超高速開発時代
の到来と
ICTの活用
Advent of Rapid Software Development
- Indispensable software development method in global age -
Cat: ICT
Pub: 2014
#1431a
Takaaki Seki (ICT Management Partners Association); 関隆明(ICT経営パートナーズ協会会長)
14z20u/18117r
Title
Advent of Rapid Software Development
超高速ソフトウェア開発時代の到来
Index
- Introduction:
- Productivity of Japan:
- Difference of ICT investment trend between US & Japan:
- Serious issues in developing ICT system:
- Diversified development of ICT system:
- Why rapid software development is focussed?:
- Movements of major ICT Vendors:
- Extremely Rapid Application Development Community (xRad):
- ICT Human resources with integrated knowledge:
- Expansion of function of IT Coordinator:
Tag
CIO; Effectiveness of ICT; Productivity;
Why?
- Here is the essence based on the latest presentation made by the author, chairman of ICTM-P; however some data are updated as Rapid Development should be iteratively revised.
- Ref: 4925seki_presen13Fe.pptx; 4z20productivity_japan.xlsx
- 以下は、ICTM-P会長関隆明の最新の講演資料に基づくが、一部資料は最新にものに置き換えている。超高速開発は、繰り返して修正するのが常だから。
Original resume
Remarks
>Top 0. Introduction:
- Various experts gathered in "ICT Management Partners Association" established in Nov. 17, 2011, aiming to support particularly SMB in Japan through ICT-enhanced management.
- ICT system is just a convenient tool, not the object of the organization; corporate staff should be more productive and intelligent to survive in rapidly changing environment.
- Agile software development methodology is focussed; which is most effective method not only in developing software but in maintaining it adjusting in today's changeable requirements.
- "Extremely Rapid Application Development Community (xRAD)" , established in Aug.6, 2013, where IT vendors and users could exchange views. The author is also the head of the xRAD.
- Also, a related book of rapid software development was published in May 19, 2014.
0. 序文:
- 2011/11/17:
ICT経営パートナーズ協会設立
- 2013/8/6:
超高速開発コミュニティ設立
- 2014/5/19:
"超高速開発が企業システムに革命を起こす"の本出版
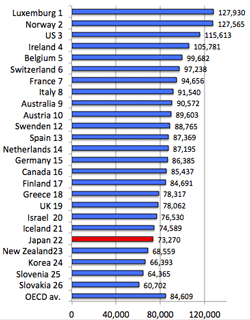
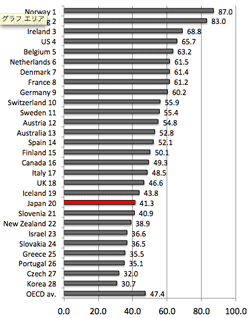
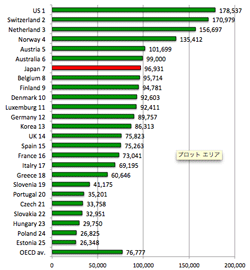
>Top 1. Productivity of Japan:
- Productivity Ranking:
Productivity = GDP (ppp)/# of workers, or GDP (ppp)/working hour
- Productivity all per worker, 2013: OECD countries: ppp adjusted (below left)
- Productivity all per hour, 2013: OECD countries: ppp adjusted (below center)
- Productivity manufacturing, 2012: OECD; exchange rate adjusted (below right)
- Productivity of Japan:
- OECD Report (2011) says that Japanese works annually 1,700 hours, compared with other advanced countries are 200-300 hours less (1,400-1500 hours).
- Japanese productivity is about $40/head, compared with US $60.
- Part timer: 6/8 hours are practical, but 6/12 hours are big different.
出展:日本生産性本部 (Japan Productivity Center) 2014
- 日本の生産性はOECD諸国中、下位:なぜか?
- 但し、製造業は7位
- 労働生産性/労働者: 22位
- 労働生産性/労働時間: 20位
- 大勢が薄く長く勤務しているからか。
Productivity all; per worker, 2013
Productivity all; per hour, 2013
Productivity manufacturing, 2012
>Top 2. Difference of ICT investment trend between US and Japan:
- Recognition of importance of ICT systems for corporate management:
- US: strongly yes more than 75%;
- US corporation positions ICT as a core factor of the corporate strategy.
- Japan: strongly yes around 16%
- Use of cloud computing:
- US: already using private cloud computing in several divisions: about 50%
- Japan: never heard of cloud computing or doesn't know it well: about 46%
- Who becomes CIO in Japanese companies?:
- mostly promoted from the top of Information System division.
