Shia Muslims
- Emerging Minority of Islam -
Cat: HIS
Pub: 2006
#: 1814b
Keiko Sakurai (桜井啓子)
18923u
Résume
Remarks
>Top 0. Introduction: Rising Shia Muslims:
- Shia, or Shiah as a collective or Shi'i or Shi'ite individually; called 'Shi'ah Ali' or 'ash-Shia'
- 1979: Iran Islamic Revolution by Ayatollah R. Khomeini (1902-89)
- overthrew Muhammad Reza Shah Pahlavi dynasty.
- established the union of religion and politics. (Vilayat-e Faqih, Guardianship of the Islamic Jurist)
- called US a devil state.
- 2006-14: Nuri K. al-Maliki, leader of Siite Dawa Party, was Prime Minister of Iraq.
- Emerging Siites in key area of Islamic countries.
- Shiite religious leaders are hierarchical, while Sunni are not.
- Ali al-Hussini al-Sistani (1930-, commonly known as Ayatollah Sistani), described as the spiritual leader of Iraqi Shia Muslims.
- >Top Major differences between Sunni and Shia:
- Sunni believe that Muhammad had no rightful heir and that religious leader should be elected through a vote among the Islamic community.
- Shia believe that only Allah can select religious leaders; all successors must be direct descendants of Muhammad's family. Ali was the rightful heir.
- Both groups perceive the Mahdi as the sole ruled of the Islamic community. Sunni hold that Mahdi has not yet been born, while Shiites believe that the Mahdi was born in 869 and will return to Earth under Allah's orders.
- Contribution of Aisha bint Abu Bakr (or Ayesha, 613/14-678) as a wife of Muhammad (She is engaged at nine and married at ten, when Muhammad 53, as the third and youngest & beloved wife.); She delivered pubic speeches and helped both men and women to understand the practices (sunnah) of Muhammad.
- Sunni values her contribution in spreading Muhammad's message (2210 hadiths, including inheritance, pilgrimage and eschatology) including 44 years after his death.; Abu Bakr was influential in the community.; she avenged Uthman's death participating in the Battle of the Camel.
- Shia have negative view of Aisha, and accuse her of hating Ali.; Shia believe that Ali had been appointed by Muhammad as a successor; but Abu Bakr had two advantages; long personal friendship and his role as father-in-law; Being the daughter of Abu Bakr tied Aisha to honorable titles.
- Both Sunni and Shia consider same Prophet, same Quran, worship same God Allah but have differences when it comes to the leaders. Sunnis don't believe in Imamas and Shia don't believe in Sunni Caliphas.
- They also have disputes over Fathimah bint Muhammad's death.
0. 序文: 台頭するシーア派:
- Ration of Shiites:
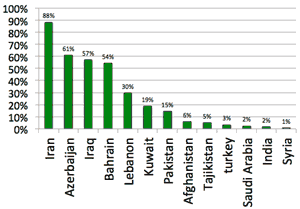
- スンニーはとシーア派の違い
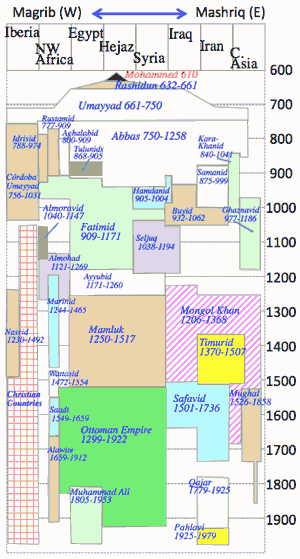
>Top 1. Establishment Shia Muslims:
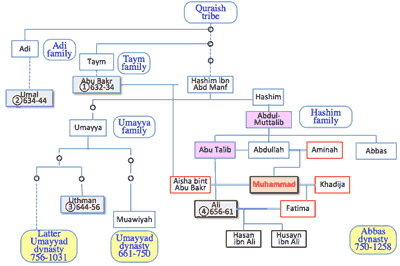
- 570c: Muhammad
ibn Abd Allah ibn Abd al-Muttalib; born in Mecca, was orphaned at an early age, and was raised by uncle Abu Talib.
- at age 40, first revelation in the cave.
- 595; married Khadija (40 years).
- 610; started preaching these revelations publicly.
- 622; he and his followers migrated to Medina (Hijra, the beginning of Islamic Calendar).
- 632; after returning from the Fairwell Pilgrimage, he fell ill and died.
- >Top Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abu Talib (601-661); then married Fatima, daughter; rasing two sons Hassan and Hussayn; became 4th caliph (656-661).
- This is primarily contrasts with that of Sunni Islam.
- Abu Bakr of Taym family became the firs caliph (632-634).
- Abu Bakr designated Umal as the second caliph; who conquered Sasanian Persia; later designated six candidates including Ali.
- But Uthman became the third caliph, who contributed to compile Quran, however, who favored Umayya family.
- 654 Muawiyah, leader of Umayyadh family fought with Ali.
- Muawiyah became caliph of Umayyad dynasty after the death of Ali; Shia Islam rejected Muawiya.
- Shia Isla regarded Ali as the first Imam.
- Majority of Islam accepted caliph of Umayyad dynasty as well as four caliphs after Muhammad; caliph should be selected among the most appropriate adult man unless designated by the previous caliph; neither pedigree of the prophet nor ability of deep understanding quran is questioned.
- necessary Islamic knowledge could be found in words and deeds of the prophet (sunna)
- Muawiya seized power as the first caliph of Umayya dysnasty in Damascus.
- >Top 680/10/10: Battle of Karbala:
- the battle of a small group of Husayn ibn Ali and much larger military detachment of Yazid I, 2nd caliph of Umayyad dynasty.
- This played a central role in shaping the identity of the Shia.
