
Mathematics to understand Deep Learning
Category: ICT
Published: 2017
#1711b
Yoshiyuki & Sadami Wakui (涌井良幸・貞美)
up 17810
Title
Mathematics to understand Deep Learning
ディープラーニングがわかる数学
Index
Tag
; Axon; Back propagation method; Chain rule; Convolution layer; Cost function; Data dependent; Dendrite; Demon-Subordinate Network; Displacement vector; Gradient descent; Lagrange multiplier method; Learning data; Minimization problem; Neural network; Neurotransmission; Recurrence formula; Regression analysis; Sigmoid function; Similarity of pattern; Square error; Stress tensor; Synapse;
Résumé
Remarks
>Top 0. Introduction:
- Activity of Neuron:
0. 序文:
- ニューロンの働き
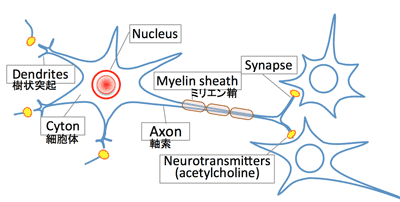
>Top 1. How to express activity of neuron:
- Neuron is composed of:
- Cyton: cell body (=neuron)
- Dendrites: Input of information
- Axon: Output of information
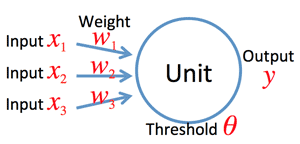
- >Top Unit step function vs. Sigmoid function (differentiable):
- Unite step function: Output is 0 or 1.
- Sigmoid function (σ(z)=11+e−z):
Output is arbitrary number.
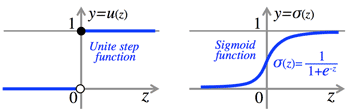
- Activation function:
y=a(w1x1+w2x2+w3x3−θ)(θ:threshold)
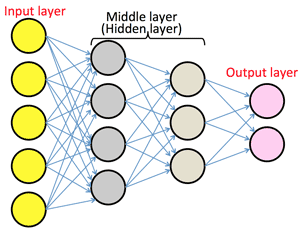
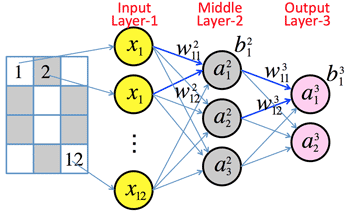
- >Top Neural Network: (>Fig.)
- Input layer - Middle layer - Output layer:
- Input layer: no input arrows; output only.
- Middle (Hidden) layer: actually process the information
- this layer reflects intention of the planner.
- 'hidden demons' in the middle layer have particular properties, which are different sensitivity of a specific pattern.
- Output layer: output as the total of neural network.
- Deep Learning: neural network having many deep layers.
- Fully connected layer: All units of the previous layer point to the next layer.
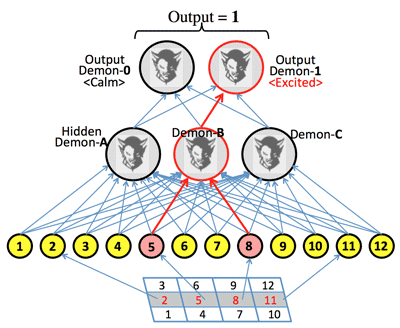
- >Top Compatibility of Demons and their subordinates: (>Fig)
- Pixel 5 & 8 ON
- Subordinate 5 & 8 excited
- Hidden Demon-B excited
- Output Demon-1 excited
- The picture was judged to be "1".
- Thus, compatibility or bias of each Demon leads the answer; The network decides as a whole.
- >Top AI Development phases:
Gen.
Period
Key
App.
1G
1950s-60s
Logic dependent
Puzzle
2G
1980s
Knowledge dependent
Robot; Machine translation
3G
2010-
Data dependent
Pattern recog; Speech recog.
1. ニューロンの働きの表現:
- Neurotransmission (神経伝達):
- Input zは、以下2ベクトルの内積:
z=(w1,w2,w3,b)(x1,x2,x3,1)
- Neural Network:
- Demons and their subordinates:
- Subordinates reflect vividly 4 & 7, and 6 & 9.
