルを通じた広範なマーケティングを展開中。
>Top 3. Appian
- Appian is a Leader in this Magic Quadrant. Its LCAP (version 20.1) offers low-code app building, rich multi experience capabilities, business process orchestration, automated decisioning, AI/ML and RPA. The platform focuses on complex processes such as end-to-end case management and other applications requiring sophisticated automation, rules and analytics. Its technological differentiators include full-stack automation capabilities, prebuilt no-code integration with various AI services, and end-to-end life cycle support for DevOps. Appian has operations in every major world region, with a focus on large enterprises. Its 2020 roadmap includes enhancements to AI- service integration, DevOps capabilities, RPA and expanded AI support for application development.
- Strengths:
- Product: At the core of Appian’s LCAP strength is its rich process-driven application development. Appian’s ability to offer a complete stack of low-code automation tooling that can handle complex workflows, business rules and case management along with RPA is a key differentiator. Added to that, it offers low-code tools to build multi experience apps to enable customer and employee experiences.
- Market understanding: Appian brings in a complete end-to-end solution for its customers by enabling low-code capabilities to build business applications, perform complex process orchestration, and automate routine repetitive tasks with RPA. Customers looking for a full- stack automation platform should consider Appian’s LCAP.
- Overall viability: In a crowded market with many small, privately owned vendors, Appian stands out as a stable, publicly traded company with a focus on low-code technology. Although smaller than many of its competitors, Appian has many enterprise customers and government agencies running its platform, which should ensure its long-term viability in this market.
- Cautions:
- Application development: Some of Gartner’s Peer Insight reviewers found that Appian’s low- code development product is more suitable for professional developers. Appian’s proprietary expression and scripting language is typically an inhibitor for “citizen developers” building algorithmic expressions. Although Appian has built some collaborative features to support multiple personas — including both citizen and pro developers — Gartner has not yet seen much adoption.
- Sales execution and pricing: Appian pricing has been observed as highly variable in Gartner inquiries. Recently, the vendor has made some changes with a simplified basic subscription model, an annual “Quick Start License” and other options that may allay customer concerns in future.
- Business model: Appian has a high proportion of professional services revenue associated with its LCAP business. While some of these services are likely legacy business process reengineering consulting, and others related to large projects associated with its targeting of larger enterprises, the proportion of services to product revenue implies more specialist developer requirements.
3. Appian:
- Appianは、この4象限評価ではリーダー。同社のLCAP (Version 20.1)は、ローコードアプリ構築、リッチマルチエクスペリエンス機能、ビジネスプロセス・オーケストレーション*、自動意思決定、AI/ML、RPAを提供します。このプラットフォームは、エンドツーエンドのケースマネジメントなど高度な自動化、ルール、分析を必要とする複雑なプロセスに焦点を当てている。その技術的な差別化要因は、全面的な自動化機能、さまざまなAIサービスとの事前のノーコードでの統合、DevOpsのエンドツーエンドのライフサイクルサポートなど。Appianは、大企業を中心に世界の主要地域で事業を展開中。その2020年のロードマップには、AI-サービス統合、DevOps機能、RPA、アプリ開発におけるAIサポートの拡大などの強化が含まれている。
- 強み:
- AppianのLCAPの強みの核となるのは、豊富なプロセス駆動型のアプリ開発です。複雑なワークフロー、ビジネスルール、ケース管理をRPAとともに扱えるローコードオートメーションツールの完全なスタックを提供するAppianの実力は、重要な差別化要因である。さらに、顧客や従業員の体験を可能にするマルチエクスペリエンス*・アプリを構築するためのローコード・ツールを提供している。
- 市場の理解: Appianは、ローコードでビジネスアプリを構築し、複雑なプロセス・オーケストレーション*を実行し、RPAで日常的な反復作業を自動化することで、顧客に完全なエンドツーエンドのソリューションを提供している。フルスタックの自動化プラットフォームを探している顧客は、AppianのLCAPを検討の価値がある。
- 全般的な展望: 多くの小規模個人経営のベンダがひしめく市場において、Appianはローコード技術に特化した安定した上場企業として目立っている。競合他社に比べて規模は小さいが、Appianは多くの企業顧客や政府機関が、同社のプラットフォームを採用しており、この市場での長期的な存続を確かにするものである。
- 留意点:
- アプリ開発: GartnerのPeer Insightのレビュアーの中には、Appianの低コストのコード開発製品はプロのIT開発者に適しているという人もいる。Appianの独自の表現とスクリプト言語は、Citizen開発者がアルゴリズム表現を構築する上では、一般的に阻害要因となる。Appianは、Citizen開発者とプロのIT開発者の両方を含む複数のペルソナをサポートするために、いくつかの協業体制を構築しているが、まだあまり採用されていないと見ている。
- セールスの実行と価格設定: Appianの価格設定は、非常にばらつきがあると思われる。最近では、シンプルな基本サブスクリプション・モデル、年間クイック・スタート・ライセンス、その他のオプションなどの変更を行っており、将来的には顧客の懸念を払拭できるかもしれない。
- ビジネスモデル: Appianは、LCAP事業に関連するプロフェッショナルサービス収益の割合が高い。これらのサービスの中には、レガシービジネス・プロセス・リエンジニアリングのコンサルティングや、大企業を対象とした大規模プロジェクトに関連するものもあると見られるが、製品売上に対するサービス比率は、より専門的な開発者の要求を反映している。
>Top 4. AuraQuantic (formerly AuraPortal)
- As of 1 September 2020, AuraPortal has changed its name to AuraQuantic.
AuraQuantic is a Niche Player in this Magic Quadrant. It provides low-code and BPM development tools for automating business operations. Its business is mostly focused in the EMEA and LATAM regions, and its clients tend to be midsize organizations with a majority in the banking and insurance sectors. AuraQuantic’s LCAP provides a process-centric application platform with multiple separate graphical editors for different functions such as portals and SQL scripts. Future plans include adding AI-based decision management, RPA and AI assistance for developers. It also expects to invest in expanding its community and marketplace.
- Strengths:
- Process and business logic: Coming from a BPM background, AuraQuantic has sophisticated support for process and decision management. It undertook an early transition into low-code development tools and provides a good platform for citizen developers to build extensible process- or data-centric applications.
- Market understanding: AuraQuantic aims to help its customers to achieve greater productivity through automation. It is constantly improving its offering by evolving its UX (forms) design and runtime, augmenting decisions and application development with AI, and adding process mining features. AuraQuantic has strengthened its position within the Microsoft-centric market segment, increasing its visibility in the Microsoft partner community.
- Industry strategy: AuraQuantic is enhancing its support for the government, financial services, insurance and healthcare industries. Utilizing its strong knowledge of the financial services industry, AuraQuantic is providing specific solutions and associated marketing campaigns around web and mobile case management, lending, and risk and compliance solutions, as well as improving customer journeys for its clients.
- Cautions:
- Product: Support for multiple developer personas is limited. Aura Quantic provides a comprehensive and easy-to-use process and data model designer, but currently has a limited library of components to support citizen developers, with additional components a roadmap entry. There is only limited support for professional developers outside of creating integrations.
- Platform ecosystem: The AuraQuantic marketplace is very basic compared with other vendors in this Magic Quadrant, and is not monetized. The restricted choice of application templates and connectors limits the value of the marketplace to developers and discourages contributors. AuraQuantic currently offers limited process patterns. Enterprises and independent software vendors (ISVs) looking for a vibrant ecosystem may need to consider alternatives.
- Overall viability: Aura Quanticisa small vendor, relative to most others in this Magic Quadrant. Its historic focus is on BPM rather than the faster-growing LCAP market. While the vendor shows some strength in territories like LATAM, a lack of brand awareness could impact long- term growth elsewhere. A future rebranding may help address this if marketed accordingly.
4. AuraQuantic (以前のAuraPortal):
- 2020/9/1よりAuraPortalはAuraQuanticに名称変更した。
AuraQuanticは、この4象限評価ではニッチ・プレーヤー。ビジネスオペレーションを自動化するためのローコードおよびBPM開発ツールを提供している。同社のビジネスは、主に中東とラテンアメリカ地域に集中しており、顧客は銀行や保険セクターを中心とした中規模組織が多い。AuraQuanticのLCAPは、ポータルやSQLスクリプトなどの機能別に複数の独立したグラフィカル・エディタを備えたプロセス中心のアプリ・プラットフォームを提供している。将来的には、AIによる意思決定管理、RPA、開発者向けのAI支援などを追加する予定。また、コミュニティやマーケットプレイスへの投資も期待されている
- 強み:
- プロセスとビジネスロジック: BPMのバックグラウンドを持つAuraQuanticは、プロセスと意思決定管理のための洗練されたサポートを備えている。また、ローコード開発ツールへの移行を早くから行っており、Citizen開発者が拡張可能なプロセスやデータ中心のアプリを構築するための優れたプラットフォームを提供している。
- 市場の理解: AuraQuanticは、自動化によって顧客の生産性を向上させることを目的としていり。UX*デザインやランタイムの進化、AIによる意思決定やアプリ開発の増強、プロセスマイニング機能の追加など、常に提供情報を改善している。AuraQuanticは、Microsoftを中心とした市場セグメントの中での地位を強化し、Microsoftのパートナーコミュニティでの認知度を高めている。
- 業界戦略: AuraQuanticは、政府、金融サービス、保険、ヘルスケア業界へのサポートを強化している。金融サービス業界に精通していることを活かし、Webやモバイルでの案件管理、融資、リスクやコンプライアンスのソリューション、顧客のカスタマージャーニーの改善など、具体的なソリューションや関連するマーケティングキャンペーンを行っている
- 留意事項:
- 製品: 多数の開発者ペルソナへのサポートは限定的である。Aura Quanticは、包括的で使いやすいプロセスとデータモデルのデザイナーを提供するが、現在、Citizen開発者をサポートするコンポーネントのライブラリは限られており、追加のコンポーネントはロードマップのエントリーとなっている。プロのIT開発者向けのサポートは、統合機能の作成以外は限られている。
- プラットフォームのエコシステム: AuraQuanticのマーケットプレイスは、この4象限評価の他のベンダーと比べて非常に基本的なものであり、収益が上がっていない。アプリ・テンプレートやコネクターの選択肢が限られているため、開発者にとっての市場での価値が制限され、エコシステムへの貢献者の意欲が削がれている。AuraQuanticは現在、限られたプロセスパターンを提供している。活発なエコシステムを求める企業や独立系ISVは、他の選択肢を検討する必要があるかもしれない。
>Top 5. Betty Blocks:
- Betty Blocks is a Visionary in this Magic Quadrant. Its LCAP is mainly focused on citizen development. Its operations are mostly focused in Western Europe and the U.S. Its clients cross different enterprise sizes and primarily target B2B use cases. Betty Blocks is known for its technology innovation and is targeting ease of development, component (“block”) reuse and governance. It has enhanced its container* deployment, developer environment and extensions mechanism, and is planning autogenerated user experiences to speed application delivery.
- Strengths:
- Product strategy: Betty Blocks has successfully identified and delivered on two of the major drivers for low-code-based productivity — composable applications maximizing reuse, and simplicity of development (composition) of applications. These enable reuse and speed of development and its “blocks” mechanism encourages ecosystem development.
- Innovation: Betty Blocks continues to innovate around technologies such as container-based distribution and deployment, GraphQL for external application integration, and cloud-native extension mechanisms. This innovation approach includes rapidly iterating where technologies don’t prove effective, such as moving from serverless functions to container-based code for extensibility.
- Sales execution: Betty Blocks continues to grow and extend its customer footprint, despite increasing competition in citizen development from other vendors. Part of the reason for this is a more aggressive pricing model, although like many other LCAP providers this may evolve in the future.
- Cautions:
- Marketing strategy: BettyBlocks’ citizen development marketing strategy faces growing competition, in particular from the “quasi freemium” model and ubiquity of Microsoft Power Apps. Its ecosystem may not be able to compete with such larger established vendors. For now, Betty Blocks continues to grow in part by exploiting the Microsoft Partners program in the U.S.
- Geographic strategy: While Betty Blocks has some APAC customers, its growth in 2019 was solely from EMEA and the U.S., making it less likely to be adopted for some worldwide enterprise initiatives, and potentially reducing its overall growth.
- Industry strategy: BettyBlocks’ Block Store remains unmonetized, potentially reducing ISV and OEM ecosystem growth. This means that while its LCAP users are from across all industries, and Betty Blocks claims a vertical-driven focus across its marketing and sales, any vertical market growth is more likely to be organically driven rather than partner-led.
5. Betty Blocks:
- Betty Blocksは、この4象限評価ではビジョナリー。同社のLCAPは、主にCitizen開発者の育成に重点を置いている。同社の顧客はさまざまな規模の企業で、主にB2Bのユースケースを対象としている。Betty Blocksは、技術革新で知られており、開発の容易さ、コンポーネント("Block")の再利用やガバナンスを目標としている。また、コンテナ*配置、開発環境、拡張メカニズムを強化し、自動生成されたユーザーエクスペリエンスを計画することで、アプリの導入を迅速化している。
- 強み:
- 製品戦略: Betty Blocksは、ローコードベースの生産性を向上させる2つの大きな要因、すなわち再利用を最大限にするcomposable*アプリと、アプリ開発 (compostion)の簡素化を特定し、実現することに成功した。これらにより、再利用と開発スピードの向上を実現し、Blockという仕組みがエコシステムの構築を促進している。
- イノベーション: Betty Blocksは、Container*ベースの配置や導入、外部アプリとの統合のためのGraphQL、クラウドネイティブな拡張メカニズムなどの技術を中心に革新を続けている。このアプローチには、サーバーレス機能から拡張性のためのContainerベースのコードへの移行など、技術が有効でない場合に迅速にiterateすることも含まれる
- 販売実績: Betty Blocksは、Citizen開発において他のベンダとの競争が激化しているにもかかわらず、顧客数の増大を続けている。この理由の一つは、より積極的な価格設定にあるが、他の多くのLCAPプロバイダと同様に、これは将来的に変化する可能性がある。
- 留意事項:
- マーケティング戦略: BettyBlocksのCitizen開発者へのマーケティング戦略は、特にMicrosoft Power Appsの準フリーミアムモデルとその普及により競争が激化している。BettyBlockSのエコシステムは、このような大規模な既存ベンダには対抗できないかもしれない。今のところ、Betty Blocksは、米国のMicrosoft Partnersプログラムを活用することで成長を続けている。
- 地理的戦略: Betty Blocksにはアジア太平洋の顧客もいるが、2019年の成長は中東と米国のみであったため、世界的企業に採用される可能性は低く、全体の成長が減少する可能性がある。
- 業界の戦略: BettyBlocksのBlock Storeは未だに収益が上がっておらず、ISVやOEMのエコシステムの成長を妨げる可能性がある。つまり、BettyBlocksのLCAPユーザはすべての業界に亘っており、BettyBlocksはマーケティングとセールスにおいて垂直方向に注力していると主張しているが、垂直方向の市場成長はパートナー主導ではなく、もっと組織的に推進される可能性が高い。
>Top 6. Creatio:
- Creatio (formerly bpm’online) is a Niche Player in this Magic Quadrant. Its LCAP offering is Studio Creatio, which provides low-code process management and process-based application development for its CRM SaaS business, as well as other use cases. Creatio’s operations are global with a strong presence among small enterprises in the EMEA and North America regions. In 2019, Creatio added a free edition, additional AI services and higher performance mobile support. It is planning to enhance the extensibility of its platform by adding a UI based on the Angular framework*, further AI support for process and application development, and is expanding its ecosystem.
- Strength:
- Market understanding: Creatio has a good understanding of customer priorities for LCAP and its support for SaaS for customers is evident in its “Everyone a Developer” messaging. It recognizes the need to increase IT productivity, reduce time to market and increase business IT collaboration. Creatio targets business developers with reduced technical skill requirements.
- Sales execution: Creatio has showcased a decent growth in this market. This is driven by value for money, with attractive pricing for B2C users for its portal offering and simplified per-user pricing for B2E users. Creatio sales are supported by a strong global network of more than 700 partners that sell its products across 110 countries and 14 different languages.
- Market responsiveness: Creatio Studio has evolved low-code development features in response to customer needs. These include allowing nontechnical business developers to create their own custom machine learning (ML) models and an intuitive drag-and-drop case designer capability. The vendor has also developed its Creatio Academy and Community services to train and engage with developers and expand its ecosystem.