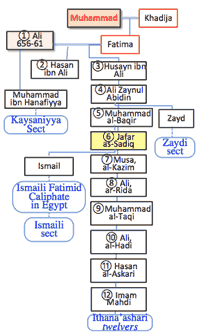
- Only survivor of Karbala, Ali Zaynul Abidin became 4th imam.
- 740 Zaid ibn Ali again revolted against Umayyad dynasty, but was defeated; the remains organized Zaid sect.
- 750 Abbasid caliphate: one of Hasim family.
- overthrew the Umayyad caliphate; first centered in Kufa, then founded Baghdad; which became a center of science and culture (golden age of Islam).
- but transformed into Sunni hegemony by major Arab, oppressed Shia Islam.
- >Top Taqiya; permitted to conceal their religion when under threat of persecution. (⇔ Shahada)
- >Top 733-765: 4th imam, Jafar as-Sadiq; established Islamic law (sharia; fiq)
- Ismaili Fatimid Caliphate in Egypt (909-1171)
- 7th imam, Musa al-Kazm was poisoned by Abbas dynasty.
- when 10th imam Ali al-Hadi, 10th caliph of Abbas dynasty suppressed Shiia and destroyed tomb of Husain.
- Gaiba (hidden Imam); occultation in Shia believes that messianic figure, or Mahdi, who is an infallible male descendant was born but disappeared and will one day return.
- 874-940: short hidden Imam; 940-now: long hidden Imam.
- >Top Prince of martyrdom - Husayn ibn Ali:
- Muhammad was raised by Abu Talib, the father of Ali; on the other side, raised 30-year-younger Ali as if his own son.; he made Ali marry his own daughter Fatima in 622 just after the Hejira; having pedigree of his grandsons of Hassan and Husayn.
- 3rd imam; took intransigent attitude in Kufa; resisting oppression by Yazid ibn Muawiya (647-683), Umayyad 2nd cariph. (Karbala paradigm - justification of Islamic revolution against royalism.)
- in 680 Muharram 10th (Ashura); and martyrdom talks and dramas (friends are in green and white costume, and enemies in red).
- >Top Doctrine: essential beliefs of five principles. (Usul ad-Din)
- Monotheism: God is one and unique.
- Justice: moral rightness baed on ethics, fairness, and equity, along with the punishment of the branch of said ethics.
- Prophethood: God sends emissaries, or prophets to guide mankind.
- Leadership: Imams are divinely appointed
- Last Judgment: God's final assessment of humanity; (the Day of Resurrection)
1. シーア派の成立:
- Muhammud Genealogy:
- Shia Imam:
- Holy sites:
- Mecca: Al-Haram Mosque
- Medina: Al-Nabbawi Mosque
- Jerusalem: Al-Aqsa Mosque
- Kufa: Kufa Mosque
in addition for Shia:
- Karbala: Imam Husayn Shrine, Al Abbas Mosque
- Najaf: Imam Ali Mosque
- Samarra: Al-Askari Mosque
- Mashhad: Imam Reza Mosque
- シーア派五信:
- 神の唯一性
- 神の正義
- 預言者
- イマーム
- 来世
- Five Pillars of Islam イスラム五行;
(シーア派十行):
- ■信仰告白: Shahada, Faith (lā ʾilāha ʾillā-llāhu muḥammadun rasūlu-llāh)
シーア派は以下追加: Ali is the wali of allah.
- 礼拝: Salah, Worship
- 喜捨: Zakat, Charity
- 断食: Sawm (Ramadan), Fasting
- 巡礼: Hajj, pilgrimage to Mecca
- 五分の一税: Khums
- ジハード(努力): Jihad
- 善行: Enjoining good
- 悪行の阻止: Forbidding wrong
- 預言者とその家族への愛: Tawalla
- 預言者とその家族の敵との絶縁: Tabara
>Top 2. Political power and Shia:
- 1501-1736 Safavid dynasty:
- Ismail-Ⅰ (1501-24); founder of the Safavid dynasty; revival of an efficient state in Iran; its bureaucracy and for its fine arts.
- Twelver sect of Shia Islam to be the official religion; separating its strong Sunni neighbors - the Ottoman empire to the west and the Uzbek confederation to the east.
- One genealogy claimed that Ismael's ancestors was a lineal descendant of Ali.
- 1736-1802 Afsharid Dynasty:
- the dynasty was originated from the Turkic Afshar tribe.
- Nader Shah deposed the last member of the Safavid dynasty and proclaimed himself Shah of Iran.
- Nader was brought up as a Shia but later espoused the Sunni faith.
- Nader aimed to weaken the Safavids in his religious reforms since Shia Islam had always been a major element.
- many Shia ulamas fleed from the country to Shia cities like Karbala.
- but Sunnism could not succeed in Iran, which Shia survived.
- Behbahani (1704/05-91) grew up in Najaf, then lived in Isfahan for thirty years, then shifted to Karbala, establishing the authority of Mujtahid in Islamic law in Shia tradition.
- >Top Four major Shia cities:
- Al-atabat al-aliyat or Al-atabt al-Muqaddasa: holy Shia shrine cities of Iraq; location of tombs of Shia imams are important centers of devotion, pilgrimage and scholarship
- Najaf, Karbala, Kadhimiya, and Samarra
- >Top Qajar (or Kadjar) dynasty in Iran, and Awadh dynasty in India: both are Shia dynasties.
- Qajar dynasty (1794-1925): Turkic origin fro Aqjar tribe; lost many Caucasus lands (Georgia, Dagestan, Azerbaijan and Armenia) )to Russia in 19C.
- the Battle of Ganja (1804) during Russo-Persian War (1804-13).