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
- Demon-Subordinate Network:
>Top 2. How the neural network learns:
- >Top
Regression Analysis:
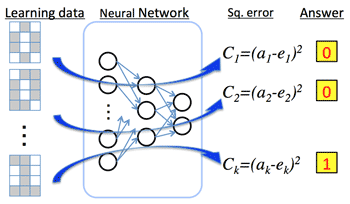
Learning with teacher or without teacher: (>Fig.)
- With teacher: Learning data (or Supervised data)
- To minimize the errors between estimate and correct answer;
'Least-square method'; 'Regression Analysis'
- Total of errors: cost function CT
- Weight parameter can take negative value, unlike the case of biology.
2. ニューラルネットワークはどう学ぶのか:
- Regression Analysis (回帰分析):
>Top 3. Basic mathematics for neural network:
- Inner products: a・b=|a||b|cosθ
- Cauthy-Schwarz inequality:
- −|a||b|≤a・b≤|a||b|
- −|a||b|≤|a||b|cosθ≤|a||b|
- Similarity of pattern:
- A=(x11x12x13x21x22x23x31x32x33)
- F=(w11w12w13w21w22w23w31w32w33)
- Similarity=A・F=w11x11+w12x12+...+w33x33
- Similarity is proportional to the Inner product of A and F.
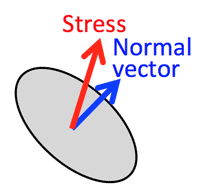
- Stress tensor: (>Fig.)
- Stress tensor (T)=(τ11τ12τ13τ21τ22τ23τ31τ32τ33)
- Google: 'Tensor-Flow'
- Matrix product:
- AB=(c11c12…c1pc21c22…c2p⋮⋮⋱⋮cn1cn2…cnp)=cij=m∑k=1aikbkj
- Hadamard product:
- A∘B=(aij・bij)1≤i≤m1≤j≤n
- Transposed matrix:
- tBtA (>¶)
- >Top Differential: (Composite function = Chain rule)
- dydx=dydududx
- ∂z∂x=∂z∂u∂u∂x+∂z∂v∂v∂x
- ∂z∂y=∂z∂u∂u∂y+∂z∂v∂v∂y
- (e−x)′=−e−x
- y=eu,u=−x: then, y′=dydududx=du・(−1)=−e−x
- 1f(x)′=−f′(x){f(x)}2
- σ(x)=11+e−x (Sigmoid function)
- σ′(x)=σ(x)(1−σ(x)) (>¶)
- Multivariable function: Partial differential (derivative):
- ∂z∂x=∂f(x,y)∂x
- limΔx→0f(x+Δx,y)−f(x,y)Δx
- ∂z∂y=∂f(x,y)∂y
- limΔy→0f(x,y+Δy)−f(x,y)Δy
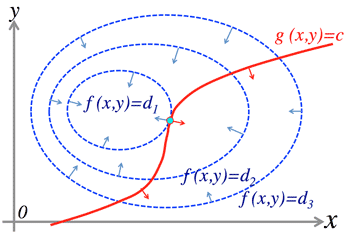
- >Top Lagrange multiplier method: Finding local maxima and minima of a function subject to equality constraints.
- Maximize f(x,y) subject to g(x,y)=0
- F(x,y,λ)=f(x,y)−λ(g(x,y)−c)
- ∂F∂x=∂F∂y=∂F∂λ=0
- Approximate formula:
- f(x+Δx)≈f(x)+f′(x)Δx
- f(x+Δx,y+Δy)≈f(x,y)+∂f(x,y)∂xΔx+∂f(x,y)∂yΔy
- Δz≈∂z∂xΔx+∂z∂yΔy
- Δz≈∂z∂wΔw+∂z∂xΔx+∂z∂yΔy
- ∇z=(∂z∂w,∂z∂x,∂z∂y),
Δx=(Δw,Δx,Δy)
- >Top Gradient descent: (>Fig.)
- Δz=∂f(x,y)∂xΔx+∂f(x,y)∂yΔy
- When Δz becomes minimum: two vectors are in the opposite direction.
