 |
Islamic FinanceFinace pouring over the world
|
Cat: ECO |
HIdeki Nukaya (糠谷英輝) |
12204u/18209r |
Title
Islamic Finance
イスラム金融
Index
Tag
; GCC; Five Pillars of Islam; OIC; Riba; ; IICRCA; Ijarah (lease); Islamic banks; Mudarabah (partnership); Murabahah (credit) ;Musharakah (JV); Sharia; SRI; Sukuk; Takaful; LFX/DIFX ;
Why?
- To understand the Arab society, we must know not only its history, climate, culture, religion and oil resource, but "Islamic Finance", whose origin, function and impact.
- This book gives us the concise and just answers of it.
- アラブ社会を理解するにはその歴史、気候、文化、宗教、石油資源だけでなく、イスラム金融について、その起源、機能、インパクトについて知る必要がある。
- 本書はその簡潔で適切な回答を与えれくれる。
Résumé
Remarks
>Top 0. Preface:
- Asset value: $1.2T; huge oil dollars refluxes.
- London, Singapore and Malaysia actively promote it.
- 1981: GCC (Gulf Corporation Council)
- Six Member countries: SKBQUO (Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, Oman)
- External asset: $1.55T (2006 est): Cf. Chinese reserve $2.88T
- Background of its expansion:
- Recurrence to Islam, particularly after 9.11
- increase of oil money
- enormous capital needs in ME countries
- economic connection with ME and other asian countries.
- technological innovation in finance
- Investment by UAE:
- Mandarin Oriental New York
- Pan-United Marine (Singapore)
- European Aeronautic Defense and Space (EADS); Airbus
- Mirage (Las Vegas)
- CityCenter (Las Vegas)
- OMX (Swedish-Finnish stock exchange)
- HSBC (UK)
- Standard Chartered (UK)
- Deutsche Bank
- New Silk Road (of finance):
0.
序:
- ロンドン、シンガポールなど積極振興
- 1981:
- GCC (湾岸協力会議):
- 対外資産:$1.55T
- 拡大の背景:
- イスラムへの回帰
- オイルマネーの増加
- 中東での資金需要
- 他のアジアとの経済的つながり
- 金融技術革新
- UAEによる投資
- Mandarin Oriental NY
- Pan-United Marine
- EADS
- Mirage
- CityCenter
- OMX
- HSBC
- Standard Chartered
- Deutsche Bank
- 金融の新たなシルクロード:
>Top 1. Basic knowledge of Islamic finance:
- Where will be the financial center?
- Bahrain, Dubai, Qatar, Saudi Arabia?
- Sharia is religious and social norms: Sharia law comprises: شريعة
- Quran القرأن
- Sunnah سنة
- Ijma إجماع
- Qiyas (deductive analogy) قياس
- religious norm: Ibadart عبادة
- social norm: Muamalat
Muamalat prescribes Islamic finance.
- The six articles of belief:
- Belief in God (Allah) Shahada الشهادة
"There is no god but God, Muhammad is the messenger of God." لا إله إلا الّلة محمد رسول الّلة
- Belief in the Angels (mala'ika) ملأكة
- Belief in the Books (kutub): Qurʾān القرأن
- Belief in all the Messengers (rusul) رسل
- Belief in the day of Resurrection (al-akhira) يوم القيامة
- Belief in Destiny (Fate) (qadar) قدر
- >Top Five Pillars of Islam:
Arkan-al-islam أركان الإسلام
- creed (shahada) الشهادة
- daily prayers (salat) صاوات
- almsgiving (zakāt): Zakat 2.5% زكاة
- fasting during Ramadan (sawm) صوم
- pilgrimage to Mecca (hajj) حج
- No separation of politics and religion
-
 >Top OIC (Organization of the Islamic Conference):
>Top OIC (Organization of the Islamic Conference):
- established in 1969
- Member countries: 57
- Observer: 5
- covering 1.3B population
- Denomination in Muslim:
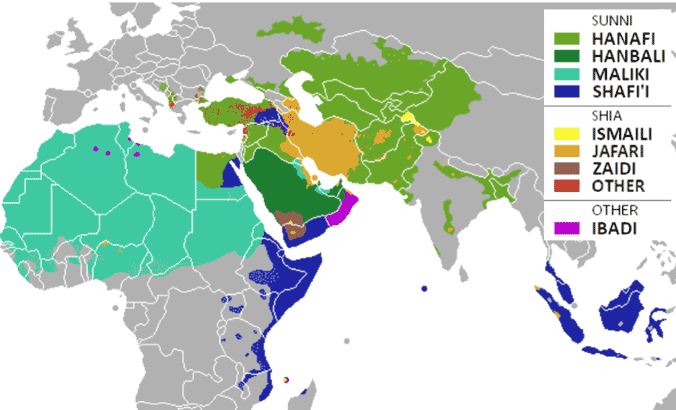
- Sunni: سني
- Hanafi: Egypt, Turkey, Syria, S-Asia
- Hanbali: Saudi Arabia, UAE
- Maliki: N/W-Africa
- Shafii: SE-Asia
- Shia: الشيعة
- Ismaili: Pakistan, Pakistan, India
- Jafari (Twelvers): Iran, Lebanon
- Zaidi: Yemen
- Ibadi: (distinct from Sunni & Shia) Oman
- Total population of Muslim: about 1.62B (23%; around 1/4)
- Christians are now around 1/3. But muslims will outnumber in 2030s.