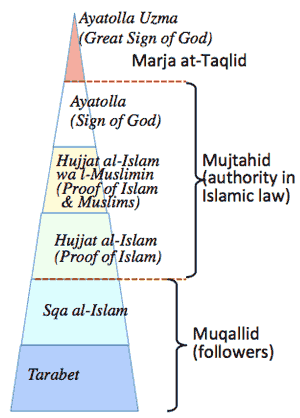
- >Top Hawza; seminary where Shia Muslim clerics are trained.
- Training institutions for mujtahid; a recognized expert who mastered Islamic law by decades' training.
- Marja' taqlid (or Marja dini); source to imitate/follow; a title given to the highest level Shia authority; a Grand Ayatollah; after Quran, and the prophets and imams, maraji are the highest authority on religious laws.
- who has supported ulama (scholar, or the learned one, who got official licence to teach called ijazat); through times this system has been maintained by Islamic merchants and landowners through religious taxes like zakat and jizya; such ulama survived as independent organizations in the Ottoman empire and Qajar dynasty.; ulama advised and guaranteed transaction or legal know-hows based on the Islamic law. (just like legal or accountant advisers in capitalism.)
- Najaf has been the center of mujtahid, having twenty or more religious schools (hawza) with several thousand students, among which Iranian students share nearly one third.
- >Top Wahhabism (18C):
- religious movement founded my Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahahb (1703-1792), described as ultraconservative, fundamentalist or puritanical to restore pure monotheistic worship; negated traditional Sunni practices; started such reform movement in sparsely populated Najd.; formed a pact with Muhammad bin Saud (1687-1765); the House of Saud as politico-religious alliance with Wahhabi sect.
- 1932 proclamation of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia; 5 million Wahhabis in the Gulf region (compared with 29M Sunni and 89M Shia).
- the majority of Sunni and Shia Muslims disagree with wahhbism as a vile sect, denouncing Wahhbism a source of global terrorism, inspiring the ideology of the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL).
- majority of Shia in Iraq were converted to Shia since 19C by the change life style (from nomadic to settled farming life), particularly in southern Iraq.
- Conversion to Shia meant to resist to the ruling Sunni of the Ottoman empire.
- Shia situation is different from that of Iran; Shia gained support from Safavid dynasty, while Shia in Iraq have been supported by merchants and professionals opposing to the the empire.
- >Top Persian Tobacco Protest; a Shia revolt in Iran again 1890 tobacco concession granted by Nasir al-Din Shah of Persia to UK, granting UK control over growth, sales and export of tobacco.; 1891 fatwa (legal opinion) against tobacco use issued by Grand Ayatollah Mirza Hassan Shirazi.
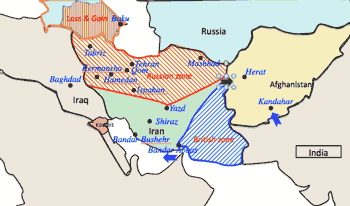
- 1905-1911 Iranian Constitutional Revolution:
- establishment of parliament in Persia during the Qajar dynasty.
- the monarch Mozaffar ad-Din Shah Qajar signed the constitution in 1905, but died shortly after and replaced by Mohammad Ali Shah.
- in Aug. 1907 Anglo-Russian agreement divided Iran into Russian zone in the north and British zone in the south. UK switched their support to Shah Muhammad Ali, 6th Qajar Shah, abandoning the Constitutionalists.
- the constitutional forces marched to Tehran, forced Muhammad Ali Shah's abdication in favor of his young son Ahmad Shah Qajar and reestablished the constitution in 1909.
- 1921 Persian Coup; establishment of the Pahlavi dynasty in 1925.
- Mujutahid in Iraq support such Constitutional movement in Iran; but some mujutahid objected the constitutionalists due to the contradiction between the modern constitution and Islamic laws.
- 1917:
- Russian army retreated due to 1917 Russian Revolution; UK tried to colonize whole Iran in 1919.
2. 政治権力とシーア:
- Al atabat (シーア派聖地)
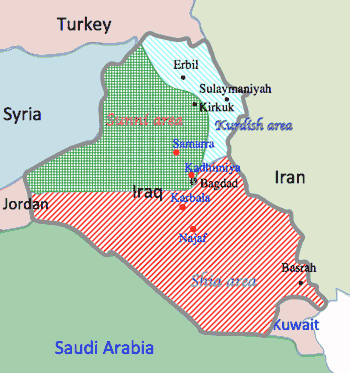
- シーア派の4大拠点
- カジャール朝 (1794-1925):
- ハウザ:
- マルジャ・タクリード;
グランド・アヤトラ
- Hierarchy of Shia Ulama:
- ワッハーブ派
- ムハマド・アブドゥル・ワハーブ
- シーア派のイラクへの移住
- タバコ・ボイコット運動
- Qajar朝(19C):
>Top 3. Foundation of Modern State and Shia Muslims:
- 633: Islam fought with Seasoned dynasty in Mesopotamia, and won at the battle of al-Qadisiyyah.
- Khalid ibn al-Walid (592-642), military commander of Rashidun Caliphs (Sword of Allah, praised by Muhammad and Abu Bakr), contributed to expand Islamic dynasty.
- 651 Sassanid dynasty was extinct at the age of Usman.
- Islam occupied Persia, absorbing Persian technology and science; most of the scholars are Persian, and its language written in Arabic character became an international language.; many Zoroastrian fled to India (Parsi in Gujarat Province).
- 873-999 Samaniyan dynasty (now in Uzbekistan and Tajikistan); capital at Samarkand and Bukhara; Tajikistan currency somoni is named after Ismail Samani.; Persian literature.
- >Top 934-1062 Buyid dynasty (Al-e Buye); founded by Ali ibn Buya, capital at Shiraz, the first Iranian Shia dynasty.
- 11-12C: Turkish dynasties such as 1) Ghaznaviayn (955-1187) centered in Afghanistan; 2) Seljuq dynasty (1038-1308); 3) Khwarazmian dynasty (1077-1231); these dynasties adopted Persian language and Persian civil officials.
