 |
A Cold-War Analysis of Emerging Power Containment
|
Cat: ECO |
Mitsuhiro Maeda (前田充浩) |
11709u/18211r |
Title
A Cold-War analysis of emerging power containment;
a superimposed model between Prestige Games and Knowledge Games.
智のゲームとしての冷戦史観
国民国家と情報智業の重畳モデルの試み
Index
Tag
; Aid fatigue; ASEAN; Hierarchical targets; Kumon sigmoid; Knowledge game; Neoliberalism; NIS; Prestige game; Strong developmentalism; Washington Consensus; Weak developmentalism; White/black ideology; ;
Why?
- The author published this report at the symposium of Soicioinfornomics Society on June 18, 2011, who has the carrier background at METI and is an expert of this theme.
- He describes clear explanation of the present economic situation surrounding Japan with the analogy of the Cold War analysis between US-Japan, and US-China as Knowledge games.
- 著者は本レポートを2011/6/18の情報社会学会で発表した。著者はMETI官僚の経験を踏まえてた本テーマでのエキスパートである。
- 日本を取り巻く現在の経済状況を日米、米中間の冷戦になぞらえて、智のゲームとして明確に説明している。
Key
phrase and tag
注・コメント
>Top 0. 序:
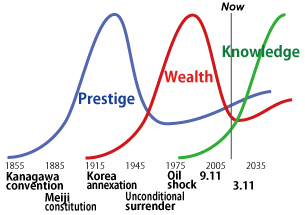 Kumon Sigmoid:
Superimposed three sigmoid games in modernization
process.
Kumon Sigmoid:
Superimposed three sigmoid games in modernization
process.
- Militalization:
Prestige game by nation states
- Industrialization:
Wealth game in the global market by national industries
- Informatization:
Knowledge game by global netizens
- Neet (Not formally but socially employed, educated and trained.
- Simple, Social, Share
0.
Preface:
- 公文俊平:近代化におけるS字カーブ重畳モデル
- 軍事化 (政治化):
国民国家による威のゲーム
- 産業化 (経済化):
産業企業による世界市場での富のゲーム
- 情報化 (ソーシャル化):
情報智業による地球智場における智のゲーム
- 共働/通識/共貨
>Top 1. Superimposed two models:
- Rule and practice of the international community
- Advanced countries:
- make the rule and practice
- confine the emerging countries by the rule.
- Emerging countries: requires to change the rule and practice
- dissent the regime
- >Top Prestige game:
- expansion by military and diplomatic powers
- Knowledge game:
- expansion by persuasive power
1.
重畳モデル:
- 国際社会のルールと慣行:
- 先発国
ルールと慣行を作る
ルールによって新興国を封じ込める
- 新興国
そのルールに抵抗
- 威のゲーム:
- 軍事力・外交力による拡大
- 智のゲーム:
- 説得力による拡大
>Top 2. Cold-War model:
- "White" ideology:
- The ideology of advance countries which try to confine emerging countries by the established rule and practice.
- "Black" ideology:
- The ideology of emerging countries which try to change the rule and practice established by the advance countries.
- >Top Hierarchical targets:
- Target level-1:
- domestic people of the subject country
- enable to increase the number of sympathizers
- Target level-2:
- people of advanced countries (more than $10,000 GDP per capita)
- Target level-3:
- people of developing countries.
- Competitive phase and oppositional phase
- Competitive phase to the target level-1:
- Persuade domestic people to believe superiority of white ideology.
- Competitive phase to the target level-2:
- Persuade people of advanced countries to believe superiority of white ideology.
- Competitive phase to the target level-3:
- Persuade people of developing countries to believe superiority of white ideology.
- Oppositional phase to the target level-1:
- Persuade people of the rival country to reclaim from black (or white) ideology.
- Oppositional phase to the target level-2:
- Persuade people of advanced country to reclaim from black (or white) ideology.
- Oppositional phase to the target level-3:
- Persuade people of developing country to reclaim from black (or white) ideology.
- Competitive strategy:
- First to persuade people of developing countries, then people of advanced countries, finally people of the rival country.
2.
冷戦モデル:
- 白思想:
- 新興国を封じ込めようとする先発国の思想
- 黒思想:
- 台頭して国際社会のルールを変更しようとする新興国の思想
- 白思想と黒思想は、智のゲームでも争っている。
- 説得対象の階層化:
- 第1階層:
冷戦主体国の内部の人々
- 第2階層:
先進国の人々
- 第3階層:
途上国の人々
- 競合側面と対抗側面
- 競争側面の第1階層
- 競争側面の第2階層
- 競争側面の第3階層
- 対抗側面の第1階層
- 対抗側面の第2階層
- 対抗側面の第3階層
- 競争戦略:
- まずは途上国の国民、次に先進国の国民、最後に対抗国の国民の順で説得する。
>Top 3. East-West Cold War :
- Scramble in developing countries:
- East 's ideology looked easy to understand.
