IT Industry
2014
Cat: ICT
Pub: 2014
#: 1424a
Kanzo Kobayashi (小林寛三)
14930u/18117r
Titile
IT Industry in Japanese Economics 2014
2014年日本経済の中のIT産業
Tag
Why
- This is the snapshot of IT Industry in Japanese Economics 2014, summerizing latest available data and topics.
- Refereces: various white papers of METI, MPT and MOFas well as Indsutrial assoications, etc.
Résumé
Remarks
>Top 0. XXX:
0. XXX:
>Top 1 Rapid proliferation of ICT worldwide:
- Proliferation in 2000: 75% in a part of EU, Japan, Korea, and 50% in US & Australia, and only 25% in most developing countries.
- In 2012: more than 75% in most countries including developing.
- Internet users worldwide: 2.92B (growing 12% CAGR) in 2014, and will 5.5B in 2025.
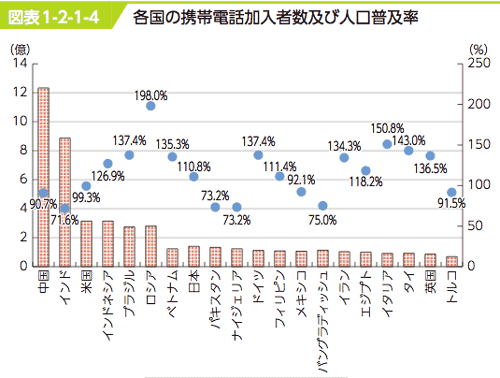
- Mobile phone subscribers and proliferation rate worldwide: <Fig>
- Subscribers: 6.7B in 2013, will grow 9.3B in 2019.
- Mobile phone users worldwide:
- Smart phone: 1.2B in 2005, increased to 1.04B worldwide as of 2014/1 (38% growth yoy), with more than 50% share in mobile phone terminals.
- In China & India, low price model less than $150.
- Smart phone users will increase 1.8B (share 39% in mobile users) in 2014 of all mobile users; attaining 2.5B (share 49%) in 2017.
- SNS users worldwide 2014:
- 2.33B worldwide, 11% CAGR
- Facebook: more than 1.4B (36% CAGR)
- Twitter: more than 250M (71% CAGR)
- Mobile phones suppliers:
- Samsung, Huawei, ZTE
- Xiaomi (China), Micromax (India), Mi-Fone (Africa)
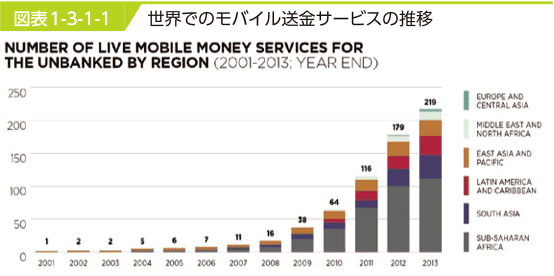
- Mobile Remittance Service:
- Migrant workers worldwide 232M used mobile remittance $414B
- more than half (52%) are used in sub-African countries.
- Safaricom in Kenya operated 'M-Pesa' mobile remittance service; confirmed by ID and SMS at both side of agent or kiosk (96K shops in Kenya).
- Average remittance amount is $29 per each in 2013.
- MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses):
- 2012 became the year of MOOC. ; open online education course via wed, associated with top universities.
- MOOC platforms: Coursera (Stanford), edX (Harvard), Udacity(Stanford), Future learn (UK), Open2Study, OpenEd.
- Mobile Health:
- HIV patients: 30M in 2000, increased 35M in 2012; of which 71% are Sub-Sahara countries.
- Prevention of HIV using mobile phone: helping to take constantly ARV (Anti-RetroViral) drugs.
- TRACNET (Tracement and Research of AIDS Center) in Rwanda
- Literacy education by mobile devices: even India, illiteracy rate is 25% of men and nearly 50% of women. (by NPO Worldreader)
1. ICTの急激な浸透:
- 携帯電話人口普及率
- モバイル送金:
>Top 2. International competitiveness by ICT
- Positive correlation of economic growth and ICT:
- 1987 Robert Solow's Paradox: "You can see the computer age everywhere, but in the productivity statistics."; defined as discrepancy of IT investment and productivity.;
- But this paradox became a thing of the past.
