
What is IoT?
- From technical innovation to social innovation -
Cat: ICT
Pub: 2016
#: 1909b
Ken Sakamura (坂村健)
19627u
Résumé
Remarks
>Top 0. Prologue:
- IoT is an integrated technologies of not only ICT, but also device control and information processing; also needs business knowledge, privacy and system design of social scale.
- IoT is rather easier to be understood not by technological viewpoint but by actual cases of various applications.
0. 序文:
- system design: 制度設計
>Top 1. IoT and ubiquitous computing:
- IoT and ubiquitous computing (or highly functionally distributed system, HFDS):
- IoT is an open network to support social life beyond individuals and organization, not only connection things.
- >Top Hype Cycle: Gartner provides the maturity of emerging technologies through five phases: 1) technology trigger, 2) peak of inflated expectations, 3) trough of disillusionment, 4) slope of enlightenment, and 5) plateau of productivity.
- In 1991, Ubiquitous computing: coined by Mark Weiser of Xerox Pal Alto Research.
- RFID (Radio Frequency IDentification): can be read as a package in a storehouse by radio frequency, (not by optical reading)
- TRON as an open OS is earlier (1984) than Linux (1991).
- TRON is open realtime OS kernel design, particularly used in electronic device such a mobile phones, appliances (ITRON).
- TRON itself does not specify the source code for the kernel, but is a set of interfaces and assign guidelines for creating the kernel; allowing different companies to create their own versions of TRON, which will be proprietary of the implementor.
- TRON requires priority scheduled processing in small embedded chip (rather poor resource).
- TRON is used in spacecraft like Hayabusa, or spacerocket (H2A).
1. IoTとユビキタス・コンピューティング:
- hype: extravagant promotion
- Hype Cycle (Gartner)
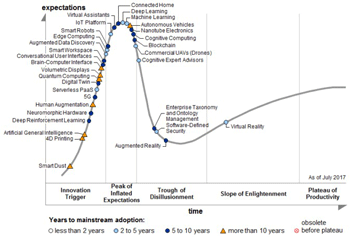
1)黎明期, 2)流行期, 3)幻滅期, 4)回復期, 5)安定期
>Top 2. Open system connecting the world:
- Open systems connect the world:
- there are many social systems which need human decision and control; the most optimal control of these systems can realize more secure, comfortable, less-energy, and less-resource social systems.
- Big data analytics and cloud computing technology as well as minute embedded chip technology have realized ubiquitous computing.
- Embedded system:
- the architecture is composed of UI, sensor, embedded chip, effector, and feedback mechanism of these function for specific tasks.
- German IoT: Industrie 4.0 promoted by all-German organizations, aiming 1.7% growth with higher wages in major six industries, such as chemical, automobile, machine, electronics, agriculture, and ICT.
- US IoT: Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC) composed of GE and other major US corporations.
- Many data are collected from many embedded sensors as Big Data; necessary data are very limited, but others are accumulated into cloud servers which will be analyzed and used for preventive maintenance and other purposes.
- Japanese IoT: almost closed IoT like Toyota Kanban System, or Komatsu's KOMTRAX, or IHI's SORACOM; It is serious that Japan had leaded in OT (Operational Technology) of each enterprise group, but is left behind as an open IoT.
- The boundary of open IoT is ambiguous; hence such openness will cause innovation in society.
- Internet based on best effort and open architecture could take a lead over strict and guarantee-base architecture of VAN or OSI (Open Systems Interconnection).
- Traffic system is exceptionally open system, supported by various laws and insurance.
2. 世界をつなぐオープンシステム:
- preventive maintenance: 予防保全
>Top 3. Proof of Concept experiment of IoT:
- Traceability of things:
- expiration date or defective products; such as medicines, foods, building parts
- maintenance record; such as aircraft parts, fire alarms, playground equipment, streetlight, , bridge, tunnel, or other street furniture
- VCM (Value Chain Management) has more versatile applications than SCM.
- Travel guide, or disaster information; convenience of RFID should be used multi purposes.
