忍び寄る |
Creeping Great Depression |
Cat: ECO |
Keita Shibayama (柴山桂太) |
14726u/18208r |
Title
Creeping Great Depression
忍び寄る大恐慌
Index
- Preface:
- Plunge into Silent Great Depression:
- Does globalization bring peace & prosperity?:
- End result of economic war:
- Excessive globalization causes protectionism:
- Inseparable relationship of nation & capitalism:
- Diagnosis of pathology of Japanese economy:
- Survival strategy after Great Depression II:
Tag
Second Great Depression; Neoliberalism; Youth bulge; Globaliztion-II; Military expenditures; Beggar thy neighbor; Collapse of Breton-Woods; Globalization Scenario; Minsky moment; Lost Two decades; Modern Mercantilism; Sociali investment
Why
- There are many books describing about prolonged economic stagnation of Japan; this book clearly mentions persuasive issues of present Japanese economy comparing with the former Great Recession.
- Here are the essential key words from the book.
- 日本の長引く経済停滞を論じた本が数多いが、本書は前の大恐慌と比較して現在の日本経済の課題を説得力をもって指摘している。
- 以下本書から本質的なキーワードを抜き出す。
Essence
Remarks
>Top
1. Plunge into silent Great Depression::
- Lehman crash in 2008 was a change of economic trend which had lasted two decades.
- Maximum economic crisis since WWII in the scale of crush of bubble economy.
- Credit bubble economy continued 2002-2008 had collapsed due to extreme expansion of credit leverage and soaring of real estate price in US and EU.
- Chain links of bubble collapse was expanding to east Europe and east Asia.
- Caused bad influence to the triangle trade; Japanese high-tech parts to China, then assembled and exported to US/EU.
- Comparison of the Great Depressions of last (1st) and now (Second Great Depression):
- Governments' active intervention:
- injected public fund to AIG, BOA, GE, etc totaling about $1T worldwide
- Increase of debt ratio is a driving force of capitalism; expanding scale of economy by more investment and consumption.
- Government took enormous intervention to avoid further economic collapse unlike in 1920s.
- In US, wages of top 10% increased 65% more than that of lowest 10%, with no increase in the middle class.
- Since 2001, Bush administration promoted 'Ownership society' of real estate through FNMA and FHLMC, rather than taking policies of tax reform and income redistribution.
- During 1990s US continued high interest policy to induce foreign fund.
- Stock of GDP is much bigger than flow of GDP.
- In 2007 US subprime loan amount was only 20% of total housing loan, but it was securitized and distributed around the world. (Financial epidemic, or financial worldwide supply chain.)
- Government pump-priming measures are usually after-treatment in Neoliberalism:
- Proactive measures are impossible, because it is too big and too rapid.
- By-product of monetary easing: currency competitive devaluation -> risk of currency war -> serious impact on emerging countries -> complicated crisis
- Globalization could not be destined.
- Youth bulge: increase of young generation causes unstable society (political instability, terrorism, revolution, civil war, etc.)
- Globalization is neither a linear process nor inevitable, when we observe history after economic depression.
1. 静かなる大恐慌に突入:
- 実質GDP成長率比較:
- 公的資金注入:計$600B
- 米:$250B
- 独:$112B
- 英:$90B
- 仏:$56B
- 日:$200B
- アイルランド
- €750B金融支援要請
- 第二次世界大恐慌
- 米国:住宅バブル
- 政府はいつも事後処理
- 事前対策は不可能
- 新自由主義
- 金融緩和の副作用
- 若者人口(15-29)増加:30%超
- Gunnar Heinsohn
- 新自由主義
- グローバリゼーションは過去の歴史から見て不可避ではない。
>Top
2. Does globalization bring peace & prosperity?:
- What had been the Globalization-I?
- London in 1919: rich Englishmen consider how to invest their wealth to any global product, business, or resources; their global communication was always wired with their telephone.
- They believed the Pax Britanica would be sure and grow further.
- But actually a war (WWI) started in Europe in July 1414.
- Globalization-I has finished by the two wars - WWI and WWII.