- One-party domination looked attractive to most of governing leaders in developing countries.
- White ideology:
- Economic growth theory
- Development aid through ODA
- Neo classical economics
- Walt Whiteman Rostow: "The Stages of Economic Growth; A non-communist manifesto" (1960), Take off theory
- 1960: DAG (Development Assistance Group), then DAC (Development Assistance Conference)
- 1961: OECD (Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development)
- 1964: UNCTAD (UN Conference on Trade and Development)
- Black ideology:
- Deficit of market mechanism
- Monopoly
- Expansion of disparity in wealth (Unemployment)
- Business fluctuation (depression, or crash)
- End of the cold war:
as a result of the Knowledge game.
- shock therapy
3.
東西冷戦:
- 途上国における争奪戦
- 白思想:
- 経済成長
- ODAを通じた開発援助
- 新古典派経済学
- W.W. Rostow
経済成長理論, Take off theory
- 黒思想:
- 市場メカニズムの欠点を指摘
- 独占
- 格差拡大
- 景気変動
- 冷戦終結
- ソ連東欧におけるショック療法
>Top 4. US-Japan Cold War
- Washington Consensus:
- White ideology:
1980-2008
- coined in 1989 by John Williamson; standard reform package based on IMF, World Bank, and US Treasury Dept.
- neoliberal policies: emphasize market mechanism, reduce government deficits, various deregulation, export-lead growth
- >Top Japan: Black ideology as emerging country
- this policy has been overlooked by US due to the Cold War.
- development-focused policy
- Strong NIS: 'National Innovation System": comprehensive national development plan, such as x-Year Plan.
- Weak NIS: even US promoted NIS named "Innovate America"
- Priority industry
- Promotion of technical advancement
- ward off excessive competition
- protectionism
- What is "strong NIS policy?
- "Law of decreasing relative cost
4. 日米冷戦:
- ワシントン・コンセンサス
- 米国:白思想
- 1989 John Williamsonが提唱
- 新自由主義政策:市場メカニズム、公的債務削減、規制緩和、輸出指向成長
- 日本:黒思想
- 冷戦時代は米国から大目に見られてきた。
- 開発主義政策
- NIS:
- 日:"e-Japan"構想など
- 米:"Innovate America"
- NIS政策とは
- 費用逓減の法則
>Top 5. Struggle for ASEAN:
- 1990s struggle for ASEAN between US and Japan:
- 1981: "Look East policy" by Mahathir of Malaysia
- 1990: EAEC (East Asia Economic Caucus); regional free trade zone proposed by Mahathir.
- 1994: Expansion of ASEAN
- 1995: Vietnam
- 1997: Myanmar and Laos
- 1999: Cambodia
- Japanese develomentalism:
- 1987 New AID Plan by MITI
- AEM (ASEAN Economic Ministers)+MITI
- International Division of Labor
- 1995: ASEAN+3 (=APT)
- 1997 Asian Currency Crisis:
- Crony capitalism
- Knowledge game of anti-black ideology
- functionable market mechanism
- 2001/4-06/9: Koizumi cabinet
- Derelict of strong developmentalism
- >Top Neoliberalism (emphasis of market mechanism)
5. ASEAN争奪戦:
- 1990年代の日米間ASEAN争奪戦
- 1981: Mahathir
- 1984: ASEAN拡大
- 195-99: VMLC
- 日本の開発主義
- 国際分業体制
- 1995: ASEAN+3
- 1997: アジア通貨危機
- クローニー資本主義
- 機能する市場メカニズム
- 2001-06: 小泉内閣
- 強い開発主義の放棄
- 新自由主義
>Top 6. Struggle for Central Asia:
- Yen credit
- Conditionality attached with yen credit
- 1993: Kyrgyzstan
- 1994: Kazakhstan
- 1995: Uzbekistan
- 1997: Turkmenistan
- Administrative guidance as informal measures
- difficult to be applied
6.
中央アジア争奪戦:
- 円借款
- 円借款に伴う融資条件
- 1993: キルギス
- 1994: カザフスタン
- 1995: ウズベキスタン
- 1997: トルクメニスタン
- インフォーマルな行政指導
- 適用困難
>Top 7. Struggle for Africa:
- 1990s: Aid fatigue
- 1993: TICAD (Tokyo International Conference on African Development)
- 1998: TICAD-II
- Whereas, 2000: Millennium Challenge Account of US
- 1997: Peak of Japanese ODA amount;
gradual diminution of ODA;
decline of strong developmentalism
- 2003: TICAD-III
- 2004: One village, one product movement
- 2008: TICAD-IV
7. アフリカ争奪銭:
- 1990年代:援助疲れ
- 1993: アフリカ開発会議
- 1998: アフリカ開発会議(第2回)
- 1997: 日本のODAピーク、
- 以後漸減
強い開発主義の放棄?