- Automatic generating element:
- Energy harvesting from environment, such as sunlight, room light, difference of humidity or vibration; partly realized in solar watch or solar calculator.
- >Top From IoT to IoE (Internet of Everything):
- IoT identify not only a certain thing, but also its location. The information of location should be more detailed and structured; e.g., two adjacent doors in an apartment are significantly different information for visitors, but the location of inside the house is not so important.
3. IoTの実証実験:
>Top 4. Open IoT:
- Industrie 4.0:
- A factory functions as an living organization or a robot factory; connecting each machine and each part, tracing each process of fabrication, supply of parts, management of products, and maintenance of machine if needed.
- German Industrie 4.0 is grandeur concept which connect with other related factories or industries, aiming to function as an unified ecosystem; which enables to respond small-lot production or customized production, or even change order, etc.
- German emphasize the such Industrie 4.0 could maintain competitive production with higher wages.
- But this concept is still confined in manufacturing industry; if it is applied more widely, including consumers' environment which give data estimating demand and disposal of goods; or expand to apply to other industries (agriculture, etc.)
- US Industrial Internet mostly focusses to operation and maintenance of facilities, covering aircraft engine, facilities of utility services and medical instrument, etc.; preventive maintenance based of the Big data is quire effective, not only to minimized maintenance cost but also prevention of accident.
- Thus the essence of Industrie 4.0 is openness of IoT, whose philosophy is derived from the openness of the Internet.
4. オープンIoT:
- small lot production: 少生産
- automatic generating element: 自律発電素子
- 発電の分散化:
- 昔から鉱石ラジオや自転車ダイナモのように、電波や回転で発電を行う仕組みはあった。
- <IoTとEnergy Harvesting>:
- 電気料金(平均): ¥20/kWh
- 乾電池(単3): ¥30/2000mAh☓1.5V=3Wh,
¥10K/kWh=AC電源の500倍
- エネルギー源は光、力学、熱、バイオ
>Top 5. Services provided by IoT:
- Service area of IoT applications is very large; services with thinner adhesion with society is easier to be realized; e.g., services (productivity) in a factory is rather easier.
- The target area of services is expanding from 1) particular corporation, 2) particular corporate group, 3) particular industry, and so on.
- IoG (Internet of Guest); recognition of each guest is the base of service industry. (omotenashi)
- Service 4.0:
- 1) Service1.0 telephone service, 2) Service2.0 copy & fax service, 3) Service3.0 Internet&digital telecom service, 4) Service4.0 IoT service.
- 2020 Tokyo Olympic:
- The Olympic should be a significant trigger of major social transformation.
- Many advanced ICT technology will be serviced by 2020, such as Free WiFi, automatic machine translation, digital signage, 4K/8K broadcasting.
- Expansion of usage by electronic money will be a realistic service.
- Face recognition is also useful, but privacy problem remains due to limitless usage of such data in Japan. (memory limit of FeliCa card such as Suica is about 6K byte.)
- >Top VRM (Vendor Relationship Management):
- This is the opposite service of CRM; each customer managed vendors which relates the customer.
- VRM is realization will be an important infrastructure 'Omotenashi' (hospital services for customer).
5. IoTによるサービス
- adhesion: sticking together of different substances, 密着度
- VRM: CRMの対局; =おもてなし精神
>Top 6. The world enabled by open infrastructure:
- Best efforts vs. Guaranteed services:
- Road traffic vs. Rail traffic
- In the case of road traffic, there are various responsibility entities, police, car maker, car repair shop, driver, and pedestrian.; 'Proceed with caution' is a kind of best-effort, which is considered as vulnerable (or flexible) system.
- In driving car, the destination is not fixed, which will be changeable or flexible; while rail traffic the destination is rigid and guaranteed.
6. オープンのインフラがもたらす世界:
- 道路交通と鉄道交通の違い
>Top 7. Products changed by IoT:
- Increase of function:
- E.g.: digital camera is increasing its function, just like PC, having facial recognition to focus particular persons with profiles and other data; which has the risk of leaking personal data.