- Largest Islam countries: Indonesia (12.7%), Pakistan (11.0%), India (10.9%) , Bangladesh (9.2%). About 20% in Arab countries.
- Turkey: 74.7M (98.6% Islam)
- Central Asia: Kazakhstan 8.9M (56%); Kyrgyzstan 4.9M (89%) ; Tajikistan 7.0M (99%); Uzbekistan 26.8M (97%); Turkmenistan 4.8M (93%); Azerbaijan 8.8M (98%)
1.
イスラム金融の基礎知識:
- どこが金融センターになるか?
- バーレーン、ドバイ、カタール、サウジか
- 金融センターの要素
- 効率的な金融取引
- 透明な管理
- 高い信頼性
- シャーリア (根拠法)は以下から成る
- クルアーン
- スンナ
- イジュマ
- キヤース
- シャーリア宗教とモラルの法
- 宗教規範:イバダート
- 社会規範:ムアマラート
ムアマラーとがイスラム金融を規定
- イスラム教六信:
- 唯一全能の神(アッラーフ)
- 天使の存在(マラーイカ)
- 啓典(神の啓示、キターブ)
- 預言者(ラスール)
- 来世(アーヒラ)
- 定命(カダル)
- イスラム教五行:
- 信仰告白(シャハーダ)
- 礼拝(サラー)
- 喜捨(ザカート)
- 断食(サウム)
- 巡礼(ハッジ)
- イスラム諸国会議 (OIC): 1969設立。加盟57ヶ国
- イスラム教には政教分離なし
- スンナ派
- ハナフィー派:エジプト・トルコ
- ハンバル派:サウジ、UAE
- マリキ派:北・西アフリカ
- シャフィー派: 東南アジア
- シーア派
- イスマイール派:パキスタン・インド
- ジャファリ (12イマーム派): イラン・レバノン
- ザイド派:イエメン
- イバディ派:オマーン
- イスラム教徒数:1.62B、人口の23%
- キリスト教徒は現在は1/3。2030年にはイスラム教徒の数がそれ以上になる。
- イスラム教徒多い国
- インドネシア:12.7%
- パキスタン:11%
- インド10.9%
- バングラディッシュ:9.2%
- アラブ諸国:20%
- トルコ
- 中央アジア:キルギス、タジキスタン、ウズベクス単、トルクメンすタン、アゼルバイジャン
-
>Top Islamic banks:
- Features of Islamic banks:
- no- interest operation: enforcing borrowers to make small amount of fixed-term deposit.
- 1980s: starting from loan and deposit, then project finance, syndicate loan, insurance
- 1990s: lease, stock trade
- 2000s: bond, investment fund
- Since 2003: expanded services including wholesale, investment bank functions.
- >Top Restrictions due to Sharia:
- prohibition of interest (Riba or usury ) ربا
- prohibition of excessive risks due to uncertainty (Gharar)
- prohibition of gambling and speculation (Non-haral products )
- prohibition of transaction of taboo goods and services (Haraam or forbidden)
- >Top Shariah Committee:
There is no global standard of judging conformity with Shariah.