- (Δx,Δy)=−η(∂f(x,y)∂x,∂f(x,y)∂y)
- Δx=(Δx1,Δx2,...,Δxn)=−η∇f,
where Δx is a displacement vector; η is a small positive number;
- ∇f=(∂f∂x1,∂f∂x2,...,∂f∂xn)
3. ニューラルネットワークのための基本数学:
- Stress tensor:
- 転置行列:
- ¶ A=(a11…a1n⋮⋮am1…amn)
- B=(b11…b1p⋮⋮bn1…anp)
- (i,j) element of AB(=(j,i) element of
t(AB)):
- (ai1ai2…a1n)(b1jb2j⋮bnj)
=n∑k=1aikbkj
- (j,i) element of tBtA:
- (bj1bj2…bnj)(ai1bi2⋮bin)
=n∑k=1bkjaik=n∑k=1aikbkj
- ∴t(AB)= tBtA
- ¶ σ′(x)=−1+e−x(1+e−x)2=e−x(1+e−x)2=1+e−x−1(1+e−x)2
=11+e−x−1(1+e−x)2σ(x)−σ(x)2=
- Lagrange Multiplier (ラグランジュ未定乗数法):
Blue lines are counturs of f(x,y)
Red line shows the constraint g(x,y)=c
- 勾配降下法 (Gradient descent method)
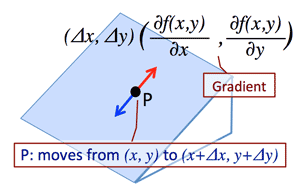
- Displacement vector (変位ベクトル)
- ¶ z=x2+y2;Δx=−η∇z=(2x,2y)
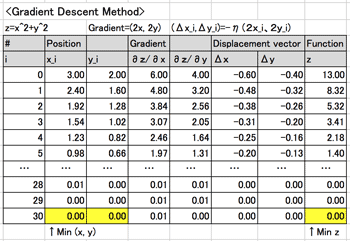
>Top 4. Cost function of neural network:
- Gradient Descent (Sample): (>Fig.)
- <Middle layer>
- (z21.z22.z23)=(w211w212w213…w2112.w221w222w223…w2212.w231w232w233…w2312)(x1.x2.x3.….x12)+(b21.b22.b23)
- a2i=a(z2i)(i=1,2,3)
- <Output layer>
- (z31.z32)=(w311w312w313.w321w322w323)(a21.a22.a23)+(b31.b32)
- a3i=a(z3i)(i=1,2)
- <C=Square error>
- C=12{(t1−a31)2+(t2−a32)2}
- <CT=Cost function>
- CT=64∑kCk
- Ck=64∑kCk12{(t1[k]−a31[k])2+(t2[k]−a32[k])2}
- Applying Displacement Descent:
- Δx=(Δx1,Δx2,...,Δxn)=−η∇f (where ∇f is Gradient)
- (Δw211,…,Δw311,…,Δb21,…,Δb31,…)
- =−η(∂CT∂w211,…,∂CT∂w311,…,∂CT∂b21,…,∂CT∂b31,…)
4. ニューラルネットワークのコスト関数:
- 勾配降下法 (例):
>Top 5. Back propagation method:
- Square error; Minimization problem of Cost function:
- C=12{(t1−a31)2+(t2−132)2}
- δlj=∂C∂zlj(l=2,3,…)
- ∂C∂w211=\frac{\partial C}{\partial z_1}^2}
{\partial z_1^2}{\partial w_{11}^2}
- z21=w211x1+w212x2+…+w2112x12+b21
- ∂C∂w211=δ21x1=δ21a11
- >Top <General formula>: from partial differentail to recurrence formula.
- ∂C∂wlji=δljal−1i
- ∂C∂blj=δlj
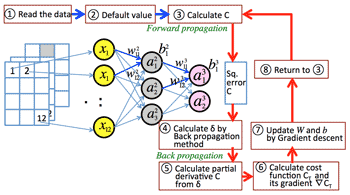
- Forward & Back Propagation:
- <Forward Propagation>
- Read the data.
- Set up the default data.
- Calculate C.
- Square error C.
- <Back Propagation>
- Calculate δ by Back propagation method.
- Calculate Cost function CT and its gradient ∇CT.
- Update Weight W ana bias b by Gradient descent method.
- Return to 3.
