 |
Essence of Oil Economics Beyond geopolitical viewpoint
|
Cat: ECO |
Kazuhiko Fuji (藤 和彦) |
up 12421 |
Title
Essence of Oil Economics
石油を読む:地政学的発想を超えて
Index
Tag
; Arbitrage; BTC pipeline; CNPC; ESPO; HHI; Kazakhstan-China pipeline; MTBE ; Oil reserve; ; OPEC-OAPEC; North Sea Brent; Natural gas; Sea lane; Supermajors; Tech innovation; WTI; VLCC;
Why?
- Energy problem, including oil and oil gas, and sustainable energy is getting a noticeable issue of global economics, particularly after sharp rise of oil price in 2004, and the fatal accident at Fukushima nuclear plant in 2011.
- Oil is still major source of energy and its economics directly affects global economis.
- Here covers wide range of topics of the present oil economics.
- エネルギー問題は、石油や天然ガス、再生可能エネルギーを含め、特に2004年の石油高騰、および2011年の福島原発の大事故の後、再度、注目テーマになりつつある。
- 石油はまだ主要なエネルギー源であり、その経済は世界経済に直結する。
- ここでは石油経済の現状を広くカバーしている。
Original resume
Japanese resume
>Top 0. Introduction:
- Unit:
- bbl = 159 litter
- bbl/d x 53 = ton/y (sp.gr = 0.9)
- pipeline capacity (diameter: 1220 mm) : 80 - 90 K ton
- oil 1 ton ≒ gas 1000 sq.m
0. 序:
- 単位:
- 1バーレル=159リットル
- バーレル/日 x 53 = ton/年
- パイプライン容量:直径1220 mm
- 石油1トン≒ガス1000 m3
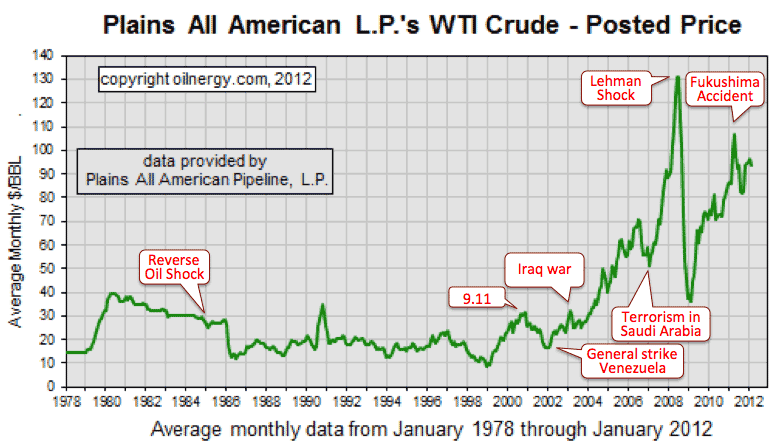
>Top 1. Real culprit of oil price:
- WTI (West Texas Intermediate) Crude Oil Price 1978 - 2012: (Above chart)
- 2004.10.12: WTI Oil Price surged to $54.45 /bbl due to Hurricane attack to the US refinery.
- Re: Unit: bbl /d = 50 ton/y
- Recent sharp rise is due to future purchase, not reflected real supply and demand.
- >Top The shortage is not crude oil, but light crude oil.
- Demand of WTI and North Sea Brent oil, rather than ME Oil.
- Gasoline price surged more than $2/gallon in US since 2004.
- Ban of gasoline additive MTBE (Methyl Tert-Butyl Either) to raise octane number in CA.
- Reverse Oil Shock since 1985: stagnant oil price less than $20/bbl.
- M&A of oil industry: Former Seven Sisters, now Supermajors:
- ExxonMobil: Standard Oil of NJ, and Standard Oil of NY: Sales $391B (2014)
- Royal Dutch Shell (Dutch 60/UK 40): $421B
- BP: Anglo-Persian Oil: $359B
- Chevron: Standard Oil of CA, Gulf Oil, and Texaco: $200B
- TOTAL: CFP: Euro 236B
- ConocoPhilips: $56B
- World share of Supermajors:
- Oil share : 10% of production, 3% of oil reserve
- Reasons for shrinking activities by Supermajors:
- less investment and less inventory policies by Supermajors.