- Globalization tend to cause more serious friction between nations.
- US enormous investment had escaped from Europe after crush of the stock market in 1929.
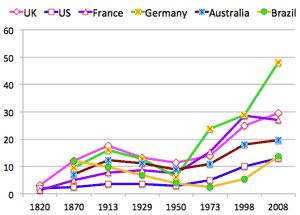
- Export of commodity ration in GDP (1820 - 2008): <figure>
- Now in Japan, there are rare discussions about possible fault of globalization.
- We have experienced twice of deglobalization after the wars; first was after the bubbly investment in US railways, second was in recovery investment in Europe.
- Liberalism-I emphasizing the merit of free trade and automatic adjustment mechanism of foreign exchange under the gold standard.
- Peace with capitalism; mutual investment and mutual trade dependance decreases war risk.
- Before WWI, though UK was the first expert partner of Germany, while Germany was the second export partner of UK, they entered into war in WWI.
- WWI was an event which was beyond expectations even for then sensitive investors.
- WWI:
- Many causes of WWI, such as:
- Competition of colonization by European major powers
- German ambition
- Decline of UK hegemony
- Internal class struggle
- Globalization-I had changed power balances of the major nations.
- Export drive by emerging countries:
- In 1887: 'Made in Germany' display became mandatory.
- Now: US 'China Free' movement appeared.
- Accelerating deglobalization, and then...
- What would be Globaliztion-II
- Present governments have more freedom in monetary policies; no more tight money policy under the Gold standard.
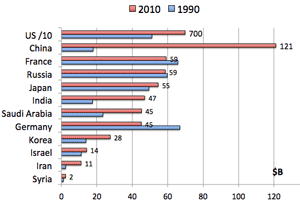
- Military expenditures:
- Only Europe decreased military expenditures; Asia and US are increasing.
- GDP Shares:
- In 19C: UK shared 9%; now US shares 25%
- After 208, geopolitical risks are changing.
- Further globalization may cause further unstable geopolitical situation.
2. グローバル化は平和と繁栄をもたらすか
- Export ratio (%) in GDP
- 軍事費の推移 (1990 -2010)
by Stockholm Int'l Peah Research Inst. (Iran=2007)
- 冷戦後削減は欧州だけ
- WWIは想定外の出来事
- 新興国による輸出攻勢
- 当時はドイツ
- 現在は中国
- 第二次グロバリゼーション
- 軍事費の増大
- 超大国のGDP世界シェア
- 英国は9%
- 米国は25%
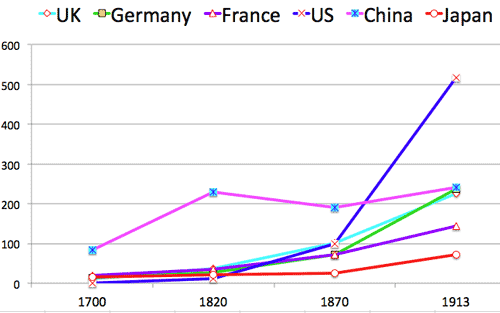
- Source: Maddison Historical GDP (ppp) Data (US$B)
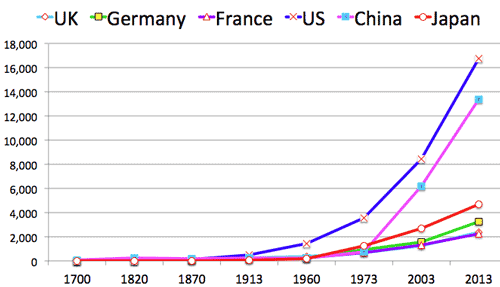
(1700-1913) US$B: 左図の一部拡大
3. End result of economic war:
- Currency war mentioned by Brazilian finance minister at G20:
- Competitive devaluation.
- US quantitative easing policy and Chinese manipulation of exchange value are a kind of aspects of currency war.
- Beggar thy neighbor policy: US quantitative easing policy affects Brazil and other emerging countries to less competitive in exporting products to US.