- 2004: Dubai: International Islamic Centre for Reconciliation and Commercial Arbitration (IICRCA)
- Malaysia: National Shariah Advisory Council; Shariah Committee
- Pakistan: Shariah Board; Shariah Advisor
- Kuwait: Shariah Supervisory Board
- UAE: Higher Shariah Authority; Sharia Supervision Authority
- Bahrain: National Shariah Board; Shariah Supervisory Committee
- Qatar: Sharia Supervisory Board
- Islamic finance scheme:
- >Top Murabahah: (up to 5 years) مرابحة
credit purchase ; sale of goods at a price, including a profit margin. the selling price must be clearly stated beforehand.
- Ijarah: (up to 12 years) إيجار
lease, rent or wage; selling the benefit of use or service for a fixed price or wage, such as plant, office automation, vehicle
- >Top Mudarabah: مضاربة
partnership; capital investment comes from the first partner, while management and work is exclusive responsibility of the other party (called "mudarib").
- >Top Musharakah: مشاركة
Joint venture; profits made are shared between the partners according to the invested capital. A working partner gets a grater profit share.
- Re: 'Sukuk' is Islamic bond. صكوك
- 'Takaful' is Islamic insurance. التكافل
-
イスラム銀行の特徴
- 金利なし:借り主に少額の定期預金を義務化
- 1980年代:当初は預金・ローンから、プロジェクトファイナンス、シンジケートローン、保険
- 1990年代:リース、株式取引
- 2000年以降:債券、投資ファンド
- 2003年以降:卸売分野、投資銀行機能
- シャーリア委員会:
- マレーシア、パキスタン、クウェート、UAE、バーレーン、カタールのシャーリア委員会など
- イスラム金融の仕組み:
- ムラーバハ:クレジット支払
- イジャーラ:リース
- ムダーラバ:パートナーシップ
- ムシャーラカ:J/V
Real transaction
Profit-loss sharing
Murabahah
Ijarah
Mudarabah
Musharakah
Correspond to
Purchase
Lease
Entrustment
Investment
Profit sharing
Fixed amount
Fixed amount
Flexible
Flexible
Loss sharing
-
-
Total loss
Proportional
Project participation
-
-
×
○
Financial product
Short-term
Long-term
Short-term
Long-term
Islam deposit, Islam loan, Trade finance, Credit card, Interbank transaction、Sukuk
Islam loan, Trade finance, Sukuk
Islam loan, Sukuk, Takaful
Islam loan, Sukuk
>Top 2. Situation of Islamic banks:
- Difference with other general banks:
- Customers are depositors or borrowers in general banks, while in Islamic banks the relationship will be buyers and sellers, or entrepreneur and investor.
- Scheme of Islamic banks:
- Islamic banks only:
- Concomitance: General banks and Islamic banks (Islamic windows as a part of the general bank)
- Account of general bank and that of islamic bank (or windows) are strictly separated; but administrative staff are common.
 Growth of Islamic banks:
Growth of Islamic banks:
- Islamic banks in Malaysia:
- also rapidly growing in GCC countries
- getting active in wholesale division rather than retail division.
- Activities of Islamic banks:
- Islamic banks of Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and Qatar opened in Malaysia.
- Kuwait Financing House is buying off Malaysian RHB Bank, as well as Indonesian Bank.
- Dubai Islamic Bank opened office in Pakistan.
- National Commercial Bank of Saudi Arabia acquired 60% equity of Turkish Finance Bank in Turkey.
- Kuwait Finance House owns 625 equity of Kuwait-Turkey Bank.
- Al Baraka Banking Group in Bahrain has 230 branches in 10 countries; planning to expand 74 branches in 5 years in Syria, Pakistan, South Africa, Turkey, Indonesia; then they are expanding even in Malaysia, China, and India.
- ABC (Arab Banking Corporation) Islamic bank in Bahrain.
- Western banks promote Islamic finance:
- US: Citibank, JPMorgan Chase
- Europe: HSBC, Standard Chartered, BNP Paribas, Deutsche Bank, ABN Amro, UBS, Calyon (CA)
- Islamic finance is operated as one of the financial means.