- SPR (Strategic Petroleum Reserve) by DOE, 2005: 727 Mbbl (=21Mbbl x 34 days of US oil consumption) in artificial caverns in salt domes in Gulf of Mexico.
- Oil: from geopolitical items to sensitive commodity:
- expansion of global oil market
- volatility of oil price like casino game
- weakling of political impact of OPEC countries:
- oil emergency stockpile in advanced countries.
- Chinese position in oil market:
- Oil consumption (Top-7)
Mbbl/d
- US 18.9; China 8.2; Japan 4.4 India 3.0; Russia 2.7l; Brazil 2.5l, Germany 2.4
- China became oil importing country since 1993; import dependency 50% (2009), 65% (2015), then70% (2020)
- Major sources of import: ME, Russia, Kazakhstan
- >Top Companies:
- CNPC: China National Petroleum Corp (Petro China)
- Sinopec: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
- CNOOC: China National Offshore Oil Corp.
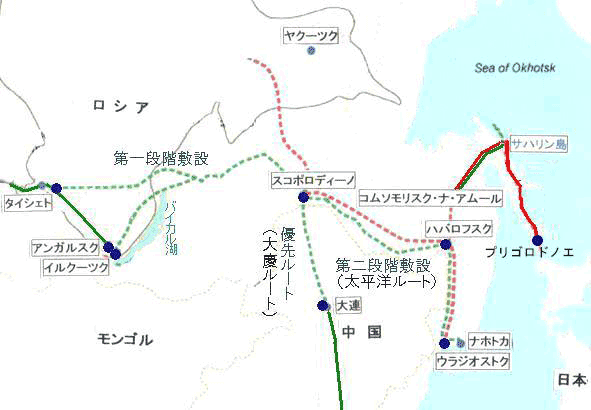 >Top Eastern Siberia - Pacific Oil Pipeline (ESPO): Key to oil diplomacy for Russia, China and Japan:
>Top Eastern Siberia - Pacific Oil Pipeline (ESPO): Key to oil diplomacy for Russia, China and Japan:
- Common route: Taishet - Skovorodino: 2,700km
- Chinese route: Skovorodino - Daqing: 1,000km, construction cost $2.9B, capacity 0.6Mbbl/d; Export to China only.
- Pacific ocean route: Skovorodino - Pervoznaya, Nakhodka: 2,100km; construction cost $6.5B; capacity 1Mbbl/d; Export to Japan, Korea, US, etc.
1. 原油価格の真犯人:
- 世界の石油価格推移: 1978 - 2012: (上記表)
- 不足しているのは、軽質油であって、原油ではない。
- 需要は、WTI, 北海ブレントであって中東の石油ではない
- ガソリン価格は、米国CA州で$2/gallon 以上
- オクタン価向上のための添加剤MTBEの禁止措置 (CA州)
- 1985年以来の逆オイルショック:$20/bbl以下のレベル
- 石油会社のM&A: スーパーメジャー:
- エクソンモービル
- ロイヤル・ダッチ・シェル
- BP
- シェブロン
- トタール
- コノコ・フィリップス
- スーパーメジャーの世界シェア
- 石油生産の10%、埋蔵量にお3%
- スーパーメジャーの活動縮み志向
- 投資抑制、低在庫政策
- 米国のSPR (戦略的石油備蓄): 727 Mbbl
- 石油:戦略物資から市況商品へ:
- 世界石油市場の拡大
- カジノゲームのような価格変動
- OPEC諸国の政治的インパクト低下
- 先進国での石油緊急備蓄
- 石油市場における中国の状況:
- 石油消費国
Mbbl/d
- 米国18.9;中国8.2;日本4.4
- 中国は1993年以来石油輸入国へ
- 輸入先:中東、ロシア、カザフスタン
- 中国の石油関連会社:
- CNPC (中国石油天然気集団公司)
- Sinopec (中国石油加工股份有限公司)
- CNOOC (中国海洋石油総公司)
- 東シベリア〜太平洋パイプライン (ESPO):
- 共通ルート 2,700km:タイシェット〜スコボロディーノ;
- 中国ルート: スコボロディーノ〜大慶 1,000km;建設費$2.9B;
- 太平洋ルート:スコボロディーノ〜ペルボズナヤ (ナホトカ) 2,100km;建設費$6.5B;日本、韓国、米国向けなど
- >Top OPEC (Organization Petroleum Exporting Countries)
- Members: 12 countries
- Chart:
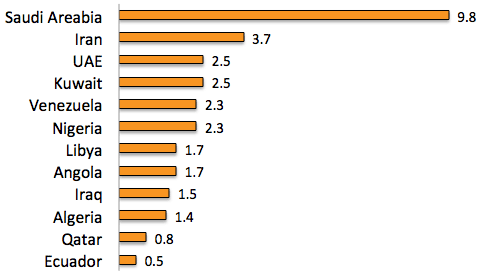 Oil Production (Mbbl/d)
Oil Production (Mbbl/d)
- Oil production of OPEC has been slumbered during these two decades.