- <Matrix representation>
- (δ31δ32)=(∂C∂a31∂C∂a32)∘(a′(z31)a′(z32))
- (δ21δ22δ23)=[(w311w321w312w322w313w323)(δ31δ32)]∘(a′(z21)a′(z22)a′(z23)
5. 誤差逆伝搬法 (BP法):
- C: 二乗誤差
- δlj: Unitの誤差の定義
- <コスト関数CTの最小化問題>
- 最小条件の方程式
∂CT∂x=0,∂CT∂y=0,∂CT∂z=0
- 勾配降下法:
勾配(∂CT∂x,∂CT∂y,∂CT∂z)
- 誤差逆伝搬法:
Solved partial differential value by
recurrence formula.
- Forward propagation & Back propagation:
>Top 6. Translation to neural network language:
- Favorite pattern of a demon:
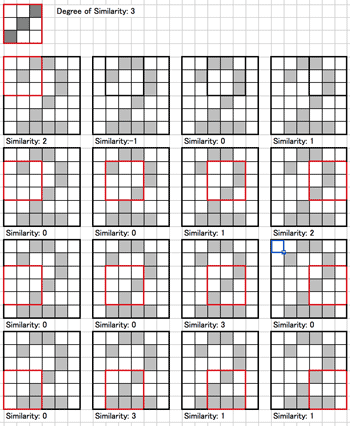
- Gradient of Cost function CT
- >Top Convolution layers:
=(∂CT∂wF111,…,∂CT∂w011−11,…,∂CT∂bF1,…,∂CT∂b01,…,)
- 1st term: Partial differential of filter.
- 2nd term: Partial differential of unit weight of output layer.
- 3rd term: Partial differential of unit weight of 'convolution' layers.
- 4th term: Partial differential of unit weight of output layer.
6. ニューラルネットワークの言葉に翻訳:
- Feature Map by convolution of Filter-S:
-
2
1
0
1
0
0
1
2
0
0
3
0
0
3
1
1
- Convolution layers (畳み込み層):
- Picture >Similarity >Convolution (Weight) >Convolution (Output) >Pooling:
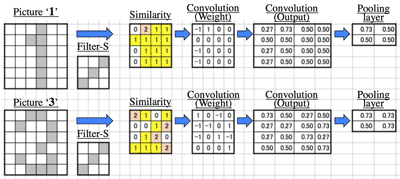
Comment
- Mathematics for deep learning relates mostly partial differential. Recurrence formula are easier for computer to calculate than partial differentials, and are used instead.
- It is interesting to understand how AI understand analog picture to digitized recognition, by doing complicated mathematical calculations. It is as expected that computing ability in quick calculation is a decisive factor.
- Computer itself is no more smart but is only speedy in calculation.
- ディープラーニングの数学は、特に偏微分に関連する。コンピュータにとっては、偏微分より漸化式の法が得意なのでよく代用される。
- AIが複雑な数学計算によって、どのようにアナログな図をデジタル認識するのかは興味深い。それにしても予想通り、コンピュータの計算力の早さが決め手である。
- コンピュータ自体がスマートという訳ではなく、単に計算が速いだけなのである。
 |
Mathematics to understand Deep Learning
|
Category: ICT |
Yoshiyuki & Sadami Wakui (涌井良幸・貞美) |
up 17810 |
Title |
Mathematics to understand Deep Learning |
ディープラーニングがわかる数学 |
|---|---|---|
Index |
||
Tag |
; Axon; Back propagation method; Chain rule; Convolution layer; Cost function; Data dependent; Dendrite; Demon-Subordinate Network; Displacement vector; Gradient descent; Lagrange multiplier method; Learning data; Minimization problem; Neural network; Neurotransmission; Recurrence formula; Regression analysis; Sigmoid function; Similarity of pattern; Square error; Stress tensor; Synapse; | |
Résumé |
Remarks |
>Top 0. Introduction:
|
0. 序文:
|
>Top 1. How to express activity of neuron:
|
1. ニューロンの働きの表現:
|
>Top 2. How the neural network learns:
|
2. ニューラルネットワークはどう学ぶのか:
|
>Top 3. Basic mathematics for neural network:
|
3. ニューラルネットワークのための基本数学:
|
>Top 4. Cost function of neural network:
|
4. ニューラルネットワークのコスト関数:
|
>Top 5. Back propagation method:
|
5. 誤差逆伝搬法 (BP法):
|
>Top 6. Translation to neural network language:
|
6. ニューラルネットワークの言葉に翻訳:
|
Comment |
|
|