- ICT is one of factors of TFP (Total Factor Productivity), which effect in total output not caused by traditional input of labor and capital; usually value adding factors such as technological development including ICT investment, process know-how, and other intangible fixed assets.
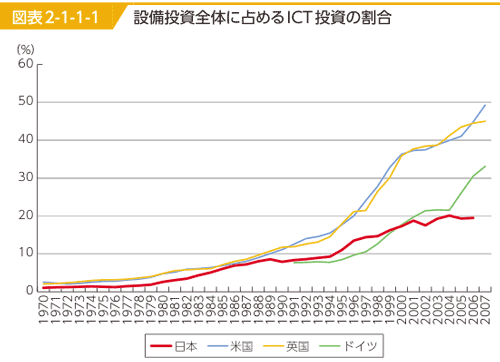
- But the level of Japanese ICT investment has been lower than US & European countries particularly since 2000; probably due to uncertainty of increasing corporate profitability by ICT investment.
- Intangible Fixed Assets: (by Corrado, 2005)
- Computerised information: Software (package SW and internally developed SW)
- Innovative property: R&D, technical know-how, design, copyright and patents, etc.
- Economic competencies: Corporate unique human capital, expenses for branding & CM
- ICT Utilization by Industries:
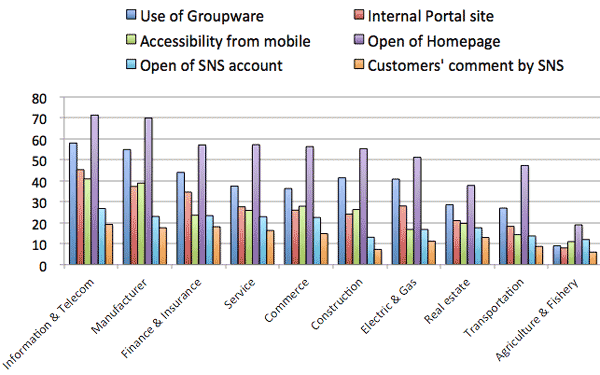
- Top five industries of intensive users of ICT: 1) Information & Telecom, 2) Manufacturer, 3) Finance & Insurance, 4) Services, 5) Commerce.
- Utilization of SNS is relatively lower; less than 20% in top three industries.
- Sensor technology (RFID, IC tag, etc.) and M2M are mostly used in manufacture industry.
- Mobile technology (GPS, etc) is mostly used in transportation industry.
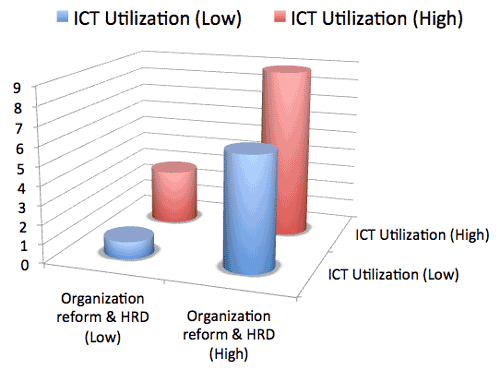
- ICT utilization as well as organizational reform and HRD matter:
- KPI for corporate management improvement:
General
Corporate Managemt
1) Accurate and rapid decision-making by top management
2) Reform of organizational structure
3) Corporate Plan and its execution
Customer Relation
4) Development of new market
5) Improvement of customer satisfaction of existing market
6) Creation of new business model reflecting customer requirements
Staff Relation
7) Improvement of work efficiency per head
8) Improvement of motivation & satisfaction of employees
9) Utilization of internal information & activation of exchange
Business
Profitability
10) Increase of sales in the new market
11) Increase of sale in the existing market
12) Improvement of ROI
Efficiency
13) Compression of inventory
14) Reduction of staff
15) Improvement of business process
Value Add
16) Ability of products marketing
17) Collaboration with partners
18) Collaboration with other industries
- Survey results: (n=4016) 17% of companies replied that their increase of sales due to ICT investment, typically in manufacturing industry.
- ICT investment caused to increase about 0.5% raise of GDP.