- Similar devaluation domino phenomena in 1930s, tends to move to more bloc economy.
- 10% devaluation means:
- is equivalents to 10% custom tax as well as 10% subsidy for export.
- direct impact to exporting countries, giving inflation pressure.
- then backward flow of money, and collapse of bubble economy.
- Global imbalance:
- Currency war between advanced countries and emerging countries.
- Worldwide imbalance of current account; enormous current deficit of US.
- Quantitative easing policy; weaker US$ and €.
- Possible burst of bubble economy; like Lehman crush.
- Increase of Asian domestic demand is expected
- Competitiveness of US manufacturing industry
- De-industrialization, or hollowing industrial structure, could not be easily reversed:
- origin of competitiveness compose of:
- accumulation of technology and knowledge
- related knowledge and technology for design and manufacturing knowhow.
- tangible and intangible capitals of supporting industries including service and agriculture.
- US manufacturing assumes fabless industry, mostly outsourcing to Asia.
- US emphasizes in inducing foreign money than balancing own current account.
- Collapse of Breton-Woods System:
- a system to control Capitalism without protectionism.
- US$ is the key currency as the most credit power after WWII.
- But now US is the the most debt country, and has lost power to maintain world economical order. Pax Americana is challenged worldwide by many regional conflicts and wars.
- Function of GATT, IMF and World Bank
- But this system is getting unstable according to US current deficit increases since 1960s.
3. 経済戦争の果てに:
- 通貨戦争:
- ブラジル財務省G20で公言
- 通過切り下げ競争
- 近隣窮乏化政策
- 10%通過切り下げの効果
- 10%関税と10%補助金
- 根源は、グローバルインバランス
- 先進国と新興国の通貨戦争
- 世界的な経常収支不均衡;米国の輸入超過
- バブル経済;
リーマンショック
- 脱製造業の動き
- ブレトンウッズ体制
- 米国ドル基軸通貨
- 当時は最大の債権国、
現在は最大の債務国
- IMFと世銀の役割
4. Excessive globalization causes protectionism
- The Globalization Paradox: Dani Rodrik
- Among these 3 factors, only 2 factors could be chosen.
- New Breton-Woods System pursued:
- G20: Opening of Pandra Box.
- Karl Polanyi "Great Transformation", 1944:
- Globalization Scenario-1:
- Sacrifice of 'Democracy":
- Less competitive industry or faction; like agriculture or labor condition could be sacrificed by globalization.
- Globalization Scenario-1:
- Sacrifice of National sovereignty:
- Regional union like EU, finally aiming World government.
- In EU, why German taxpayers needs to bear to sustain Greek economy.
- Number of nations never decreases after WWII.
- Globalization Scenario-1:
- Sacrifice of Hyper Globalization:
- Globalization could not continue long; around 30years.
- Domestic labor and welfare policies are essential to defend from hyper globalization.
- Sudden unemployment destroy home and community, and land for agriculture.
- "Self-defence of society" against market economy
- Karl Polanyi mentioned:
- protectionism, fascism, and new deal policy were self-defence or pursue of national stability against market caprice; market principle vs. community principle
- land and labor are essentially foreign to market mechanism.
- Globalism vs. Protectionism;
- Direct protectionism; public aid; Buy America Law;
- Ingenious Protestantism;
FTA (Free Trade Agreement) or EPA (Economic Partnership Agreement)
4.行き過ぎたグローバル化がもたらす保護主義
- The Globalization Paradox
- Global political trilemma
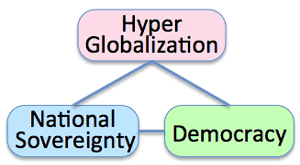
- 上記3つの内2つしか選択できない→グローバル化のパラドックス
そのどれかが犠牲になる
- さまざまな形の保護主義
>Top
5. Inseparability relationship of nation and capitalism
- Economic crisis in every decade: Capitalism may go without control.
- 1987: Black Monday
- 1997: Asian currency crisis
- 2007: Subprime crisis
- 2017: the next crisis?