- very rate promoted from the top of Business division or Production division
- What is effectiveness of ICT:
- US:
- Rapid delivery of product & services; 54%
- Effective delivery and quantity of external information: 34%
- Effective operation of business process, and decrease of working hours; 28%
- Japan:
- Effective operation of business process, and decrease of working hours; 44%
- Share of internal information: 41%
- Decrease of personnel cost: 26%
- Expectation for ICT (Reasons of increase of ICT budget): >right figure
- US: mostly aggressive or strategic; sales increase, market analysis, change of business model.
- Japan: mostly defensive or inter-efficiency purpose
- Serious management issues of Japanese companies in using ICT:
- Recognition of importance of ICT system to become a competitive company.
- Should consider seriously 'rapid software development method'
2. ICT投資傾向の日米差:
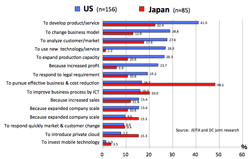
- アンケート(2013)結果
- クラウド利用度
- CIOについて
- IT投資のこれまでの効果
- ITに関する期待
- 日本におけるIT活用上の問題
- ICT技術の経営に及ぼす影響について日本の経営者は、概して真剣でなく怠慢
- CIOの機能不全;なぜか
- ソフト開発の現場の課題;
大勢が薄く長時間の傾向
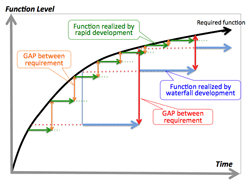
>Top 3. Serious issues in developing ICT system:
- Inconsistency between corporate goal and function of ICT system
- Not useful; small percentage (23%) replies that the system is satisfactory.
- Too slow in development; due to customized software developed by labor-incentive.
- Problems in ICT system development:
- Less initiative of the user company:
- Less leadership of the top
- Too much dependence on the SIer.
- First selecting a tool syndrome
- insufficiency of project management covering management & ICT
- Adherence to waterfall-type development:
- expensive investment and elongated development period
- discrepancy between user's requirement and description of RPF; causing frequent amendments or reworks.
- inappropriate operation after the cut over due to rapid environment change.
- too much cost for maintenance (70%+), and not enough positive investment (20%+); exact opposite ratio of US/EU.
3. ICTシステム開発上の大問題:
- ICT化の大きな問題点:
労働集約型個別開発中心
- システム開発上の問題点:
経営トップのリーダーシップ
過度なベンダ依存
ツールありきの発想
プロマネの不徹底
- ウォーターフォール型個別開発への偏重:
経営要求と要件定義との乖離
手戻りの多発
維持保守に費用掛かり過ぎ
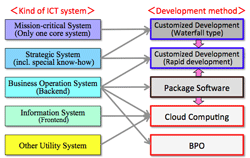
>Top 4. Diversified development methods of ICT system:
- Diversified software development:
- Waterfall type of development is needed to develop 1) advanced & big system, 2) unique strategic system.
- Rapid development method & tools should be quite effective to develop other general business systems used in the background. (particularly differentiation is needed)
- In some cases, general business systems could use optimum package software or cloud computing are if available.
- Unnecessary customization or add-ons of package software could be costly and unstable.
- The trend from using package software to using either cloud computing (due to increasing of available software) or using rapid development tool (due to advent of easy-to-use convenient tools and easiness of maintenance.)
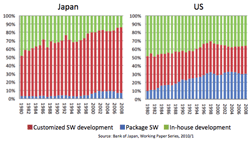
- Comparison between US and Japan:
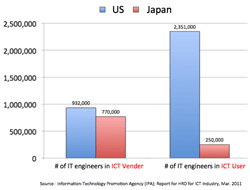
- US is balanced; customized 33%, package 30%, in-house development 37%; user companies retain lots of SE.
- while Japan sticks to customized software development by ICT vendor; customized 80%, package 6%, and in-house development 14%.
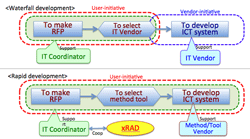
- Role of user companies:
- To establish business model, and actively participate making RFP.
- To take the initiative in selecting IT Vendor, and other resources.
- To have the ability to select 1) rabid development tool, 2) package software, or 3) cloud computing service, as the case may be.
- To play the function of project management, operation & maintenance, and risk management.
4.多様化するICT調達法:
- 超高速開発やクラウド活用事例が増えてきた;なぜか
- ユーザ企業の重要な役割
>Top 5. Why rapid development method is focussed?:
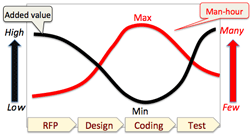
- No-coding development:
- In making software, man-hour spent for coding is the maximum, which could be regarded as the minimum value-added jobs; furthermore man-made coding necessarily contains human error, or bugs.
- These coding can be minimized in case of using rapid development tool.
- Off-shore outsourcing of this coding jobs could not be a solution:
- Labor cost is catching up rapidly in emerging countries.
- Such labor-intentive works are getting unpopular in emerging countries.