- Islamic financial affiliate:
- HSBC: HSBC Amanah
- Citibank: Citi Islamic Investment Bank
- USB: UBS Noriba Bank
- Mega Islamic Bank:
- Emaar International Bank (Dubai): capital $1B
- Global Banking Corporation, GBCorp (Bahrain): $250M
- Investment Dar Bank (Bahrain); $200M
- Noor Islamic Bank (Dubai); $1B
- Al Hilal Islamic Bank (Abu Dhabi): $1.1B
- Al Rayan Investment (Qatar) ; $100M
- Global expanding:
- Qatar National Bank: to Syria
- Abu Dhabi Commercial Bank: to India
- Commercial Bank of Kuwait acquired Al Watany Bank of Egypt.
- Risk of Islamic Banks:
- Profitability: lower transparency of pricing, which tends to be higher than general banks. They have lower fund procurement cost, such as no-interest depositors.
- Credit risk: inadequate by Sharia
- Investment risk: loss of business (Mudarabah and Musharaka)
- Market risk: fluctuaton of market price in lease (Ijarah)
- Liquidity risk: same as general banks such as fund procurement
- Profitability ratio risk: combined usage with general banks in the case of project finance; even Islamic banks can be affected by fluctuation of interest.
- Operational risk: prepared profit balance reserves or investment risk reserves.
- Restriction of Islamic Banks:
- Transparency: standard of regulatory authority, disclosure, and accounting standard.
- Interpretation of Sharia
- AAOIFI: Accounting & Auditing Organization for Islamic Financial Institutions
- Equity capital ration: not less than 12% (correspond to 27% of general bank)
- Risk ration of PSIA: 50%
- Restriction of large amount credit: not less than 10%
- Balance Sheet of Islamic Bank (Malaysia)
Assets
Liabilities
Current Assets
Cash
Investment securities
Account receivable
Lease receivable
Mortgage loan
Investment finance
Equity finance
Inventory
Fixed asset
Other non-current assets
Current account
Other liabilities
Profit Share Investment Account
(PSIA)
Profit share investment account
Profit balance reserve
Investment risk reserve
Capital
Paid-in capital
2.
イスラム銀行の実態:
- 一般銀行との違い:
- 一般銀行の顧客は預金者または借入者。一方イスラム銀行では、買主と売主、または企業家と投資家の関係
- イスラム銀行のスキーム:
- イスラム銀行だけの場合
- 一般銀行とイスラム銀行の併存
(一般銀行の一部分としてのイスラム銀行の窓口)
- 一般銀行の勘定とイスラム銀行 (窓口)の勘定は厳格に分離。但し、管理部門は共通。
- イスラム銀行の成長: (左図)
- サウジ 、クウェート、カタールのイスラム銀行はマレーシアに開設
- Kuwait Financing HouseはマレーシアRHB銀行買収
- ドバイ・イスラム銀行はパキスタンに支店開設
- サウジNational Commercial銀行は、トルコTurkish Finance銀行の60%格式取得
- バーレーンのいAl Baraka Banking Groupは、10ヶ国に230の支店開設など
- 西側諸国もイスラム金融を推進
- 米国:シティ、JPモルガン・チェース
- 欧州:HSBC、スタンダード・チャータード、BNPパリバ、ドイツ銀行、ABNアムロ、UBS
- イスラム金融の一つの金融手段として運用
- イスラム金融子会社開設
- メガ・イスラム銀行:
- ドバイ:Emaar International Bank、Noor Islamic Bank
- アブダビ:Al Hilal Islamic Bank
- バーレーン:Global Banking Corporation、Investment Dar Bank
- カタール:Al Rayan Investment
- グローバルな拡大
- Qatar National Bank:シリア
- Abu Dhabi Commercial Bank:インド
- Commercial Bank of Kuwait:エジプ
- イスラム銀行のリスク
- 収益性:銀行監督基準、情報公開、会計基準
- 信用リスク:無利子預金者の存在
- 投資リスク:ムダーラバ、ムシャーラカの場合
- 市場リスク:イジャーラ
- 流動性リスク:
- 利益率リスク:金利の影響は受ける
- 運用リスク:各種準備金
- イスラム銀行への規制:
- 透明性:監督当局の基準、情報開示、会計原則
- イスラム金融機関会計監査機構
>Top 3. Islam finance market:
- Scale of Islamic finance:
- Around $1T; will grow $1.8T in 2014.
- Growth: 15-20% annually
- Share in the world financial asset: 1% or more.