- increase of function has required more development cost, but having no corresponding returns (diminishing returns)
- Open IoT: aims to realize enhanced services combination of cloud services and each device function.
- Open IoT can make the surrounding environment into user interface of different devices in more preferable ways. (natural user interface)
- a) function of digital camera: UI, sensor, embedded computer, display
- b) Aggregate computing at home: UI, sensor, cloud, one big display on the wall.; this system other environmental data, such as temperature, air flow, sound, vibration, and recognition of other things.
- Open IoT can make the space itself as a surrounding big camera.
- Automatic driving used 360-degree bird-view sensors, which will be a future camera recognizing surrounding environment.
- >Top Future design: an integrated function of various embedded systems, cloud, and human; for this purpose, Open Camera API, or human motion sensor will be indispensable.
7. IoTで製品はどう変わるのか:
- diminishing returns: 収益逓減
- Open IoTは、各デバイスのopen APIが必要
- 環境自体をインターフェイスに
>Top 8. Dillemma of global competition or of Japanse comptetiveness:
- Programming ability is indispensable from younger generation, same as 'reading, writing, and counting'.
- Users who has the ability of programming can make preferable environment required for individual life and works.
- It is needed that specialists of various fields who can program as users, not the programming specialits.
- Compulsory programming education started in Israle since 2000, and in UK since 2014; and in US new education program for programming was published in 2015.
8. 世界競争と日本のジレンマ:
- プログラムできる各分野の専門家必要
- プログラム初等教育の義務化: IoT時代の読み書き計算
>Top 9. Pursuing Open Innovation:
- US learn from many mistakes or failure of experiences; or even justify 'changes" based on various failures.
- Such failures are used to rationalize to change the promoting organizatrion or staff; which seems a kind of effecrtive way to eliminate vested or established interest group:
- The case of deregulation of power utitilies in US is one of these samples.
- In Japan, failures are not recognized from the beginning, so that social closed system or the established organizations remain and regist against any kind of changes.
- The case of thermial for mobile phone is a typical example.
- Mobile phone carriers aid for development of terminals which are didcated to be used for the carriers (with SIM locked); this closed business model caused a temporary success of such as i-mode service of NTT-DoCoMo (who subsided as much as Y10B)
- When smart phone appeared in the market, Japanese carrieers enforced to use only preinstalled application in all designated terminals for the carrier.
- In 2007 Apple published i-phone, which was developed from PC culture. (resurgence of the black ships)
- This is a battle between closed governance vs. open governance.
- It is getting clearer that openness, best-effort, or mash-up contribute more rapid innovation in the network society.
- Closed business model such as keiretsu or association of particular corporate group backed by Japanese unique culture emphasizing closedness, elaborateness, reconcilement, self-containment, or guarantee could not follow any more the rapid pace of development by open architecture.
- Steve Jobs of Apple could not appear in Japanese market; Japnese traditonl policy is base to 'targeting policy' usually designated by J-Gov or major keiretsu group, which is the farest from the theroy of evolution or innovation.
- In 1991, NHK broadcast 'Electronics technology-intensive Japan', but where has gone such slogan nowadays?
- >Top Review of privacy policy: privacy should be regarded as an exlusively controllable right of the individual. But the privacy information should be properly used by other legitimate organizations according to particular cases (such as disater or emergency). (Legitimacy of intention)
- Public in the network society should be reviewed from the viewpoint of social responsibilty of the individual.
- Importance of open data:
In Japan, there are may national issues, such as deteriolation of social infrastrucutre, energy crysis, theat of natural disastger, sustainability of medical systems, aging society, dependecy and safety of food, etc.; some porting of these issues could be solved or relieved by open data.
- Governance changes are urged in Japan; from concentrated to distibuted architecutre, and from closed to open system.
9. オープン・イノベーションを求めて:
- vested/established interest group: 既得権者
- resurgence: revival
- elaborateness: 緻密さ
- reconcilement: 摺合せ
- self-containment: 自己完結
- legitimacy intention: 意図の正当性
- 米国は多くの挑戦・失敗事例から学ぶ
>Top 10. Starting from network and identification:
- To identify things, space, and cocept in the real world:
- IoT (Internet of Things) is different from the conventional ICT; because IoT connect all situation of things, on which various services are added.