- The increase of production has been done by non-OPEC like Russian and North Sea.
- Saudi Arabia has taken cautious attitude in increase of their production.
- Also Supermajors are also deliberate on active development, fearing sudden price decline.
(Their break even price would be $20-25 /bbl)
- >Top Russian situation:
- 2006: Yukos was wiped out, due to tax evasion of Mikhail Khodorkovskii, CEO.
- Production: 9.9 Mbbl/d, nearly equal to Saudi Arabia
- Oil related companies:
- Gazprom: Natural gas monopoly
- Lukoil: largest oil producer
- Rosneft: oil and gas exploration company
- TNK-BP: J/V with BP
- Bashneft: largest oil refining company
- Transneft: pipeline monopoly
- New wellbore technology induced:
- oil layers management technology
- horizontal well technology
- fracturing technology
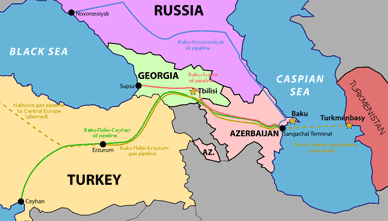 >Top Export infrastructure is bottle neck:
>Top Export infrastructure is bottle neck:
- The Bosporus straits:
- Oil export pass the strait: 2.7 -3 Mbbl/d
- Turkey government restrict the passage of tanker (>200m length) in the daytime only, with minimum interval of 90 min.
- BTC Pipeline: Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan Pipeline; completed 2005, 30% owned by BP; 1,770km
- Russo-China honeymoon relation since 2005 from Russo-US.
- OPEC (石油輸出機構):
- 加盟国:現在12ヶ国
- 生産量:左図。
- 過去20年間停滞。
- むしろ増産は、非OPECであるロシア、北海原油
- サウジアラビアは増産に慎重
- スーパーメジャーも、価格下落を恐れて慎重
- ロシアの状況:
- 2006:ユコス解体
- M. Khodorkovski逮捕
- 生産量:9.9 Mbbl/d
- 石油関連会社:
- Gazprom: 天然ガス
- Lukoil: 最大石油生産
- Rosneft: 石油ガス開発
- TNK-BP: BPとの合弁
- Bashneft: 石油精製
- Transneft: パイプライン
- 新掘削技術導入:
- 油層マネジメント技術
- 水平坑井技術
- フラクチャリング技術
- 輸出インフラがボトルネック
- ボスポラス海峡
- 石油輸出量: 2.7-3 Mbbl/d
- トルコ政府による海峡通過制限
- BTCパイプライン: Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhanパイプライン、2005年完成、1,770km
- 中ロ石油蜜月時代:2005〜(それまでは米ロ蜜月時代)
>Top 2. Resources Paranoia - China:
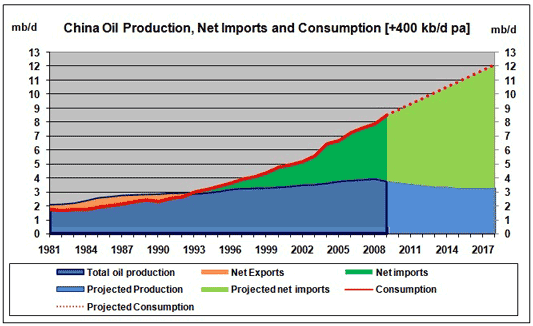 China became oil importing country since 1993:
China became oil importing country since 1993:
- 2004: Wen Jiabao emphasized resources of oil and natural gas will be essential factor of Chinese economic development.
- Ban of oil export from Daqing in Heirongchiang oil field.
- Rapid transition from bicycles to private cars:
- in 2030: surpass the number of US cars.