- Thus, use of rapid software development would be a solution.
- Features of rapid software development tool:
- Repository:
- Business rules management
- Design information management
- Operation & maintenance management
- Automatic generation (programming)
- Automatic generation into various languages (Java, C, C#, COBOL, Ruby,...)
- Remarkable features:
- Easy change of design by revising business and/or data.
- Programming skills are not particularly required.
- Automatic designing of database
- Flexible change or addition after cut over
5. 超高速が注目される理由:
- WF型スクラッチ開発の弊害
- 基幹業務に適したアプリが過小
- クラウド利用は経営業務熟知してから利用すべき
- 作らない開発への動き
- ソフト開発の自動化必須
→リポジトリ
→ソースコード自動生成
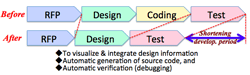
>Top 6. Movements of major ICT Vendors:
- Movements of major IT vendor may cause 'productivity revolution' in software development.
- NTT Data:
- 'TERASOLUNA' Series
- automatic generation of 100% source code; automatic verification
- business specific tool; open system
- challenging integrated automation of program design and testing
- TIS:
- 'Xenlon' <神龍 (Shén lóng)
- aiming to high productivity and high grade in application development.
- application framework Kit, programming guide
- automatic generation of source code
6. 大手ICTベンダの動き:
- 大手ベンダも実は、自社内のソフト開発効率UPに活用中
→SEの新たな役割
- ユーザ企業もこの動向注目すべき
- ソフト開発≠コーディング
>Top 7. Extremely Rapid Application Development Community (xRad):
- Extremely Rapid Application Development Community (xRad) was established in Aug. 6, 2014.
- # of members including ICT vendors, users, and individuals, totalling 171 as of Dec.1, 2014.
- Vision:
- To realize rapid management.
- To change ICT industry into more attractive.
- Mission:
- To raise the recognition of 'rapid development of software', including its idea, method, and tools.
- To promote educational activities how to use and assess rapid development of software.
- To furnish practical know-how's for engineers
- Major Activities:
- To introduce case studies
- To introduce various 'rapid development of software' tools
- To introduce how to connect the upper stream and downstream, i.e., system installation.
- To indicate the conditions by user-centric development.
- To have workshops to solve the issues of ICT division.
- To promote seminars, particularly for corporate executives or mangers
- To promote member community and exchange of autonomous information.
- To issue Mail magazine
7. 超高速開発コミュニティ:
- 企業のスピード経営実現
- 魅力あるIT業界への変革
- ITベンダ、ユーザ企業参加の中立的団体
- 実践的情報交換・啓蒙の場
個別開発を批判する者は
個別販売より市場拡大を

- URL: info@x-rad.jp
- Organization:
Chairman: Takaaki Seki
Secretary companies:
>Top 8. ICT Human resources with integrated knowledge:
- The leader of project team for ICT system development using rapid development tools should need following expertise:
- Basic knowledge:
- Business knowledge; corporate strategy, business process, understanding of business activities, features of the market.
- ICT knowledge; technical insight in actual installation, fusion with business knowledge
- Innovation ability; knowledge of methodology, tool, dialogue & facilitation ability
- Practical ability:
- To realize value; designing of as-is/to-be model, creation of new value for customer & society, business development process
- To discover value; understand, sense of resonance, value discovery process
8. ICT融合人材:
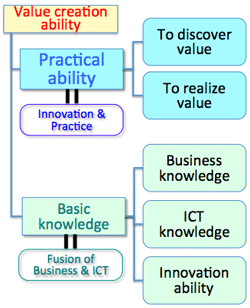
Source: ITC guideline
>Top 9. Expansion of function of IT Coordinator:
- IT Coordinators (ITC), qualified consultants recommended by METI, can have more functions when they use rapid development of software tool; because,
- ITC is a coordinator to converge management and ICT system.
- ITC has knowledge background of corporate management and practical business know-how, and can lead in designing and modeling of the to-be systems.
9. ITコーディネータの活躍領域拡大:
- ITコーディネータの本来の役割期待
Comment
"What is extremely rapid development?":
- 1. This sentence contains three terms: "extremely", "rapid", and "development". In Japan, usually young generation like to say, 'extremely cute' (cho-kawaii). The term of extremely is used in the same context. In business, some extreme things may happen, which are usually several % change; in some cases, several ten % change may be possible in exceptional and shorter period. Then what would be the case of several hundred %, or several times of change? People may call such a phenomenon a kind of supernatural, or paranormal, which are separated from usual phenomena. There must be some special reasons in these exceptions. In the case of rapid software development tool has the reasons; which will arrange and collect all data into a visible single database called depository, eliminating human errors as much as possible. It is difficult to make people widely believe such an abnormal situations in any time.
