Résumé |
Remarks |
>Top 0. Prologue:
- 2009.6.17: CFPA (Consumer Finance Protection Agency):
an act to promote the financial stability of US by improving accountability and transparency, 1) to end too big to fail, 2) to protect American taxpayer by ending bailouts, 3) to protect consumer from abusive financial services practices, ...
- We are living on the age of money; money is not the leading actor, but the age is; industries & politicians that the age requires lead the age, and the money streams along it.
- Paradigm change: made by the majority of the age; from Bush to Obaba
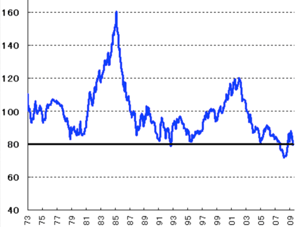
- US$ Index: showing downtrend since 2002.
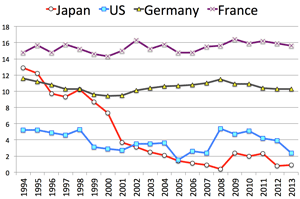
- Saving Rate:
- US recovered since 2008 crisis, due to the devaluating of houses 30%, stock 40%.
- Japan shows downtrend since 2001; saved ¥35.6T in 1997, abut only ¥6.3T in 2007
- The indices of 1) income, 2) stock, 3) saving rate is mutually related according to the economic trend.
- 'Deleverage' is proceeding; reduction of leverage ratio, or percentage of debt; often associated economic recession.
|
|
>Top 1. The advent of Obama:
- 2009/4: US government financed $5B to GM, and $500M to Chrysler.
- 2009/6: GM filed for chapter-11 with total debt $172.8B; US government owns 60%, Canadian government 12% (GM became Government Motors)
- Saab Automobile AB was rejected financial support from Swedish government.
- 2009: Obama became president, while 2003-12 Hú Jǐntāo; 2012- Xí jìnpíng
- 2008/5: Obama rescued JP Morgan, merged Bear Sterns.
- 2008/9: But Lehman Brothers was extinct.
- Financial derivatives: outstanding balance of future option $500T; where JP Morgan $77T, Bear Sterns $13T; 30% of the balance is unclear.
- Counterpart Risk caused credit contraction:
- Deleverage of financial institutions; decreasing risk taking
- Decreasing risk taking mindset
- OTC (Over-the-counter) risk: forfeiture of benefit of time
- Too big to fail:
- Nomura purchased Europe and Asia divisions of Lehman Brothers at $240M.
- Berklays Invest Banking division of Lehman Brothers at $250M.
- Stress test; to recover the credit from the market:
- Gloom of East Europe:
- Housing loan denominated Euro or Swiss Franc; causing enormous exchange risk since collapse of the bubble economy.
- Austrian and Dutch banks to East Europe at 80 -90% of GDP.
- Russia also borrowed enormous loan denominated Euro.
- Exploitative capitalism around 1991
- 1999; G20:
- G7+ BRICs4+'A kiss at me' (9) = 20
- Australia, Korea, Indonesia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Argentine, Turkey, Mexico, and EU
- 2008: G20 Summit: Summit on Financial Markets and the World Economy; covering 90% of world GDP and 80% of world export, and 2/3 of world population.
Finance Minister and Central Bank Governors plus various international organizations
|
1. オバマ登場:
- 2008: JP Morgan救済
- 2009: GM/Chrysler救済
|
>Top 2. Financial crisis repeats itself:
- 'Boom & burst': crowd behavior
- Unlimited money supply:
- Age of Barter exchange:
- Age of Precious metal as an agent for material:
- Ma - Me -Ma
- 16C: Potosi silver mine
- Age of Convertible currency:
- Ma - Mo (=Me) - Ma
- 1816: Gold standard; Sovereign coin (UK)
- Leverage limited
- Age of Nonconvertible currency:
- Ma - Mo -Ma
- 1971: Nixon shock; floating exchange rate
- Age of quantitative easing, QE:
- Leverage unlimited
- Liquidity trap;
- volatility high = high risk high return
- Historical volatility (HV);
- Implied volatility (IV);
- Difficult financial crisis:
-
| Japan |
Public debt; Deflation; Aging society & disparity |
| US |
Fiscal cliff; Poor middle; Housing loan; Big3 |
| Russia |
Raw materials prices; Economic sanctions |
| China |
Expand domestic demand; disparity |
| India |
Budget deficit |
| East Europe |
Repayment difficulty; Ukraine |
| EU |
Bad loans; Disparity among members |
| Dubai |
Bubble in real estate |
- Empirical rule:
- MTBB (Mean Time Between Bubble): about 5 years, which is needed to forget the former bubble.
- Occurrence conditions of regional bubble:
- Prolonged recession in major GDP countries
- Excess fund worldwide
- Lavish stimulus measure adopted in some countries.
- Magnificent development stories
|
2. 金融危機は繰り返す:
- 日本のバブル経済と崩壊
- Bubble boom and burst in Japan: TSE
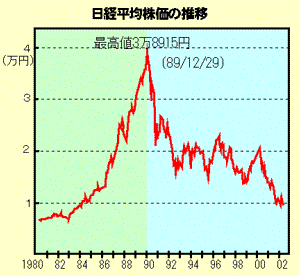
- 通貨の無期限発行時代
- 物々交換時代
- 貴金属代用時代
- 兌換紙幣発行
- 不兌換紙幣
- 異次元の金融緩和
- 次のバブル発生までの期間
- 局地バブルの発生条件
- 主要GDP国の不況
- 世界的資金ダブつき
- 大盤振る舞いの景気対策
- 壮大な開発ストーリー
|
>Top 3. American Capitalism:
- US has deliberately and systematically pursued both military and financial hegemonies since WWII; but its status begins to shake.