- Chinese car demand:
13M/2009 -> 18M/2010 -> 20M?/2020
- Gasoline is cheaper in China: about 1/3 of Japan.
- China is increasingly dependent on ME oil: 58% -> around 70% in 2015
- Chinese oil majors:
- CNPC, CNOOC, Sinopec: no more business restrictions
- obtained mining rights in such as Indonesia, Sudan, Angola.
- Package deal: bargaining power as a big oil & gas consumer.
- imports 50% from ME, 25% from Africa.
- Premier Wen Jiabao was specialist of oil and mineral resources development.
- >Top Kazakhstan-China oil pipeline:
Silk road pipeline
- CNPC and KazMunayGas
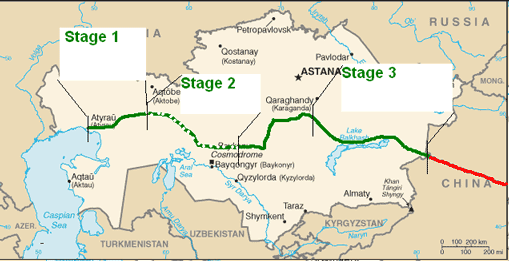
- Signed in 1997, finally completed in 2009.
- Length 2,228 km from Atyrau in Kazakhstan to Alashnkou in China's Xinjiang.
- Capacity: 120 Kbbl/d, then will be upgraded 400 Kbbl/d
- Cost: $700M
- Resource Paranoia:
over response to oil resources potentiality:
- Spratly Islands:
- located in South China Sea.
- comprises more than 30,000 islands and reefs.
- claimant nations:
- Brunei, China, Malaysia, Philippines, Taiwan, Vietnam
- have no indigenous inhabitants
- undermined oil and natural gas potential
- Senkaku Islands (Pinnacle Islands):
- effectively controlled by Japan
- dispute over island ownership
- oil and natural gas potential, but its exploitation cost could be expensive.
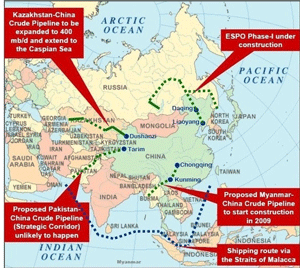
- >Top Sea lane defense:
- Straits of Hormuz
- Straits of Malacca
- only 200 nautical mile (360 km) wide between Malay peninsula and Sumatra island.
- 23 m deep, which is scarcely enough for VLCC (300K tons tanker)
- 164 ships per day (6.8 ship per hour)
- Straits of Sunda:
- too shallow for VLCC
- Strait of Lombok
- longer route
- New oil route plan:
- Myanmar - Kunming, Yunnan pipeline plan
- 1,500 km
- Trans Malay peninsula pipeline
- Strategic Petroleum Reserves (SPR):
- 90 days storage of prior year's net oil imports
2. 資源パラノイア・中国:
- 中国は1993年以降石油輸入国に転じた。
- 2004:温家宝首相発言;石油と天然ガスは中国経済の発展にとって死活問題。
- 大慶油田の輸出凍結
- 自動車社会:2030年には米国を抜く
- 中国の自動車需要:
13M/2009 -> 18M/2010 -> 20M?/2020
- ガソリンは安価 (日本の1/3)
- 中東依存度上昇:58%→70%/2015
- 中国の石油大手
- CNPC, CNOOC, Sinopec
- 中東から50%、アフリカから25%輸入
- カザフスタン・中国パイプライン(シルクロード・パイプライン)
- 1997年調印、2009完成
- 総延長2,228km
- 輸送容量:120 Kbbl/d、今後400 Kbbl/dに増加予定
- 費用:$7億
- 石油利権への過剰反応
- 南沙諸島:
- 尖閣列島:
- シーレーン防衛:
- ホルムズ海峡
- マラッカ海峡
- 幅200海里
- 深度23m
- 164隻/日通過
- スンダ海峡
- 浅すぎる
- ロンボック海峡
- 遠回り
- 新石油ルート計画:
- ミャンマー〜昆明間パイプライン
- 1,500km
- マレー半島横断パイプライン
- 戦略的石油備蓄 (SPR)
- 90日分
>Top 3. Mythology of oil:
- Global oil market:
- is not only the market for the end product, but whole process of oil industry, inducing exploration, extraction, trade, transportation, refining, sales, and consumption, etc.