- No government bond in ME countries
- Share of Islamic banks:
(2006)
- Kuwait: 23.5%
- UAE and Malaysia: 12-13%
- In 2011: it may attained 25%, with asset worth $1.2T
- Indonesia and Pakistan: 3%
- Bahrain: 6.5%
- Islamization of banks:
- Iran: 1984 Interest-free bank law
- Pakistan: 1985 Islamic banks law
- Problems: widening disparity, and shortening of lending period
- Indonesia: 1992 Dual banking system
- Share of Islamic banks: 2%, planning to attain 9% by 2011
- Saving Account iB, Current Account iB: IB means Islamic Banking
- Fixed installment scheme is popular, such as Home Financing iB1
- India:
- RBI (Reserve Bank of India) is making a feasibility study for Islamic banking in India. So far they are operating as NBFC (non banking financial companies).
- 61% of Indian stocks are regarded as Sharia-compliant stocks, which are promoting to attract Islamic money.
- Turkey:
- Islamic banks are thriving since 2001; share is around 6%
- Financial Products by Islamic banks:
Financial Products
Possibility
Japanese
Stock
○
株式
Preferred Stock
△
優先株
Warrant
×
In Malaysia ○
ワラント
Structured Bond
×
仕組債
Bill
○
no endorsement
手形
Commercial Paper
○
no endorsement
コマーシャルペーパー
Bond (fixed profit)
△
債券 (固定収益払)
Bond (fluctuating profit)
△
債券 (変動収益払)
Index bond
×
指数リンク債
Convertible bond
×
In Malaysia ○
転換債
SWAP
×
スワップ
Option
△
オプション
Commodity futures
×
商品先物
Financial futures
×
金融先物
- >Top Islamic insurance "Takaful":
- Insurance had been originally regarded as Sharia non-compliant, because it is uncertain, gambling, and interest accrued.
- But insurance per se is mutual assistance, which is one of Islamic obligation.
- Takaful, Islamic insurance was born in Sudan in 1979.
- Family Takaful: equivalent to life insurance
- General Takaful: equivalent to damage insurance
- Islamic investment fund:
- >Top This is regarded as a kind of SRI (Socially Responsible Investing) fund.
- Examples of Sharia-incompatible investment:
- Real estate investment more than 5% used for general bank, pet shop, movie theater, music instrument shop, hotel, precious metal shop.
- In Malaysia: Sharia-compatible stock: 86.1% of listing share brands, and 64.6% of aggregate market value.
- S&P Japan 500: Sharia-incompatible brands: pork, alcohol, tobacco, entertainment, bank, trading company, securities company
- Standard of Sharia-compatibility, which exclude:
- Debt-to-asset ratio: more than 33% (due to zakat should be less than 1/3)
- Non-operating income ratio: more than 5% (due to 5% is negligible)
- Account receivable to asset ratio: more than 45% (due to dead storage of profit)
3.
イスラム金融市場:
- イスラム金融の規模
- $1T程度:$1.8T (2014)
- 成長率:年15-20%
- 世界金融資産中のシェア:1%程度
- 中東の国には国債なし
- イスラム銀行シェア: 2006
- クウェート:23.5%
- UAE、マレーシア:12-13%
2011には25%との情報あり
- インドネシア、パキスタン:3%
- バーレーン:イスラム銀行の総資産額:$12.2B (シェア 6.5%)
- イスラム銀行化:
- イラン: 1984、ゼロ金利銀行法
- パキスタン: 1985イスラム銀行法
但し、格差拡大、貸付期間短期化の課題あり
- インドネシア:
- シェア:2%
- 住宅ローンなど固定支払に人気
- インド
- RBIが導入検討中
- インドの株式の61%はシャーリア適格
- トルコ
- 2001年以降、イスラム銀行急成長中、シェア6%
- イスラム銀行における金融商品一覧 <左図>
- イスラム保険"タカフル"
- 保険はそもそもシャーリア不適格と見なさてきた。不確実、賭博性、金利発生。
- しかし保険は本質的に相互扶助
- タカフルは1979円にスーダンで登場
- ファミリー・タカフル:生命保険
- ジェネラル・タカフル:損害保険
- イスラム投資資金:
- これは一種のSRI (社会的責任投資)
- シャーリア不適格投資の例:
- 以下業種5%以上の不動産
一般銀行、ペットショップ、映画館、楽器店、ホテル、貴金属店
- S&P Japan 500が規定するシャーリア不適格銘柄:
豚肉、アルコール、たばこ、娯楽、銀行、商社、証券会社
- シャーリア不適格の基準:以下の除く
- 資産負債比率33%以上
喜捨は1/3以下
- 営業外収益比率5%以上
5%以下なら無視
- 資産売掛金比率45%以上
非流動的な富の退蔵
>Top 4. Islamic bond market:
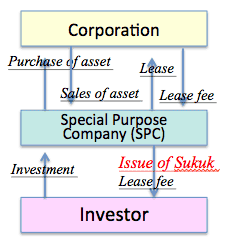 What is Islamic bond "Sukuk", or طكوك ?