- Multiplier Effect:
- Prof. Iizuka and Prof. Shinozaki have calculated how real GDP will increase by the investment of ¥1T annually from 2014 through 2016; in which GDP will increase considering the multiplier effect; 1) by general investment, and 2) by ICT investment:
-
2014
2015
2016
by ICT investment
1.119
1.819
2.311
by General investment
0.950
1.181
1.198
- By ICT investment, real GDP of ¥1T in 2013 will increase ¥1.12T in 2014, ¥1.81T in 2015, and ¥2.31T in 2016 respectively.
- Thus ICT investment will be a driving force of GDP, or becoming a pillar of economic growth.
- Japanese government proclaimed that Japan would be the most advanced ICT-centric country in the world as follows:
- need to break economic deadlock situation
- establish driving forces of economic growth engine
- pursue to realize sustainable economic growth
- take the most of the opportunity of Tokyo Olympic Games in 2020.
- promote National ICT promotion by the integrated efforts of all ministries.
- The T0-Be image of Japanese society as the most advance ICT-centric country:
- Create new industries and new services using ICT technology.
- Public open data and utilization of big data
- Open innovation in such as agriculture and other industries using ICT
- Regional development, including all remote islands
- Break-through in the visual contents industry using next-generation AV technologies.
- Message of Japanese culture at Tokyo Olympic Games in 2020
- Aim to be the most safest and robust society against natural disaster.
- establish long-life and healthy society
- natural disaster resilient society
- effective and safe energy management
- safe and ecological transportation system
- diversified and world life balanced employment
- Realized to access one-stop public service anywhere in Japan.
- effective and accessible e-Government services
- improve of central and local government ICT systems
- ICT governance of public ICT systems
- Cf: London Olympic 2012:
- called World largest Digital Olympic with three themes (S3);
- Social Media: use of Twitter; 125 times of that of Beijing Olympic 2008
- Security: Technical Operation Center (TOC) and separated Surveillance System
- Sustainability/Scalability: Energy saving measures, IP telephone, WiFi hot spot (1800), Access load balancing
2. ICTによる国際競争力強化:
- ICT investment ratio in all capital investment: 2014 EUKLEMS
- ICT化の進展と組織改革・人的資本への取組:
ICT Growth Strategy II
Vision
Creation of innovations through networking various goods and services using state-of-the-art ICT technologies
Approach
Regional Vitalization
Solution of Social Issues
Tokyo Olypics 2020
Key Projects
- ICT City
- Geographical Space City
- Smart Agriculture
- Medical: Smart Platinum Society
- Education: Education × ICT
- Disaster Prevension: Public Information Commons
- Trasportation: Intelligent Transportation System
- Diversity Promotion; Telework, etc.
- Renewal of Social Infrastructure
- e-Government
- ICT-related New Business: Venture Support
- More Free WiFi Services
- Global Communication: Multi Language Support
- 4K/8K Visual Service
(4K test broadcast started 2014/6; 4K=3840 x 2160 pixels; 4 times precise of HVTV)
- Overseas Broadcasting
Common Platform
Platform
- Geographical Space Platform: Guide to disaster prevension
- ICT-centric City Construction: Common ID
- Use of Big data and Open data: Agriculture, Medical, & Social Infrastructure
Infrastructure
- Free WiFi Services: Tourist resort and Disaster prevention center
- 4K/8K Utilization: Broadcast, Medical, and Education
- Ubiquitous Network; Mobile newtwork and M2M/IoT/Social Fabrication (3D Printer)
- World Top-Level ICT Infrastructure: Review of competition policies
Environment improvement
- HRD: Programming, and Data science educcation
- R&D: Capacity enlargement of network, Multi language voice translation, Wearables sensor, Robot, Bionics, User-friendly interafce, etc.
- Information Security: Personl data
>Top 3. Structure of ICT Industry:
- Layer of ICT Industry:
-
Related
Non-ICT Industry
Social Infrastrucutre
Manufacture, Finance, Agriculture, etc.
Service
Upper Layer
Contents & Application
Platform
ICT Service
System
Cloud
Data Center
Telecom
Core (IP)
Access
Terminal
Communication machine
Mobile Base Station
Roulter & Switch
Terminal
Mobile Phone
PC, TV, etc.