- 1220: occupied by Mongol Empire; Ilkhanate (1256-1353, capital Tabriz)
- 1353-1507 Timurid Empire (capital: Samarkand-Herat);
- 1501-1736 Safavid dynasty: Ismail-Ⅰ, capital Tabriz -Qazvin -Isfahan ; promoted Twelver, which became state religion; in 1598 Abbas-Ⅰ transferred the capital to Isfahan.
- 1638 Iraq area was occupied by the Ottoman Empire.
- 1789-1925 Qajar dynasty of Turkic origin (capital Tehran).: Russia and Britain invaded and partly colonized; in 19C Russia comprised Georgia, Dagestan, Azerbaijan and Armenia.
- 1905-1911 Iranian Constitutional Revolution, requiring Parliament; 1907 Constitution had been a backbone of Iranian nation-state.
- Russo-Japanese War (1904-05), and Bloody Sunday in Russia (1905) gave serious impact to Iran.
- 1917 Russian Revolution caused to renounce all privileges in Iran held by Russian Empire, while in 1919 British aimed to make Iran its Protectorate.
- >Top 1925-1979 Pahlavi dynasty: founded by Reza Shah Pahlavi, a former Persian Cossack Brigade; succeeded by his son Mohammad Reza Shah Pahlavi, the last Shah of Iran; the official name the Imperial State of Iran was adopted; aimed modern state
- adopted Shia as the national religion.
- reform into education in Western style; forcing promoting examination.
- derived authority of legal services from ulama; limiting only graduated of law faculty of universities.
- during WWII Reza Shah approached Nazi Germany, which gave excuses to UK and USSR to occupy the country, being abdicated to his son Mohammad Reza Shah Pahlavi.
- 1951-53 Mohammad Mosaddegh, prime minister of Iran; nationalized Anglo-Persian Oil Company (AIOC, later BP).
- 19 Aug. 1953: Operation Ajax, Coup d'état by CIA at the request of MI6.; Mosaddegh was imprisoned, then put under house arrest until his death in 1967.
- >Top 1963 White Revolution; promoting Western nationalism by Muhammad Reza Pahlavi (Pahlavi-Ⅱ) including improving:
- formation of literacy corps; illiteracy ratio from 95% to around 50%
- agrarian reform; resale to the peasants at 30% below the market value.
- women's suffrage
- monogamy
- causing expansion of rich-poor gap and corruption; depressing Shia ulama and rising popularity of Ruhollah Khomeini, as well as serious inflation.
- >Top 11 Feb. 1979 the Islamic Republic of Iran, ending 2500-year-old Persian monarchy.
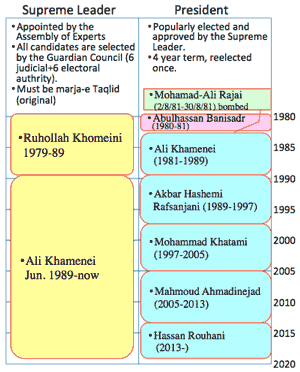
- Sayyid Ruhollah Musavi Khomeini (1902-1989) known as Ayatollah Khomeini, leader of 1979 Iranian Revolution, learned Njaf, became Iran's Supreme Leader; was succeeded by Ali Khomeini in 1989.
- spent more than 15 years in exile.
- referring to US as the Great Satan and USSR as the Lesser Satan.
- Vilayate Faqih (Guardian Jurist): Khomeini published the rule of the Islamic jurist; which includes not only jurisdiction or religious tax, but also sovereignty of the country.
- IRP (Islamic Republican Party); formed in 1979; was disbanded in 1987 due to internal conflicts.
- Iraq after WWI:
- until WWI, Iraq had been a province of the Ottoman Empire (1299-1922) since conquer of Bagdad.
- But Safavid dynasty (1501-1736) and Qajar dynasty (1796-1925) had influenced Iraq due to protection of the holy places.
- 1920; Iraq became British Mandate of Mesopotamia; while Shia and Sunni Muslims jointly rebelled against UK.
- Faisal ibn Husayn of Hashim family(Faisal-I, 1921-1933) was granted by British the territory of Iraq to rule it as a kingdom.
- Kuwait was separated; and Kurdish self-determination in the Kurdistan area was not considered.
- Faisal-I promoted pan-Arabism by the unity of Sunni and Shia.
- There are three major ethnic groups in Iraq; Sunni Arab in central & norther area, Shia Arab in southern, and Sunni Kurd in northern mountainous area.
- >Top Faisal-Ⅱ (1939-1958):
- allied with British Empire in WWII.
- Abd al-llah served as regent for Faisal II (1939-53); who was killed in 14 July Revolution in 1958 Iraqi coup d'état; overthrew the Hashemite monarchy, established the Iraqi Republic.
- >Top Abd al-Karim Qasim to power as Prime Minister until 1963;
- was overthrown in the Ramadan Revolution Feb. 1963 coup d'état by Bath Party.
- Nov. 1963 Iraq coup d'état by Abd as-Salam Arif.
- >Top Saddam Hussein Abd Al-Majid al-Tikriti (1937-2006); President of Iraq (1979-2003), leader of Arab Socialist Baath Party, a mix of Arab nationalism and socialism.; played key role in 1968 coup d'état (17 July Revolution).
- position of power backed by Sunni Arabs, only a fifth population; suppressed Shia and Kurdish movements; maintained power during the Iran-Iraq War and the Gulf War.