- How to control Capitalism?
- Adam Smith (1723-1790): The Wealth of Nations
- Karl Marx (1818-1883): Das Kapital; may expand disparity and cause class struggle
- Max Weber (1864-1920): economic activity is only valued by money
- Joseph A. Schumpeter (1883-1950); Evolutionary economics; innovation
- John M. Keynes (1883-1946): capitalism emphasizing uncertainty; investment by half-rational people; the essence is debt economics.
- Fried rich A. Hake (1899-1992): business cycle
- Milton Freedman (1912-2006): government and pressure group which distort capitalism.
- Hyman P. Min sky (1919-1996): Financial instability hypothesis;
- accumulation of debt by non-government sector may cause bubble economy.
- collapse of bubble economy is called (Minsky moment)
- Capitalism grows by the leverage of debt, including consumption and investment
- Capitalism is both dynamic and unstable.
- National debt - an economic discovery:
- Origin: England Bank to accept national debt from the government; nationals became creditor.
- started as fund raising for war expenditure
- National debt market promoted to make Credit Market, and developed democracy.
- bank loan interests are connected with that of national debt as the benchmark.
- Globalization of corporations:
- High-level business is difficult to ship; which needs skilled human resources, organization and network.
- Simple labor and even R&D could be shifted overseas
- Globalization could not coincide with development of Capitalism and Nation; capital without national guarantee and nation without capital support.
5. 国家と資本主義の不可分の関係:
- 10年毎の危機
- 資本主義をどう制御するか
- カール・マルクス
- マックス・ウェーバー
- ジョセフ・シュンペーター
- ジョン・ケインズ
- ミルトン・フリードマン
- ハイマン・ミンスキー
- Minsky moment
- 債務をテコに成長する資本主義
>Top
6. Diagnosis of pathology of Japanese economy:
- Japanese 'Lost Decade' in 1990s or 'Lost Two Decades' (1990-2010):
- 2 decades of liberalization (deregulation and structural reform)
- Junichiro Koizumi (Premier 2001-06)
- Gradual decline of manufacturing industry:
- GDP share: 35% in 1970x to now 20% or less.
- Export dependence ratio: 10% in 1990 to 18% in 2007
- more than 20% in 1930s (15.7% in 1929 and 26.1% in 1936)
- Toyota grew through globalization: sales amount Yen 9.1T in 1990 to 18.9T in 2010
- But labor cost stagnated during two decades.
- Japanese economy became vulnerable by globalization:
- In advanced countries, only Japan suffered both minus growth in 1998 and 2009 after Asian currency crisis (1997) and Lehman crush (2008).
- Epicenter of Lehman crush was in US and Europe.
- Low growth of GDP is common among advanced countries, and is no problem.
- But it is problem that Japan became more sensitive or valuable to global economy due to increase of export dependency twice in last two decades.
- Violent price fluctuation or volatility may occur in natural resources and food material, which will sure give serious affect to Japanese economy.
- Furthermore, Japanese domestic disparity is also serous; over-concentration to Tokyo area (35.7M, 30% of total population after scrambling for HR and 34% of GDP) while other region decreasing population.
- Atypical employment is also serious problem in Japan, causing serious disparity among generations.
- Participation to TPP (Trans-Pacific strategic Partnership agreement) is also controversial issue in Japan as a conflict between industries.
- Globalization tends to require big government:
- People require safety net such as unemployment, deteriorating labor environment and welfare due to the impact of globalization.
- Japan had been a kind of small government, mainly due to lower export dependency ratio.
- Globalization and reduced budge are becoming unstable factor or contradiction
- Losing balanced economy: plunging into risky phase of economics
- natural and nuclear disaster in 2011
- aging and less children population
- enlarging disparity between cities, generations, gender, industries and size of companies.
- Efficiency first culture - Modern Mercantilism.
- It is unhealthy that expanding administration cost and shrinking community and family
- Strategic options:
- More globalization and more concentration and efficiency with bigger government.
- or mild (versatile) globalization and mid concentration and efficiency with mild sized government.