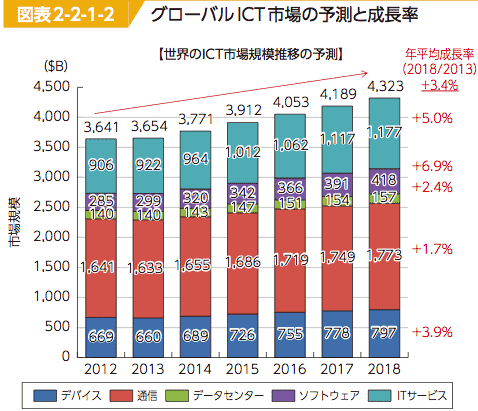
- Global ICT Industry:
- Global ICT market will expaned from $3.8 in 2012 to $4.3T in 2018 (CAGR 3.4%).
- Within this, mobile communication grows more than 10%, while corporate IT service more than 5%.
- North American market shares more thatn 40% in corporate IT service, Software, and Data Center.
- Mobile communication and devices are growing in China and India both in market share and growth. Data Center is expected to grow the highest.
- ICT Industry tends to shift from hardware production to software and telecom services.
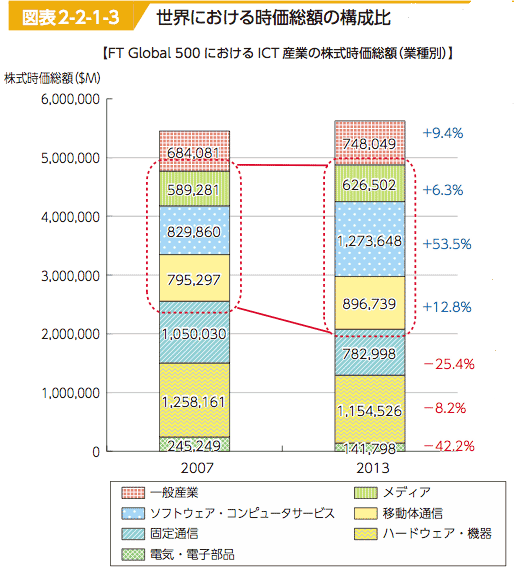
- Market Capitalization (FT):
- Topics of ICT Industry
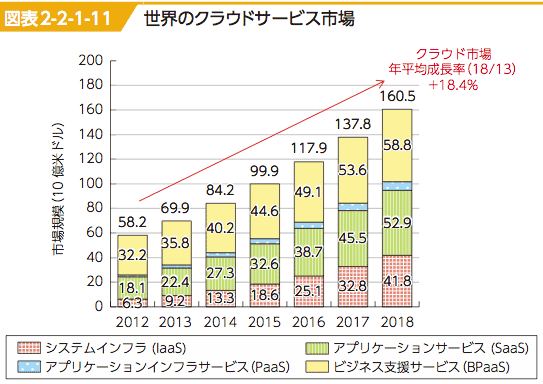
- Clous Service Industry is growing worldwide, particularly North America and Asia-Pacific region where many data centers are constructed.
- In addition cloud services for customers such as storage, music and game are expanding.
- Cloud services for business will $70B in 2013 to $160B in 2018 (CAGR 18.4% compare to general ICT 3.4%)
- Various Cloud Services:
- IaaS: Server, CPU, Storage infrastructure
- PaaS: Platform service
- SaaS: all cloud services inclduing application
- BPaaS: (Busienss Process as a service): equivalent to BPO service shared by multiple users with less customization.
- In mobile services, shift from voice communication to data is obvious; Voice ARPU (Average Revenue Per User) shows minus growth, while Data ARPU positive growth; 44% of all revenue are from data communication.
- Technical advancement in telecom:
- Investment in core network vs. access network is about 40: 60, which shows IP related machines share is growing.; PSTN (Public Switched...)/ISDN decrease while VoIP increases.
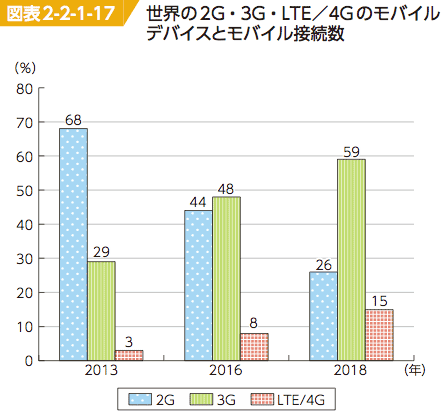
- Mobile telephone: 2G is still major worldwide, while in Japan shift to LTE/3.9G is rapid. LTE/4G is growing CGAR 50%. Thus the generation shift from 2G to 3G, and then to LTE/4G is quire rapidly occuring.