- >Top 1980-88: Iran-Iraq War:
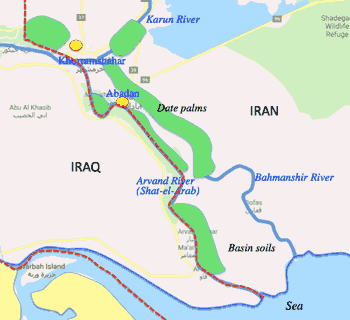
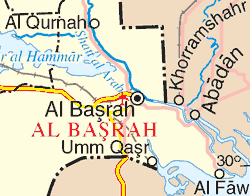
- Khuzestan Province; one of 31 provinces of Ira, bordering Iraq, its capital is Ahvaz and major city Abadan.
- During the Iran-Iraq War, Iraq invaded Khuzestan Province; Saddam Hussein felt confidence that Arab population of the area would react enthusiastically; but the resistance to the invasion was fierce, stalling the Iraqi military advance.; the largest refinery at Abadan was destroyed, never to fully recover.; many famous palm groves were annihilated.
- by 1982 Iranian forced pushed back Iraqi forces out of Iran, which became a turning point in the war.
- Some ethnic groups in Khuzestan complain over the distribution of the oil revenue.
- In 2003, US George W. Bush and UK Tony Blair falsely accused him of possessing weapons of mass destruction and having ties to al-Qaeda.
- in 2006, Saddam was sentenced to death related to 1982 killing of 148 Iraq Shia; and executed on Dec. 2006.
- Bahrain:
- connected by 25km King Fahd Causeway; composed of 33 small islands.
- Capital Manama; 1.4M population
- Majority about 60% are Shia; 10-20% are Iranian Shia
- 19C; famous for its pearl fisheries.
- 628; one of the earliest areas converted to Islam.
- 1521; occupied by Portuguese,
- but 1602-1717; expelled and dominated by Safavid dynasty.
- in late 1800s; became a Protectorate of UK.
- Bahrain and Qatal are independence, and other 7 emirates organized UAE.
- 1971; declared independence; in 2002 declared a kingdom..
- early 1780s, Sunni al-Khalifa ruled.
- 1975: Sheikh Khalifa terminated the Congress to maintain the privilege.
- Bahrain had the first post-oil economy in the Gulf. (banking and tourism)
- Kuwait:
- 15-30% Shia Muslims:
Iranian Muslims are more than Arabic ones.
- 18C: Sheikh Al-Sabah maintained good relations with rich Iranian Shia merchants.
- In 1975 election, 10 members out of 50 are Shia, including Shia minister into four.
- Lebanon:
- Ottoman Lebanon:
- 1920 French Mandate:
- État du Grand Liban.
- multireligeous countries: Christian 40% (Catholic Maronite, Greek Orthodox, Catholic, and Protestant) than Islam (Shia Druse, Shia Twelver, Alawi syncretic sect, and Sunni)
- 1943 Independence; Beirut was called Paris in Middle East.
- Maronite President Maronite; Sunni Prime minister; Shia Congress chairman.
- Congress: 54 Christian, 20 Sunni, 19 Shia, and 6 Druze (Shia Ismailism)
- 1982-; Hizb Allah (God Party) radical Shia supported by Iran;
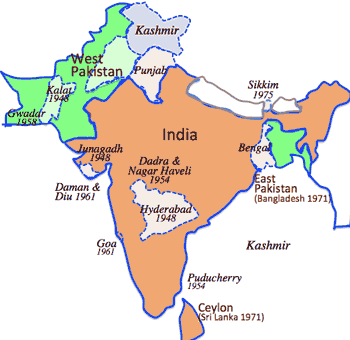
- India:
- Indian Shia: 10-35%
- Taqiya, religious dissimulation (prudence or fear)
- India Shia liven mostly in Gujarat province
- >Top Pakistan:
- 1940 All-India Muslim League includes many Shia; adopted Lahore Resolution (Two-Nation Theory).
- Monhandas Karamchand (Mahatma) Gandhi (1869-1948) satyagrah (nonviolent resistance); pursued harmonious relationship of different religions.
- 1958 Ayub Khan (1907-74) forcibly assumed the presidency through coup.
- 1947-49, 65-66, 71, and 1999: Indo-Pakistani Wars.
- 1971-77 Butt government (Shia)
- Afghanistan:
- the population is 35M, mostly composed of Pashtuns, Tjiks, Hazaras and Uzbeks.
- Shii Iranian Pashtun shares 45% of Afghanistan, and 11% of Pakistan; the language is Pashutuns, an East Iranian language, belonging Indo-European Family; the second language is Pakistan.
- Shia ratio 10-15%
- 1919 declared independence after the Anglo-Afghan War; Zahir Shah, reigned from 1933-73.
- 1978 a coup d'état by the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) supported by USSR.
- Civil war waged by guerrilla mujahideen backed by Pakistan and US against regime forces.
- 1979-89: Soviet-Afghan War; US supported anti-Soviet mujahideen by FIM-92 Stinger surface-to-air missiles.
- >Top 1994 Taliban emerged as a movement of Pashtun students (talib) from Islamic madrassas (schools) in Pakistan.
- Taliban controlled Kabul and proclaimed their Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, imposing strict form of Sharia.
- 1996-2001; Al-Qaeda network of Osama bin Laden was operating.
- 9 Sept. 2001, Massoud was assassinated by Arab suicide attack in Panjshir province.
- 11 Sept. 2001 attacks were carried out in US; in Oct. 2001, US launched Operation Enduring Freedom; US war in Afghanistan officially ended on 28 Dec. 2014 (the longest in its history).
- Dec. 2001, Afghan Interim Administration under Hamid Karzai was formed after the Taliban government was overthrown.