What is Islamic bond "Sukuk", or طكوك ? - Scheme of Ijarah Sukuk: (Ijarah is Leaseback)
- pays a periodic coupon using rental income under the lease.
- Sukuk certificate represents proportional ownership of the underlying asset.
- Sukuk maturity is average five years.
- Islamic bond in Malaysia
- BBA (Bai' Bithaman Ajil) house finance: 36%
- Murabaha (purchase): 24%
- Musharakah (investment) 22%
- Global Issuance of Sukuk:
- $236M/2000 -> $20B/2006 -> $50B/2007
- 2007: Malaysia $28B; GCC $19B; 2007
- Sukuk market:
- Malaysia: 67% (Ringgit basis)
- UAE: 16%
- Pakistan: 8%
- Bahrain: 3%
- Saudi Arabia: 2%
- GCC countries have no needs of public bond, and mostly depend on stock.
- Trend of Sukuk:
- Global Sukuk is issued in 12 countries, including Germany, UK, US.
- Bahrain issues public Sukuk, while Malaysia issues one-year public Sukuk.
- Issuance volume is getting bigger and longer.
- TUAE issued the biggest Sukuk $3.5B in 2006.
- Sukuk maturity period:
- 1-5 years: 40.7%
- 5-10 years: 33.5%
- 10-15 years: 20.6%
- 15-20 years: 0.2%
- 20year or more: 5.0%
- Sukuk option: sellout option, convertible to stock
- Saudi Arabia increases issuance of Sukuk.
- Issuance procedure of Sukuk is getting standardized.
- Sukuk is affected by general bond, particularly yield ratio.
- >Top Sukuk is listed in the stock exchange
- Labuan International Financial Exchange (LFX) in Malaysia
- Dubai Stock Exchange (DIFX)
- European banks, Insurance companIes, Pension fund shows keen interest in Sukuk.
- 2006: 20-40% bought by the West, now is estimated about 70-80%.
- World Sukuk investors: Europe 47%, ME 33%, Asia 20%
- Banks 54%; Fund managers 35%; Central banks 7%; Insurance & Pension fund 4%
- Issues in the future:
- Issuance by crossborder: both foreign currency basis or local currency basis
- Malaysia and GCC countries are small.
- More liquidity is required
- Standardized Sharia-compliant market.
- Currency unification of GCC countries; which contributes more expansion of Islamic finance.
- Function of London market; how to circulate enormous oil dollars.
- Sukuk can be global barometer securities.
- Expansion of issuance market, distribution market, and global investors.
