>Top 4. How HF is operated:
- One day of HF manager:
- 06:00: I usually get up, and go to bed around 24:00 caring about Dow-Jones average in NY. Lack of sleep is a taboo, in particular after 1:00.
- The trend of watching news has changed from focusing high-tech industry to watch wider news of economics, politics, and society; concurrently reviewing validity of ratio of the portfolio.
- 07:30-08:00: I arrive at the small office, checking mails from analysts from securities companies; making questions to rival analysts over telephone.
- I attend the investment committee of HF managers after 08:00; analyzing NYSE, and Nikkei Average, whether to take ¥or avoid more risk, to increase or decrease of long position, or to review new individual brands which should to included in the portfolio; sending various advice to the operating company in Singapore.
- Around 09:00: opening time of the market approaches, I feel nervous; confirming the policy with the operating company, checking fundamentals, chart, supply & demand, and other companies trends. Particularly, in down trend period of market, my stomach is in knots by adverse factor, on the contrary, in up trend of the market, I simply become very happy.
- When I attend a company introduction meeting, or factory tour, I never forget about the trend of stock market, checking the latest situation every one hour. It is useful for me to visit medium-sized companies in various districts to know them and their industry as well as local environment.
- The target of research of companies became expanded and diversified than the time of being an analyst; which are not only high-tech companies but also other industries. In an interview with new companies, I try to be all ears to the management in listening their corporate philosophy, motto, or composition of shareholders, etc, rather than the financial data, which could be available later. To have an objective stance is important and useful in making evaluation of the company. Q&A are important, which reflects level of the attendants; which will result a victory or defeat from the opportunity.
- But there still remains compatibility or familiarity about the brand in making the decision; which could not be like-dislike, but hit-miss. Timing may be also important than value of the stock then.
- Weekend: It is also a key acknowledge the way to spend the weekend; trying to pay more attention to mental and physical health; thinking about the middle or long view of changes.
- Whenever I compare the target companies with my own company, I ask myself that there might be anything to learn from them. On the other hand I assure that it's a joy for me to be able to continue stable management of my company; accumulating capital, paying salary to the staff and paying dividend and tax, and so on. To keep PL, BS, CF is getting more serious and realistic than before. To be a good owner should lead be a good analyst, too.
- >Top How to select the brand:
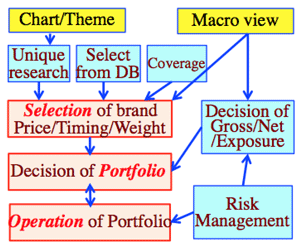
- Decide the category of the industry or sector, estimating target price from the earnings forecast of main companies, comparing the quarterly corporate report, getting comments from the sell side analyst of securities company.
- Consider the theme of the market; positioning cheaper but promising brand long position, and expensive & sluggish brand short, as well as consider a certain coverage.
- Or consider wide rage of brands, or select a certain promising brand of medium-sized companies which the securities company doesn't cover.
- Or more generally, segmenting cheaper sector and expensive sector; then select typical and the most sensitive brand in the cheaper sector brands.
- Or segment and evaluate cheaper or more expensive brands based on the database.
- In all cases, screening (selecting), valuation based on earnings forecast, and valuation and catalyst which affects stock price.
- Contingency: it needs to assume responsive actions; change long or short position, take profit, or close the position.
- >Top PER (Price Earning Ratio)= Stock price divided by per share profit; which is not an universal index, which is changeable according to Nikkei Average or interest rate.
- POR (Price Order Ratio), PCFR (Price Cash Flow Ratio), EV/EBITDA Ratio
- PBR (Price Book-value Ratio)=Stock price divided by BPS; BPS (Book-value Per Share);
- EPS (Earnings Per Share)= current net earnings divided per share.
- Loss Cut Rule: compulsory transaction to close a customers's position when the amount of loss has reached the amount computed by the method agreed with the customer in advance.
- PER is changeable:
- Higher PER shows the indication of high growth which many investors believe.
- If A company's profit per share is ¥20, and the stock is ¥400, the PER PER 20 times. If the profit per share of the next term is expected ¥30, then the stock price raise up to ¥600 as long as PER remains 20 times. If the industry average PER is 30 times, this company's PER 20 times indicates lower stock price, which may raise up to ¥600.
- The industry which tends to change profit level tends to reflect bigger PER.
- PER 20 times means the same profit level will continue 20 years, or this means yield 5%.
- Considering stock is risky, risk premium = Risk free rate + Risk premium: GB 10year 1.5%+ Japan risk premium 3.5% = 5%.
- Defect of PER:
- comparison between industry or country is difficult due to difference of tax rate and depreciation method.
- PCFR or EV/EBITDA are used instead of PER, particularly in US & EU, but this index is effective as long as capital investment affects positive; which is useless after collapse of IT bubble economy. Also these indexes reflect PL only, not reflect BS.
- DCFV is usually used in the case of M&A. But it needs to watch the latest CF whether it may not be too much.
- In making portfolio:
- Consider such as target stock price, estimated risk, total market value and volatility, correlation with Nikkei Average.
- One brand should be less than 10%; brands which have higher correlation make more risk.
- Total balance is essential; consider appropriate gross exposure and net long position.
- Consider appropriate leverage ratio; or decrease the ratio under the situation of more uncertainty of the market. (credit shrink or crunch situation)
- Consider raise the level of Net Long position in bullish trend.
- Check performance of the portfolio, including gross amount, or long/short position.
- HF usually handles 30-50 brands as the portfolio.
- Loss Cut Rule: unique in HF.
- a company has no such a rule: but empirically electronics industry applies this loss cut rule in a division which exceeds cumulative loss more than ¥200B, causing withdrawal or sales of business of the division.
- Value at Risk (VaR): maximum loss estimated by its past volatility. Risk does not distribute according to normal distribution; rather to power distribution.
- Any program or model calculating risk is changeable according to market, or corporate strategy.
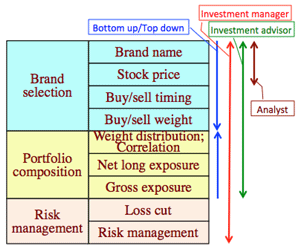
- Investment advisor vs. Investment manager:
- sell side advisor of securities company vs. buy side advisor of the client investor.
|
4.
HFの運用はいかになされているか:
- quarterly corporate report: 会社四季報
- earning forecast: 業績見通し
- catalyst: 変化の要因
- contingecy: 不測の事態
- valuation: 査定、評価額
- PER: 株価収益率
- total market value; market capitalization; 時価総額
|
Process of HF operation:
- Service value of operator:
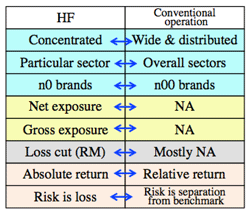
- Comparision HF vs. Conventional operation
|