3. 近代国家成立とシーア派:
- パフラヴィー朝
- モハンマド・モサッデグ
- CIA主導によるクーデター
- Operation Ajax
- 1963 白色革命
- 1979 イラン・イスラム革命
- アヤトラ・ホメイニ
- イスラム法学者による統治
(Vilayate Faqih)
- イスラム共和党 (IRP)
- WWI後のイラク
- 1939-1958, イラク・ファイサルⅡ:
- 1963 カシム政権
- バアス党政権:
- サダム・フセイン:
- イラン・イラク戦争:
- フーゼンスタン州(Khuzestan)、州都Ahvaz、人口4.7M; イラク系住民多い; 大多数はShia派; 古代より学問文化の中心
- エラム人(Elamites); Ancient Near East
- カールーン川、アルヴァンド川(シャットル・アラブ川)
- ペルシャ語とアラビア語混在地域; Iranina Arab
- 639 アラブの侵略
- イランイラク戦争では最大の被害地域
Abadan製油所の破壊、palm groves (nakhlestans)の破壊
- 1982: the liberation of Khorramshahr; turning point in the war
- Khorram Abad
- 1856: 英国の侵略
- 2005以降: Ahvazでのアラブ系住民の反乱(放牧民から都市住民への転換や石油利権の腐敗が原因)
- Yadavaan 油田; Sinopec開発中, 51%
- Sweet sugar that aflows in Khuzestan.
- バハレーン:
- スンニー派ハリファ家
- クウェート:
- スンニー派サバハ家
- レバノン:
- 仏委任統治
- インド
- Indian Peninsula 1947:
Four nations independence:
- アフガニスタン
- 1994 タリバン
- オサマ・ビン・ラディン
- 2001 アフガン臨時政府
- 主なイスラム王朝
>Top 4. The Iran Islamic Revolution and export of revolution:
- Iran Islamic Revolution was not a coup d'état promoted by some military and political elite, but a revolution participated by massive general public; which was lead by the most authoritative Marja at-Taqlid Ayatollah Khomeini (1902-89) and other ulamers counting 100 ayatollahs and more than 20,000 religious students.
- Most of the people accepted Vilayat-e Faqih (guardianship of Islamic jurist), expecting to establish fairer society (unity of religion and politics).
- Article-4 of Iranian Constitution: "Civil law, criminal law, finance, economy, administration, culture, military, politics, and other laws and regulation shall be based on the Islamic principles."
- IRS continued to strengthen influences of the Islamic jurists until when its activity was terminated in 1987.
- 1981-89 Ali Khamenei was President of Iran, consolidating key positions of three powers of legislation, administration, and judiciary by ulama.
- the Iranian congress is unicameral composed of 270 members, as well as checking organization of Constitutional Protection Council composed of 6 ulama and 6 general jurists.
- 1989 the role of Prime Minister was abolished; the power was concentrated to the President.
- Before the revolution, the authority of Marja at Taqlid had been subject to the acceptance by the people; but after the revolution which became compulsory (particularly political decision). In addition, if there are plural Marja at-Taqlid, the acceptable opinion is discretionary.
- Sayyid Mohammad Kazem Shariatmadari (1906-86) proclaimed political nonintervention of religion, objecting Vilayat-e Faqih should not be included in the Constitution, but suffered six-year home confinement by Khomeini.
- Export of Revolution:
- Jan. 1979 US Embassy hostage crisis
- >Top Iraq - Execution of Muhammad Baqir al-Sadr:
- In 1979, Saddam Hussein became president of Iraq.
- Muhammad Baqir al-Sadr (1935-80); Iraqi Shia cleric, founder of Islamic Dawa Party.
- In 1977, he was arrested following the uprising in Najaf, after publishing in defense of the Islamic Revolution.
- He was again imprisoned, tortured, and subsequently executed by Saddam Hussein. He was forced to watch the torture and murder of his sister Amina Sadr bint al-Huda.
- Concurrent execution of Marja at-Taqlid as well as his sister gave double shock and serious anger against Saddam Hussein regime.
- One of most notable works were on Islamic economics, including critiques of both socialism and capitalism, giving the basic forms for modern Islamic banks.
- in Apr. 1982 Iran expelled Iraq army from Iranian territory, turning to the offensive.
- >Top Ayatollah al-Sayyid Muhammad Baqir al-Hakim (1939-2003), a leader of SCIRI (Supreme Council for the Islamic Revolution in Iraq)
- in 2003 he was assassinated in Iraq.
- Muqtada al-Sadr (1974-) , grandson of Baqir al-Sadr, influential religious leader of the Sadrist Movement.
- In May 2018, his party won 54 seats in the first Iraqi parliamentary election.
4. イラン・イスラム革命と革命の輸出:
- イスラム法学者による統治
(ヴェラーヤテ・ファキーフ; 政教一致)
- 三権の要職にイスラム法学者を配置
- 一院制の議会と憲法擁護評議会
- ホメイニー→ハーメネイ支配体制
- Iran-Iraq Border:
- Satus quo ante bellum (戦前の現状)
⇔ Uti possidetis 保持した領土・財産はそのまま終結
>Top <Moqtada al-Sadr 1973->: or Muqtad al-Sadr ; whose nickname Mullah Atari; Sources: from various sources on the Internet as of Sept. 2018; (ムクタダー・アッ=サドル師: サドル運動、マフディー軍の指導者)
- 44 year-old Shia cleric; of Lebanese ancestry, form a family of Shia scholars.
- 4th son of the late Grand Ayatollah Mohammad Sadeq al-Sadr, who was murdered in 1999 along with two of his sons allegedly by Sadam Hussein (toppled in 2003).
- he is also the son-in-law of Grand Ayatolla Mohammad Baqir al-Sadr, who was executed by Sadam Hussein in 1980.
- his cousin is Moussa as-Sadr, the Iranian-Lebanese founder of the Amal movement.
- he lacks the religious degrees as the title mujtahid or lacks the authority to issue fatwas (religious edicts)
- he prefers for video games over the intricacies of Shia laws and theology (Mullah Atari).
