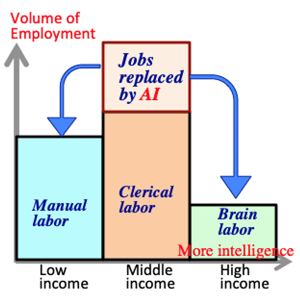
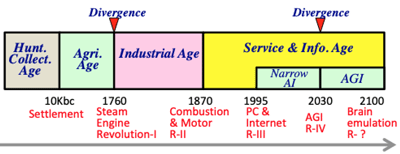
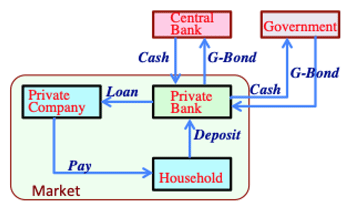
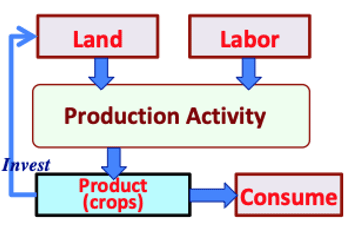
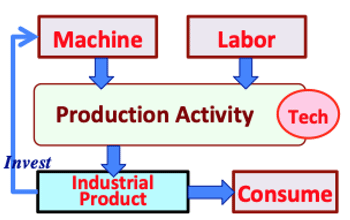
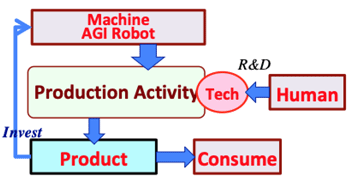
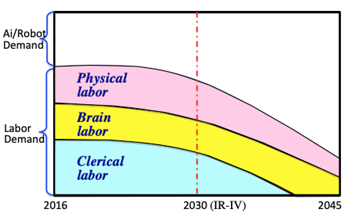
>Top 5. Necessity of Basic Income:
- Arrival of dystopia:
- Though productivity increases explosively by AGI robots, only small number of capitalists can be rich, while majority labors have no means of earnings. (Dystopia)
- Drastic public assistance to protect livelihood of majority will be urged.
- Is the enormous public livelihood assistance proper policy, or is it sustainable?
- Problems of public livelihood assistance:
- Segmentation problem: who is worth or is not.
- Household means test requires large administrative costs to prevent illegal receipt.
- It difficult to segment the rich and the poor; such as 1) a person who has no income but has large asset, 2) no income, no asset, but living together with rich family or brother, etc.
- Such society will be the Soviet like state?
- Socialism aimed to distribute the reward by the result of labor (efforts and ability).
- The main reason of failure of USSR was not a failure of distribution of reward, but was obliged to adopt 'Planned Economy' to manage state-owned enterprises (SOEs).
- The central economic authorities was totally different from the market economy; the former is centralized economy, and the latter distributed one.
- Friedrich Hayek argues that it is impossible to decide prices of goods by centralized authorities because of polarity of information; proper decision of prices must depend on people involved in local site of production and sales; thus distributed decision-making is more efficient.
- Invisible hand of God is more efficient than human visible hand.; could appear almighty super AGI by 2045?
- >Top Capitalism is like a mixed martial arts (MMA) (human connection, fortune, opportunity, inherited assets as well as each ability and efforts.)
- Various type of socialism:
- John Roemer proposes 'Coupon type Socialism' or 'Market Socialism', pursuing efficiency AND fairness, not efficiency OR fairness based on the market mechanism.
- Capitalism (particularly neoclassical economics) regards private ownership as absolute, while socialism regards public ownership as absolute (socialization of production means).
- >Top Coupon socialism aims to dissolved rights of ownership into various stakeholders; 1) investors have the right to receive returns, 2) labors have the right not to be fired, 3) community has the right to reject a certain usage (pollution, etc.), 4) executives have the right to make decisions and manage the organization, and, 5) stakeholders collectively have the right to watch proper governance.
- Coupon socialism:
Government distributes a certain coupon or voucher to all adults, who purchase
company stocks by the coupon at the list value.
- Such stocks cannot be inherited, and must be retuned to the government at the time of death, and the government distribute again the coupon to new adults.
- Such stocks can change to the stocks of other companies; but cannot change to consumer goods.; people forcibly became capitalists, and never become non-capitalists.
- Eve present capitalism has versatile ownership; such as 1) limited company, 2) non-profit organization, 3) partnership joint-venture, 4) private ownership, 5) public corporation, 6) labors governing corporation, etc.; or in other words, ownership is restricted in the rights of assignment and accumulation. (or, Principal-Agent relationship; executives of company are agent for capitalists)
- A shift from advanced capitalism to market socialism could be considerable.
- Socialism tends to distribute or diffuse the profit, while capitalism to concentrate; then what about the case of National-capitalism?
- >Top John Roemer's coupon socialism could not be conscious of AGI, but it sounds preferable in pure mechanized economy where only capitalists can earn the reward.
- Who owns stocks of the highly automated company? 1) the government owns all the stock looks like conventional socialism, or 2) all people own all the stock is similar to the coupon-socialism.
- the problem of coupon-socialism:
Prior to start coupon-socialism, the government needs to deprive of all the existing stocks from capitalists; such negation of private ownership causes serious political resistance.
- The idea of drastic change of inheritance tax system and redistribution of stock could be possible.
