>Top 2. The theme of financial engineering is risk:
- Risk: potential of gaining or losing something of value caused by uncertain action.
- our life if full of various risks; such as disease, accident, or disaster
- agriculture by weather, fishery, hunting, and mineral exploration.
- MTS (make-to-stock) to BTO (built-to-order)
- from hunting to stock-farming; from fishery to aqua farming cultivation
- >Top Risk Management:
- Minimax principle
- Risk: uncertainty having probability distribution
- True uncertainty having no probability distribution
- Expected value, variance and standard deviation (SD) (or volatility in finance):
- law of large numbers; normal distribution
- >Top Risk premium:
- minimum amount by which the expected return on a risky asset must exceed the known return on a risk-free asset.
- compensation for investor who tolerate the extra risk, compared to that of a risk-free asset.
- hedger:
- speculator:
- to maximise the expected utility; convex curve to the top
- >Top the marginal utility is digressive (law of diminishing marginal utility):
- the first unit of consumption of a good or service yields more utility than the second and subsequent units.
- Variance (σ2): measures how far a data set is spread out.
- Variance (σ2): u(X)=(X−μ)2, where μ is mean.
- Standard Deviation (SD) (σ)
- St. Petersburg Paradox: (proposed by Nicolaus Bernoulli)
- a particular lottery game that leads to a random variable with infinite expected value, but nevertheless seems to be worth only a very small amount to the participants.
- People want to maximize 'expected utility' rather than 'expected profit.'
- >Top 'Indifference curve': and equal utility curve
- showing combination of two goods that gives equal satisfaction and utility. Each point on the curve indicates that the consumer is indifferent between the two.
- Risk management: (>Fig.)
- Diversified investments
- Insurance contract
- Sales of risky assets, or forward contract
- Decrease of SD by combination of investment: (>Fig.)
- the risk of combination is smaller than the weighted average.
- To minimize risk (or SD) is not the object of asset, but to maximize the return of investment. (Portfolio)
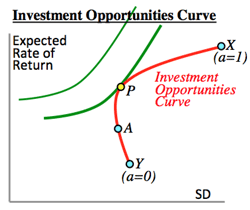
- Investment Opportunities Curve: (>Fig.)
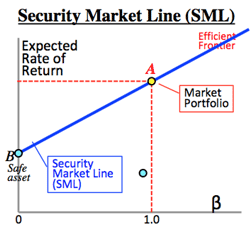
- Efficient frontier:
- An investment portfolio which occupies the efficient parts of the risk-return spectrum.; formulated by Harry Markowits in 1952.
- Tobin's Separation Theorem:
- Fund operation is available by adding no-risk asset (like government bond, cash, etc.) to the best risk-return portfolio, depending on each investor's risk allowance.
- If the risk allowance is low, the investor prefers to have more non-risk asset or risk allowance is high, the investor prefers not to have no-risk assets, or raise return ration by leverage.
- Fig:
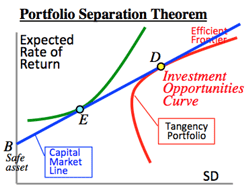
- Capital Market Line (CML); gradient of the line is risk premium.
- >Top Modern portfolio theory:
Harry Markowitz
theory had not been attention by economists. But James Tobin extended his theory, establishing the separation theorem and market value of risk.
- B point of the above figure is called safe asset, like government bond.
- A certain point as a mix of safety asset and risk asset is shown by the blue line (risk premium, or market risk premium).
- The indifference curve, an equally acceptable risk curve, which is chosen by a consumer, is shown here as green curve.
- To gain the optimized combination, this line should contact the outmost point (D) of the investment opportunities curve (red curve).
- This D point is determined irrelevantly by investors' preferences, i.e., mix of risk assets is determined independently from risk-return preferences of investors.(Tobin theorem, or Portfolio separation theorem)
- Thus, the optimized portfolio for any investor is plotted on the above blue line (Capital Market Line).
- The gradient of the blue line shows: (Risk asset return - safe asset return)/(SD of asset return); here the numerator shows risk premium of risk asset.
|
2.
金融工学のテーマはリスク:
- risk: uncertain: likely turn out well or badly
- expected value: 期待値
- probability distribution: 確率分布
- marginal utility: 限界効用
- indifference curve: 無差別曲線
- investment opportunities curve: 投資機会曲線
- capital market line: 資本市場線
|
- 期待値・分散・標準偏差
- リスクプレミアム (期待収益率):
- 限界効用逓減の法則
- St. Peterburgの逆理
- 人々が最大化するのは期待効用であって期待利得ではない。
- 無差別曲線:
期待効用が一定となる期待値と分散; 同じ効用が得られる財の組合わせ
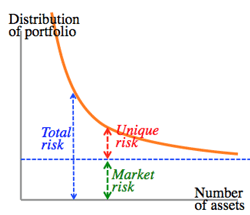
 - Market risk & unique risk:
  - モダンポートフォリオ理論:
- 低リスク銘柄と高リスク銘柄による組合せパターン
- 各人のリスク許容度に応じて株式と国債の割合を決める (効率的ポートフォリオ)
- Index fund vs. Active fund
- トービンのPortfolio分離定理:
|