- Cautions:
- Product: Creatio provides basic support for handling data schemas and validations, but lacks enterprise features such as multi cloud/multi region deployments and seamless autoscaling of applications. These can be important for some enterprise use cases.
- Innovation: In terms of integration capabilities and more recent innovations such as AI- enhanced application development, Creatio lags the Leaders in this Magic Quadrant. Although it has more than 70 out-of-the-box connectors on its marketplace, few of them are for popular enterprise applications such as SAP.
- Overall viability: Creatio is not as large as some of the vendors in this Magic Quadrant, and its focus on CRM SaaS is shared by several other larger LCAP vendors. As larger vendors enter the LCAP market, Creatio will need to grow faster to remain viable.
6. Creatio:
- Creatio (旧bpm'online) は、この4象限評価におけるニッチ・プレーヤーである。同社が提供するLCAPは、Studio Creatioで、CRM SaaSビジネスやその他ユースケースにおいて、ローコードのプロセス管理やプロセスベースのアプリ開発を提供している。Creatioはグローバルに展開しており、中東と北米地域の小企業の間で強い存在感を示している。2019年にCreatioは無料版や、AIサービスの追加、より高性能なモバイル対応を行った。今後は、Angular framework*をベースにしたUIの追加、プロセスやアプリ開発のためのさらなるAIサポートを含め、プラットフォームの拡張やエコシステムの拡大を進めていく予定。
- 強み
- 市場への理解: Creatioは、LCAPにおける顧客の優先事項をよく理解しており、顧客向けのSaaSをサポートしていることは、"Everyone a Developer"という表現にも表れている。同社は、IT生産性の向上、市場投入までの時間短縮、ビジネスITコラボレーションの拡大の必要性を認識している。Creatioは、技術的なスキル要件が軽減されたビジネス開発者[=Citizen開発者] をターゲットにしている。
- 販売実績: Creatioは、この市場でまずまずの成長をしている。これは、B2Cユーザにはポータル製品の魅力的な価格設定、B2Eユーザには簡素化されたユーザ毎の価格設定など、Value for Moneyよるものである。Creatioの販売は、700社以上のパートナーからなる強力なグローバルネットワークによって支えられており、110カ国、14の言語で製品を販売している。
- 市場への対応力: Creatio Studioは、顧客ニーズに応えてローコード開発機能を進化させてきた。これには、技術者ではないビジネス開発者が独自のカスタム機械学習 (ML) モデルを作成できることや、直感的なドラッグ&ドロップ式のケースデザイナー機能が含まれる。また、Creatio AcademyやCommunityといったサービスを通じて、開発者の育成やエコシステムの拡大に努めている。
- 留意事項:
- 製品: Creatioは、データスキーマ*や検証のサポートを提供しているが、マルチクラウド/マルチリージョンの展開やアプリのシームレス・オートスケーリングなどの企業向け機能がない。これらは一部企業のユースケースにとっては重要である。
- イノベーション。Creatioは、統合機能や、AIによるアプリ開発の強化などの最新のイノベーションの点で、このマジック・クアドラントのリーダー企業に遅れをとっている。マーケットプレイスには70種類以上のコネクタが用意されているが、SAPなどの一般的な企業向アプリのものはほとんどない。
- 全体的な展望: Creatioは、この4象限分析の他のベンダーほど規模が大きくないが、CRM SaaSに焦点を当てている点では、他のいくつかの大規模なLCAPベンダーと共通している。大規模なベンダーがLCAP市場に参入してくると、Creatioは存続するために急成長が求められる。
>Top 7. Kintone:
- Kintone is a Niche Player in this Magic Quadrant. Its LCAP is mainly focused on workforce collaboration applications for business units. Its operations are mostly focused in Japan and the Pacific Rim region, and its clients tend to be small and midsize organizations. Kintone targets simple-to-build B2E applications, which may also be provided by partners through various app stores, or by the business users themselves. It is focusing on expanding further in the U.S. using Amazon Web Services (AWS) infrastructure, and is making improvements for citizen developers in the core areas of data, communications and workflows.
- Strenths:
- Overall viability: Kintone is continuing to grow and is the leading revenue generator for its parent corporation Cybozu, a leading Japanese collaboration platform business. In addition to Japan, Kintone’s LCAP serves 15,000 customers across Asia (including China), Australia and North America.
- Business model: Kintone focuses on a collaboration model and supports thousands of partners and developers, creating a highly successful ecosystem across Asia. It is doubling its sales resources to increase adoption, helped by over 350 partners providing applications or plug-ins. Some partners operate their own Kintone app stores, and the overall partner ecosystem generates more than half of Kintone’s revenue.
- Marketing execution: Kintone focuses on its business value and brands itself as a “business workstyle” company, rather than “technology” company. It is focusing on thought leadership around its collaboration features and has run a number of successful events across Asia and the U.S.
- Cautions:
- Market understanding: Kintone continues its narrow focus on collaboration applications by citizen and business unit developers, with weak support for professional developers and IT use cases requiring sophisticated architectures. The company is missing some enterprise certifications like SOC (System and Organization Controls) and PCI (Payment Card Industry) required by certain LCAP users.
- Product: Kintone does not have a strong integration focus, relying on third parties for connectivity to other services, and REST APIs to access external databases. The tool is not ideal for complex business processes or business decision logic, and does not support headless* applications. Governance of developers and applications is also basic relative to other vendors in this Magic Quadrant.
- Innovation: Kintone’s roadmap does not prioritize the current LCAP trends such as AI data services, AI-based development or user experiences like chatbots. Kintone users — even citizen developers — could be disadvantaged in future by these omissions.
7. Kintone:
- Kintoneは、この4象限分析ではニッチ・プレーヤー。同社のLCAPは、主にビジネスユニット向けのワークフォース・コラボレーション・アプリに注力している。Kintoneは、主に日本と環太平洋地域で事業を展開しており、顧客は中堅・中小企業が中心となっている。Kintoneは、簡単に構築できるB2Eアプリをターゲットとしており、パートナーがさまざまなアプリストアを通じて提供する場合もあれば、ビジネスユーザ自身が提供する場合もある。Kintoneは、Amazon Web Services(AWS)のインフラを利用して米国でのさらなる拡大に注力しており、データ、コミュニケーション、ワークフローなどの主要分野でCitizen開発者向けの改善を行っている。
- 強み:
- 全般的展望: Kintoneは成長を続けており、親会社であるサイボウズの主要な収益源であり、日本のコラボレーション・プラットフォーム事業を牽引している。日本に加えて、KintoneのLCAPは、アジア (中国を含む)、豪州、北米で15,000社の顧客にサービスを提供している。
- ビジネスモデル: Kintoneは、コラボレーションモデルを重視し、何千ものパートナや開発者をサポートし、アジア全域で大きな成功を収めているエコシステムを構築している。Kintoneは、アプリやプラグインを提供する350社以上のパートナの協力を得て、採用率を高めるために営業リソースを倍増している。一部のパートナーは独自のKintoneアプリストアを運営しており、パートナーエコシステム全体でKintoneの収益の半分以上を生み出している。
- マーケティングの実施: Kintoneは、自社のビジネス価値を重視し、"テクノロジー"というより"ビジネス・ワークスタイル"の企業としてブランド化している。コラボレーション機能を中心としたthought (認識や考え方)リーダーシップに力を入れており、アジアや米国で数々のイベントを成功させている。
- 留意事項:
- 市場の理解: Kintoneは、Citizen開発者や現業部門の開発者によるコラボレーション・アプリに焦点を絞っており、プロのIT開発者や高度なアーキテクチャを必要とするITユースケースへのサポートは弱い。また、一部のLCAPユーザーが必要とするSOC (System and Organization Controls) やPCI (Payment Card Industry) などの企業認証を取得していない。
- 製品: Kintoneは統合化を重視しておらず、他のサービスへの接続はサードパーティ頼りであり、外部データベースへのアクセスはREST APIを利用している。このツールは、複雑なビジネス・プロセスやビジネス意思決定ロジックには適しておらず、ヘッドレス *アプリもサポートしていない。また、開発者やアプリのガバナンスも、この4象限分析の他のベンダーに比べて基本レベルの留まっている。
- イノベーション: Kintoneのロードマップは、AIデータサービス、AIベースの開発、チャットボットのようなUXなど、現在のLCAPのトレンドを優先していない。Kintoneのユーザは、たとえCitizen開発者であっても、これらの省略によって将来的に不利益を被る可能性がある。
>Top 8. Mendix:
- Mendix (a subsidiary of Siemens) is a Leader in this Magic Quadrant. Its LCAP is the Mendix Platform, which offers no-code and low-code development tools based on a model-driven, cloud- native platform architecture. It has recently added Mendix Data Hub for low-code integration and two private cloud service options — Mendix Cloud Dedicated and Mendix for Private Cloud. Mendix has offices mainly in North America and Europe, and most of its customers are in those regions. Its customers span a variety of industries. Mendix has a partnership with SAP to supply a tightly integrated LCAP with SAP HANA (also sold by SAP).
- Strengths:
- Product:
Mendix offers robust capabilities to address needs across integration, workflow, event processing and use of AI to support development. In particular, its event processing supports events as first-class citizens, providing the infrastructure for publishing, consuming and managing business events. Mendix Assist, now in its second generation, uses ML to integrate real-time, in-product, AI-assisted contextual next-step suggestions.
- Innovation:
The recently released Mendix Data Hub component allows its developers to more easily discover, assemble and orchestrate data and business capabilities, using the same Mendix visual modeling tools that it uses to build business logic and application data models. Mendix is also one of the few LCAP vendors with advanced multi experience development capabilities supporting highly customizable mobile apps, chatbots and IoT app use cases.
- Market understanding:
Mendix’s LCAP supports visual and model-driven development across a broad spectrum of developer profiles. The platform provides a separate design-time environment for citizen developers (Mendix Studio) and a more robust development environment for professional developers (Mendix Studio Pro). This dual approach optimizes collaboration of fusion teams across business units and IT, and support for the composable enterprise vision.
- Cautions:
- Sales execution and pricing:
Mendix shifted its sales to focus on the large enterprise segment. It has done well there, but its overall customer growth is not as high as other vendors in this fast-growing market. Gartner Peer Insight scores for Mendix’s pricing and contract flexibility are relatively low compared with other vendors in this Magic Quadrant. Mendix is planning new pricing and packaging to address this by the end of 2020.
- Industry strategy:
Mendix has been late to offerindustry-specific solutions with its LCAP, with only a recent introduction of an Industry Solutions team. The vendor mostly relies on its parent company Siemens for specific targeted solutions and partner ISVs for industry applications in its marketplace.
- Marketing execution:
While the acquisition by Siemens has elevated the market’s awareness of Mendix, Gartner has not seen Mendix reaching as wide an audience as other Leaders in this Magic Quadrant, particularly outside of Europe and North America. Companies looking to evaluate Mendix should investigate its regional presence and support from local partner resources.
8. Mendix:
- Mendix (Siemensの子会社) は、この4象限評価のリーダ。同社のLCAPは、モデル駆動型のクラウドネイティブ・プラットフォーム・アーキテクチャに基づいて、ノーコードおよびローコードの開発ツールを提供するMendix Platformである。最近では、ローコード統合のためのMendix Data Hubや、2つのプライベートクラウドサービスMendix Cloud DedicatedとMendix for Private Cloudを追加している。Mendixは、主に北米と欧州に事務所を構えており、顧客のほとんどがこれらの地域にいる。その顧客は様々な業界に及んでいる。MendixはSAPとパートナーシップを結び、SAP HANA (SAPが販売) と緊密に統合されたLCAPを供給している。
- 強み:
- 製品:
Mendixは、統合、ワークフロー、イベント処理、開発支援のためのAI活用など様々なニーズに対応する強力な機能を備えている。特にイベント処理では、イベントを一番の市民としてサポートし、ビジネスイベントの発行、消費、管理のためのインフラを提供している。第2世代となるMendix Assistは、MLを使用して、AIが支援するリアルタイムの製品内コンテクストに基づく次のステップの提案を統合している。
- イノベーション:
最近リリースされたMendix Data Hubコンポーネントにより、同社の開発者は、ビジネスロジックやアプリ・データモデルの構築に使用するのと同じMendixビジュアルモデリングツールを使用して、データやビジネス機能をより簡単に発見、組立て、orchestrationができるようになった。また、Mendixは、高度にカスタマイズ可能なモバイルアプリ、チャットボット、IoTアプリのユースケースをサポートする高度なmulti experience*開発機能を持つ数少ないLCAPベンダーの1つである。
- 市場理解:
メンディックスのLCAPは、幅広い開発者のプロファイルに対応したビジュアルおよびモデル駆動型の開発をサポートしている。このプラットフォームは、Citizen開発者向けの独立したデザインタイム環境 (Mendix Studio) と、プロの開発者向けのより強固な開発環境 (Mendix Studio Pro) を提供している。この2つのアプローチにより、現業部門やIT部門を超えた混合チームの協業を最適化し、全社的なビジョンをサポートする。
- 留意事項:
- 販売の実行と価格設定:
Mendixは、大企業向けセグメントに焦点を当てて営業活動を行ってきた。Mendixは大企業向けに営業をシフトしており、その成果は出ているが、全体的な顧客数の伸びは、この急成長市場の他のベンダに比べてそれほど高くはない。Gartner Peer Insightでは、Mendixの価格設定と契約の柔軟性に関するスコアは、この4象限評価の他のベンダに比べて相対的に低くなっている。Mendixは、2020年末までにこの問題に対処するための新しい価格設定とパッケージを計画している。
- 業界戦略:
Mendixは、LCAPで業界に特化したソリューションを提供するのが遅く、最近になって業界ソリューションチームを導入したばかりである。Mendixは、特定のターゲットに向けたソリューションについては親会社であるSiemensに依存し、市場での業界アプリについてはパートナーであるISVに依存している。
- マーケティング実績:
Siemensの買収により、Mendixに対する市場の認知度は高まったものの、Gartnerは、この4象限評価の他のリーダー企業と比較して、特に欧州と北米以外の地域では、Mendixがそれほど広く普及していないと見ている。Mendixを評価しようとしている企業は、その地域での存在感やローカル・パートナー・リソースによるサポートを調査する必要がある。
>Top 9. Microsoft:
- Microsoft is a Leader in this Magic Quadrant. Its LCAP consists of Microsoft Power Apps, which includes entitlements for Power Automate and the Common Data Service. Together, these form part of the Power Platform (which adds Power BI for business analytics and Power Virtual Agents for low-code chatbots). Microsoft’s operations are in locations worldwide. Its customers are in a variety of industries and of varying sizes. Power Apps operates in canvas and model-driven modes, and Power Automate provides business logic and integrations. Innovations on Microsoft’s roadmap include support for Power Apps in Microsoft Teams to deploy solutions and templates, enabling remote workers, and expanding AI and RPA accessibility.
- Strength
- Product strategy:
Microsoft enables fusion teams with no-code and advanced pro developer capabilities. Microsoft offers one of the simpler design-time tools in Power Apps, one that is used for designing canvas apps and that employs a drag-and-drop approach with an expression language that feels like Microsoft Excel. This makes it well-suited to citizen developers and business unit developers.
- API and integration services:
Power Apps and Common Data Service (CDS) have a rich set of APIs and OData endpoints available to perform full create, read, update and delete (CRUD*) operations on data to support integration with third-party iPaaS*. There are more than 300 data connectors available including cloud-service database connectors that cover Azure SQL, Azure Cosmos DB, Amazon Redshift and cloud-hosted versions of the on-premises systems.
- Innovation:
Ready-to-consume AI models allow developers to consume rich AI capabilities in their apps and flows without configuring and training a model. Prebuilt models are available to extract text from images, extract specific elements from text, categorize text, identify languages, and to perform key phrase extraction and sentiment analysis. AI Builder provides no- code support for data and visual AI models, available as an extension to Power Apps.
- Cautions:
- Market responsiveness:
In 2019, Microsoft saw wide adoption of PowerApps, in part due to availability within the vendor’s popular Office and Dynamics offerings. In October 2019, Microsoft changed these entitlement conditions, a change that disrupted many clients and appeared to confuse business partners. Microsoft grand fathering of prior license rights for deployed customers has helped in some situations.
