>Top 3. How do plants defend their bodies?
- Ultraviolet: wavelength (10-400nm), shorter than visible light ( 400-700nm) and longer than X-rays.
- Ultraviolet light is hazardous to the life, which could not land until the ozone layer was created. The life started photosynthesis in the sea, gradually accumulating oxygen in the environment.
- The ozone layer can absorb ultraviolet light, particularly the most hazardous UV-C; thereafter the life could expand its living area in the land.
- The life was born around 4B years ago, spending 3.6B years in the sea; then
the plant landed just 400M years ago, ahead of animals.
- When the life is exposed to ultraviolet light, active oxygen arises and accelerate aging process or causing skin cancer, or cataract; thus we need to avoid being exposed to ultraviolet light as much as possible.
- >Top Beautiful color of flowers:
- The plant can product antioxidant such as Vitamin-E, Vitamin-C, carotene, anthocyanin, or lycopene. Carotene is the color of carrot, anthocyanin is of egg plant, apple, or blue berry, and lycopene is of tomato or water melon.
- Strong ultraviolet radiation causes plants to protect themselves by having bright color of flowers; or beautiful color of flowers is the sign of struggling against ultraviolet light.
- >Top phosphoenolpyruvic acid (PEP):
- C4 plants have this PEP, which enable to survived low density of CO2.; such plants as corn, sugar cane, or green foxtail.; consume 250-350 g of water to increase 1 dry gram growth of body.
- C3 plants (share 90% of plants) have no such PEP, can utilize 1/3 of sunlight energy; consume 500-800 g of water to increase 1 dry gram growth of body.
- On the earth, only 25% of land areas have more than 1,000 mm annual rainfall, 55% of land have less than 500 mm (half of which have only less than 250 mm)
- The severe factors for plants are intense sunlight, high temperature, aridity.
- Such C4 plants are better suited in lower latitude areas featured with intense sunlight, high temperature and aridity.
- Under the intense sunlight, C3 plants use 1/3 for photosynthesis, and the rest 2/3 is used to make active oxygen which is harmful; C3 plant has the mechanism to dissolve such active oxygen, consuming excess energy, and producing additional CO2.
- >Top Regenerative ability of plants:
- Plant a cutting is possible.
- Plant does not care about losing a part of its body; yielding regenerate or even increase its number.
- Far-red light make a plant to grow taller; the ratio of far-red light indicates that surrounding plants are growing taller, which promotes the plant to grow taller more rapidly to gain more sunlight.
- In a same colony of plants, the inner plants tend to grow taller than the surrounding ones.
- Some kinds of plants (such as walnut, artemisia, helianthus, or cherry tree) distribute poisonous materials to curb the germination or growth of different plants.
- Or some plants retains poisonous materials (such as nicotine, atropine, or digitoxin) in its body.
- Some animals have counter-strategies: some animals eat particular food only such as silkworm eats mulberry leaves only, panda eats bamboo grass, and koala eats eucalyptus leaves.
- >Top Five senses of plants:
- These are seeing, hearing, smelling, tasting, and touching senses:
- Seeing:
- Seeds knows not only the place where it exists but surrounding situation how it is preferable to germinate.
- Hearing:
- There is an opinion that tomato tree grows more sweet tomato fruits when heard classic music than rock or pop music, which is not yet confirmed.
- Tasting:
- When floating grass is dipped in salty water (3% of salt) for 10 minutes, then float in the normal water for 2 hours; some special material is emitted from the grass. This mysterious material is imagined to be able to hasten blooming and increase the number of flowers.
- Touching:
- Bean sprout gains some incentive by touching soils, making its stem thicker and shorter.
- Feeling:
- Any plant can feel gravity; extending its stem upward and its root downward; even if it is lain alongside, its root begins to bend downward, and its step opposite.
- >Top Smelling:
- Plants have various strategies to counter invasion of pathogen such as fungus, bacteria, or virus; by coating wax on its surface or by enclosing pathogen by killing the invaded cells by themselves, emitting phytoalexin, antibacterial agent, in ten and several hours.
- SOS signals: infected leaves emit salicylic acid which evaporates immediately and transmit information of the infection to the same group of plants.
|
3. 体を守る:
- cataract: 白内障
- antioxidant: 抗酸化物質
- phosphoenolpyruvic acid (PEP): ホスホエノールビルビン酸
- Regenerative ability: 再生能力
- plant a cutting: 挿し木
- artemisia: ヨモギ
- helianthus: ヒマワリ
- pathogen: 病原体
- phytoalexin: <G. phyto, plant
|
<
Ultraviolet:>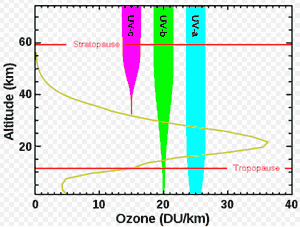
- Ultraviolet-A (UVA): 315-400 nm; not absorbed by the ozone layer.
- Ultraviolet-B (UVB): 280-315; mostly absorbed by the ozon layer.
- Ultraviolet-C (UVC): 100-280; germicidal, completely absorbed by the ozone layer.
- Vauum ultraviolet (VUV): 10-200
- Extreme ultraviolet (EUV): 10-121
- <Electromagnetic Spectrum>
- C4植物とC3植物
- C4植物は、低濃度CO2をよく吸収できる植物。最初に体内で生成するCの数が4個。
- C3植物は地球上の90%以上。C3個を最初に生成。
- 植物にとっての厳しい3条件:
3K=強光・高温・乾燥
|