- Upper stream:
- in order to maintain stable exploitation of oil, the mining company must continue drilling to find proper access to oil layers, always renewing production facilities.
- smaller size of mining companies (other than majors operating in Middle East countries) are obliged to continue such shoestring operation.
- upper stream mining operation is a high-risk industry, spending expensive excavation (about $10M per drill) as much as several tens of drilling to confirm probable oil reserve; costing from $100M to $1B.
- Thus only major oil mining companies are available in such huge risky investment.
- Downstream:
- There are such downstream market as delivery services by huge tankers, and refining operations.
- Delivery cost is less than 5% of oil price.
- While, delivery cost of natural gas much expensive.
- Oil market:
- NYMEX (NY Mercantile Exchange): the world biggest derivative market, including oil, natural gas, kerosene, gasoline, gold, silver, copper
- IPE (International Petroleum Exchange) in London: now internet-based marketplaces operated by ICE (Intercontinental exchange)
- Investors: comprises funds, financial institutions, brokers as well as oil producers and refining companies.
- >Top Three major oil price index:
- WTI: West Texas Intermediate:
- WTI is only 1Mbbl/d (=less than 2% of world oil trade volume 80 Mbbl/d)
- WTI's actual production is 0.5 Mbbl/d、but the derivative trade is more than 100 Mbbl/d
- The North Sea; Brent Crude
- Dubai (or Oman) oil
- Realtime oil statistics is unavailable.
- asymmetric nature of oil information.
- price elasticity is very small.
- Thus, oil market tends to unstable; showing cyclical trend.
- >Top Arbitrage transaction:
- 40% of global oil trade is spot basis.
- Only Japan is exceptional: 90% of oil transaction is long-term contract with ME countries.
- specific gravity is nearly equal to water (0.8 - 0.98)
- >Top half around-the-globe delivery cost is less than 5% ($1 of 1 bbl=159litter) transported by VLCC (300K tons, 21m draft)
- exporter and importer of oil are changeable.
- the end product after refinery cannot be distinguishable, which means oil selective embargo could be not be very effective.
- Oil crisis:
- price cartel after the oil crisis in 1970s,
- gulf war period in 1990-91, and
- uncertain supplying period in 2004.
- Price leaders:
- until 1970s: major oil companies called Seven Sisters controls 70% of world oil production (now only around 10%)
- >Top until middle of 1980s: price cartel by OPEC
- First oil crisis (1973-74): OPEC (mostly OAPEC) raised oil price from $3/bbl to $12/bbl (4 times)
- Nationalization of majors' interest by Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, and Kuwait (except for UAE):
- Second oil crisis (1979 -80): raised to #34/bbl. (3 times), or 11 times more compared before 1973.
- But too much raise of oil price caused sharp decline in 1986, and OPEC cartel fell down.
- Now Saudi Arabia, leader of OPEC, aims sustainable oil price learning from inefficient raise in 1970s.
- after 1980s: there are no significant price leaders.
- Present OPEC (=Organization of petroleum Exporting Countries) (now their production share about 40%) functions as cooperative organization of major oil exporting countries, or pseudo-cartel to prevent sharp decline of oil price.
- Who controls oil price? It is the market;
- say crude oil futures market at NYMEX and IPE (International Petroleum Exchange in London) ; about 40% is spot transaction.
- Japanese import from ME is exceptionally long-term fixed transaction.
- Market mechanism:
- determined by WTI and the North Sea Brent oil transaction:
- Production capacity is about 1M bbl/d, which shares less than 2% of world trade of 80M bbl/d.
- But trade volume of futures market is more than 100M bbl/d
- incompleteness of oil information: inventory information is quite incomplete(except US). IEA publishes the inventory data two month later.
- short-term price elasticity (= change in demand divided by change in price) is too small. (essential commodity)
- oil price fluctuate depend on less preestablished harmony, or shows longer cyclical change beyond 5-10 years.
- >Top Herfindahl Index (or Herfindahl-Hirshman Index, or HHI):
- is defined as the sum of squares of the market shares of 50 largest firms; which indicates decrease in competition or increase of market power.