- Sales execution and pricing:
Power Apps’ pricing model and entitlement rules, especially across entitlements for features in Office 365 and Dynamics 365 plans, are complex enough to require a 17-page licensing guide. Customers also pay extra for features such as AI Builder and the B2C portal. Customers should consider how their licensing and costs may change as their platform usage grows, and be aware of the potential for further license changes.
- Process and business logic:
Power Apps supports workflows, but the interface for business process flows is separate and only available in model-driven apps. More complex process orchestration may require the use of separate products such as Microsoft Azure Logic Apps. Additionally, the BPMN notation standard in Power Automate is only supported through tight integration with Microsoft Visio.
9. Microsoft:
- Microsoftは、この4象限評価のリーダーである。そのLCAPは、Microsoft Power Appsで構成されており、Power AutomateとCommon Data Serviceを含んでいる。これらは、Power Platform (ビジネス分析のためのPower BI、ローコードチャットボットのためのPower Virtual Agentを含む) の一部を構成している。Microsoftは、世界各地で事業を展開している。また、顧客の業種や規模も様々である。Power Appsはキャンバスとモデルドリブンのモードで動作し、Power Automateはビジネスロジックと統合化を提供する。Microsoftのロードマップ上のイノベーションには、ソリューションやテンプレートを展開するMicrosoft TeamsでのPower Appsのサポート、リモートワーカーの実現、AIやRPAのアクセシビリティの拡大などがある。
- 強み:
- 製品戦略:
Microsoftは、コードレスで高度なプロの開発者の機能を備えた混合チームを実現する。Power Appsは、キャンバスアプリの設計に使用されるシンプルなデザインタイムツールで、Microsoft Excelのような表現言語を用いたドラッグ&ドロップのアプローチを採用している。そのため、Citizen開発者や現業部門の開発者に適している。
- APIと統合化サービス:
Power AppsとCommon Data Service (CDS) では、豊富なAPIとODataエンドポイントが用意されており、データに対する完全な作成、読み取り、更新、削除 (CRUD=create, read, update, delete)*操作を実行し、サードパーティのiPaaS*との統合をサポートする。また、Azure SQL、Azure Cosmos DB、Amazon Redshift、およびオンプレミスシステムのクラウド版をカバーするクラウドサービスのデータベースコネクタを含む300以上のデータコネクタが利用可能である。
- イノベーション:
すぐに使えるAIモデルにより、開発者はモデルの設定やトレーニングを行うことなく、アプリやフローでリッチなAI機能を利用することができる。画像からのテキスト抽出、テキストからの特定要素の抽出、テキストの分類、言語の識別、キーフレーズの抽出や感覚分析を行うための構築済みモデルが用意されている。AI Builderは、データおよびビジュアルAIモデルをノーコードでサポートし、Power Appsの拡張機能として利用できる。
- 留意事項:
- 市場の反応:
2019年、Microsoftは、ベンダーの人気製品であるOfficeやDynamics製品の中で利用できることもあって、PowerAppsが広く採用された。2019年10月、Microsoftはこれらのエンタイトルメントの条件を変更したが、この変更は多くの顧客をまた、ビジネスパートナーを混乱させたようだ。デプロイされた顧客の先行ライセンス権をMicrosoftが、Grand father化したことで一部の導入済ユーザは救われた。
- 販売実施と価格政策:
Power Appsの価格モデルとエンタイトルメントルール、特にOffice 365やDynamics 365プランの機能のエンタイトルメントについては、17ページのライセンスガイドが必要なほど複雑である。また、AI BuilderやB2Cポータルなどの機能には追加料金がかかる。顧客は、プラットフォームの使用量の増加に伴い、ライセンスやコストがどのように変化するかを考慮し、今後のライセンス変更の可能性にも注意すべきである。
- プロセスとビジネスロジック:
Power Appsはワークフローをサポートしているが、ビジネスプロセスフローのインターフェイスは別であり、モデルドリブンなアプリでのみ利用できる。より複雑なプロセスオーケストレーションには、Microsoft Azure Logic Apps などの別製品の使用が必要になる場合がある。さらに、Power AutomateのBPMN記法の標準は、Microsoft Visioとの緊密な統合によってのみサポートされている。
>Top 10. Newgen:
- Newgen is a Niche Player in this Magic Quadrant. It is primarily a content management and BPMS vendor whose LCAP is provided by its process-centric development platform. Newgen’s primary geographic market is APAC, but it has demonstrated a growing presence in EMEA and North America. Its clients tend to be large and midsize organizations in the financial services, insurance and government sectors. In 2019, Newgen added support for DevOps, progressive web apps (PWAs)* and integrated RPA. Newgen further plans to add a framework for vendor-agnostic bot orchestration, enriched application templates for PWAs, and extend its integration modeler with metering and monitoring.
- Strength
- Product: Newgen provides a robust platform to automate business processes. It provides a web-based tool that can be used to develop PWAs, a visual editor for designing complex processes and decision rules, and a master data management (MDM) module for comprehensive data modelling. It also provides an AI-enabled content management system (CMS) as part of its offering.
- Sales execution and pricing: Newgen has flexible licensing and deployment options, including software-only, full SaaS and private cloud application managed service. The vendor tailors its licensing to client requirements through perpetual, subscription and value-based pricing (that is, pricing associated with business value metrics or outcomes).
- Sales strategy: Selling an LCAP as part of a process automation and content management strategy means Newgen can deliver wider enterprise value. This should make adoption easier for customers of these other services.
- Cautions:
- Platform ecosystem: Newgen’s marketplace is essentially a partner-enablement portal that consists of a few prebuilt applications, training materials and implementation guidelines. Enterprise users or partners cannot source or add application or process templates for faster development or monetization. However, a publicly available developer community and portal is on the roadmap.
- Application development: The Newgen platform is a combination of various independent components including a CMS, a process builder and a mobile app designer. The experience of building applications across these various components is inconsistent.
- Geographic strategy: Newgen’s primary customer base is in India, the Middle East and Africa. It aspires to grow in the U.S. and Western Europe through both direct presence and partners. Prospective clients in the U.S. and Western Europe need to evaluate Newgen’s local and partner abilities to meet their requirements.
10. Newgen:
- Newgenは、この4象限分析ではニッチ・プレーヤー。Newgenは主にコンテンツ管理とBPMSのベンダーで、プロセス中心の開発プラットフォームによるLCAPを提供している。Newgenの主な市場はアジア太平洋地域であるが、欧州・中東アフリカや北米でも存在感を増している。その顧客は、金融サービス、保険、政府部門の大〜中規模組織である。2019年、NewgenはDevOps、Progressive Webアプリ (PWA) *、統合RPAのサポートを追加した。さらに、ベンダに依存しないボットオーケストレーションのフレームワーク、PWA用の充実したアプリ・テンプレートの追加、メータリングとモニタリングを備えた統合モデラーの拡張を予定している。
- 強み:
- 製品: Newgenは、ビジネスプロセスを自動化するための強固なプラットフォームを提供している。PWA*の開発に使用できるウェブベースのツール、複雑なプロセスや決定ルールを設計するためのビジュアルエディタ、包括的なデータモデリングを行うMaster Data Management (MDM*) モジュールを提供している。また、AIに対応したコンテンツ管理システム(CMS)も提供している。
- 販売実行と価格。Newgenは、ソフトウェアのみ、フルSaaS、プライベートクラウドアプリのマネージドサービスなど、柔軟なライセンスと展開オプションを用意している。このベンダは、永久ライセンス、サブスクリプション、バリューベースの価格設定(つまり、ビジネスバリューの指標や成果に関連した価格設定)により、顧客の要求に合わせてライセンスを調整している。
- 販売戦略: LCAPをプロセスオートメーションやコンテンツマネジメント戦略の一環として販売することは、Newgenがより広範な企業価値を提供することを意味する。これにより、他のサービスの顧客にも導入しやすくなる。
- 留意事項:
- プラットフォーム・エコシステム: Newgenのマーケットプレイスは、基本的にはパートナ支援のためのポータルであり、いくつかの構築済アプリ、トレーニング資料、導入ガイドラインで構成されている。企業ユーザやパートナーは、アプリやプロセスのテンプレートを入手・追加して、開発や収益化を加速させることはできない。しかし、一般に公開されている開発者コミュニティとポータルは、ロードマップに含まれている。
- アプリ開発: Newgenプラットフォームは、CMS、プロセスビルダー、モバイルアプリデザイナーなど、さまざまな独立したコンポーネントの組み合わせでである。これらの様々なコンポーネントを使ってアプリを構築する経験は一貫していない。
- 地理的戦略: Newgenの主な顧客基盤は、インド、中東、アフリカである。米国と西欧では、直接的なプレゼンスとパートナーの両方を通じて成長を目指している。米国および西欧での顧客候補は、彼らの要求を満たすためにNewgenの現地およびパートナーの能力を評価する必要がある。
>Top 11. Oracle (APEX):
-
Oracle Application Express (APEX) is a Challenger in this Magic Quadrant. Oracle is well- established in the database and business applications markets. Its APEX product is mainly focused on data-oriented applications created by Oracle SQL developers. Its operations are geographically diversified and its clients are Oracle DBMS customers, although Oracle reports good solution sales to the small and midsize business (SMB) market. APEX has added high- performance user experiences for data search across large datasets, and the ability to access data from any external REST-enabled* source. Oracle is increasing the rate of investment in APEX with JavaScript server-side components and other relational DBMS data sources planned. Oracle’s alternative LCAP offering — Oracle Visual Builder — is based on its service-oriented architecture technology stack and is discussed separately.
- Srength:
- Overall viability: Oracle is a large and successful DBMS and SaaS vendor. The former ensures a large and ready audience for APEX, and a large developer base of developers that use SQL and its procedural language extension (PL/SQL)*to exploit it. A subset of this is also a large and active community of APEX users.
- Sales execution and pricing: Oracle has multiple ways to consume and purchase APEX, but it is also a free service for Oracle Database and Oracle Cloud users. For most users, its net cost is included in their DBMS platform costs. This makes APEX excellent value for any Oracle Database platform user. Oracle is extending APEX usage as it sells solutions to new markets like the SMB market.
- Marketing strategy: Oracle markets APEX as the low-code application tooling for Oracle DBMS subscribers, extending their data-oriented applications to powerful web and mobile applications, and is an ideal upgrade for Oracle Forms applications. APEX applications can be extended through JavaScript, Java and SQL to access all the advanced features of the Oracle Database platform.
- Cautions:
- Market understanding:
Most LCAPs provide multifunction application capabilities for reduced- skill development. Oracle provides separate suites with differing editing metaphors for integration, BPM and business rules, as well as Oracle Visual Builder as a service-focused LCAP. APEX users who require such capabilities can access them through separate licenses and REST API* calls (or coordination of shared data tables). While this separation of concerns ensures best-of-breed support, it requires additional configuration and developer skill requirements outside of APEX.
- Business model:
Oracle’s use of its database platform as the core engine for APEX makes APEX consumption dependent on use of its DBMS. While this remains a large market, Oracle’s market share is reducing. However, Oracle is still a market leader in DBMS, and APEX is being extended to support additional languages and to access other data sources.
- Innovation:
While Oracle’s roadmap for APEX is extensive, it is focused on catching upon capabilities like server-side JavaScript support that are already generally available elsewhere in the market. Its main function as a SQL RAD* tool is of specialist interest to most low-code consumers, even though SQL and PL/SQL* is not difficult to learn. Advanced features of the Oracle Database platform generally require SQL code to access.
11. Oracle (APEX):
- OracleのApplication Express (APEX)は、4象限評価では、挑戦者の役割である。Oracleは、Databaseやビジネスアプリでは著名である。その APEXは、Oracle SQL 開発者によって構築されたデータ中心のアプリに特化している。今までは、中小企業へのソリューション販売で評判良かったが、顧客ベースは世界中のOracel DBMS顧客に広がっている。APEXは、ビッグデータを横断的にデータ検索行なう高機能なUXと、外部のREST原則*のデータソースからのアクセスも可能ととする機能を追加した。Oracleは、JavaScriptによるサーバ側コンポーネントや他のDBMSデータへのAPEC投資を投資を増やす計画である。Oracleの別のローコード開発であるOracke Visual Builderは、サービス指向アーキテクチャ技術でこれは別項に記載。
- 強み:
- 全般的将来性: Oracleは、大規模DBMSとSaaSベンダである。前者で、SQLを使用している開発者はAPEXの大きな顧客基盤であり、SQLやその拡張版のPL/SQL*で開発している。この部分もまた大きなAPECユーザコミュニティを形成している。
- 価格政策: APEXは、Oracle DatabaseやOracle Cloudユーザにはフリーサービスで、DBMS Platform価格に含まれている。Oracleは中小企業の新規ユーザにはAPEXの使用を販売している。
- 市場戦略: Oracleは、Oracle DBMSユーザに対してAPEXをデータ中心のアプリをWebやMobileアプリにローコード開発ツール使って拡張することをマーケティングしている。APEXアプリは、JavaScrip, Java, SQLを通じて拡張することで、すべてのOracle Database platformの先進機能にアクセスできるようになる。
- 留意点:
- 市場の理解: ローコード開発によって、少ない開発スキルで多機能アプリを使えるようになる。Oracleは、統合、BPM、ビジネスルールのために別々のソフトを提供しており、またOracle Visual Builderはローコード開発サービスとして提供している。APEXユーザは、別ライセンスとREST原則*APIによってその機能を利用できる。この分離によって最善のサポートが得られるが、APEX利用者外は、別のコンフィグレーションのスキルが必要となろう。
- ビジネスモデル:
- Oracleは、APEXのコアエンジンとしてデータベースプラットフォームを使用しているので、APEXを使用するにはOracleのDBMSの使用に依存している。これは大きな市場として残る一方で、Oracle の市場シェアは減少している。とはいえOracleは、DBMS市場のリーダーであり、APEXは他言語のサポートや他のデータソースへのアクセスができるように拡張されてきている。
- イノベーション:
- APEXのロードマップは広範囲に亘るが、すでの他では一般的に利用可能なサーバ側のJavaScriptのサポート機能を追加しようと重点を置いている。SQLやPL/SQL*自体の学習は難しくないが、SQL 高速開発ツールとしての主な機能は、ほとんどのローコードユーザにとっては専門的な関心事である。Oracle Databaseプラットフォームの高度な機能にアクセスするには、一般的にSQLコードが必要である。
>Top 12. Oracle (Visual Builder)
- Oracle Visual Builder is a Visionary in this Magic Quadrant. Oracle is well-established in the database and business applications markets, as well as in Java Enterprise Edition (JEE) pro-code tooling. Its Visual Builder product is mainly focused on professional developers customizing Oracle SaaS products for multi experience*, as well as consumers of the wider Oracle Integration Cloud stack. Its operations are geographically diversified. Visual Builder provides services access and coordination with a multi experience front end. Oracle’s vision is of a unified DevOps and low- code stack, released recently as Visual Builder Platform. Oracle’s alternative LCAP offering — Oracle APEX — is based on its RBMS technology and is discussed separately in this research.
- Strengths:
- Overall viability: Oracle is a large and successful DBMS and SaaS vendor. The latter increasingly relies on Visual Builder as the primary development and extension mechanism, and Oracle SaaS is a major growth engine for Oracle. Therefore, Visual Builder will be increasingly employed for Oracle SaaS development and customization, and potentially for those customers constructing new SaaS.
- Product:Visual Builder includes the Oracle JET engine for mobile and web development, and provides ready access to multi experience UIs. The paradigm of event-driven “action chains” to provide advanced user experiences, on top of a full REST API and catalog access, alongside developer automation tooling (including DevOps and test-case generation) is instrumental in Oracle’s Visionary placement in this Magic Quadrant.
- Pricing:
Almost uniquely among the vendors presented in this Magic Quadrant, Oracle’s pricing for Visual Builder is resource-based and therefore dependent only on consumption — with no dependency on user counts or other metrics that can discourage adoption. This makes Visual Builder much more accessible for new use cases.
- Cautions:
- Market understanding:
Oracle’s policy of separating out specialist products for standard LCAP functions (such as business processes and often integrations) means that Visual Builder customers need to learn and license additional components for these capabilities. Indeed, the majority of Visual Builder users acquire it as a component of Oracle Integration Cloud (which itself is not an LCAP). This puts Visual Builder into the category of more specialist tooling compared with the more multifunction offerings that increasingly are embedding those capabilities.