- LTE (Long Term Evolution) is the technology enhanced 3G; usually called super-3G or 3.9G which wil be a bridge to 4G or partly include 4G function with download more than 100Mbps and upload more than 50Mbps, which are nearly same speed as broadband fiber service. But terminals and base stations need to be replaced for LTE/4G specification.
- In Japan, NTT DoCoMo and Softbank adopted W-CDMA, while au adopted CDMA2000, both are developping HSPA/HSDPA and 1xEV-DO respectively for 3.G services. But both groups are expected to adopt same LTE in the next 4G.
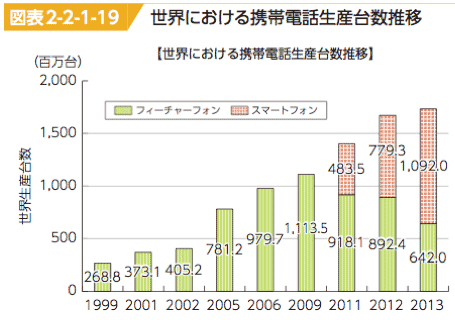
- In 2013, the share of smartphone exceeds feature phone terminals in world production.
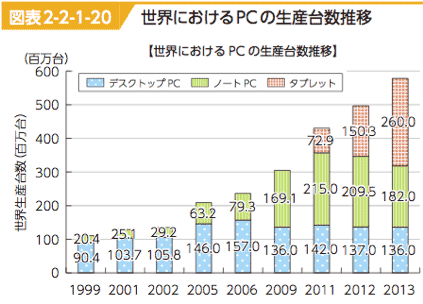
- In 2009, note PC exceeds Desktop PC. And in 2013 Tablet exceeds 40$ in world production.
3. ICT産業の構造:
- ICT産業のレイヤー<左表>
- 世界ICT市場規模推移
- ICT産業規模 (地域別)
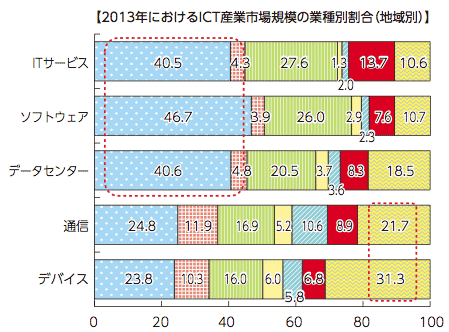
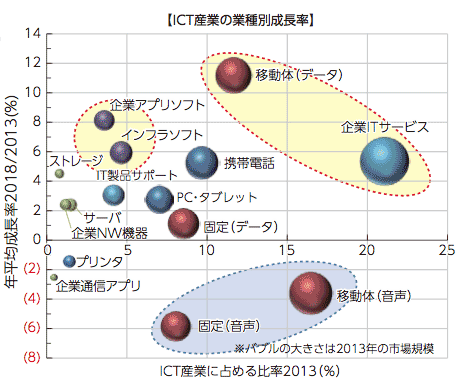
- ICT産業業種別成長率
- 世界のクラウドサービス市場
- 世界のモバイルデバイス進化
- 世界携帯電話生産台数
- 世界PC生産台数
- Major ICT companies (Sales more than $10B)
US
Japan
China (+HK)
Taiwan
Korea
Ger
Oth. EU
- Apple
- GE
- AT&T
- Verizon
- HP
- MS
- Comcast
- Google
- Intel
- Cisco
- NTT
- Panasonic
- SONY
- Toshiba
- NTTDoCoMo
- KDDI
- Mitsubish Elec.