- monopoly: 1^2=1
- two 50% share each: 2 x 0.5^2 = 0.5
- one 50%, one 30%, one 20%: 0.5^2 + 0.3^2 + 0.2^2 = 0.38
- one 50% and five 10% share: 0.5^2 + 5 x 0.1^2 = 0.3
- one 30%, one 20%, five 10% shares: 0.3^2 + 0.2^2 + 5 x 0.1^2 = 0.09 + 0.04 + 0.05 = 0.18
- US Dept. of Justice considers; HHI 0.01 - 0.18 is moderately concentrated, and above 0.25 to be concentrated.
- Natural gas market is totally different from oil market.
- >Top Oil reserve:
- Minable ore reserve:
- production-ratio is estimated about 40 years.
- this had been 30 year about 25 years ago.
- this minable years must be maintained by continued exploration activities using latest drilling technologies.
- the balance between newly discovered oil reserve and consumption
- directional and horizontal drilling technology have opened new resources and improved productivity:
- Also hydraulic fracturing technology increases the yield of a well after the reservoir is fractured by injecting fluids under high pressures.
- oil recovery ratio raised to 50-70% from the former around 30%.
- Production cost:
- ME: $2/bbl
- small oil fields in Texas: $17/bbl
- Exploration ratio:
- Number of drillings per possible oil field: US is the biggest
- Extended Reach Drilling (ERD) technology:
- 2011: the world longest borehole at Odoptu fields Sakhlin-I, with 12km deep and horizontal desplacement of 11km
- Zonal Isolation technology: filled hollows and gaps by ethanol bentonite.
- Japan should invest for:
- promotion for new exploration activities of natural resources
- technological innovation for resources development
3. 石油神話:
- 世界の石油市場:
- 最終製品のみならず、石油産業の全プロセス、即ち。探鉱、採掘、取引、輸送、精錬、販売、消費などを含む市場
- 上流工程:
- 石油の安定創業を図るために、油層への最適アクセスを維持するために、生産設備の更新を迫られる。
- 中規模鉱山会社は、このような自転車操業状態
- 石油の上流工程はハイリスク産業、鉱量確保のため高価な掘削作業を続けなければならない。$10M/本の掘削を数十本で、1〜10億ドルの費用がかかる。
- 下流工程:
- 大型タンカーによる輸送
- 精錬操業
- 輸送コストは、原油価格の5%以下
- 天然ガスの輸送コストは非常に高い。
- 石油の価格リーダーはいない。
- オイル市場:
- NYMEX: NYマーカンタイル市場、世界最大の先物市場 (石油、天然ガス、灯油、ガソリン、金銀銅)
- IPE: London、現在はICE
- 投資家:石油採掘業者、精錬業者の他、ファンド、金融機関、ブローカー
- 三大石油指標:
- WTI
- 北海ブレント
- ドバイ (オマーン) オイル
- リアルタイムの石油統計がない
- 情報の非対称性
- 価格弾力性が極めて低い
- 石油市場は不安定、循環トレンド
- 裁定取引:
- 国際石油取引の40%はスポット取引
- 日本だけは90%の取引が中東との長期契約
- 密度は水とほとんど同じ (0.8 - 0.9)
- 輸送コストは、製品の5%以下
- 輸出者と輸入者は変動する。
- 精錬以降は区別できない;差別的な禁輸措置はあまり効果的でない。
- 価格リーダー:
- 1970年代の石油危機以降の価格カルテル
- 1990-91の湾岸戦争
- 2004年の不安定供給
- 価格リーダー:
- 1970年代までは、セブンシスターズが世界石油生産の70%支配 (現在は約10%)
- 1980年代、OPECカルテル
- 第一次石油ショック (1973-74)
$3から$12/bblへ
- サウジ、イラン、イラク、クウェートによるメジャー権益の国有化 (UAEを除く)
- 第二次石油ショック (1979-80)
$34/bblに上昇 (1973年の11倍)
- あまりにも急激な上昇で、1986年には需給減。OPECカルテル崩壊
- 現在は、OPECリーダーのサウジが、1970年代の反省から、持続可能な石油価格を目指す。
- 1980年代の後は価格リーダー不在
- 現在のOPEC (生産量は約40%)は、主要石油輸出国の協力機構
- 誰が石油価格を支配しているか
- それは石油市場
- NYMEXやIPE
- 日本の中東からの輸入は長期固定価格。
- 市場メカニズム:
- WTI、北海ブレントの石油取引
- 生産量は、1M bbl/d (世界の2%)
- 但し、先物取引は 100M bbl/d
- 情報の非対称性:在国、需給統計
- 短期の価格弾力性:極めて小さい
- 石油価格変動:5-10年の長期変動
- ハーフィンダール指標
- 上位50社の市場シェアの二乗の合計。
- 0から1までの数値で、市場の独占度 (支配力)を示す。
- 米国の司法省によれば、0.25 以上は独占状態
- 天然ガス市場は、石油市場とは全く異なる。
- 石油埋蔵量
- 可採鉱量:
- 可採年数は約40年
- 新規埋蔵量と消費量のバランス
- 水平抗井技術:石油回収率50-70%に上昇 (それまでは約30%)
- 大偏距掘削技術
- 地層分離技術:エタノールベントナイトにて孔隙を閉塞
- 今後の日本の投資:
- 新規資源開発の推進
- 資源開発のための技術革新
>Top 4. New energy strategy:
- Structural change of oil demand:
- Demand for light crude oil surges:
- WTI (West Texas Intermediate) soars.