- Marketing execution:
Oracle does not make much effort to market Visual Builder. Its recent release of Visual Builder Platform was communicated as a blog post, and Gartner inquiries for it are rare. So while Oracle appears to recognize the vision of SaaS plus PaaS, it seems reticent to promote itself in this area. It also fails to market the advantages and differences of its two separate LCAPs (see also Oracle APEX), likely causing reduced adoption.
- Platform ecosystem:
Visual Builder provides easy component access to its business objects and Oracle SaaS services, but Oracle does not promote a rich third-party ecosystem for its customers and partners to market to and share. This means that, despite an advantageous pricing model and multi experience capabilities, Oracle Visual Builder provides a less-rich target audience for potential OEMs.
12. Oracle (Visual Builder):
- OracleのVisual Builderは、この4象限評価では、Visionaryである。Oracleは、データベースとビジネス・アプリは、JEEのプロ・コード・ツールの分野同様に市場で定評がある。OracleのVisual Builderは、オラクルのSaaS製品をMulti experience*向けにカスタマイズするプロの開発者や、より広範なOracle Integration Cloud stackの消費者を主な対象としている。その事業は広範囲に展開している。Visual Builderは、サービスへのアクセスと連携をmulti experience として提供する。オラクルのビジョンは、統一されたDevOpsと低コストのコードスタックで、それは最近Visual Builder Platformとして公表された。オラクルが提供する別のLCAP製品であるOracle APEXは、RBMS技術をベースにしており、本調査では別途記述する。
- 強み:
- 全般的な実行力: Oracle社は、大規模で成功したDBMSおよびSaaSベンダーである。後者は、主要な開発および拡張メカニズムとして Visual Builder への依存度を高めており、Oracle SaaS は Oracle の主要な成長エンジンである。したがって、Visual Builderは、Oracle SaaSの開発とカスタマイズにますます採用されるようになり、新たなSaaSを構築する顧客にも採用される可能性がある。
- 製品: Visual Builderには、MobileおよびWeb開発用のOracle JETエンジンが搭載されており、multi experience・UIにすぐにアクセスできるようになっている。高度なUX*を提供するイベント駆動型の'Action chains'のパラダイムは、完全なREST API*とカタログ・アクセスに加えて、開発者の自動化ツール(DevOpsとテストケースの生成を含む)を備えており、Oracleがこの4象限評価でVisionaryに評価したのはそのためである。
- 価格政策: OracleのVisual Builderの価格設定は、リソースベースであるので、使用量に依存し、ユーザ数やその他指標には依存しない。このため、Visual Builderは新しいユースケースにも対応しやすくなっている。
- 留意事項:
- 市場の理解。標準的な LCAP 機能 (Business Procesや多くの統合など) のために専門製品を分離するというOracleの方針は、Visual Builder の顧客がこれらの機能のために追加のコンポーネントを学び、ライセンスを取得する必要があることを意味する。実際、Visual Builder ユーザーの大半は Oracle Integration Cloud (それ自体は LCAP ではないが)のコンポーネントとして Visual Builder を取得している。このため、Visual Builder は、これらの機能を組み込むことが多くなっている多機能製品と比較して、より専門的なツールに属している。
- マーケティング実績: OracleはVisual Builderの販売にあまり力を入れていない。最近リリースされたVisual Builder Platformはブログで紹介されただけで、Gartnerからの問い合わせにも回答なし。OracleはSaaSとPaaSの組み合わせという展望を認識しているが、この分野でのプロモーションには消極的なようだ。また、2つの独立したLCAP (Oracle APEXも参照) の利点や違いをアピールできておらず、採用率の低下を招いている。
- プラットフォーム・エコシステム: Visual Builderは、ビジネス・オブジェクトやオラクルのSaaSサービスへの容易なコンポーネント・アクセスを提供しているが、Oracleは、顧客やパートナーがマーケティングや共有を行うための豊富なサードパーティ・エコシステムを推進していない。即ち、有利な価格モデルとMult Experience機能を備えているにもかかわらず、Oracle Visual Builderは潜在的なOEMのターゲット層が少ない。
>Top 13. OutSystems
- OutSystems is a Leader in this Magic Quadrant. Its LCAP is the OutSystems platform, which supports cloud, on-premises and hybrid solutions. OutSystems focuses on enterprise application development for agile and continuous customer delivery. Its operations are primarily in Europe and North America, but it also has an increasing presence in APAC. Its customers mainly come from those regions and tend to be large enterprises across service, product and public sector organizations. OutSystems is enhancing its DevOps* and data management capabilities by adding builders for workflow and UX* to make development easier.
- Strengths:
- Application user experience: OutSystems UI is a built-in user interface framework containing multiple templates and UI patterns. It provides a comprehensive set of accessibility-ready, customizable app building components. The company’s Live Style Guide feeds from the branding and UI customizations that are specific to the customer and is used as a live library of UX patterns available for use by the developer. Customers can also create their own UI patterns from the ground up and reuse them.
- Developer persona and software development life cycle (SDLC*) support: Multipersona* developer experience provides a standards-based architecture that is secure and scalable. This ensures that all citizen-developed apps that are deployed are robust and can seamlessly be evolved by a pro developer as complexity increases. A full-stack visual low-code language helps facilitate knowledge transfer and promotes collaboration between nontechnical and pro developers in fusion teams.
- Architecture Applications can work with various services and data sources, both from OutSystems or from a range of on-premises or cloud-based services from third parties. This ensemble of services constitutes the data fabric*, providing loosely or strongly coupled APIs to perform transactions and data sources that enable the mash up of data across services. Through its Architecture Dashboard, OutSystems provides interdependency analysis and code pattern analysis across application components and versions.
- Cautions:
- Application development: While OutSystems has developed Workflow Builder to address the use case of citizen development, it is still not generally available. This new capability is yet to be proven, but is required for the vendor to catch up with other competitors that have more established offerings for citizen IT support.
- Process and business logic: OutSystems’ LCAP is increasingly used for automation of business processes and supports accelerators for data design including Excel import, as well as a relational model designer and a selection of templated schema*. However, it is not yet competitive in all aspects of process-centric application development, especially with regard to aspects such as complex decision modeling and process optimization.
- Product strategy: OutSystems tends to be favored by professional developers, rather than citizen developers, while most LCAPs target a more mixed developer persona. In the area of technical support, Gartner Peer Insights reviewers have been generally positive, but a few have given OutSystems comparatively low scores for the level of support provided.
13. OutSystems:
- OutSystemsは4象限評価のリーダーである. そのプラットフォームはクラウド、オンプレミス、ハイブリッドをサポートする。OutSystemsは、大企業アプリ開発を迅速に導入することに注力。主要市場は欧州と北米、だがアジア太平洋でも成長している。その顧客は民間・公共の製品・サービスに及ぶ。OutSystemsは、ワークフローやUX能力を通じて、DevOpsやデータ管理を改善する。
- 強み:
- アプリのUX: OutSystemsのUIは、組み込みのUIフレームワークで多様なテンプレートとUI型を持つ。普遍的なaccessibility-readyやカスタマイザブルアプリ構築コンポーネントを提供する。同社のLive Style Guideは、顧客毎のUIを提供し、UXのライブラリーとして開発に利用する。顧客は、自社のURタイプを作成して再利用できる。
- SDLCのサポート: 多様な顧客の経験によってスケーラブルなアーキテクチャを提供。Citizen開発のアプリでも堅牢シームレスで、プロ開発によって進化させることを可能にする。ローコード言語は、知識移転や非技術やプロ開発者の混合チームでの協力を支援する。
- アーキテクチャアプリは、OutSystemsや第三者のオンプレミスやクラウドからの多様なサービスやデータソートと一緒に機能する。いわゆるData fabric*を構成し、APIを提供し、データソース間の移動やmash upを可能にする。そのArchitecture Dashboardを通じて、アプリやバージョンのコードパターンなどの分析を提供する。
- 留意点:
- アプリ開発: OutSystemsは、Workflow Builderを開発して、また一般的になっていないCitizen開発に着目してきた。この新たな機能は未知数だが、Citizen開発者支援としては他競合製品に追いつくことが期待される。
- プロセスとビジネスロジック: OutSystems社のLCAPは、ビジネスプロセスの自動化のために使用されることが多くなっており、Excelのインポートを含むデータ設計のためのアクセラレータや、リレーショナルモデルデザイナー、Template Schema*の選択をサポートしている。しかし、プロセス中心のアプリ開発のすべての側面、特に複雑な意思決定モデルやプロセス最適化などの側面ではまだ競争力がない。
- プロセス・ビジネスロジック: OutSystemsのローコード開発は、ビジネスプロセスの自動化に利用され、Excelからの移行やRDB設計者やtemplated schemaの選択など。但し、現状では、プロセス中心のアプリ開発、とっくに複雑な意思決定モデリングやプロセス最適化の面での競争力はまだない。
- 製品戦略:
OutSystemsのローコード開発は多様な顧客を対象にしているものの、Citizen開発者というようりプロの開発者に人気がある。Gartnerの評価でも上昇してきているが、まだ一部には低レベル評価に留まっている面もある。
>Top 14. Pega:
- Pega (Pegasystems) is a Visionary in this Magic Quadrant. Its LCAP is a component of the Pega Infinity platform, which offers built-in iBPMS*, MXDP*, CRM and RPA capabilities. Pegasystems has operations across the world and a focus on large enterprise customers. Pega Infinity is mainly aimed at business process automation that requires web, mobile and conversational apps. Pega has invested in making its platform micro services-based* and enhancing its serverless messaging. Its roadmap includes a complete UI upgrade and a desktop application focused on nontechnical business users. Additionally, the vendor has announced a serverless and distributed process management solution.
- Strengths:
- Overall viability: Pega has grown steadily as a public company for many years and the Pega Infinity platform has a solid track record. Pega also has a large ecosystem that includes a broad array of implementation partners with strong business and industry capabilities across the world. It has a strong North American presence and a rapidly increasing customer base in Europe and APAC. Prospective customers should feel confident about the viability of Pega and its platform.
- Innovation: Pega has introduced Process Fabric, a business portal to coordinate user access to processes and applications. It also provides a UI design system and was an early provider of citizen developer governance tooling.
- Product offering: Pega Infinity extends its LCAP with process-driven development, case management, augmented analytics*, rules management and RPA services. This combination of included technologies is attractive to large enterprises that want end-to-end, intelligent and event-driven process automation. Pega enables unified multipersona* developer experiences with Pega App Studio and Dev Studio. It also supports other user roles such as data scientists with Prediction Studio.
- Cautions
- Product strategy: Pega’s marketing efforts have yet to succeed in redefining the Pega brand for the LCAP market. Pega built a product strategy centering around its flagship process platform, and most of its customers use Pega Infinity for end-to-end complex process automation that depends on sophisticated iBPMS* needs. Pega’s focus on combining too many different features catering to different markets is confusing and dilutes its focus on the needs of LCAP buyers.
- Sales execution and pricing: Users of Gartner’s client inquiry service that are also Pega customers talked about an unpredictable utility pricing model often resulting in higher than expected cost of operations. They also mentioned additional budget requirements for significant professional services to ensure successful deployment.
- Business model: Pega’s business model supports a large, if declining, consulting business to help customers fully implement its major features. In addition, Pega’s pricing involves add-on fees for some abilities, such as AI assistance for developers and disconnected mobile support. That this can result in relatively high per-user pricing is confirmed by users of Gartner’s client inquiry service.
14. Pega:
- Pegaは、4象限評価ではVisionaryである。そのローコードはPega Infinity platformであり、組み込まれたiBPMS*, MXDP*, CRM, RPA機能を提供する。Pegasystemsは、世界中で大企業中心に展開している。特に、Web, Mobile、従来のアプリ対象にビジネスプロセス自動化に注力している。Pegaは、マイクロサービスベース*のプラットフォームやサーバレスメッセージングに投資してきた。その工程表は、UIの向上やデスクトップアプリを非技術者向け開発を重視して、サーバレスや分散プロセス管理を発表している。
- 強み:
- 展望: Pegaは、上場企業として着実に成長してきており、そのPega Infinity platformは確実に浸透してきている。また世界中にビジネスパートナーを広範に含むエコシステムを持っている。北米には強固な拠点が、また欧州やアジア太平洋でも急速に顧客を増やしており顧客にとっても頼りがいがある。
- イノベーション: Pegaは、ユーザがプロセスとアプリを連携させるビジネスポータルとしてProcess Fabricを導入した。それはUIデザインシステムを初期のCitizen開発者のガバナンスツールとして提供する。
- 製品提案: Pega Infinityは、ローコード開発によるプロセス重視、ケース管理、拡張分析、ルール管理、RPAサービスの導入を促進する。これら技術の組合せは大企業のインテリジェントやイベント起動プロセス自動化などの要求に合致している。Pegaは、Pega App StudioやDev Studioによって多様な開発経験を可能にする。さらにPredicition Studioによってデータサイエンティストをサポートする。
- 留意点
- 製品戦略: Pegaブランドは、ローコード開発市場はまだマーケティングの努力が成功していない。Pegaは、プロセスプラットフォームを中心の製品戦略を構築し、多くの顧客はPega Infinityを使ってiBPMSの要求に基づく複雑なプロセス自動化に利用した。
- 価格政策: Pegaの顧客の声として、予想より高い運用費用を生じるユーティリティ価格モデルについて話題にしていた。さらにシステム配備のプロフェッショナルサービスに対する追加予算にも言及した。
- ビジネスモデル: Pegaのビジネスモデルは、顧客フルに支援するコンサルティングビジネスが特徴である。さらにPegaの価格は、AIやMobileサポートは別料金としてAdd-onされる。これらが相対的にユーザ当たりの価格上昇になっている。
>Top 15. Pronto Forms:
- ProntoForms is a Niche Player in this Magic Quadrant. Its LCAP is the ProntoForms platform, which offers no-code development tools for building mobile apps and web forms that can be deployed on a Universal Windows Platform (UWP) app. It has added more support for customer- facing forms and adjusted its pricing to support site licensing for larger deployments. ProntoForms has offices in Canada, and most of its customers are in North America. Its customers span a variety of industries but are focused on field service and frontline work.
- Strengths
- Application development: The ProntoForms platform has an intuitive no-code, web-based tool that uses a drag-and-drop approach to app building — ideally suited to nontechnical citizen developers. It focuses on mobile app development and offers robust capabilities in this area, such as offline data synchronization, bar code scanning, push notifications and SMS support.
- Vertical strategy: Pronto Forms targets the app requirements of field service and frontline worker for its LCAP. It has a strategic partnership and integration with ServiceMax. It is also one of the few LCAPs that supports Windows client application and UWP apps, which are still utilized by field service organizations.
- Sales execution and pricing: ProntoForms has shown good growth numbers in terms of new customers added, although most of these are smaller enterprises. Its pricing model is relatively simple based on its B2E focus, and is based on either the number of users, the volume of transactions, or an enterprise site license based on large numbers of users.
- Cautions
- Product strategy:
Although Pronto Forms has demonstrated success in its targeting of field service apps for its LCAP, its over all strategy is lagging many of the vendors featured in this Magic Quadrant. For example, it lacks any significant presence outside of North America, only deploys on AWS, and does not support headless, API-driven services on its platform. Companies that need multi cloud support or to create headless applications may find better options elsewhere.
- Innovation:
Compared with other vendors in this Magic Quadrant, ProntoForms has not shown significant innovations in its LCAP. Advanced capabilities such as AI-augmented development, integrated multi persona* developer experience, and governance capabilities for citizen development and collaboration are lacking — and are also not evident on ProntoForms’ immediate roadmap. Companies needing more advanced functionalities should evaluate other vendors in this Magic Quadrant.
- Operations:
ProntoForms mainly operates in North America, and while it has customers in other parts of the world, Gartner does not see the company being competitive outside this geography. It also lacks service implementation partners to help deliver applications if needed. In Gartner Peer Insights reviews, ProntoForms’ lowest score was for quality and availability of end-user training. For these reasons, companies should carefully evaluate the fit of its operational resources.