- Another problem is uncertainty of value of stocks; if the company became unprofitable, the dividend would be zero; or if it became bankrupted, the stock be valueless; as all income depends on dividend and value of the stocks, the concerned people could be no-income.; the last resort could be needed in such cases.
- >Top Basic Income (BI) (or called Universal Basic Income (UBI) particularly campaigned by presidential candidate Andrew Yang as the most appropriate system in the pure mechanized society.
- BI is the universal system to distribute minimum living expenses to each individual.
- The origin of BI come from the idea of 'negative income tax'.
- BI is a kind of social security system, or national dividend.
- Even now in Alaska, the revenue is distributed to the local residents as a kind of BI. (Alaska's Permanent Fund Dividend, APFD; from the state-owned profit from oil and gas production.)
- The idea of BI is widely considered worldwide, but there is no nation which accepted this system nationwide.
- Many prominent economists proclaims BI such as James Tobin, John Galbreith, Milton Freedman, Friedlich Hayek, etc.
- They submitted recommendation of BI to Richard Nixon, but not accepted.
- In other countries, the support is spreading; in Netherland, Switzerland, Finland.
- In Japan the discussion about BI is being focussed in mostly among economists, including Yasushi Harada of BOJ wrote the book 'Basic Income.'
- >Top Advantage of BI: the author strongly support BI, without regard to the development of AI.
- BI is totally different from 'selective social security' system; BI is universally payable to each individual national.; BI never humiliate the payee as specially selected receivers, whether in poor or being in sick or unemployed.
- BI never reduce motivation of working, because the amount is never reduced.
- In addition, there will be no substantial increase of administrative cost by introduction of BI.
- BI is considered to replace the support for the poor.; but the support for the disables should be maintained.
- The major objection to BI:
- Q: Financial resources are limited to support BI system.
- A: if the resources are shorted, tax increase or deficit JG-bond could be justified.
As the BI system is a prominent social security system, and as long as it improves national life, there will be no choice of not adopting BI, even if corresponding financial burden is needed.
- Q: Another objection is that BI may cause hyper-inflation.
- A: it depend on the scale of BI. The impact of ¥10k per month would be negligible. But if it became ¥400k per month, it might cause serious inflation. It is considered that ¥70k per month could cause 2-3% inflation which is acceptable.
- An idea of BI of ¥70k per month:
- The total financial resource will be about ¥100T; to be covered by tax revenue of income tax or consumption tax.
- ¥100T looks enormous, but the point is the balance of revenue and payment; rich people will be net loss, while the poor be net profit; averagely it is neutral to the fiscal burden.
- In addition, BI basically no administrative cost is needed unlike other support allowances; BI could be remitted monthly to each bank account tied with my number system started 2016/1.
- After introduction of BI, other allowances such as 1) government support for pension fund, 2) child-care allowance, 3) unemployment insurance, 4) livelihood subsidies, 5) other income security in agriculture, 6) various subsidies for SMB, or public utilities, etc.; totally ¥3.6T could be used for BI. (source: Basic Income by Y. Harada)
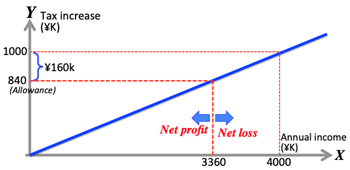
- Case Study: >Fig.
- BI allowance ¥70k per month (=¥840k per year)
- necessary financial resource: ¥6.4T (¥10T - ¥3.6T)
- income tax increase ¥64T (=¥250T ☓ 25%) (Total Japanese income is about ¥250T; and 25% is additional income tax for BI; progressive taxation is not considered here.)
- present average individual income is about ¥4m per year, who pays ¥1m as additional tax.
- ¥1m additional tax looks enormous, but such payer can be paid ¥840k as BI per year; so the net burden is only ¥160k.
- similarly, a single person who earns ¥3.36m will be even in paying additional tax ¥0.84m and receiving BI ¥0.84m.
- 3 family household who earns ¥4m per year will pay additional tax ¥1m but will receive BI ¥2.52m (¥0.84 ☓3)
- Japanese average household income is about ¥5m, and average number of family is 2.5; then this HH will pay ¥1.25m and will receive ¥2.1m (net +¥0.85m)
- Single old person home receives basic pension of ¥0.96m per year will be halved to ¥0.48m (state liability 50% will be abolished). But such person can receive ¥0.84 BI per year; the total revenue will be ¥1.32m (net +¥0.36m)
- Rich family's case of ¥2m income with 4 family; will pay additionally ¥5m and will receive ¥3.36m (net -¥1.64m)
|
5.
ベイシック・インカムの必要性:
- Break even of BI: annual income and tax increase
HH income
per year (¥M) |
HH family |
receive
BI |
pay
add tax |
Net revenue |
| 4 (Indiv av.) |
3.0 |
2.52 |
1.00 |
1.52 |
| 5 (HH av.) |
2.5 |
2.10 |
1.25 |
0.85 |
| 0.96(pensioner) |
1.0 |
0.84 |
-0.48 |
0.36 |
| 10 (middle) |
3.0 |
2.52 |
2.50 |
0.02 |
| 20 (rich) |
4.0 |
3.36 |
5.00 |
-1.64 |
| 100 (richer) |
4.0 |
3.36 |
25.00 |
-21.64 |
- Simpler calculation:
(number of family*¥1M)
- (25% additional tax)
|