- in Apr. 2003, he organized Mafdi Sadr Bureau and began providing services throughout Sadr City (from health care to food & water); Sadr City is former Saddam City, a suburb of Bagdad); also organized Mahdi Army in 2003 and disbanded in 2008..
- he continually criticized US military presence in Iraq.; he wishes to create Islamic democracy.
- in Apr. 2007, he called a rally in Najf, demanding al-Maliki agree an timetable for withdrawal of US troops in Iraq.
- in Aug. 2008, he moved to Qom.
- in 2015 he formed an alliance with Iraqi Communist Party and secular groups under an umbrella of security and corruption concerns.
- 12 May 2018, the result of 4th election in 2018 election after 2003 competing in parliamentary 329 seats: (165 seats needed to form the government)
- ○Moqtadr al-Sadr bloc (Sadrist Movement): 54 seats
- ●Hadi al-Ameri bloc: 48 seats
- ○al-Abadi (PM) bloc: 42 seats
- ●Nuri al-Maliki (former PM) bloc: 25 seats
- the current prime minister is Shia, the speaker of parliament is Sunni, and the president a Kurd.
- he reached out to dispossessed Shiites and marginalized Sunni, while keeping Iran at bay.
- he became a symbol of resistance to foreign occupation.
- the election dealt a blow to Abadi; but managing competing interests of US and Iran, particularly against Islamic State.
- Sadr contacts with neighboring countries, including Saudi Arabia.
- he was denounced by US as a pro-Iranian proxy, but he also opposed Iranian interference as well as that of other countries.
>Top 5. Post Khomeini and multipolarization:
- Ayatollah Khomeini (1902- 3 Jun. 1989) died at 86 in the following year of the cease-fire of Iran-Iraq War.
- the successor problem is difficult due to; 1) the Constitution says the supreme leader should be Marja At-Taqlid, 2) stance to vilayat-e faqif, and 3) credibility and support consensus in Shia community as well as people's popularity, and 4) alternation of generations.
- >Top Sayyid Ali Hosseini Khamenei (1939-); second Supreme Leader of Iran, as well as, Rafsanjani as the President.
- Jun. 1981; Khamenei suffered assassination attempt, losing the use of his right hand; but won a landslide vote (97%) in the presidential election in Oct. 1981.
- Khamenei's status as marja is controversial. Teachers of Qom declared Khamenei a new marja. Several ayatollahs, however, declined to recognize him as such.
- if khums (20% of the gains) is paid to Khomeini by non-Iranic Islams would be inconsistent with country where they live.
- >Top East-West neutrality:
- Khomeini adopted the policy of East-West neutrality.
- When in Nov. 1979, US Embassy hostage crisis happened, then President Abolhassan Banisadr pursued to solved the incident by the Internal law; thereafter he was impeached by the parliament in 1981.
- Sept. 1980- Aug. 1988 Iran-Iraq War:
- Iraq invaded Iran; worrying about Iraq's Shiite majority to rebel against the Baathist government; also Iraq planned to annex the oil-rich Khuzestan Province and the east bank of the Shatt al-Arab (Arvand Rud), taking advantage of Iran's post-revolutionary chaos.
- US, USSR, France, and most Arab countries supported for Iraq, while Iran was largely isolated.
- The tactics were used including large-scale trench warfare. (status quo ante bellum; both sides claim victory.) ⇔
- the end of war resulted in neither reparations nor border changes.
- >Top In 1989, Rafsanjani (1934-2017) won 96% of the votes in the presidential election.
- demonstrated his practical skills to reform Iran from the war regime.
- in 1997, Seyyed Mohammad Khatami (1943-) was elected 5th President of Iran.
- established International Institute for Dialogue among Cultures & Civilization.
- emphasized 1) rule of law, 2) establishment of civil society, and 3) freedom of expression; but mostly prevented from conservative authority; while in Jan. 2002 State of the Union Address, US George W. Bush proclaimed Iran, Iraq, and North Korea as axis of evil.
- Impasse of unity policy of religions and politics:
- contradiction of the end of dictatorship and creation of fare society; but Virayat-e Faqih by an agent of 'Hidden Imam' creates a new type of dictatorship and inequality.
- Is it inviolable, or are plural interpretations not allowed?
- Change in consciousness of young people:
- religion became a political ideology or regime, particularly for young people grown up after the Revolution.
- A public opinion survey shows 80% of youth (15-29) rarely go to Friday praying, and more than 50% go to mosque other than funerals.
- Also the survey shows that more than 40% a person could be devout without doing worship (salah).
- also objecting the policy which doesn't allow government position to whom doesn't support vilayat-e faqif.
- In addition, Shia community has been sustained by khums paid by Shia Muslims. But the ruling ulama control enormous national fund; thus decrease of khums caused more dependance of ulama to the nation.
- Political power became more superior than religious authority.; many Marja at-Taqlid must be obedient to lower ranked Khamenei.
- What for the export of the Revolution? is it for Iran?
- Aug. 1990 - Feb. 1991 The Gulf War:
- Nov. 1989: the fall of Berlin wall.
- Aug. 1990: Iraq invaded Kuwait.
- Jan. 1991: US (multinational force) conducted air attack to Iraq.
- Shia rose up in revolt; but Shia marja at-Taqlid objected such rebellion.
- both US and Saudi Arabia neglected such Shia movement.
- Sadam Hussein government survived longer until 2003.
- 11 Sept. 2001 synchronized terrorists (Sunni radicals) attack to US.
- 20 Mar. 2003 - 14 Dec. 2011: Iraq War started by George W. Bush and ended by Barrack Obama.
- Shia organization kept watching the situation, because of the lessons of aftermath of the Gulf War.
- Jul. 2003 established Iraq Governing Council; majority of 25 ministers were Shia. (IGC was disbanded in Jun. 2004 after establishment of Iraq Interim Government.)