15. Pronto Forms:
- ProntoFormsは、この4象限評価におけるNiche Playerである。同社のLCAPはProntoFormsプラットフォームで、Mobileアプリや Universal Windows Platform (UWP) アプリに展開できるWebフォームを構築するためのコードレス開発ツールを提供している。ProntoFormsは、顧客向けフォームのサポートを強化し、大規模な導入のためのサイトライセンスをサポートするように価格を調整した。ProntoFormsは、カナダに事務所を構え、顧客の多くは北米にいる。同社の顧客はさまざまな業界に亘っているが、field serviceや現場の仕事に重点を置いている。
- 強み:
- アプリ開発: ProntoFormsプラットフォームには、コードを使わない直感的なWebベースのツールがあり、Citizen開発者に理想的なDrag &Drop方式でアプリを構築することができる。Mobileアプリの開発に重点を置き、オフラインでのデータ同期、バーコード・スキャン、プッシュ通知、SMSサポートなど、この分野で強力な機能を提供している。
- 垂直展開: Pronto FormsのLCAPは、フィールドサービスや現場作業員のアプリ要件をターゲットにしている。ServiceMax社との戦略的パートナーシップとの統合を実施している。また、Field service企業で利用されているWindowsクライアントアプリケーションやUWPアプリをサポートしている数少ないLCAPの一つである。
- 販売の実行と価格設定: ProntoFormsは、新規顧客の増加という点では良好な成長を示しているが、ほとんどが中小企業。価格モデルは、B2Eに特化した比較的シンプルなもので、ユーザー数、トランザクション量、または大規模なユーザー数の企業サイトライセンスのいずれかである。
- 留意点:
- 製品戦略: Pronto Formsは、LCAPでフィールドサービスのアプリをターゲットにして成功を収めているが、その全体戦略は、この4象限評価の多くのベンダに遅れをとっている。例えば、Pronto Formsは、北米以外では大きな存在感がなく、AWSでしか展開しておらず、プラットフォーム上でヘッドレスやAPI駆動のサービスをサポートしていない。マルチクラウドへの対応やヘッドレスアプリケーションの構築を必要とする企業は、他の選択肢の方が良いかも知れない。
- イノベーション:
この4象限評価の他のベンダーと比較において、ProntoFormsはLCAPで大きなイノベーションを示していない。AIを活用した開発、統合されたマルチペルソナ*の開発者エクスペリエンス、市民の開発とコラボレーションのためのガバナンス機能などの高度な機能が不足しており、ProntoFormsの当面のロードマップにも見られない。より高度な機能を必要とする企業は、この4象限の他のベンダーを評価すべきである。
- オペレーション: ProntoForms は主に北米で事業を展開しており、世界の他の地域にも顧客を持っているが、この地域以外では同社が競争力を持っていないと見ている。また、必要に応じてアプリを提供するためのサービス提供パートナーも不足している。Gartner Peer Insights のレビューで、ProntoForms のスコアが最も低かったのは、エンドユーザ・トレーニングの品質と利用可能性であった。これらの理由から、企業は自社の運用リソースの適合性を慎重に評価する必要がある。
>Top 16. Quick Base
- Quick Base is a Niche Player in this Magic Quadrant. Its LCAP is the Quick Base platform, which offers low-code integration, workflow and app development capabilities underpinned by a proprietary in-memory database. The vendor acquired Cloud pipes in 2019, and that technology is released as Quick Base Pipelines. Quick Base has offices mainly in the U.S., but has an emerging presence in Bulgaria for European operations. The majority of its customers are in North America, with a small percentage in EMEA and APAC. Its customers span a variety of industries, but the manufacturing and professional services segments make up a high proportion of its business.
- Strengths
- Market understanding:
Quick Base has started to expand beyond its citizen development focus by targeting more complex application use cases and enterprise IT organizations. Its acquisition of Cloud pipes has further expanded its integration and automation capabilities, which are important in this market. Quick Base’s LCAP is now more prepared to help unite business and IT teams to integrate and build workflow-driven business applications.
- Application development:
Quick Base’s LCAP has a strong focus on ease of use for the developer experience. Now, with its Pipelines component, it has added no-code integration and automation features. Adding business logic can be done visually through triggers or actions, but can be also scripted for more complex use cases.
- Customer support:
Quick Base garners a relatively high score for service and support in Gartner Peer Insights reviews. In particular, its quality of technical support, which is included with its base offering, received high marks. Quick Base now also offers 24/7 support for international customers.
- Cautions:
- Geographic strategy: Expansion beyond North America is still a work in progress for Quick Base. It will not have extended its data centers outside of the U.S. into Europe until later in 2020, lagging many of the vendors in this Magic Quadrant. Quick Base has established an R&D center in Bulgaria, but its go-to-market strategies are still in development through service partner channels. Also, it is working on improvements in the platform to support internationalization and regional requirements around the world.
- Ecosystem: Quick Base has a public application exchange where customers, developers and partners can share apps an d solution components. However, the site can be difficult to navigate, and many of the applications serve the needs of small businesses.
- Innovation: Over the past year, Quick Base has solidified its operations, but still lags behind many in innovation. The acquisition of Cloud pipes has provided a catchup on integration and workflow features, but the vendor’s LCAP trails competitors that have already added AI assistance to their tooling, advanced mobile app capabilities, and multipersona developer support.
16. Quick Base:
- Quick Baseは、この4象限評価ではニッチプレーヤである。そのLCAPはQuick Base platformで、独自のインメモリーデータベースに支えられたローコードのインテグレーション、ワークフロー、アプリ開発機能を提供している。同ベンダーは2019年にCloud pipesを買収し、その技術はQuick Base Pipelinesとしてリリースしている。Quick Baseは主に米国に事務所があるが、欧州事業のためにブルガリアにも拠点を設けている。顧客の大半は北米にあり、中東アフリカとアジア太平洋に亘っており、製造業とProfesional serviceの分野が高い割合を占めている。
- 強み:
- 市場の理解:Quic Baseは、市民向けの開発を中心とした事業から、より複雑なアプリのユースケースや企業のIT組織をターゲットにした事業へと拡大を始めている。Cloud pipesの買収により、この市場で重要な統合と自動化の能力がさらに拡大した。Quick BaseのLCAPは、ビジネスチームとITチームを統合し、ワークフロー主導型のビジネスアプリを構築するための支援を行っている。
- アプリ開発: Quick BaseのLCAPは、開発者の使いやすさを重視している。今回のPipelinesコンポーネントでは、ノーコードでの統合と自動化の機能が追加された。ビジネスロジックの追加は、トリガーやアクションを使って視覚的に行うことができるが、より複雑なユースケースの場合はスクリプトで行うこともできる。
- カスタマーサポート: Quick Baseは、Gartner Peer Insightsのレビューにおいて、サービスとサポートに関して比較的高い評価を得ている。特に、基本サービスに含まれるテクニカルサポートの品質が高く評価されている。Quick Baseは、海外の顧客にも24時間365日のサポートを提供している。
- 留意点:
- 地理的な戦略: Quick Baseは、北米以外の地域への進出はまだ途上にある。米国外のデータセンターを欧州に拡張するのは2020年後半になる予定で、この4象限評価のベンダーの多くに遅れをとっている。Quick BaseはブルガリアにR&Dセンターを設立したが、サービス・パートナー・チャネルを通じた市場参入戦略はまだ開発中。また、国際化や世界中の地域的な要件をサポートするために、プラットフォームの改善に取り組んでいる。
- エコシステム: Quick Baseには、顧客、開発者、パートナーがアプリやソリューション・コンポーネントを共有できる公開アプリ・エクスチェンジがある。しかし、このサイトは操作が難しく、アプリの多くは小企業のニーズに対応したものとなっている。
- イノベーション: 過去1年間、Quick Baseは事業を強化してきたが、イノベーションの面ではまだ多くの企業に遅れをとっている。Cloud pipesの買収により、統合やワークフローの機能では追いついたものの、このベンダのLCAPは、ツールでのAI支援、高度なモバイルアプリ機能、Multi persona*の開発者サポートなどですでに追加している競合他社に遅れをとっている。
>Top 17. Salesforce
- Salesforce is a Leader in this Magic Quadrant. Its Salesforce Platform is broadly focused on development of business applications of various levels of complexity, use cases and developer skills. Its operations are global, and its LCAP clients tend to be large enterprises across industries with existing investments in Salesforce solutions. The company’s strategy is to expand its LCAP support for integration, orchestration and composition, and to unify its runtime technologies for shared development and governance.
- Strengths
- Overall viability: The continuing strong growth of the overall Salesforce business, and its industry-leading ecosystem of partners, provide strong drivers for adoption of the company’s LCAP offering. Well-executed business leadership enables the company to grow through acquisitions without disrupting its core investments in customer experiences.
- Business model: The continuing popularity of Salesforce SaaS offerings with both existing and new customers has formed a strong channel for the company’s platform services, including its LCAP. Hundreds of native AppExchange partner applications have extended the Customer 360 Platform. Most customers of Salesforce SaaS or AppExchange-delivered, partner-built SaaS use Salesforce Platform capabilities to extend and customize the application experiences.
- Innovation: Salesforce is building a unified development and governance environment that bridges multiple Customer 360 Platform technology stacks (Heroku and Apex). This promises to deliver a broad, multipersona development experience that empowers customers of different skills to operate based on shared IT goals within business-IT fusion teams. New mobile features in Salesforce Platform have also advance Salesforce’s multi experience capabilities.
- Cautions
- Architecture: The fundamental architecture of the Salesforce Platform (formerly Force.com) differs from the newer forms of distributed-cloud-native infrastructure. Modernizing it without affecting customers may be a challenge and business users may face new requirements for maintenance of their production applications.
- Integration:Despite the acquisition of MuleSoft in 2018, Salesforce’s LCAP is still lacking low- code support for integration and API management, and its process management is relatively limited. Both of these abilities are essential to modern application design and delivery.
- Market strategy: The vast majority of Salesforce Platform users a real sousers of Salesforce CRM, and most of them rely on CRM data in their new applications. Because of this, Salesforce Platform remains mostly applicable to clients using Salesforce SaaS.
17. Salesforce:
- Salesforceは、この4象限評価のリーダーである。同社のSalesforceプラットフォームは、様々なレベルの複雑さ、ユースケース、開発者のスキルを持つビジネスアプリの開発に幅広く対応しています。同社はグローバルに事業を展開しており、LCAPの顧客は、Salesforceソリューションに既存の投資を行っている様々な業界の大企業が多い。同社の戦略は、統合、オーケストレーション、コンポジションのためのLCAPサポートを拡大し、開発とガバナンスを共有するためにランタイム技術を統一することである。
- 強み:
- 全体的な展望: Salesforceの事業全体の継続的な力強い成長と、業界をリードするパートナーのエコシステムは、同社のLCAPサービスを採用するための強力なドライバーとなっている。ビジネスリーダーシップがうまく機能しているため、顧客体験に対する中核的な投資を妨げることなく、買収による成長が可能となっている。
- ビジネスモデル:SalesforceのSaaS製品は、既存顧客と新規顧客の両方から継続的に支持されており、LCAPを含む同社のプラットフォームサービスの強力なチャネルとなっている。何百ものネイティブAppExchangeパートナーのアプリがCustomer 360 Platformを拡張している。Salesforce SaaS または AppExchange で提供されたパートナーが構築した SaaS の顧客のほとんどは、Salesforce プラットフォームの機能を使用して、アプリ体験の拡張やカスタマイズを行っている。
- イノベーション: Salesforceは、Platformテクノロジースタック (HerokuおよびApex) をつなぐ、統一された開発およびガバナンス環境を構築している。これにより、様々なスキルを持つ顧客が、現業とIT部門の混合チームの中で共有されたIT目標に基づいて業務を行うことができ、幅広いマルチペルソナの開発体験を提供している。また、Salesforce Platformの新しいモバイル機能は、Salesforceのマルチエクスペリエンス機能を進化させた。
- 留意事項:
- アーキテクチャ: Salesforce Platform (旧Force.com) の基本的なアーキテクチャは、新しい形態の分散クラウド・ネイティブ・インフラストラクチャとは異なる。顧客に影響を与えずに最新化することは難しいかもしれないが、ビジネスユーザーは本番アプリの保守のために新たな要求に直面するかも知れない。
- 統合: 2018年にMuleSoftを買収したにもかかわらず、SalesforceのLCAPは統合とAPI管理のためのローコードサポートがまだ不足しており、プロセス管理も比較的限定されている。これらの能力はいずれも、現代のアプリケーションの設計と提供に不可欠なものである。
- 市場戦略: Salesforce Platform のユーザの大半は、Salesforce CRMを実際に利用しており、そのほとんどが新しいアプリで CRM データを利用している。そのため、Salesforce Platformは、Salesforce SaaSを利用している顧客に多く適用可能である。
>Top 18. ServiceNow
- ServiceNow is a Leader in this Magic Quadrant. Its Now Platform App Engine (Orlando release) is broadly focused on customizing ServiceNow SaaS and building new enterprise workflow applications. ServiceNow’s operations are geographically diversified and its clients tend to be enterprise scale. In the past year, the vendor has created a Guided App Creator for citizen developers, introduced the new Now Design System and user experience, and improved its chatbot services. ServiceNow is expected to add more process, automation and citizen development support in forthcoming releases, and continue to enhance its related integration and AI products.
- Strengths:
- Overall viability: Service Now is a popular SaaS provider whose Now Platform supports both its SaaS and App Engine; the latter is both developed and used by its own developers. ServiceNow’s continued strong year-over-year growth (31%) makes it a low-risk selection as an LCAP vendor.
- Innovation: ServiceNow was among the first to deliver an integration platform for LCAP users (Integration Hub) and provide asset management and real-time monitoring. These are IT service management requirements that have driven wider platform development, but are also useful for other workflow applications. The vendor’s future roadmap includes new automation and metrics design abilities that are usually the domain of BPMS and enterprise architecture vendors.
- Platform ecosystem: ServiceNow has encouraged third parties (including IBM) to deliver the ServiceNow applications that now make up nearly one-third of new business for App Engine. As well as the usual common data model abilities, there is an app store supported by 700 software vendors and a component store serving 400,000 registered developers.
- Cautions:
- Sales execution and pricing: ServiceNow is on its third pricing model in as many years, as it struggles to identify the ideal formula for customer value. Gartner Peer Insights scores for its evaluation and contract negotiation are at the low end of the range for vendors in this Magic Quadrant. App Engine customers need to be wary of some separate, additional costs such as premium connectors for Integration Hub, but other services like Now Intelligence (AI) are included in the price.
- Marketing strategy: ServiceNow has traditionally marketed it self as a SaaS- first vendor with LCAP as a means of customization or extension of its SaaS offerings, with its LCAP providing more of a SaaS customization service. Its recent platform-first initiative, which highlights Now Platform and the services that run on it, may correct this in future, but a client based entirely on App Engine is still rarely seen by Gartner.
- Process and business logic: While App Engine increasingly competes with iBPMS for business workflows, its Flow Designer has been considered less graphical than many of its competitors. This can make application complexity more difficult to understand, but a new Process Automation Designer from Summer 2020 will improve its usability.