- IoT needs to have certain mechanism to distiguish or identify things in the real world (context awareness)
- >Top ucode (ubiquitous code); fixed lengh number of 128bit (2128)
- Using this ucode, computer can recognized things, location, and relation between them.
- uID archtecture does not limt media (ucode tag) on which ucode is attached.; there will be various media such as RFID tag, active cell with battery, attached to metals, or washable materials, etc.
- Information of things or location is installed in a database of the cloud computer; which separates identified number and its information. The latter information could be easily updated.
- The elements of such identification are the data of 'when, where, what, who corresponding to the ucoded things.
- ucode is distributed among any things which should be identifed, such as organization, or production lot, etc.
- ucode means unisquitous, universal, uniform and unique code.
- Difference between ucode and JAN (Japanese Article Number) code:
- JAN dode: 13 digits code.; 2 digits for country code (Japan is 45 or 49), following 7 digits are maker's code, and the remained 4 digts are code of product item and check digit.
- This JAN code can be read by POS cash register machine.
- But ucode contains more vertitle information on the cloud; which can express recall notice of defective products, etc.
10. すべてはネットワークと識別から始まる:
- context awareness: contexts that they collect from each user, and method by which they convey this information to other users.
>Top 11. Aiming for Aggregate Computing Model:
- Embedded system in IoT age:
- to realize the best performance of TRON as realtime OS.
- Though UNIX-like OS is most appropriate in the cloud, including Big data processing, it is too heavy for the embedded system OS.
- The embedded OS should concentrate at particular realtime function, such as deciding focussing and shutter speed of camera, assigning other general processing to the cloud computing.
- This division of roles should be applied to middleware as well as OS; OS itself tends to be minimized or specialized in limited function, leaving other additional function to middleware or applications.
- >Top Contradiction of Open IoT:
- The Open IoT means everything could be connected freely by the Internet; which could be available beyond the controls of makers or administrators. But what will the governance management in this case? What will be in the case of natural disasters?
- E.g.: there will be read-only API and controllable API in the case of elevator control in a building. The residents can call the elevator cage using controllable API and their smartphones, but visitors can wait and use the elevator using read-only API.
- Thus Open IoT aims more flexible governance management, while embedded OS should have limited function with realtime response (contradiction).
- Generally, flexible access control at the cloud computing is needed to respond to the changes of policies or right of stakeholders, mange by the white or black list, or discover other service requirements.
- Smart House:
- hitherto smart house concept (so-called 'Home automation network') is promoted by particular electronic makers using their own products. A-maker's products connects A-maker's cloud only.
- Change of computer architecture since 1980's:
- most of processing had done within the node, then had sent via expensive telecommunications.
- But now the telecom cost became almost zero; which means that it is right to minimize computing resources at the node.
- The 5G world can use mobile network as much speedy as in-house WiFi network; this means the home server useless.
- The aggregate computing is that we aim to connect every home electronics directly to the network by the Internet protocol (TCP/IP)
- The edge node should be a faucet, the output of various services; the maker continues to provide updated services via connected appliances.
- It could be a nightmare that once some particular appliances were open-IoT'ed, connecting to the big giant's network; this mean the maker would be an affiliate of the giant's network.
- The case of smart phone market occurred in such a situation; Japanese mobile phone makers went down and lost the device market.
- In the aggregate computing model, the makers can provide their services via their own cloud computing, accumulation the related big data as well as business know-how's.
- The enclosure strategy is not preferable, but moderate level of proprietary services is preferable for actual business.
- Aggregate Computing (>Fig.)
- This architecture aims to optimize the integrated intelligence level of the combination of local and cloud environments.
- The essence of the aggregate computing is direct connection of the local node and the particular cloud; where there will no need of having complex governance management of the local side.
- The local node is connected with the particular cloud by virtual tunnelling circuit.