- gasoline for cars and planes, and kerosine for heaters
- natural gas for power generation and industries.
- Demand for heavy crude oil is unpopular:
- Dubai oil is heavy and contains more sulphur.
- C-type heavy oil demand for paper & pulp industry.
- Japanese refineries are equipped for desulfurization plants
- >Top Technological innovation:
- IT utilization for exploitation
- Knowledge-base management
- demand increase for natural gas
- hybrid car and EV
- Evolutional system moves intermittedly between the following two phases
- Red Queen's hypothesis: "It takes all the running you can do, to keep in the same place."
- In reference to an evolutionary system, continuing adaptation is needed in order for a species to maintain its relative fitness amongst the systems being coevolved with.
- Evolutionarily Stable Strategy, ESS:
- Not only biological evolution, but also technological innovation or business style may follow this pattern.
- What had happened at the oil crisis in 1970s:
- Oil price soared 4 times in the first oil crisis in 1973, and furthermore 3 times in 1979; almost 10 times higher during the twice crisis.
- Reallocation function of the oil market: spot trade, reallocation trade.
- Assurance of stable supply:
- risk diversification is most important: one source, one route is risky.
- Oil is not a strategic goods, but an important goods.
4. 新エネルギー戦略:
- 石油需要の構造変化:
- 軽質油に対する需要増
- WTI上昇
- 自動車・航空機用ガソリン、暖房用経由
- 発電・産業用へは天然ガス
- 重質油に対する需要停滞
- ドバイ油は重質かつ高硫黄
- 紙パルプ業界向け重油の需要
- 日本の精錬所は脱硫装置装備
- 進化システムは以下2相を間欠的に動く
- 赤の女王仮説:"種・固体・遺伝子が生き残るためには進化しなければならない。"ことの比喩
- 進化的に安定な戦略 (ESS):
- 生物進化のみならず、技術革新やビジネススタイルもこのパターンを踏襲
- 安定供給:
- リスク分散が重要:1資源1ルートへの依存がリスキー
- 石油は、重要物資ではあるが、戦略物資ではない。
>Top 5. Natural Gas:
- Natural gas is the ultimate fossil energy:
- History has been pursue of higher calorie and higher hydrogen energy:
- from charcoal to coal, oil, then natural gas
- the highest hydrogen-contained fuel: methane, CH4
- CO2 emission per calorific value is about 55% of that of coal.
- Calorific value: Natural gas 13,300 kcal/kg
- Coal 5000-7000; Oil 9250 kcal/kb
- Non-toxicity: methane and LNG
- Re: Natural gas reserve:
- Source: The Economist, Briefing the future of natural gas, Aug. 2011
- more reserves (60 years) than oil (40 years)
- natural gas reserved layer is deeper than oil in general.