6. 日本経済の病理を診断する:
- 失われた20年
- グロバリゼーションに伴う日本経済のもろさ
- グロバリゼーションは大きな政府を求める
- 均衡を失った経済
- 現代の重商主義
- Source: GD growth (annual %), The World Bank
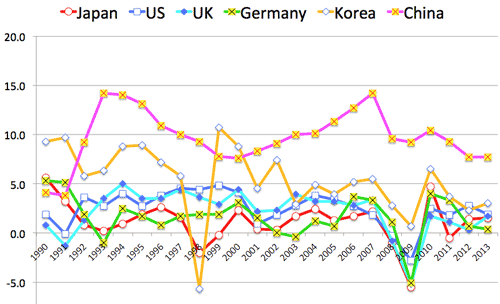
左図の一部拡大
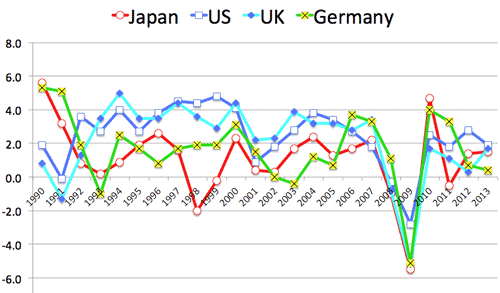
>Top
7. Survival strategy after Great Depression II:
- Globalization is sure to be inverted:
- Turning around globalization and deglobalization.
- Scenario of deglobalization is needed; easing tensions among nations.
- Confrontation between advanced domestic-oriented countries and emerging global-oriented countries;
- Soft landing approach is needed to shift from globalization to deglobalization, or vice versa.
- Extreme views must be avoided; such as capitalism inevitably pursues globalization or role of capitalism ended.
- Money flow is getting hyper sensitive to risk.
- Sociali investment: as Keynes emphasized.
- Expansion of concept: 1) economic capital, 2) social capital, 3) cultural capital;
- human relationship is a social capital in a way of getting no-currency return through spending time for friend and community.
- HR includes creditability among people and organization, education and knowledge.
- Expansion of capital concept:
- Traditional sociology and accountancy could not properly evaluate invisible capital properly.
- more power of thought
7. 恐慌以降の世界を生き抜く:
- グローバリゼーションは反転する
- 社会資本:
- 社会資本の概念拡張
- 非貨幣的なリターン追求
- 人材は信頼性、教育、知識
- 資本概念の拡張
- 従来の社会学、会計学は無形資本への分析不得手
- 更なる思想の力
Comment
- This book describes key controversial issues such as globalization, big government, disparity and competitiveness.
- 本書はグローバリゼーション、大きな政府、格差、競争力など話題の論点に言及している。
Title |
Creeping Great Depression |
忍び寄る大恐慌 |
|---|---|---|
Index |
|
|
Tag |
Second Great Depression; Neoliberalism; Youth bulge; Globaliztion-II; Military expenditures; Beggar thy neighbor; Collapse of Breton-Woods; Globalization Scenario; Minsky moment; Lost Two decades; Modern Mercantilism; Sociali investment | |
Why |
|
|
Essence |
Remarks |
||
>Top
1. Plunge into silent Great Depression::
|
1. 静かなる大恐慌に突入:
|
||
>Top2. Does globalization bring peace & prosperity?:
|
2. グローバル化は平和と繁栄をもたらすか
|
|
(1700-1913) US$B: 左図の一部拡大
|
3. End result of economic war:
|
3. 経済戦争の果てに:
|
||
4. Excessive globalization causes protectionism
|
4.行き過ぎたグローバル化がもたらす保護主義
|
||
>Top
5. Inseparability relationship of nation and capitalism
|
5. 国家と資本主義の不可分の関係:
|
||
>Top
6. Diagnosis of pathology of Japanese economy:
|
6. 日本経済の病理を診断する:
|
|
左図の一部拡大
|
>Top
7. Survival strategy after Great Depression II:
|
7. 恐慌以降の世界を生き抜く:
|
Comment |
|
|