- The complex application system is installed at the cloud side, whose API is open to be connected with other IoT services under the enhanced governance management.
- The cloud computing system identifies and verifies each device having each ucode (ubiquitous code).
- Features of the aggregate computing contains the architectures of thin client, SaaS of applications, and cloud environment; all of these have been developed to eliminate anxiety of security, governance of the user's devices as well as to take advantage of lowering cost of telecommunication.
- ucode: Number of ucode is composed of 128 bits of number, i.e.,
- >Top Open data:
- The author established VLED (Vitalizing Local Economy organization by open Data & big data, in order to promote the importance of using open data, which enables social transformation and innovation.
- ODPT (association fro Open Data of Public Transportation)
- In London, TfL (Trasport for London) governs all tranffics including metro, taxi, rental bycicles, while in Tokyo there is no such integrated governance. On the contrary, in Tokyo there are 14 railway companies, 38 bus compnaies, 1100 taxi companies excluding private taxi services.
11. アグレゲート・コンピューティング・モデルを目指して:
- >Top Aggregate Computing:
Flexible access control
アグレゲート・コンピューティング
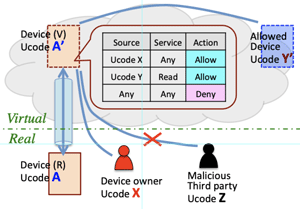
- 1980年代以降のコンピュータアーキテクチャの変遷
- ノード内処理中心
- 通信料金が高かった
- 各メーカの囲い込み政策
- データをオープン化すると、ネットの巨人(GAFA)の下請けになる恐れ
- 携帯端末メーカの凋落
- 一般社団法人オープン&ビッグデータ活用・地帳創生推進機構
- Level of Open Data:
- L1: PDF
- L2: Excel, Word
- L3: CSV, XML
- L4: RDF (Resource Description Framework); RSS (RDF Site Summary) はその一部; 主語+述語+目的語からなる記述方法
- L5: Linked-RDF
- ucode: 128 bit =2128
Comment
- The author clarifies the essence of Open IoT as Open API of each IoT device, and advocate various makers to make such Open API.
- Closed IoT tends to make more complicated devices with too many function and difficult interface, as well as expensive prices.
- Programming ability is indispensable to make individual environment as preferable interface.
- 著者はOpen IoTの本質は、各デバイスをOpen APIであるとしている。
- Closed IoTは、結局、過剰機能と困難なインターフェスおよび高価格商品を生むだけである。
- プログラム能力は、個々の環境を望ましいインターフェイスにする上で必須。
What is IoT?- From technical innovation to social innovation - |
Cat: ICT |
|
Ken Sakamura (坂村健) |
19627u |
Résumé |
Remarks |
|
>Top 0. Prologue:
|
0. 序文:
|
>Top 1. IoT and ubiquitous computing:
|
1. IoTとユビキタス・コンピューティング:
1)黎明期, 2)流行期, 3)幻滅期, 4)回復期, 5)安定期 |
>Top 2. Open system connecting the world:
|
2. 世界をつなぐオープンシステム:
|
>Top 3. Proof of Concept experiment of IoT:
|
3. IoTの実証実験: |
>Top 4. Open IoT:
|
4. オープンIoT:
|
>Top 5. Services provided by IoT:
|
5. IoTによるサービス
|
>Top 6. The world enabled by open infrastructure:
|
6. オープンのインフラがもたらす世界:
|
>Top 7. Products changed by IoT:
|
7. IoTで製品はどう変わるのか:
|
>Top 8. Dillemma of global competition or of Japanse comptetiveness:
|
8. 世界競争と日本のジレンマ:
|
>Top 9. Pursuing Open Innovation:
|
9. オープン・イノベーションを求めて:
|
>Top 10. Starting from network and identification:
|
10. すべてはネットワークと識別から始まる:
|
>Top 11. Aiming for Aggregate Computing Model:
|
11. アグレゲート・コンピューティング・モデルを目指して:
|
Comment |
|
|