- Emerging impact of Moqtada al-Sadr: (>above column)
- Revived Shia festivals; marching to Karbala by 1M Shia Muslims.
- Shia Study Center at Qom, Iran:
- in 2004, the center accepted religious students from 70 countries.
- 1985 Khomeini opened religious study center for women; students from Pakistan, Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Iraq, Thailand, Myanmar, China, Albania, etc.
5. ポスト・ホメイニーと多極化
- アヤトラ・ホメイニ死去 (1989)
- 後継者ハメネイ最高指導者
- 東西不偏政策
- バニサドル大統領
- 1980- 1988 イラン・イラク戦争
- 国境沿いのフーゼスタン州:
- 1989 ラフサンジャニ大統領
- 1997 ハタミ大統領
- 祭政一致政策の行き詰まり:
- 若者の意識変化:
- 1990-1991 湾岸戦争
- 2011.9.11: 同時多発テロ事件:
- イラン・コムでのシーア派教育センター
- 女性の宗教教育の充実
>Top 6. Islamic Grossary: <イスラム用語集>
- arkan al-Islam: five pillars of Islam;
- shahada: faith: lā ʾilāha ʾillā-llāhu muḥammadun rasūlu-llāh
- salah: prayer: fajr (dawn), dhuhr (noon), asr (afternoon), maghrib (evening), and isha (night); wudu (washing)
- zakat: charity
- sawm: fasting
- hajj: pilgrimage to Mecca
<addtitional practices of Shia:>
- khums: annual taxation (20%) o the gains that has not used for a year; is paid to the imams
- jihad: the greater stuggle & the lesser struggle
- enjoying good
- forbidding wrong
- tawalla: expressing love towards good.
- tabarra: expressing disassociation twards evil
- Charismatic authority: fragile; cannot last beyond the lifespan of the charismatic individual.
- eid al-fitr: religious holiday, particularly in the end of Ramadan.
- eid ul-adha: festival of sacrifice in the last thee days of hajj.
- fatwa: authoritative legal opinions which qualified jurist or mufti can give.
- fiqh: knowledge
- gaiba: hidden Imam
- hadith: actions and silences compiled and verified
- hijab and abaya: traditonal attire of women
- hukm; as hukm of Allah, ruling
- ijazt at-tadris wa l-ifta: license to teach and issue legal opinions
- ijma: consensus, valid source of law (Sunni); the status is ambiguous (Shia)
- ijtihad: interpretation of Islamic law
- ibadah: worship or religious ritual such as salat (prayer), hajj (pilgrimage), sawm (fasting), zakat (tithing)
- imam: a worship leader; ismah (impeccability)
- Islamic laws: Quran, sunnah (authenic hadith), qiyas or aql (Shia), ijma (juridicl consensus)
- kaaba: cube-shaped building, house of God; hills of Safa and Marwah
- khums: annual taxation 20% payable to the imams
- madhhab: major schools of law;
(Shafii in Egypt, Hijaz & Yemen; Maliki in West Africa; Hanfi in Turkey & Central Asia; Hanbali in Gulf)
- madrasa: religious instituions, place of learning
- marja at-taqlid: supreme authority in Shia community
- mullah: vicar, master, or gurdian; Mullah Atari
- qiyas: analogy or interpretations
- Quran: God's words messaged by the Prophet
- ra'y: practice
- sharia: Islamic canonical law
- taqiya or taqiyya: ( 'prudence, fear) precautionary dissimulation or denial of religious belief and practice in the face of persecution (praticularly in Shia); kitman has more specific meaning of dissimulation of silence or omission.
- talib: Islamic students
- thobe or thawbe (Arab garment for men) and keffiyeh, ghutra or agal (headdress) :
- ulama: (ulema, fem, alimah, sg, uluma, pl); schola, the learned ones
- ummah: Islamic community
- usul: hamza, sad and lam which refers to basis; Usul al-fiqh
- vilayat-e faqif: guradianship of the Islamic jurist
- waqf: religious endowments
- zakat; jizya (per capita yearly tax); kharaj (land tax); ushr (on harvests); khums (paid to Shia imams, 20% of gains, )
Comment
- The difference of Sunni and Shia looks bigger than that of Catholic and Protestant.
- In Japanese proverb, Hatred for close relatives is bigger than ordinary person.
- Shia is minor in number, but in term of oil producing area and persons involved, Shia would be majority.
- Then what about scale of the political & religious impact?
- スンニー派とシーア派の違いは、カソリックとプロテスタントの違いよりも大きいようだ。
- 日本語の諺に、近親憎悪というのがある。
- シーア派は数では少数だが、石油生産の地域とそれに関わる人間という上では多数となろう。
- では政治的・宗教的な影響力はどうだろうか?
Shia Muslims- Emerging Minority of Islam - |
Cat: HIS |
|
Keiko Sakurai (桜井啓子) |
18923u |
Résume |
Remarks |
>Top 0. Introduction: Rising Shia Muslims:
| 0. 序文: 台頭するシーア派:
|
>Top 1. Establishment Shia Muslims:
| 1. シーア派の成立:
|
>Top 2. Political power and Shia:
|
2. 政治権力とシーア:
|
>Top 3. Foundation of Modern State and Shia Muslims:
|
3. 近代国家成立とシーア派:
|
>Top 4. The Iran Islamic Revolution and export of revolution:
|
4. イラン・イスラム革命と革命の輸出:
|
>Top <Moqtada al-Sadr 1973->: or Muqtad al-Sadr ; whose nickname Mullah Atari; Sources: from various sources on the Internet as of Sept. 2018; (ムクタダー・アッ=サドル師: サドル運動、マフディー軍の指導者)
|
|
>Top 5. Post Khomeini and multipolarization:
|
5. ポスト・ホメイニーと多極化
|
>Top 6. Islamic Grossary: <イスラム用語集>
|
Comment |
|
|