4. イスラム債権市場:
- イスラム債券スクークとは:
- イジャーラ・スクークの仕組み<左図>:
- マレーシアにおけるスキーム別社債発行シェア
- スクーク市場:
- マレーシア: 67% (リンギ建)
- UAE: 16%
- スクークのグローバル発行
- 2007: マレーシア$28B、GCCは$19B
- スクーク市場
- マレーシア 67%
- UAE 16%
- スクークのトレンド:
- グローバル化:12ヶ国、独・英・米含む
- バーレーンによる公的債券としてのスクーク発行
- スクークの償還期間:
- 1-5年:40.7%
- 5-10年: 33.5%
- 10-15年: 20.6%
- スクーク・オプション:売却オプション、株式転換
- サウジアラビアはスクーク発行増加中
- スクーク発行手続きの標準化進展中
- スクークも利回りなど一般債権の影響受ける。
- スクークは証券取引所に登録
- マレーシア LFX
- ドバイ DIFX
- 欧州銀行、保険会社、年金資金はスクークに興味あり
- 2006:西側20-40%購入。今や70-80%購入
- 世界のスクークへの投資者:欧州47%、ME33%、アジア20%
- 銀行54%、ファンドマネジャー35%、中央銀行7%、保険会社・年金4%
- 今後の課題:
- クロスボーダーでの発行:外貨建て、地場通貨建て
- さらなる流動性
- シャーリア適格の標準化
- GCC諸国の通貨統合問題
- ロンドン市場の役割:膨大なオイルダラーの還流
- スクークは国際的な指標銘柄に
- 発行市場、流通市場、グローバル投資家の拡大
>Top 5. Expansion of Islamic finance:
- International organizations related Islamic finance:
- Accounting and Auditing Organization for ISlamic Financial Institutions; Bahrain, 1991
- General Council for Islamic Banks and Financial Institutions; Bahrain, 2001
- International Islamic Financial Market; Bahrain, 2001
- Islamic Financial Services Board, Malaysia, 2002
- Liquidity Management Centre; Bahrain, 2002
- International Islamic Rating Agency; Bahrain, 2002
- International Islamic Centre for Reconciliation and Commercial Arbitration; Dubai, 2004
- International Centre for Education in Islamic Finance; Malaysia, 2006
- IIFM (International Islamic Finance Market; Bahrain) signed cooperative agreement with ICMA (International Capital Market Association; London)
- IIFM also signed with ISDA (International Swaps and Derivatives Association; New York) in 2006 to develop Islamic derivative transaction.
- London market is most active: "City is the gateway to Islamic finance"
- Muslims in UK: 1.8M, 3%; richer than the average.
- UK realized policies which will not unfavorable to Islamic finance, including:
- avoidance of double taxation of SDLT (Stamp Duty & Land Tax)
- deemed interest of the Islamic interest equivalent portion
- deemed bond of the Islamic bond (Sukuk)
- Islamic banks in UK:
- Islamic Bank of Britain: retail
- European Islamic Investment Bank: wholesale
- Singapore market is also active:
- Muslims in Singapore: only 0.6M.
- MAS (Monetary Authority of Singapore) approved Islamic commodity transaction by Islamic bank, and deemed that its distributed profit is substantially interest, also exempted from consumption tax related to the transaction.
- OCBC (Oversea-Chinese Banking Corporation) started Islamic finance in Singapore and Brunei.
- Gulf Finance House (Bahrain) opened office in Singapore.
- Maybank (Malaysia) started Islamic finance in Singapore.
- European and American major banks began Islamic financial services, particularly asset management.
- Islamic Bank of Asia (IBA) was established by DBS and GCC countries.
- Hong Kong market:
- Cooperation between China and GCC countries; including FTA agreement
- Possible investment into China will be around $250B.
- Chinese movement of deregulation of Foreign capital.
- New York market:
- There are 6 -8M muslims in US, but they are mostly distributed.
- Sentiment since 9.11 incident.
- Institutional change is needed to promote Islamic finance.
- But US banks are active in GCC countries:
- Morgan Stanley Saudi Arabia
- Goldman Sacks agreed with National Commercial Bank (Saudi Arabia)
5. イスラム金融の拡大:
- イスラム金融関連の国際機関:
- イスラム金融機関会計監査機構;バーレーン, 1991
- イスラム銀行・金融機関評議会;バーレーン, 2001
- 国際イスラム金融市場;バーレーン, 2001
- イスラム金融サービス委員会;マレーシア, 2002
- 流動性管理センター;バーレーン, 2002
- 国際イスラム格付機関;バーレーン, 2002
- 国際イスラム調停センター;ドバイ,2004
- イスラム金融教育センター;マレーシア, 2006
- IIFM (バーレーン)はICMA (ロンドン)と協力協定調印
- IIFMは、またISDA (スワップ・デリバティブ協会, NY)と提携
- ロンドン市場は最も活発:
"シティはイスラム金融のゲートウェイ"
- 英国のイスラム教と:1.8M (3%)、中流以上
- イスラム金融にい不利にならない政策
- 二重課税会議
- みなし金利措置
- みなし債券措置
- 英国のイスラム銀行:
- イスラミック・バンク・オブ・ブリテン
- ヨーロピアン・イスラム投資銀行
- シンガポール市場
- イスラム教徒:わずか0.6M
- MAS (金融当局)は、イスラム銀行による商品取引を認可。みなし金利措置および取引に伴う消費免税
- OCBCはシンガポールとブルネイでイスラム金融開始
- ガルフ・ファイナンス・ハウス (Bahrain)はシンガポール支店開設
- メイバンク (Malaysia)はシンガポールでイスラム金融開始
- 欧米の銀行もイスラム金融開始、特に資産運用
- DBSとGCC諸国合弁で、IBA(Islamic Bank of Asia) を設立
- 香港市場:
- 中国とGCC諸国との協力関係;FTA含め
- 中国への投資:$250B
- 中国による外資規制緩和の動き
- NY市場
- 米国内イスラム教徒:6-8M、但し各地に分散
- 9.11事件以降の感情
- イスラム金融を進めるには制度変更が必要
- 但し、米国の銀行はGCC諸国では活発
- モルガン・スタンレー・サウジ荒倍阿
- ゴールドマンサックスは、サウジのナショナル商業銀行と提携
>Top 6. Perspective of Islamic finance in Japan:
- Cons:
- Muslim population is too small in Japan.