18. ServiceNow:
- ServiceNowは、この4象限評価のリーダーである。同社のNow Platform App Engine (Orlandoリリース) は、ServiceNow SaaSのカスタマイズや新しいエンタープライズ・ワークフロー・アプリの構築に幅広く対応している。ServiceNowの事業は地理的に分散しており、その顧客は大企業が多い。この1年で同ベンダーは、Citizen開発者向けのGuided App Creatorの作成、新しいNow Design SystemとUX*の導入、チャットボットサービスの改善などを行った。ServiceNowは、今後のリリースでプロセス、自動化、Citizen開発のサポートをさらに追加し、関連する統合製品やAI製品の強化を続けていくとみられる。
- 強み:
- 全体的な展望: Service Nowは人気の高いSaaSプロバイダーで、Now PlatformはSaaSとApp Engineの両方をサポートし、App Engineは自社の開発者が開発して使用している。サービスナウは、前年比で31%という高い成長率を維持しており、LCAPベンダーとしてはリスクの低い選択である。
- イノベーション: ServiceNowは、LCAPユーザのための統合プラットフォーム(Integration Hub)をいち早く提供し、資産管理とリアルタイム・モニタリングを実現した。これらはITサービス管理の要件であり、プラットフォームの開発を促進してきたが、他のワークフローアプリにも有用である。このベンダの将来のロードマップには、通常はBPMSやエンタープライズ・アーキテクチャーのベンダの領域である新しい自動化やMetrics設計の能力が含まれている
- プラットフォームのエコシステム:ServiceNowは、IBMを含むサードパーティにServiceNowのアプリを提供することを進めており、現在、App Engineの新規ビジネスの1/3を占めている。通常の共通データモデル機能に加えて、700社のソフトウェアベンダがサポートするアプリストアと、40万人の登録者が利用するコンポーネントストアがある。
- 留意点:
- 販売の実行と価格政策: ServiceNowは、過去数年間で3つ目の価格設定モデルを採用し、顧客価値を高めるための理想的な方法を見出すのに苦慮している。その評価と契約交渉に関するGartner Peer Insightsのスコアは、この4象限評価のベンダーの中では低い方。App Engine利用の顧客は、Integration Hubのプレミアムコネクタなど、別途追加費用が発生することに注意する必要があるが、Now Intelligence (AI) のような他のサービスは価格に含まれている。
- マーケティング戦略: ServiceNowは従来、SaaS-firstトのベンダとして自社を売り込み、LCAPはSaaSのカスタマイズや拡張の手段として提供してきたが、LCAPはどちらかというとSaaSのカスタマイズサービスを提供している。最近のPlatform-firstの取り組みでは、Now Platformとその上で動作するサービスを強調しているため、将来的にはこの点が修正されるかもしれないが、App Engineのみをベースにした顧客はほとんど見られない。
- プロセスとビジネスロジック: App Engineは、ビジネスワークフロの分野でiBPMSとの競争激化しているが、そのフローデザイナーは、多くの競合他社に比べてグラフィカルではないと考えられてきた。そのため、アプリの複雑さを理解するのが難しくなっているが、2020年夏からの新しいプロセス自動化デザイナーにより、その使い勝手が改善される予定である。
>Top 19. TrackVia
- TrackVia is a Niche Player in this Magic Quadrant. Its LCAP product is mainly focused on low-cost, process-driven citizen development. Its operations are mostly in the U.S. and Europe, and its clients tend to be small to midsize companies with less than 1,000 employees targeting B2B applications. TrackVia focuses on simplicity of development and targets replacing Microsoft Excel as a typical use case. Its roadmap includes better support for offline use, UI updates and enhanced workflow support.
- Strengths
- Market understanding: Track Via is a small vendor that understands the need to focuson key strengths, which in its case means low-code solutions for specific markets and use cases. For TrackVia, this includes a focus on financial services, manufacturing and cannabis production. The latter clearly indicates the company’s ability to react to new and niche market conditions and scenarios.
- Application development: TrackVia provides alow-cost platform focusing on ease of development that can deliver sophisticated applications involving web, mobile and business processes. It can provide mobile solutions for field operations and exploits Apache Groovy for extensions.
- No-code application development: TrackVia’s focuson simplicity of application development using a low-code, process-centric approach enables it to address citizen, business unit and IT development.
- Cautions
- Overall viability: TrackVia has been acquired by Primus Capital, a private equity company. Its size and growth are at the bottom end of the inclusion criteria for this Magic Quadrant. Customers need to understand that this combination may force TrackVia to change strategy in future, although at this time there is no change.
- End-user experience: TrackVia provides a BPM-type,portal-style user experience for all applications or processes that are allocated to the user. This lack of application independence may be a limitation for some use cases, although TrackVia is planning to improve the UI according to its roadmap.
- Product strategy: TrackVia eschews the need for an app store or template ecosystem,which limits the LCAP platform’s ability to evolve to the capacity of TrackVia to deliver improvements internally, and discourages reuse across different teams. While TrackVia is exploring some advanced topics like AI-assisted development, it is less advanced in supporting AI functions for data stored on the system or explicitly supporting multiple developer personas.
19. TrackVia
- TrackViaは、この4象限評価ではNiche Playerである。同社のLCAP製品は、主に低コストでプロセス駆動型のCitizen開発に焦点を当てている。同社は主に米国と欧州で事業展開しており、顧客はB2Bアプリを対象とした従業員数1,000人未満の中小企業が多い。TrackViaは、開発の簡易性を重視し、Microsoft Excelの置き換えを典型的なユースケースとしている。ロードマップには、オフラインでのサポート、UIの更新、ワークフローのサポートの強化などが含まれている。
- 強み:
- 市場理解: TrackViaは小規模ベンダであり、重要な強みに集中する必要性を理解している。それは、特定の市場やユースケースに対するローコードソリューションを意味する。TrackViaの場合、これは金融サービス、製造業、Cannabis生産に焦点を当てていることを意味する。後者は、新たなニッチ市場の状況やシナリオに対応する同社の能力を明確に示している。
- アプリ開発: TrackViaは、開発のしやすさを重視した低コストのプラットフォームを提供しており、Web、Mobile、ビジネスプロセスを含む洗練されたアプリを提供することができる。また、フィールドオペレーション用のモバイルソリューションを提供することができ、拡張機能としてApache Groovyを利用している。
- ノーコードのアプリ開発: TrackViaは、ローコード、プロセス中心のアプローチを用いてアプリ開発を簡素化することで、Citizenや事業部門、IT部門での開発に対応している。
- 留意点:
- 総合的な展望: TrackViaは、私企業であるPrimus Capitalに買収された。その規模と成長性は、この4象限評価の下端に位置している。現時点では変化はないが、この組み合わせにより、将来的にTrackViaの戦略が、変更を余儀なくされる可能性があることを顧客は理解する必要がある。
- エンドユーザ・エクスペリエンス : TrackViaは、ユーザに割り当てられたすべてのアプリやプロセスに対して、BPM型、ポータル型のユーザー・エクスペリエンスを提供している。このアプリの独立性の欠如は、いくつかのユースケースでは制限となるかもしれないが、TrackViaはロードマップに沿ってUIの改善を計画している。
- 製品戦略: TrackViaはアプリストアやテンプレートエコシステムの必要性を排除しており、LCAPプラットフォームの進化はTrackViaが社内で改善を行う能力によって制限され、異なるチーム間での再利用が妨げられる。TrackViaはAIによる開発支援などの先進的なテーマに取り組んでいるが、システムに蓄積されたデータに対するAI機能のサポートや、多数の開発者のペルソナを明確なサポートはあまり進んでいない。
>Top 20. Zoho
- Zoho is a Visionary in this Magic Quadrant. Primarily a SaaS vendor for SMEs, its LCAP offering — Zoho Creator — is focused on enabling citizen and professional developers to build business applications faster. Its operations are global, and most of its customers are smaller organizations in North America and the EMEA region. Zoho added a process blueprint design capability and data AI services in 2019, and also provides separately a serverless function PaaS for extending Creator applications. The vendor is expecting to add RPA, more collaborative development features, a test automation suite, and AI-augmented application development support.
- Strengths
- Product: Zoho Creator is a mature platform that supports diverse developer person as for multi experience application development. To empower nontechnical citizen developers, it provides graphical process, data and UI designers. For professional developers, it provides a low-code application development language, Deluge, along with support for Java, JavaScript, XPath and Node.js. Its comprehensive feature set is comparable with the largest LCAP vendors included here.
- Market understanding: Zoho has long acknowledged the need for, and role of, low-code development for its customers, and the need for business applications outside of its SaaS offerings. Zoho provides enterprise-class features such as multi region and multi cloud/on- premises deployments and backups, vertical and horizontal auto scaling, and rich application performance monitoring. It also plans to add the necessary governance abilities to establish developer guardrails to administer fusion teams.
- Innovation: Zoho displays an innovative focus on the LCAP market with its existing AI features, together with serverless functions for pro-code extensions. Its process blueprint is indicative of the merger of business-process-centric and low-code development features. Zoho’s roadmap is extensive compared with other vendors in this Magic Quadrant, and addresses automation (including RPA), multi experience (including augmented and virtual reality), collaboration, testing and governance.
- Cautions
- Business model: Zoho remains entrenched in the smaller enterprise market, despite its enterprise features, and is largely unseen in larger Gartner clients. It supports customers with a relatively small professional services arm for application delivery, and is still in the early stages of attracting large solution provider partners, although it does have many smaller partners.
- Marketing execution: Zoho’s marketing reflects its business mode land lacks visibility with potential enterprise customers. It has invested in promotional activities including events (Zoholics) and content (Decode), but as yet has struggled to increase its mind share among enterprise customers for LCAP.
- Process and business logic: While Zoho Creator provides visual process and decision models, it does not support the relevant enterprise standards such as BPMN that would allow collaboration with other enterprise tooling. However, it plans to add more BPMN-based elements and practices to the platform in future, and supports business logic in serverless functions.
20. Zoho:
- Zohoは、この4象限評価ではビジョナリーである。主に中小企業向けのSaaSベンダーである同社のLCAP製品であるZoho Creatorは、市民やプロの開発者がビジネス・アプリを迅速に構築できるようにすることに注力している。また、同社はグローバルに事業を展開しており、顧客の多くは北米や中東アフリカ地域の中小企業である。Zohoは、2019年にプロセス・ブループリント・デザイン機能とデータAIサービスを追加し、Creatorアプリを拡張するためのサーバーレス機能のPaaSも別途提供している。同ベンダーでは、RPAや共同開発機能の充実、テスト自動化スイート、AIによるアプリケーション開発支援などの追加を見込んでいる。
- 強み:
- 製品: Zoho Creatorは、多様な開発者をサポートする成熟したプラットフォームであり、Multi Experience*・アプリの開発を可能にする。非技術のCitizen開発者のために、グラフィカルなプロセス、データ、UIデザイナーを提供している。プロのIT開発者には、ローコードのアプリ開発言語 Deluge を提供し、Java, JavaScript, XPath, Node.js をサポートしている。その包括的な機能セットは、ここに含まれる最大のLCAPベンダに匹敵します。
- 市場の理解: Zoho は、顧客にとってのローコード開発の必要性と役割、そして SaaS 以外のビジネス・アプリの必要性を長い間認めてきた。Zoho は、複数の地域、複数のクラウドとオンプレミスへの展開とバックアップ、垂直・水平方向の自動ス ケーリング、豊富なアプリ・パフォーマンス・モニタリングなど、企業向けクラスの機能を提供してい る。また、開発者のガードレールを確立し、混合チームを管理するために必要なガバナンス機能を追加する予定である。
- イノベーション: Zohoは、既存のAI機能に加えて、プロコード拡張のためのサーバーレス機能を備え、LCAP市場に革新的な焦点を当てている。そのプロセス・ブループリントは、ビジネス・プロセス中心とローコード開発機能の融合を示している。Zohoのロードマップは、この4象限評価の他のベンダに比べて広範囲であり、自動化(RPAを含む)、マルチ・エクスペリエンス(拡張現実と仮想現実を含む)、コラボレーション、テスト、ガバナンスに取り組んでいる。
- 留意点:
- ビジネスモデル: Zohoは、企業向けの機能を備えているにもかかわらず、中小企業市場での地位を確立しており、Gartnerの大企業の顧客にはほとんど見られない。アプリ・デリバリーのための比較的小さなプロフェッショナル・サービス部門で顧客をサポートしており、大規模なソリューション・プロバイダのパートナーを獲得するには時期尚早の段階にあるが、小規模なパートナーは多く抱えている。
- マーケティングの実施状況: Zohoのマーケティングは、そのビジネスモードを反映しており、潜在的な企業顧客に対する認知度が低い。イベント(Zoholics)やコンテンツ(Decode)などのプロモーション活動に投資しているが、LCAPの企業顧客でのシェア拡大には苦戦しているようだ。
- プロセスとビジネスロジック: Zoho Creatorは、プロセスや意思決定のモデルを視覚的に提供しているが、BPMNのような他の企業ツールとの連携を可能にするような企業標準をサポートしていない。しかし、将来的にはBPMNベースの要素やプラクティスをプラットフォームに追加し、サーバーレス機能でビジネスロジックをサポートすることを計画している。
>Top 21. Vendors Added and Dropped
- We review and adjust our inclusion criteria for Magic Quadrants as markets change. As a result of these adjustments, the mix of vendors in any Magic Quadrant may change over time. A vendor’s appearance in a Magic Quadrant one year and not the next does not necessarily indicate that we have changed our opinion of that vendor. It may be a reflection of a change in the market and, therefore, changed evaluation criteria, or of a change of focus by that vendor.
- Added
- AuraQuantic: A vendor from the iBPMS market that satisfies our criteria for LCAP.
- Newgen: A vendor from the iBPMS and CMS market that satisfies our criteria for LCAP.
- Dropped
- K2: This vendor is focusing instead on the case management market.
- Kony: This vendor was acquired and is focusing now on the multi experience development platform (MXDP)* market.
- Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria:
To qualify for inclusion, each vendor must:
- 1. Demonstrate a go-to-market strategy with specific pricing for its low-code application platform (LCAP) for cross-industry application development, and not specific vertical markets and not included in some other capability or wider market.
- 2. Provide application platform capabilities that
- Include tools to develop, version, test, deploy, execute, administer, monitor and manage the applications and their relevant artifacts.
- Support the design of data schema* and application logic.
- Embed data storage and user interface(UI) features without relying on additional procured services (i.e., includes a database).
- Enable the invocation of external third-party services via APIs and/or eventtopics.
- Support some automation of platform patching and versioning.
- 3. Provide rapid application development. Each vendor must:
- Provide a low-code or no-code approach to development of UIs, business logic and data definitions.
- Support development and deployment of applications by developers in both central IT and line of business.
- Include single-step deployment.
- Include an application component repository for sharing components, integrations or applications.
- 4. Be enterprise-grade and aimed at enterprise class projects through the platform providing:
- High availability and disaster recovery.
- Secure access to applications.
- Technical support to customers.
- Third-party application access to application logic and/or data, via APIs and/or event topics.
- In addition to the above market and technical criteria, each participating vendor must adhere to the following business criteria:
- Growth: The vendor must have 20% year-over-year growth in revenue for the previous year for LCAP licenses and subscriptions, excluding professional services or other related product offerings, in the last year ending 31 March 2020.
- Revenue: The vendor must have revenue of at least $12 million for LCAP licensesand subscriptions in the last year ending 31 March 2020.
- Customer base: The vendor must have at least 400 paying customer organizations for its LCAP offering, excluding other related product offerings, as of 31 March 2020.
- International support: The vendor must have added at least 20 new, paying and named enterprise customer organizations for its LCAP in 2019, with at least 10 each within two of the following geographies: North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, and Asia/Pacific.
- We also excluded vendors that did not meet our market requirements exactly, using the following criteria:
- Require a specific, licensed, third-party component or product that is not already OEM’ed into their platform(s) — that is, branded, sold and supported directly by vendor.
- Only sell their platform(s) with, and for the use of, their professional services and consultants.
- Assume the purchase and/or installation of other unrelated products or platforms offered by the same vendor (e.g., a CRM application or content management system).
- Did not market an offering in 2019 that was described as an application development offering (e.g., a SaaS vendor that provided an LCAP as part of its SaaS license only).
- Do not offer a commercially supported enterprise offering—that is, only offer the platform(s) as open-source software.
- Evaluation Criteria; Ability to Execute
- Gartner views Ability to Execute as primarily concerned with product capabilities and sales execution and pricing. Due to COVID-19 in 2020, we dropped the customer reference survey from our process and thereby reduced the scoring of customer experience.
- Completeness of Vision:
- Gartner rates Completeness of Vision as primarily product strategy, innovation and marketing strategy. These are deemed the main drivers for future success.
- Quadrant Descriptions:
- Leaders:
LCAP Leaders are those that are demonstrating both execution (technically good product matched to good sales performance) and vision (both product innovation and commensurate marketing strategy). LCAP Leaders include major cloud SaaS providers (Microsoft, Salesforce, ServiceNow), specialist low-code providers (Mendix, OutSystems) and a hybrid process automation and low- code application vendor (Appian). These vendors have strong multifunction capabilities including application process, business logic and user experience, and moderate to strong ecosystems.
- Challengers:
LCAP Challengers are those that demonstrate strength in execution but only moderate or less vision. The single LCAP Challenger this year is Oracle with its Application Express (APEX) solution, which is widely used and technically competent, but Oracle’s vision does not match that of the Leaders or Visionaries in this Magic Quadrant. However, with continued extensions to their vision, Challengers could become Leaders in the future.