- Softbank
- NEC
- Sharp
- China Mobile
- China Telecom
- China Unicom
- Great Wall Technology
- ZTE
- Huawei
- TCL
- Lenov (HK)
- Hon Hai
- Compal Electronics
- Wistron
- TSMC
- Innolux
- Asustek
- Acer
- Inventec
- AU Optronics
- WPG
- Samsung
- LG Electronics
- LG Display
- KT Corp]SK Telecom
- SK Hynix
- LS
- LG Uplus
- BASF (De)
- Siemens (De)
- DT (De)
- Bertelsmann (De)
- Fresenius Medical Care (De)
- BSH (De)
- Vodafone (UK)
- BT (UK)
- Liberty Global (UK)
- Alcatel-Lucent (Fr)
- Orange (Fr)
- Vivendi (Fr)
- Bouygues SA (Fr)
- Ericsson (Sw)
- AB Electrolux (Sw)
- TeliaSonera (Sw)
- US: Upper layer services such as digital contens and platform services are stronger.(more thatn 20%)
- Korea and Taiwan: Device manufactures such as Samsung & LG of Korea, and Hon Hai of Taiwan are strong (80-90% share)
- Japanese main players are major ICT companies (sales more than $1B), while US, Korea, and others less than $0.1B companies shares nealy half.
- US companies are mostly profitably than 10%, while Japanese manufacturers are less profiitable except platform & telecom layer companies. But Korean manufacturers tend to be profitable, including device manufactrers like Samsung. Chinese telecom and manufactures are profitable, continue to grow in rapidly expanding market.
- In US, global monopolized companies such as Google in search engine, Facebook in social media actively invest and/or M&A ohter emerging companies. (Netwrok Externality)
>Top 4. Strenghten Japanese competitiveness:
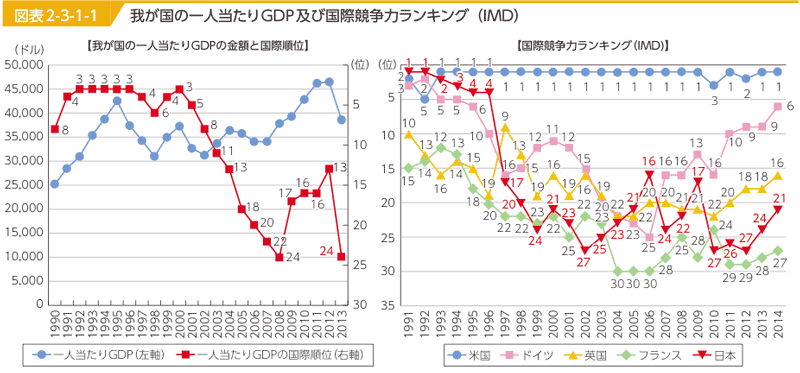
- GDP and GDP per capita:
- GDP amount is 3rd, after US and China.
- GDP per capita had kept growing since 2008, now 24th in 2013.
- IMD World Competitiveness:
- IMD world competitiveness was No.1 until 1992, but now 21st in 2013.
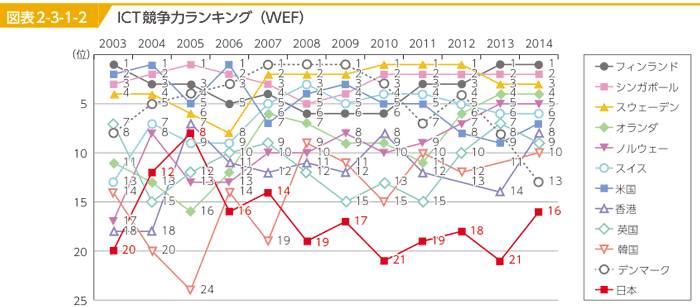
- WEF Global Competitiveness
- WEF (World Economic Forum) global competitiveness was 8th in 2005, but now is 16th in 2013.
- Japanese strengthness and weakness:
- Strengthness:
- Infrastructure
- Refinement of busineess
- Scale of market
- Innovation
- Weakness:
- Efficiency of government
- Macro economic environment, particulary pubic debt
- Venture capital
- Features:
- Japanese major players are older companies established 1930-50s.
- US and EU majore players are relatively newly established 1970-90s.
- Type of Globalization:
- International Type (Export-oritented): Traditional Japanse manufacers
- Global Type (Global-integrated): Google, Apple, Facebook, Oracle
- Multinational (Local-optimized): Local manufacturing optimized for local market
- Transnational (Global-optimized): IBM adoted this type.