- 2003: アフリカ開発会議(第3回)
- 2004: 一村一品運動
- 2008: アフリカ開発会議(第4回)
>Top 8. Consequence of US-Japan Cold War:
- Japan maintains "Weak Developmentalism"
- Last half of 1990s:
- Decline of Strong Developmentalism of Japan
- Long-term demand estimate
- Adjustment of investment plan
- Support policies; finance, technical development, deregulation
8. 日米冷戦の帰結:
- 日本は弱い開発主義を維持
- 2005: 新産業創造戦略
- 2010: 新成長戦略
- 1990年代後半:
- 日本:強い開発主義の放棄
- 主要産業における5/10/20年後の需要予測
- 国内生産計画拡大;設備投資の調整
- 支援政策:金融、技術開発、規制緩和
>Top 9. China-US Cold War:
- Beijing Consensus:
a new black ideology
- Large scale development aid without enforcing pro-human rights and democracy.
- Sustainability of debt by IMF:
- Green signal country:
Repayment capable with stress test
- Yellow signal country:
Repayment capable without stress test
- Red signal country:
Repayment doubtful without stress test
- IMF recommends that new loan should be only green signal counties.
- But China loans even yellow and red signal countries.
- Tied condition
- OECD bans tied loan to economic sector with commercial viability.
- due to 'Trade Distortion' and 'Level Playing Field'
- But China, OECD nonmember, promotes actively this tied conditioned loans to African and SE Asian countries.
- due to China itself is a developing country which needs not consider other developed countries' situation.
- Claims outstanding and new loan:
- Further new loan may cause default, or
- Further new loan may be necessary to increase repayment capacity
9.
中米冷戦:
- 北京コンセンサス:
新たな黒思想
- 人権、民主主義を強要しない大規模開発援助
- 債務持続性 (IMF):
- 緑色シグナル国:
ストレステスト付きで返済可能
- 黄色シグナル国:
ストレステストなしで返済可能
- 赤色シグナル国:
ストレステストなしでも返済疑問
- IMFは、新規融資は緑色シグナル国のみ
- 中国は、黄色、赤色シグナル国にも融資実施
- タイド条件:
- OECD加盟国は、政財セクターに対するタイド条件の融資を禁止
- '貿易歪曲性'、'公正な競争機会'の理由による
- OECD非加盟国の中国は、アフリカ、東南アジア諸国にタイド条件での融資を積極的に実施
- 中国自身が発展途上国であり、他の先進国の事情を考慮する必要性なし
- 債務残高と新規融資:
- 新規融資は債務不履行の可能性あり、または
- 返済能力増加のためには、追加の新規融資が必要
Comment
- People mostly believes the Cold War was finished, but actually it continues in a different filed, ie, as a Knowledge Game.
- But, why Japanese government appeals to its own national that Japan is now battling the Cold War for its survival?
- Otherwise, is the government not confident to get majority support from its nations? Is it the policy that people should be only followers without understanding it.
- 多くの人々は冷戦は終了したと思っている。だがそれは別のフィールドで、智のゲームとして継続している。
- しかし、なぜ日本政府は、現在日本が生存のための冷戦を闘っていることを自国民にアピールしないのか?
- あるいは、政府は日本の多数の支持を得る自信がないのか? 民は之を由らしむべし、之を知らしむべからずの政策か?
Title |
A Cold-War analysis of emerging power containment; |
智のゲームとしての冷戦史観 |
|---|---|---|
Index |
||
Tag |
; Aid fatigue; ASEAN; Hierarchical targets; Kumon sigmoid; Knowledge game; Neoliberalism; NIS; Prestige game; Strong developmentalism; Washington Consensus; Weak developmentalism; White/black ideology; ; |
|
Why? |
|
|
Key phrase and tag |
注・コメント |
>Top 0. 序:
|
0. Preface:
|
>Top 1. Superimposed two models:
|
1. 重畳モデル:
|
>Top 2. Cold-War model:
|
2. 冷戦モデル:
|
>Top 3. East-West Cold War :
|
3. 東西冷戦:
|
>Top 4. US-Japan Cold War
|
4. 日米冷戦:
|
>Top 5. Struggle for ASEAN:
|
5. ASEAN争奪戦:
|
>Top 6. Struggle for Central Asia:
|
6. 中央アジア争奪戦:
|
>Top 7. Struggle for Africa:
|
7. アフリカ争奪銭:
|
>Top 8. Consequence of US-Japan Cold War:
|
8. 日米冷戦の帰結:
|
>Top 9. China-US Cold War:
|
9. 中米冷戦:
|
Comment |
|
|