- Visionaries:
Visionaries in LCAP are those that demonstrate strengths in vision, but only moderate or less enterprise execution. LCAP Visionaries include SaaS providers (Oracle Visual Builder, Zoho), a citizen development vendor (Betty Blocks), and a hybrid process automation and low-code application vendor (Pega). These vendors display various approaches to innovation, but do not meet the same execution standards as the Leaders in terms of business levels or business models.
- Niche Players:
LCAP Niche Players have insufficient vision to be Visionaries, and insufficient execution to be Challengers. They include various and overlapping submarkets: hybrid process automation and low-code application vendors (AgilePoint, AuraQuantic, Creatio, Newgen, TrackVia), citizen development (Kintone, QuickBase), and field operations support (ProntoForms). While niche in the context of this Magic Quadrant, these vendors may be good choices for specific scenarios, domains and ecosystems, and in particular their pricing models are likely to be more relevant to a wider audience.
- Context:
- This Magic Quadrant covers the top 18 vendors and 19 products in the LCAP market. Low-code application platforms cover a wide range of vendors including those that are:
- SaaS-centric vendors, delivering LCAP for SaaS customizations, extensions and net new applications.
- IT-centric, rapid application development LCAP vendors, providing productivity to IT development teams and replacing or supplementing pro-code environments such as native Java EE, .NET or cloud-native platforms.
- LCAP providers for business unit application development, typically focusing on business processes and often using technologies that have evolved from BPMS or iBPMS.
- Citizen IT or development vendors, targeting simpler workflows and data sharing applications, but increasingly overlapping in capabilities with the other LCAP types with a larger emphasis on no-code/configuration mechanisms.
- Gartner clients choose LCAP for their increased productivity, and the ability to deliver applications quickly with reduced team sizes including fusion teams using agile methodologies.
- Use cases are typically as follows:
- Citizen development: Building line-of-business, web-based, data-oriented applications by business citizen developers using no-code development from one day to two weeks. Targets B2E scenarios.
- Business unit IT application: Building new enterprise applications involving web, mobile, data, business logic and external services including SaaS services, within eight weeks. Targets B2B and B2E scenarios.
- Enterprise IT business process application: Automate long-running, changeable and complex business processes, workflows and case management involving sophisticated business logic, external services and multiple end-user roles. Targets B2E scenarios.
- Fusion team-developed composite application: Assemble application experiences from a portfolio of multi sourced building blocks such as packaged business capabilities, SaaS, API products in marketplaces, existing data sources, event channels, cloud services and custom local services. These are custom application experiences for specific end-user roles and individuals.
- Independent software vendor (ISV) mobile and web application for SaaS: Build SaaS and ISV applications involving rich user experience on web and mobile, including end-user management and billing. Targets B2B and B2C scenarios.
- Market Overview:
- The market for low-code application platforms (LCAPs) continues to grow with a high level of interest from Gartner clients in “low code” for both application development and other application- related uses such as integration and AI services.
- Large SaaS vendors such as Salesforce and Microsoft dominate the market, with their SaaS competitors introducing new LCAP entries, such as ServiceNow competitor Cherwell introducing an LCAP offering, or Salesforce competitor Xiaoshouyi promoting its LCAP called IngageApp PaaS.
- The overlap with the business process automation vendors continues to grow, reflected in AuraQuantic and Newgen being added to the LCAP Magic Quadrant vendor list for 2020. Some other vendors have specialized away from the general LCAP market, such as K2 moving to case management automation, and Temenos acquiring Kony and refocusing on the MXDP market.
- Of the major vendors in the Application Infrastructure and Middleware Services (AIMS) market, Salesforce has achieved No. 2 status in revenue based primarily on its Salesforce Platform LCAP, behind only IBM. Salesforce represents a large proportion of LCAP market revenue. Oracle’s No. 3 status in AIMS is supported by its two independent LCAP offerings that are given separate attention for this edition of the Magic Quadrant. At No. 4 is AWS, which recently introduced a beta version of its LCAP offering, Amazon Honeycode. Microsoft at No. 5 has Power Apps as its LCAP — a prime component of its Power Platform strategy. SAP and IBM both offer Mendix on their marketplaces. Meanwhile, the perils of low-code lock-in were demonstrated by Google cancelling its App Maker product and acquiring the wholly separate and incompatible AppSheet instead.
-
- Table 1: Ability to Execute Evaluation Criteria:
Source: Gartner (Sep. 2020)
-
Evaluation Criteria
評価基準
Weighting
Product or Service
製品・サービス
High
Overall Viability
実行可能性
Medium
Sales Execution/Pricing
販売価格
High
Market Responsiveness/Record
市場の反応
Medium
Markeing Exeution
マーケティング力
Medium
Customer Experience
顧客経験
Low
Operations
運用
Low
- Completeness of Vision:
- Gartner rates Completeness of Vision as primarily product strategy, innovation and marketing strategy. These are deemed the main drivers for future success.
- Table 2: Completeness of Vision Evaluation Criteria
-
Evaluation Criteria
評価基準
Weighting
Market Understanding
市場の理解
Medium
Market Strategy
市場戦略
High
Sales Strategy
販売戦略
Medium
Offering (Product) Strategy
製品戦略
High
Business Model
ビジネスモデル
Low
Vertical/Industry Sttategy
垂直/産業戦略
Low
Innovation
イノベーション
High
Geographic Sttategy
地理的戦略
Low
21. 追加削除したベンダ:
- 4象限評価表には、市場の変化に応じて入れ替えを行った。毎年入れ替えが起こるが、Gartnerとして意見を変えたのではなく、市場の変化を反映して、各製品の評価や注目度を変えた結果である。
- 追加:
- AuraQuantic: iBPMS (Intelligent BPM Suites, 定型のみならず非定形業務・SNSへの対応を含めたBPM)ベンダ
- Newgen; iBPMSやCMS市場からの参入
- 削除:
- K2: Case Management市場 (医療症例管理)に特化
- Kony: このベンダは買収され、今はMulti Experinece Development Platform (MXDP)*に特化
- 追加・削除の基準:
4象限の評価表に入るには、各ベンダは以下条件を満たす必要がある。
- 1. 業界横断的にローコードアプリを新製品投入が明確であること。特定産業向けではないこと。
- 1. 業界横断的なローコードアプリプラットフォーム (LCAP)について、特定の価格政策での新製品投入が明確であること。それは特定の垂直産業向けでもなく、その他の能力のより広い市場展開でもない。
- 2. 以下のようなアプリプラットフォーム機能を提供していること。
- アプリとその成果物の開発、バージョン管理、テスト、導入、実行、管理、監視、管理のためのツールを含むこと。
- データスキーマ*およびアプリ・ロジックの設計をサポートすること。
- 追加の調達サービスに依存することなく、データストレージおよびユーザーインターフェース(UI*)機能を組み込むこと(例:データベースを含む)。
- APIやイベントトピックを介して外部のサードパーティサービスを呼び出すことができること。
- プラットフォームへのパッチ適用やバージョン管理の自動化をサポートすること。
- 3. 高速アプリ開発を提供する。各ベンダーは
- UI、ビジネスロジック、データ定義の開発において、ローコードまたはノーコード開発の方法を提供すること。
- 全社IT部門と現業部門の両方の開発者によるアプリ開発と導入をサポートすること。
- シングルステップの導入を含むこと。
- アプリ・コンポーネント・リポジトリを含むことで、コンポーネント、統合、アプリを共有を図ること。
- 4. 企業レベルのプロジェクトを対象とした、企業クラス対象のプラットフォームであること。
- 高可用性とディザスタリカバリ(DR)
- アプリへのセキュアなアクセス
- 顧客への技術サポート
- APIまたはイベントトピックを介した、アプリロジックまたはデータへのサードパーティアプリのアクセス。
- 各ベンダーは、上記の市場および技術的基準に加えて、以下のビジネス基準を遵守する必要がある。
- 成長性: ベンダは、2020/3/31までの過去1年間において、プロフェッショナルサービスやその他の関連製品の提供を除く、LCAPライセンスおよびサブスクリプションの収益が、前年比で20%増加していること。
- 収益性: ベンダは、2020/ 3/ 31 日までの過去 1 年間に、LCAP ライセンスおよびサブスクリプションの収益が12 百万ドル以上であること。
- 顧客基盤: ベンダは、2020/3/ 31時点で、LCAP 製品 (他の関連製品を除く) について、少なくとも 400社 の有料顧客数を有していること。
- 国際的なサポート: ベンダは、2017 年にその LCAP のために少なくとも 20 の新規の有料の企業顧客を追加していること。北米、南米、欧州、中東アフリカ、アジア太平洋地域のう内、2地域でそれぞれ10社以上あること。
- 当社の市場基準を満たしていないベンダは除外した。即ち
- 特定のライセンスされたサードパーティ製の特定のコンポーネントや製品であり、すでにOEMされたものを自社のプラットフォームに組み込んでいないこと、即ち、ベンダによって直接ブランド化されて、販売され、サポートされていること。
- 自社のプラットフォームやその利用、あるいはプロフェッショナルサービスやコンサルタントを販売していること。
- 同じベンダが提供する他の無関係な製品やプラットフォーム (CRMアプリやコンテンツ管理システムなど) の購入/または導入を想定していること。
- 2019年にアプリ開発提供物と記載して販売しなかった(例:SaaSライセンスの一部としてLCAPを提供したSaaSベンダ)。
- 商業的にサポートされたものを企業向けに提供していないこと (即ち、オープンソースソフトウェアとしてのみ提供している場合)。
- 評価基準: 以下の実績評価
- Gartnerは、実績とは主に製品の能力と販売実績、価格政策に関係するものと考える。2020年にCOVID-19を実施するため、顧客参考調査をプロセスから削除し、それにより顧客経験のスコアリングを減らした。
- ビジョンの完成度
- Gartnerは、Completeness of Visionを評価している。それは、主に製品戦略、イノベーション、マーケティング戦略である。これらは、将来の成功のための主要な要因であるとみなしている。
- 4象限評価:
- リーダーズ:
LCAPリーダーとは、実行力(技術的に優れた製品とそれに見合った販売実績)とビジョン (製品の革新とそれに見合ったマーケティング戦略) の両方を示している企業を指す。LCAPリーダーには、主要なクラウドSaaSプロバイダ (Microsoft、Salesforce、ServiceNow)、ローコード専門プロバイダ (Mendix、OutSystems) 、プロセスオートメーションとローコードアプリのハイブリッドベンダ (Appian) が含まれる。これらのベンダは、アプリ・プロセス、ビジネス・ロジック、UXをを含む強力なマルチファンクション機能と、中程度から強力なエコシステムを備えている。
- チャレンジャー:
LCAPチャレンジャーとは、実行力はあるが、ビジョンが中程度かそれ以下であることを示す。今年のLCAPチャレンジャーは、OracleのApplication Express(APEX)で、これはソリューションとして広く利用されており、技術的にも優れているが、Oracleのビジョンは、この4象限評価のリーダーやビジョナリーとは異なる。しかし、ビジョンを継続的に拡張することで、チャレンジャーは将来的にリーダーになる可能性がある。
- ビジョナリー:
LCAPにおけるビジョナリーとは、ビジョンにおいては強みを発揮するが、企業としての実行力は中程度かそれ以下である。LCAPビジョナリーには、SaaSプロバイダ (Oracle Visual Builder、Zoho) 、Citizen開発用ベンダ (Betty Blocks)v、ハイブリッド・プロセス・オートメーションとローコード・アプリのベンダ (Pega) が含まれる。これらのベンダは、イノベーションへの様々なアプローチを示しているが、ビジネスレベルやビジネスモデルの点で、リーダーの実行基準に至っていない。
- ニッチプレーヤー。
LCAPニッチプレーヤーは、ビジョナリーになるにはビジョンが不十分であり、またチャレンジャーになるには実行力が不十分である。ハイブリッド・プロセス・オートメーションやローコード・アプリケーションのベンダー(AgilePoint、AuraQuantic、Creatio、Newgen、TrackVia) 、Citizen開発 (Kintone、QuickBase) 、フィールド・オペレーション・サポート (ProntoForms) など、様々なサブマーケットがあり重複している。今回の4象限評価ではニッチなベンダだが、これらは特定のシナリオ、ドメイン、エコシステムに適した選択肢である可能性があり、特にその価格モデルはより多くの人々に受け入れられる可能性が高いと考えられる。
- 背景:
- この4象限評価では、LCAP市場における上位18社のベンダと19製品を対象とした。ローコードアプリ・プラットフォームは以下のような幅広いベンダをカバーしている。
- SaaSを中心としたベンダで、SaaSのカスタマイズ、拡張、新規アプリのためのLCAPを提供。
- ITを中心とした迅速なアプリ開発を行うLCAPベンダで、IT部門の開発に生産性をもたらし、Native Java EE、.NET、Cloud-native platformのプロコード環境の代替または補完をしている
- 事業部門のアプリ開発を行うLCAPプロバイダで、通常はビジネスプロセスに焦点を当て、BPMSやiBPMSから発展した技術を使用することが多い。
- Citizen開発ベンダで、よりシンプルなワークフローとデータ共有アプリを対象としているが、他のLCAPタイプと機能が重複してきており、コードレスやコンフィグレーション・メカニズムに重点が置かれている。
- Gartnerの顧客は、生産性の向上を図ることや、アジャイル手法を用いた混合チームや小規模チームによってアプリを迅速に制作できることから、LCAPを選択している。
- ユースケースは一般的に以下である。
- Citizen開発: 現業部門の開発者が、コードレス開発を利用して、1日から2週間で、現場システム、ウェブベース、データ指向のアプリを構築する。B2Eのシナリオを対象とする。
- 現業部門のITアプリ開発: Web、Mobile、データ、ビジネスロジック、SaaSサービスを含む外部サービスを含む新しい企業アプリを8週間以内に構築する。B2BおよびB2Eを対象とする。
- 全社ITビジネスプロセスアプリ開発: 洗練されたビジネスロジック、外部サービス、複数のエンドユーザの役割を含む、長期的で変更可能な複雑なビジネスプロセス、ワークフロー、ケース管理を自動化する。B2Eを対象とする。
- 混合チームによる複合アプリの開発: パッケージ化されたビジネス機能、SaaS、市販のAPI製品、既存のデータソース、イベントチャネル、クラウドサービス、カスタムローカルサービスなど複数のソースから構成されたビルディングブロックからアプリを組み立てる。これらは特定のエンドユーザの役割や個人のためのカスタムアプリ・エクスペリエンスである。
- 独立ソフトベンダ (ISV) のSaaS向けモバイルやウェブアプリの開発: エンドユーザの管理や課金など、ウェブやモバイルでのリッチなユーザ・エクスペリエンスを含むSaaSやISVのアプリを構築する。B2BおよびB2Cを対象とする。
- 市場概況:
- LCAP*の市場は成長を続けており、ガートナーの顧客は、アプリ開発だけでなく、統合やAIサービスなど、アプリに関連する用途でも'ローコード'に高い関心を寄せている。
- SalesforceやMicrosoftなどの大手SaaSベンダが市場を支配しており、ServiceNowの競合企業であるCherwellがLCAPの提供を開始したり、Salesforceの競合企業であるXiaoshouyi [Neocrm, 销售易, 中国の企業向けCRM provider] がIngageApp PaaSというLCAPを推進するなどSaaSの競合企業が、新たなLCAPエントリを発表している。
- ビジネスプロセス自動化ベンダとの重複は継続しており、AuraQuanticとNewgenが2020年のLCAPの4象限評価リストに追加されたことに反映されている。他にも、K2がケース管理自動化に移行したり、TemenosがKonyを買収してMXDP市場に再注力するなどLCAP市場全般から特化しているベンダもある。