- Composition of natural gas:
(Source: Wiki)
- Alaska: Methane 99.81%; Ethane 0.07%
- Brunei: Methane 89.83%; Ethane 5.89%
- Abu Dhabi: Methane 82.07%; Ethane 15.86%
- Transportation:
- Pipeline: North America, Russia-East Europe, North Africa-EU (about 96%)
- LNG tanker: ME and SE Asia to Japan (about 4%)
- Use application:
- Thermal electric power plant (about 2/3)
- City gas
- Automobile
- Physical properties:
-
Methane
Ethane
Propane
Butane
M-formula
CH4
C2H6
C3H8
C4H10
M-weight
16
30
44
58
Boiling point ºC
-161.5
-88.7
-42.2
-0.5/-11.7
Critical temp ºC
-82.6
32.2
96.7
152/135
Critical press
45.4
48.8
42
37.7/36
Sp. gr, b.p
0.425
0.546
0.580
0.605/0.590
Sp.gr, 0ºC
0.554
1.047
1.522
2.006
- Strategic viewpoint of Japan:
- Diversification of energy supply source
- Diversification of energy (from oil to natural gas)
- Installation of pipeline, particularly north Asian oil/gas pipeline network
- Promotion of import from Sakhalin natural gas
- Bridging solution from denuclear plant, and sufficient development of sustainable energy.
5. 天然ガス:
- 天然ガスは究極の化石エネルギー:
- 高カロリー、高水素化の歴史
- メタンは、最高水素化エネルギー
- 発熱量:天然ガス13,300、石炭5000-7000、石油9250 kcal/kg
- 無毒性:メタンもLNGも
- 天然ガスの埋蔵量:左図
- 石油より多い(60年)
- 石油地層より深い
- 天然ガスの組成:
- アラスカ:メタン99.81%
- ブルネイ;メタン89.83%
- アブダビ:メタン82.07%
- 輸送:
- パイプライン (96%)
- LNGタンカー (4%)
- 用途:
- 火力発電
- 都市ガス
- 自動車
- 物理特性:左表
- -160で液化
- 比重0.42
- 日本のエネルギー戦略の課題
- エネルギー供給源の多様化
- エネルギーの多様化 (石油から天然ガスへ)
- パイプラインの敷設;特に北アジアのパイプラインネットワーク
- サハリン天然ガスの輸入促進
- 脱原発、再生可能エネルギーの本格開発までのつなぎソリューションとして
Comment
- Natural resources can be secured not only money, but also national strategy and long-term investment for technology and human expertise.
- In Japanese 'yudan' literally means oilless situation, actually means 'unvigilant, unwarily, or unguarded.
- Japanese proverb 'Yudan taiteki' literally means 'Oilless situation becomes a big enemy', which corresponds to 'Idleness is the devil's worship.'
- Also, Japanese 'Aburawo uru' literally means 'sell oil', actually means 'idle one's time away' , 'shoot the breeze', or 'small talk.'
- Then what will be the translation of 'Abura uri abura uri uri abura uri' (Oil seller sells oil together with shooting the breeze.); what about this translation, "Big oil trade can be done after many small talks."
- To secure oil, seemingly glorious vainness is needed.
- 天然資源を確保するには、マネーだけなく、国家戦略と技術や専門家への長期投資が必要である。
- 日本語の「油断」は、警戒を怠ること。
- 「油断大敵」はIdleness is the devil's worship. (怠慢は悪魔の称賛)
- また、日本語の「油を売る」は、米語では、"shoot the breeze"と言い、これは無駄話、だぼらを吹くの意味。
- では、"油売り油売り売り油売り"は、どう訳すべきか。"Big oil trade can be done after many small talks."というのはどうだろうか?
- 石油を確保するには、一見壮大な無駄が必要である。
Title |
Essence of Oil Economics |
石油を読む:地政学的発想を超えて |
|---|---|---|
Index |
||
Tag |
; Arbitrage; BTC pipeline; CNPC; ESPO; HHI; Kazakhstan-China pipeline; MTBE ; Oil reserve; ; OPEC-OAPEC; North Sea Brent; Natural gas; Sea lane; Supermajors; Tech innovation; WTI; VLCC; |
|
Why? |
|
|
Original resume |
Japanese resume |
>Top 0. Introduction:
|
0. 序:
|
 |
|
>Top 1. Real culprit of oil price:
|
1. 原油価格の真犯人:
|
|
|
>Top 2. Resources Paranoia - China:
|
2. 資源パラノイア・中国:
|
>Top 3. Mythology of oil:
|
3. 石油神話:
|
>Top 4. New energy strategy:
|
4. 新エネルギー戦略:
|
>Top 5. Natural Gas:
|
5. 天然ガス:
|
Comment |
|
|