- Japanese banks have little Islamic customers.
- Key viewpoint: Function of "Japan in Asia"or "Japanese bridging ME Asia and East Asia."
- Pros:
There will be the following cases:
- Japanese firms utilize Islamic finance.
- Japanese banks participate project finance in ME countries.
- Collaboration of Japanese banks and Islamic banks in various financial services; particularly in Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, etc.
- Islamic finance invest Japanese stock market.
- Japanese investors invest to Islamic finance.
- Joint financial institution like "Islamic Bank of Asia" established in Singapore in 2007 as an affiliate of DBS (Development Bank of Singapore) (60%) and GCC countries (40%).
- Problems:
- Legislative preparations:
- Can banks treat installment sale (Murabaha) or lease (Ijarah)?
- Which ministry governs Islamic banks; MOF (Financial Service Agency) or METI?
- Double taxation such as consumption tax and stamp duty.
- Interest limitation law, and Investment law.
6.
日本におけるイスラム金融の展望:
- 否定的要素:
- 日本におけるイスラム人口希少
- 日本の銀行はイスラム顧客が希少
- キーポイント:アジアにおける日本、中東と東アジアをつなぐ日本としての役割
- 肯定的要素: 以下のケースが考えられる。
- 日本企業がイスラム金融を利用
- 日本の銀行は中東諸国でプロジェクトファイナンスに参加
- 日本の銀行とイスラム銀行との金融サービスでの協力、特にマレーシア、シンガポール、インドネシア等
- イスラム金融の日本株式市場への投資
- 日本の投資家がイスラム金融へ投資
- シンガポールの"Islamic Bank of Asia"のように合弁での金融機関設立
- 課題:
- 法的整備
- 割賦販売 (Murabaha)やリース (イジャーラ)の取り扱い
- 監督官庁は、財務省 (金融庁)か経済産業省か
- 二重課税問題:消費税や印紙税
- 利息制限法や出資法
Comment
- To understand and relate Islamic countries, there are three genre of specialties: Oil & energy business, Islamic culture including arabic language and religion, and then Islamic finance.
- イスラム諸国を理解し関係するには、3つの専門分野がある。石油・エネルギービジネス、イスラム言語・宗教を含む文化、そしてイスラム金融である。
Title |
Islamic Finance |
イスラム金融 |
|---|---|---|
Index |
||
Tag |
; GCC; Five Pillars of Islam; OIC; Riba; ; IICRCA; Ijarah (lease); Islamic banks; Mudarabah (partnership); Murabahah (credit) ;Musharakah (JV); Sharia; SRI; Sukuk; Takaful; LFX/DIFX ; | |
Why? |
|
|
Résumé |
Remarks |
>Top 0. Preface:
|
0. 序:
|
>Top 1. Basic knowledge of Islamic finance:
|
1. イスラム金融の基礎知識:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 2. Situation of Islamic banks:
|
2. イスラム銀行の実態:
|
>Top 3. Islam finance market:
|
3. イスラム金融市場:
|
>Top 4. Islamic bond market:
|
4. イスラム債権市場:
|
>Top 5. Expansion of Islamic finance:
|
5. イスラム金融の拡大:
|
>Top 6. Perspective of Islamic finance in Japan:
|
6. 日本におけるイスラム金融の展望:
|
Comment |
|
|