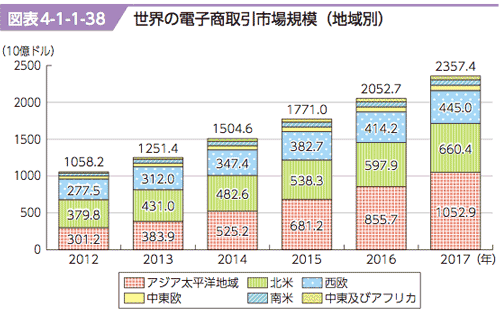
- e-Commerce:
4. 日本の国際競争力強化:
- 電子商取引
>Top 5. Change of Work Style:
- Japanese labor force is decreasing:
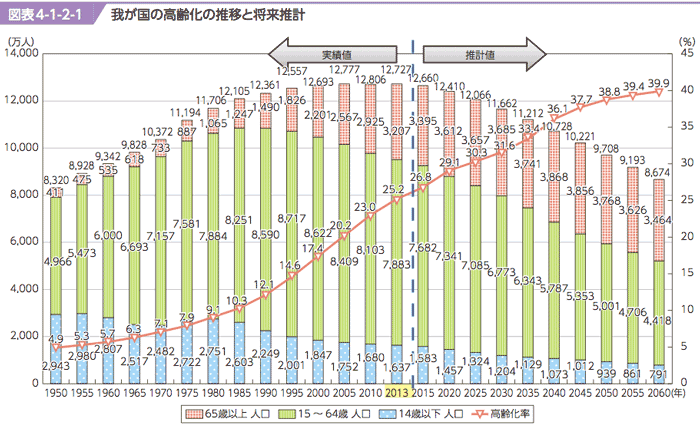
- Senior generation (≦65) shares 23% in 2010, will increase 40% in 2060 world unprecedented level.
- Labor force generation (15-64) was 79.0M, lower than 80M level in 2013/10, which will decrese 44.2M in 2060.
- New type of work style:
- Telework: F-chair (Flexible chair)
- Crowd sourcing: software development, HP making, Reporting, Data input, Questionnaire, etc.
- Japanese potential labor power:
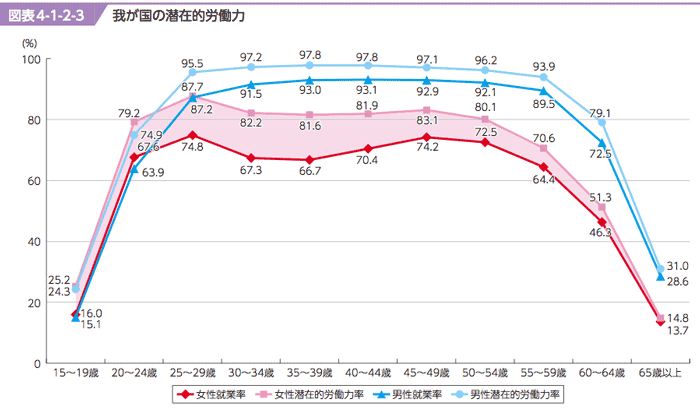
- M-Curve phenomenon in women's labor power in 20-30s generation, who leave their jobs due to marriage, having baby, and childcare.
- The peak of the gap was 25-29 in 1975, which was shifting right nowadays 35-39 due to late marriage in 2013.
- Increase of family caregivers: senior generation divided labor force was 2.77 in 2010, will be 1.28 in 2060.
5. ワークスタイルの変化:
>Top 6. XXX:
6. XXX
Comment
IT Industry |
Cat: ICT |
|
Kanzo Kobayashi (小林寛三) |
14930u/18117r |
Titile |
IT Industry in Japanese Economics 2014 |
2014年日本経済の中のIT産業 |
|---|---|---|
Tag |
||
Why |
|
|
Résumé |
Remarks |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 0. XXX: |
0. XXX: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 1 Rapid proliferation of ICT worldwide:
|
1. ICTの急激な浸透:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 2. International competitiveness by ICT
|
2. ICTによる国際競争力強化:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ICT Growth Strategy II
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 3. Structure of ICT Industry:
|
3. ICT産業の構造:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 4. Strenghten Japanese competitiveness:
|
4. 日本の国際競争力強化:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 5. Change of Work Style:
|
5. ワークスタイルの変化: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 6. XXX: |
6. XXX |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Comment |