- Emphasis on "Economic rationality", pursue of profit; which contains:
- Corporate capitalism; stock principle
- Contracturism
- Market fundamentalism; Market principle
- Small government; deregulation, self-responsibility
- Global financial system; only US has veto power, and authority of personal affairs.
- IMF: SAP (Structural Adjustment Program) deteriorates emerging countries economics by enforcing diminishing equilibrium policies of 1) higher interest, 2) curtailed budget, 3) exchange rate maintenance (60% in the case of Philippines)
- World Bank: IBRD+IDA+IFC+MIGA+ICSID);
- Global trading system; GATT(1995)→WTO; WTO covers not only trade of goods (car, computer, space, agriculture, .... ), but finance, ICT, intellectual property, trade of services (finance, insurance, medical, ... )
- Features:
- Securitization
- Market valuation
- Leverage
- Financial engineering
- Double standard; US adopted expanding equilibrium of policies; 1) lower interest, 2) weaker $, 3) monetary relaxation; and Special-301 (Omnibus Foreign Trade & Competitiveness Act, 1988)
- Key currency: 60% of foreign currency reserves owned by foreign countries is US$; as a weapon of economic sanctions
- Corporate Capitalism vs. Democracy;
- 51% share controls everything; or 51% of 51% (26.1%) can control affiliate operating company via holding company
- Moral hazard; stock option; insider trading;
- window-dressing
- M&A and money game, neglecting core business
- Regulation enforces inconvenience or inefficiency on the ground of public interest;
|
3. アメリカ流資本主義
- 経済合理性追求による利潤追求
- 株式主義
- 契約主義
- 市場原理
- 小さな政府;規制緩和、自己責任
- 資金援助機構
- 貿易機関
- 特徴
- 株式主義 vs. 民主主義
- 51%による完全支配
- モラルハザード
- 粉飾決算
- 政治のSilver democracyは?
|
>Top 4. Socializing US:
- Obama administration:
- 2009/5: CFPA (Consumer Finance Protection Agency)
- does not believe self-cleaning action; SIV (Structured Investment Vehicle)
- Change of policies:
- Environment
- Green New Deal
- Employment
- Medical & Insurance reform: 15M US citizen are not insured.
- Minimize of 'Legacy cost'; medical and pension fund for retired staff of major companies.; ¥1.5K per each car of GM
- Community centric compliance, governance, or CSR; not only for shareholders
- Separation of board chairman and CEO.
- Pursue of tax evaders (more than 4,000) accounts in USB of Switzerland; Bank Security Act.
- Product Liability Law or similar restriction for financial products
- Obama's solution process
- Participation to discussion; Cooperation
- Commitment to the decision; Commitment
- Sharing of the result; Collaboration
- Development of emerging countries causes poverty issues in the advanced countries:
- replaceable labors in the advanced countries
|
4. 社会主義化する米国:
|
>Top 5. G2 Age will start:
- Fiscal stimulus in G2: China 15% of GDP in 3 years
- China requires new finanancial rules; AIIB
- Pursuing Well-off society
- G2 appears since 2008
- US issued $780B bond
- 2008/11: China changed to expand domestic demand.
- Chinese foreign exchange reserve exceeded $2T: bought $760B US bond.
- Give & take relationship between G2:
- World provider & world consumer
- World creditor & world debtor
- Socialisic market economy vs. Capitalism promoting socialistic policies
- Hú Jǐntāo, engineer vs. Obama, lawyer; both men of action
- Plan for remodeling China (infrastructure, agriculrure, social security, environmen, efficiency)
vs. Green new deal; maintaining order and credit conditions
|
5. G2時代の幕開け:
|
>Top 6. Superficial couple of capitalism and democracy:
- Globalization of not only corporation but also nation.
- Limit of nation;
- Global cooperation; environment, nuclear disarmament, WTO
- EURO: who is the leader?
- ECB exists, but
- sovreign rights such as 1) currency issuance, 2) national bond issuance, 3) national budget (within 3% deficit), 4) national taxation, and 5) no full function of central government
- Democracy:
- evaluated by degrees of personal satisfaction
- deseminating policies; powers tend to be dispersed and diluted.
- Capitalism is evalued by money.
- Globalization; 2 employments in emerging countries correspond to 1 unemployment in advanced country.
- Socialism:
- Elitism by one party dictatorship:
- Limit of social welfare:
- safety net to maintain the regime
|
6. 資本主義と民主主義の仮面夫婦:
|
>Top 7. What Japan should do?
- Galapagos Japan: the lost two decades;
- moderate declining by deflation; mind plus in real GDP
- Export industries are profitable; Toyota, Panasonic
- Employment adjustment; increasing atypical employment
- Increase of overseas investment by private sector; decreasing 'Home bias'
- 2009: Trade deficit
- Aging society; female 86.5, male 79.29;
- Unsatisfacting next generation; almost retiring not yet inheritance
- Public pension issue;
- revenue transfer mechanism between generations;
- Global economy promotes shift of the industry (souce of wealth) to overseas;
which will not be inherited to the domestic next generation.
- Pension issue is a systematic fatigue; nation, industry, community, and change of population pyramid
- Aging society: Silver democracy Japan:
- Legacy cost
- Institutional fatigue of Japanese pension fund:
- BB (Best Before) Date;
- disappearance of home bias;
|
7. 日本の進むべき道:
|