- AIMS (Application Infrastructure and Middleware Services) 市場の主要ベンダの中で、Salesforceは、主にSalesforce platformのLCAPに基づく売上で、IBMに次ぐ第2位の地位を獲得した。Salesforceは、LCAP市場の収益の大きな割合を占めている。Oracleは、AIMSにおける第3位の地位を、今回の4象限評価によって占めている。第4位のAWSは、LCAP製品であるAmazon Honeycodeのベータ版を発表した。Microsoftは第5位で、Power Platform戦略の主要コンポーネントであるPower AppsをLCAPとして提供している。SAPとIBMは、自社のマーケットプレイスでMendixを提供している。一方で、ローコードロックインの危険性は、GoogleがApp Maker製品を中止し、全く別の互換性のないAppSheetを買収したことで明確になった。
- ガートナーはCompleteness of Visionを、主に製品戦略、イノベーション、マーケティング戦略と評価している。これらは、将来の成功のための主要なドライバーとみなされる。
>Top 22. Glossary:
- 2FA=Two-factor authentication
- 3GL=Third generation language, 4GL=Fourth generation language
- AI Engineering: DataOps (Dataの発生現場での入手と利用)+ModelOps(開発→検証→改善→実装の迅速化)+DevOps(SW開発と運用; Sytem開発life Cyleの短縮化)
- AIMS=Application Infrastructure & Middleware Servicrs
- Angular Framework: Googleが開発したJavascript frameworkで、Webアプリ開発では、React (Facebookが開発したJavaScript Library; (Declarative, Componet-based, Learn once - write anywhere)と並んで人気。
- APAC=Asia & Pacific; Cf: APEJ (APAC Except Japan); NCSA (North, Central & South America =Americas); EMEA (Europe, Middle East & Africa); LAC (Latin America & Caribbean)
- Augmented Analytics: 拡張分析; AIを使って、データ分析に専門家でない経営層などによるデータ分析を可能にする技術d; 1) 自然語対応、2) 自動化, データのパターンと分析 (Smart Discovery), 3) 業績予測など (Super Predict)
- B2E=Business to Employee
- CI/CD=Continuous integration/Continuous delivery
- Composable Infrastructure: コンポーザブルインフラ; =IaC (Infrastructre as Code) =SDI (Sofware Defined Infrastructure); 物理サーバ、Storage, Networkのcomponentを統合したsetをon-demand serviceとして提供 (HCI=Hyper Conversged Infrastructure); CI=Converged Infrastructureは、従来のインフラより迅速に実装可能なPre-configured hardware/software packageを提供; 即ち、Converged Infrastructure (=Server/Storage/Switchがrackにhandleされている)>HCI (Hyper Converged Infrastructure (統合型applianceがcomputer, network, storageの組合されている)>Composable Infrastructure (Converged I.とHCIの要素の組合せ=Computer/Network/Storage moduleを分離し、仮想networkでServerにmappingする。共通poolから動的にアプリにresourceを割り当てる。その役割はComposing softwareに依存=Intelligent Software); 今日の変動するworkloadに対応できる動的基盤を提供。必要なresourceのdeployと管理を容易にする; Composable I.の場合はDASを資料; なお、Storageには、DAS (Direct Attached Storage)/NAS (Network Attached Storage)/SAS (Storage Area Network)があり、直接接続するDASが一番accessが速い。次にStorage専用networkを構成するSAS、一番遅いのは既存LANGに接続するNASである; これらはDevOpsと親和性がある; さらに今日では、AI+SDI→AI-defined Infrastructureが試行されている。
- Container Deployment (Virtualization): OS上に隔離されたAppの実行環境を作り、1台のホスト上であたかも複数のホストが動いているような環境を実現するのが、コンテナ型仮想技術; VM型仮想化では、VMの中で別々のOSが動作する。一方VMのサイズが大きくなる。コンテナ型仮想化では、OS自体は限定されるが、実行環境(コンテナ)サイズはコンパクトになる; Micro service化を促進し、変更のサイクルの短縮化に通じる; 但し、Container同士は、Private Network経由でやり取りできるが、ホストの外側とはNAT (Network Address Translation)経由が必要となる; これを解決するのがKubernetesである。Kubernetesは、どのContainerを何台起動するかSpecで決める (Kubernetes上で仮想HostがPod); →無停止更新 (Rolling Update)機能
- Cross Industry, 業界横断
- CX=Customer Expereince, 顧客体験 (CSより広い概念; 商品サービスの金銭的・物質的な価値に加えて、商品の感情・満足感・効果を含むすべての価値, LTV=Life Time Valueにつながる)
- Data Fabric: 同一アーキテクチャ上で動作するサービスで、企業のデータ管理と分析技術を支援し、データ価値を高める(例: SalesとMarketingの最適化でDataのSilo化を防ぐ)
- Declarative Programming: 宣言型プログラミング; What (得たいもの)を宣言してProgramを構成し、How (どうやって得るか)を記述しない; 食事に例えると、Menuを宣言し、Recipeを記述しない; 条件と結果が明確にcodeに記載されておりdebagしやすい;他方 jQueryは手続き的; 簡単なMobile Appは、JavaやSwift (iOS開発言語)を使わずにJavaScriptとReactで作成可能。
- Deployment Manager: 多くのRegionに亘ってServieをDeployし、各Regionで期待通り実行できるために、サービスの段階的Roll outを調整するResource Managerの一機能; すべてのRegionにDeployされる前に潜在的問題を発見する。; >CI/CD >One-Time Deployment
- DevOps=Develpment & Operation (Developmentが新機能追求+Operationは安定稼働指向の傾向大)
- Distributed Cloud: 分散クラウド; LatencyやLocal lawsへの対応として; 1) On-premises Public Cloud, 2) IoT Edge Cloud, 3) Community Cloud, 4) 5G Mobile Edge Cloud, 5) Netwrok Edge Cloud
- DMN=Decision Model and Notation
- DR=Disater Recovery, 障害復旧 (cf: RPO=Recovery Point Objective, 目標復旧時点; RTO=Recovery Time Objective, 目標復旧時間)
- ETL=Extract, Transform & Load: Dataをcleansingして最大活用を図る; 現状では75%がデータ分析以外の作業に費やされている; Dataの整合性に欠陥があると10倍のコストが発生; >Data Fabric, >Data Stewardshp
- GTM=Go To Market Strategy, 新製品投入のaction plan; Global NW Edge Cloud環境構築; On premise→Distributed Cloud
- Headless CMS =Decoupled Architecture: Web page (Front End)と管理page (Back End)に分けた構造; >RESTful API, GraphQL API; Front endとBack endとを別々に開発できる; なおHeadless: 人がdeviceを操作するためのTouch, ScreenなどのないdeviceをHeadless deviceと呼ぶ。
- HIPAA=Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
- Hyperautomation: AI, ML, RPA, iBPMSなどによる人間の作業の最大自動化→Bz partnerとの協力による自動化拡大
- iBPMS=Intelligent Business Process Mangement Suites; 非定形業務や業務ソフト、SNS連携などを包括したBPM製品
- IDE=Integrated development environment, ソフトウェア領域が広がる中で、platformより大きなenvironmentへ発展
- Incident Mangement, IT systemの正常に利用できない事象(故障だけでなく)への対応
- iPaaS=Integration Platform as a service; これも従来のPaaSの拡大版
- ISV=Independent software vendor; ソフトウェア開発業者の多様化の象徴
- ITSM=IT Service Management, User needsに応じたITサービスの提供と改善
- IVR=Interactive voice response
- JEE=Java Enterprise Edition, 多コード開発の典型と見なされている
- jQuery: 2006年リリースのJavaScript Libraryの1つ; 特色は、1) Browserの違いを吸収、2) HTMLのDOM (HTMLの部品)操作が簡単、3)Ajax処理が簡単; なお、HTMLからのsubmit処理は同期処理方式だが、AjaxによるJavaScriptは非同期処理方式; 例 $("#title").text("タイトル変更")
- LCAP=Low-code application platform;
- LDAP=Lightweight Directory Access Protocol;
- MDM=Master data management
- MDA=Model-Driven Architecture; 設計とArchitectureを分離し、各々独立して変更できる技術; Architectureは機能とは無関係にScalability, 信頼性, 性能を対応できる (>PIM=Platform Independent Model); 初期モデル(Initial Model)は主に手動で作成するが、導出モデル(Derived Model)は、Programが自動生成する。(>Rational Rose); なお、MDA toolは、UML toolより範囲が広い。
- MDM=Master Data Management; 全社データ一元化; MDM実装方法 1) Registory型; SoRでGolden recordを持ち統一・完全性を確保, 2) 集約型; SoRとDBのrealtimeでの相互のNetwork access, 3) 集権型; SoRにmaster data構築, access権限を巡り現場の抵抗, 4) 共存型; DBにmaster data。System側からも更新可能なのでGovernanceが課題。
- Meta Programming: メタプログラミング; Logicを直接codingするのではなく、あるPattern logicを生成してProgrammingを行う手法; 主に対象言語に埋め込まれたMacro言語 (LispのMacroなど); 自動生成が言語組込み機能ではなくListのMacroによって記述される→事実上の言語文法の拡張となり、強力なProgram能力を得る; 但し、Macroは、本来の文法を逸脱した字句の置換えが起こるので、記述通りでない動作が行われ、Codeの可読性を損なう恐れがある。
- Microservice: ソフトウェア開発技法の1つで、1つのアプリをビジネス機能に沿った小さなサービスの疎結合の集合体としてModularityを高めて、少チームでの並列開発を容易化する; >Refactoring: 動作を変えずにsource codeの内部構造を整理
- MQTT=Message Queuing Telemetry transport
- MXDP=Multi-Experience Development Platform (Web, Mobile, Voice, AR, Chat, Wearable等のApp開発Platform)
- Multi Experience: Web, Mobile, Smart speaker, ARなどのmulti experience
- Multipersona Strategy: 顧客=personaとして、Whoに着目して相手に合ったContentsで刺さるmarketing戦略
- ODBC=Open Database Connectivity
- Orchestration: Compter system, Middleware, Service配備・設定・管理の自動化。仮想化やProvisioningの文脈で比喩的に使われる; またWeb service interface通じて情報交換する過程を指すこともある。
- PCI DSS=Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard; クレジットカード情報・取引情報保護のため、JCB, AMEX, Dicover, Master, Visaの国際Payment Brand5社が共同でPCIT SSC (Secirty Standard Council)を設立した。
- PII=Personally Identifiable Information, 個人を特定できる情報 (電話番号、国民識別番号、eMail address等)
- Platform-agnostic, に依存することなく
- PL/SQL=Procedural Language/Structured Query Language: Oracleが開発した非手続言語のSQLを拡張したProgramming言語; SQL単体では難しい複雑な手続処理 (Loop処理など)をまとめて処理できる; 1) Performanceに優れている、2) SQLとの親和性(SQLデータ型も共通)、 3) 移植性に優れている(特定のPlatformに非依存)、4) ProgramをDBに格納し必要な時に呼び出せる (stored subprogramとして)
- Programming Paradigm;
- PWA=Progressive Web Apps; RAD=Rapid Application Development
- RAD=Rapid Application Development
- React: UIを作るためのJavaScript Library (Facebookが開発); Reactの特徴は、1) Declarative, 2) Component-based, 3) Learn once, write anywhere; 1) Declarativeは、条件と結果が分離されて記述→読みやすいcode (一方 jQueryは手続き的処理), 2) Appの構成要素を小さなComponentの集合とするので、状態管理がしやすく拡張性がある、3) 簡単なMobile Appなら、JavaやSwift(iOS開発言語)ではなく、JavaScriptとReactで作成可能; DOM=Document Of Model技術, Web pageを更新するとき全ページを更新するのではなく、更新された一部のみ変更する仕組み→高速表示の切り替え可能、管理しやすい設計なので大規模App開発に向いている (Moduleのみの追加・削除など); JSXというXML風にDOMの出力が可能→HTMLのようにReact内に組込み可能; SPA=Single Page App, 画面遷移が少なく見やすい画面, React.jsは高速で動作する; 但し、日本で普及しているjQueryに比べて、英語のmanualが多い。
- REST API=RESTful API=Respresentational State Transfer:REST原則のAPI; Webシステムを外部から利用するためのprogramの呼び出し規約(API)の1つ; 設計原則 1) Sessionなど状態管理を行わず、やり取りされる情報はそれ自体で完結, 2) 情報操作する命令体系が予め定義・共有されている、3) すべての情報は汎用的な構文で一意に識別される、4) 情報の一部として、別の状態・情報への参照を含めることはできない。
- RPA=Robotic Process Automation; Programmingにおけるパラダイム; 各Programmingには禁じ手が存在する; Object指向Programmingは、Objectを作成し管理する; 構造化、命令形、Object指向型、関数型、Generice Programming などがある。> Multi-Paradigm Programming
- SAML=Security Assertion Markup Language
- Schema: Databaseの3層構造などの構造; OS Directoryと似た性質、但し、階層なし, DBで格納場所を別に分類できる仕組み, user名schema→public schemaの優先順位
- SDLC=Software Development Life Cycle =SLC; ソフトウェア開発の方法論; Waterfall, Spiral model, Iteration, Prototypingなど設計から構築・テスト・配備・運用・保守・廃棄まで
- Single Step Deployment
- SLA=Service Level Agreement
- SSO=Single Sign-On
- Total Experience: = UX (User Experience)+CX (Customer Ex)+ EX (Employee Ex)+ MX (Multi Ex)
- TOTP=Time-based One-time Password
- UI=User Interface
- Use Case: 活用事例; ユーザ目線でSystemの振舞 (ActorとSystemのやり取りの機能的要求)を表現・図示したもの
- UWP=Universal Windows Platform; Windowsでは従来の画面表示、スマホでは全画面表示となる; > Responsive design >Cloud First >Intelligent Cloud
- UX=User Experience
- Web Designer: 必要なスキル; 1) HTML, 共通の枠組み、2) CSS, 色などWebの外観, 3) JavaScript, 各要素に動きを加える
- Webhook: =Event Trigger; Server上である特定eventが発生すると、サーバ側からクライアント側に通知するシステム; 例: お気に入り登録すると、記事が更新されるとSNSに通知する; APIは、こちらからRequestするとResponseしてくれるが、WebhookはRequestしなくても(条件にhookしたら) Responseしてくれる。
Comment
- Gartner's four-quadrant evaluation analysis is very interesting. It is relatively clear to choose the top vendors, but it is rather difficult to choose the challengers and visionaries who follow them. We could not ignore the existence of niche players who develop their own domain. Similarly the way of individual life could also be classified in this way. Everyone wants to be the ultimate leader, but the route to get there requires continuous trainings for physical strength or brains, or the choice to live in a niche domain, hoping that the world's evaluation standards will change.
- Gartnerの4象限評価分析は非常に興味深い。トップのベンダを選択するのは比較的明確だが、むしろそれに続くチャレンジャー(実績派)とビジョナリー(頭脳派)を選ぶのが難しい。そして独自の領域に生きるニッチプレーヤーの存在も無視できない。これは個人の生き様もこのように分類できるのではと思われる。誰もが、最終的なリーダーになりたいが、そこに到る道筋は、やはり体力か頭脳かを持続的に強化していくか、あるいは、世の中の評価基準が変わることを期待してニッチに生きるしかない。
Magic Quadrant for Low Code Application |
Cat: ICT |
|
Gartner |
21313u/22817r |
Title |
Magic Quadrant for Low Code Application |
ローコードアプリ4象限評価 |
|---|---|---|
Index |
|
Résumé |
Remarks |
>Top 0. Comment:
|
0. コメント:
|
>Top 1. Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Low-Code Application
|
1. 4象限のローコード開発プラットフォーム:
|
>Top 2. AgilePoint:
|
2. AgilePoint:
|
>Top 3. Appian
|
3. Appian:
|
>Top 4. AuraQuantic (formerly AuraPortal)
|
4. AuraQuantic (以前のAuraPortal):
|
>Top 5. Betty Blocks:
|
5. Betty Blocks:
|
>Top 6. Creatio:
|
6. Creatio:
|
>Top 7. Kintone:
|
7. Kintone:
|
>Top 8. Mendix:
|
8. Mendix:
|
>Top 9. Microsoft:
|
9. Microsoft:
|
>Top 10. Newgen:
|
10. Newgen:
|
>Top 11. Oracle (APEX):
|
11. Oracle (APEX):
|
>Top 12. Oracle (Visual Builder)
|
12. Oracle (Visual Builder):
|
>Top 13. OutSystems
|
13. OutSystems:
|
>Top 14. Pega:
|
14. Pega:
|
>Top 15. Pronto Forms:
|
15. Pronto Forms:
|
>Top 16. Quick Base
|
16. Quick Base:
|
>Top 17. Salesforce
|
17. Salesforce:
|
>Top 18. ServiceNow
|
18. ServiceNow:
|
>Top 19. TrackVia
|
19. TrackVia
|
>Top 20. Zoho
|
20. Zoho:
|
>Top 21. Vendors Added and Dropped
|
21. 追加削除したベンダ:
|
>Top 22. Glossary:
|
Comment |
|
|