- 2. What is 'rapidity'? It is used as comparing to the normal works. As any resource has the limit, it is impossible to do everything rapidly. Rapid means to concentrate the resources into some specific (narrower) areas, conversely, the remained resources can be used in other areas. In the case of software development, system engineers need to make coding and debugging in most exact manner, which enforces human expertise and perseverance. By using rapid development tool, humans can concentrate themselves in the area of strength such as business process, organizational structure, priority decision in case of changes, etc.
- Lastly, 'development' is a challenge to apply what had not been existed nor used technology or know-how in the target. It is essential to recognize meaning or purpose of the development; which would be verified later whether it was really effective or not in the market. Simple acceptance of jobs as the order from the organization could not really motivate the developer. It should be reconsidered that the product was really just respond to the market needs. If there were amendable or insufficient things in the product, the next iteration of development should start, which will be almost advanced maintenance. The end of a cycle of development is the start of the next cycle. (K. Kobayashi, Secretary-General of ICTM-P)
「超高速開発を考える」:
- 1.超高速開発には3つのメッセージがある。
まず超とは、日本の若者のよく言う超カワイイと基本的には同じ意味だが、そこには予想外の驚きと発見がある。通常、ビジネスなど継続的な出来事は数%の伸びでも累積的に起こるとそれは驚異的となるが、人間の場合は、ここ一番の特別な集中力や努力によって通常の場合に比べて短期間では数十%である。ところが例外的に数倍の伸びを示すことがある。それは、何か異常なあるいは特別な事情があって従来のやり方から隔絶する場合である。超高速開発の場合は、効率的なツールを使い、デポジトリーというデータの可視化・集中化を行い、人間のエラーを最小化することで、数倍の効率を達成している。その信じがたい異常現象をどう伝えて信じてもらうかはなかなか難しい課題である。
- 2.次に高速とは、通常の作業に比べての表現である。資源に限りがある以上、すべてに対して高速にすることはできない。高速作業することは、他で使っていた資源をそこに集中させることであり、逆に高速化したことで余った資源を他に振り向けられるということである。ソフトウェア開発ではSEによるプログラミングおよびそのデバッグ作業を正確に行うことが必要で、その作業には習熟した人間の忍耐を強いてきた。超高速開発によって、今までの人的資源を、もっと人間が得意な分野、即ち、業務プロセスや組織構成のあり方、変更の場合の優先度、社内研修の徹底などに注力することができるようになる。
- 3.最後に開発とは、今まで存在していなかった、あるいはまだ活用されていなかった技術・ノウハウを実践に応用するということである。それは何のために開発するのかという原点を検証すること、そして後日達成したことが本当に市場で効果的なのかを認識することは重要である。組織の指示通りゆえに開発することでは、真のモチベーションは得られない。製品を市場ニーズとを再度検討し、変更点や不足点あれば、それは次のイテレーション開発になる。それは先進的な維持とも言える。一つの開発の終了は次の新たな開発の開始である。(小林寛三、ICT経営パートナーズ協会事務局長)
| 超高速開発時代 の到来と ICTの活用 |
Advent of Rapid Software Development- Indispensable software development method in global age -
|
Cat: ICT |
Takaaki Seki (ICT Management Partners Association); 関隆明(ICT経営パートナーズ協会会長) |
14z20u/18117r |
Title |
Advent of Rapid Software Development |
超高速ソフトウェア開発時代の到来 |
|---|---|---|
Index |
|
|
Tag |
CIO; Effectiveness of ICT; Productivity; | |
Why? |
|
|
Original resume |
Remarks |
|
>Top 0. Introduction:
|
0. 序文:
|
|
>Top 1. Productivity of Japan:
|
出展:日本生産性本部 (Japan Productivity Center) 2014
|
|
Productivity all; per worker, 2013
|
Productivity all; per hour, 2013 |
Productivity manufacturing, 2012 |
>Top 2. Difference of ICT investment trend between US and Japan:
|
2. ICT投資傾向の日米差: |
|
>Top 3. Serious issues in developing ICT system:
|
3. ICTシステム開発上の大問題:
|
|
>Top 4. Diversified development methods of ICT system:
|
4.多様化するICT調達法:
|
|
>Top 5. Why rapid development method is focussed?:
|
5. 超高速が注目される理由:
|
|
>Top 6. Movements of major ICT Vendors:
|
6. 大手ICTベンダの動き:
|
|
>Top 7. Extremely Rapid Application Development Community (xRad):
|
7. 超高速開発コミュニティ:
|
|
>Top 8. ICT Human resources with integrated knowledge:
|
8. ICT融合人材:
Source: ITC guideline |
|
>Top 9. Expansion of function of IT Coordinator:
|
9. ITコーディネータの活躍領域拡大:
|
|
Comment |
"What is extremely rapid development?":
|
「超高速開発を考える」:
|