 |
The Century of Pax Asianaアジアは近代資本主義を超える |
Cat: ECO |
|---|---|---|
Eisuke Sakakibara (榊原英資) |
09y25u/18121r |
Title
The Century of Pa Asiana
アジアは近代資本主義を超える
Index
Why?
-
The author was vice-minister of financial affairs, called Mr. Yen, clearly describes the rise of Asia in 21st. century.
-
I read this book on the opening day of Beijing Olympic Games on Aug. 8, 2008, the symbolic day of the rise of Asia.
-
 I bought this book at Boof-Off shop at 105 yen. How big the PPP (Purchasing Power Parity) against the value of this book, which may surprise even Mr. Yen.
I bought this book at Boof-Off shop at 105 yen. How big the PPP (Purchasing Power Parity) against the value of this book, which may surprise even Mr. Yen.
- 著者は、元大蔵省財務官でミスター円と呼ばれた。本書で21世紀におけるアジアの勃興を明記している。
- 本書をアジアの興隆の象徴的な日である北京オリンピック開会日の2008年8月8日に読んだ。
- 本書はブックオフで¥105で購入した。この本の価値に比べて何と大きな購買力平価であろうか。これにはさすがのミスター円も驚くであろう。
Resume
要約
>Top
0. Introduction:
- What has been the miracle of Asia in the last decade?
- What was the essence of the financial crisis in East Asian countries?
- What has been the conflict of the modernism?
- Relativize the Western civilization
- Review Japan from the perspective of the world.
- The viewpoint from Progressivism is insufficient.
- What is the position of recent rise of China and India in context of history?
"ReORIENT- economic development is in Asia, not in the West" by Andre Gunder Frank
- Industry Revolution vs. Industrious Revolution
- polytheistic Asian civilization
- Postmodernism (pomo)
0. 序章:
- 過去十年のアジアの奇跡とは?
- 東アジアの通貨危機とは
- 近代の相克
- 西欧文明の相対化
- 世界の中の日本という視点
- 進歩主義的な視点だけでは不十分
- 最近の中国・インドとの台頭の歴史的位置付け
- "リオリエント"
A. G. Frank
- 産業革命 vs. 勤勉革命
- 多神教的なアジア文明
- ポスト近代化論 (pomo)
>Top 1. What is happening in Asia now?:
- New triangle of economic engines: Japan-Korea-China:
- OECD: a saucer of Marshall Plan
- Japan joined in 1964, Korea in 1996, China an observer
- G5, then G7: in 1973 started by US, UK, France, Germany, Japan
- Globalogical: global perspective view
- "ReORINET"
- Industrial revolution vs. Industrious revolution
- British Industrial revolution: competition with cotton textile industry in India
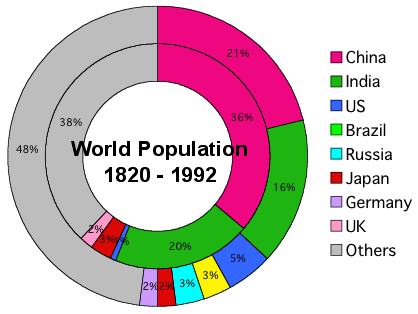
- World Population (1820 - 1992):
- First Phase (1820-1870):
- Rise of Western offshoots and downfall of Asia.
- GDP growth:1.0% worldwide, 4.3% in Western offshoots; 0.2% in Asia.
- 1841 Opium War, 1842 Treaty of Nanjing, 1858 Treaty of Tianjing
- 1858: Direct colonization of India
- European Powers deprived wealth from China and India.
- Second Phase (1870-1913):
- Pax Britannica:
- GDP growth: 2.1% worldwide
- Foreign asset balance 180% of GDP (Cf: 2003 Japan 34%, US 24% minus)
- Many Chinese and Indian merchants emigrated as overseas merchants or coolies.
- Third Phase (1930 - 1950):
- WWI, The Great Depression, and WWII
- Pax Americana
- GDP growth:1.9% worldwide, while 1.0% in Asia
- Fourth Phase: 1950-1992
- still Pax Americana
- GDP growth 1950-73: 4.9% worldwide
- GDP growth 1973-92: 3.0% worldwide
- GDP growth 1950-92: 5.55% Asia
- Rise of China and India:
- China: Reform and liberalization policy in 1978, admitted WTO membership in 2001
- India: New economy policy in 1991
- Vietnam: Economic renovation (DoiMoi)
- GDP growth estimate (World bank):
- 2000-06: 1.6% worldwide; East Asia 6.0%, South Asia 4.2%
- 2004: China 9.5%, India 8.2%
- 2006-15: 2.1% worldwide; East Asia 5.3%, South Asia 4.1%
- Saving ratio (2002)
- China 39.4%, India 24.2%, Thai 32.0%, Vietnam 28.8%
- Elementary education:
- China 95.9%, India 76.9%, Thai 86.7%, Vietnam 96.2%
- Conundrum: Where has inflation gone?
1. 今、アジアで何が起こっているのか:
- 新たな経済エンジンのトライアングル:日韓中
- OECD加盟:
- 日本1964、韓国1996、中国はオブザーバ
- G5→G7:1973: 当初は米英仏独日
- Globaligical
- ReORIENT
- 産業革命 vs. 勤勉革命
- 英国産業革命:インド木綿産業との競合
- 第1期 1820-1913
パクス・ブリタニカ
- 第2期 1930-1950:
パクス・アメリカーナ
- 第3期 1950-92
パクス・アメリカーナ
- 第4期 1950-1992
- 中国とインドの興隆
- GDP成長率:
アジアの高度成長継続
- 貯蓄率の高さ
- 初頭教育普及

>Top
2. Market integration is in process in Asia:
- Economic integration in Europe promoted by political initiative:
- 1952 ECSC (European Coal and Steel community; Jean Monnet
- 1999 Euro between banks, 2002 Euro currency
- 27 member states
- European Parliament
- European Council
- European Commission
- Court of justice
- Court of Auditor
- Economic integration in Asia: by market initiative.
- 1967 ASEAN (5): Indonesia, Singapore, Thai, Philippines, Malaysia
- 1999 ASEAN (10): Brunei, Vietnam, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia
- 1997 ASEAN+3: Japan, China, Korea
- increase of intraregional trade:
- 33% (1980) to 48% (2001) of all East Asian trade
- increase of FDI (Foreign Direct Investment)
- $144B (2000)
- Trade Intensity Index: tends to increase mutual dependency.
- Increase of parts trade:
- East Asia share: 39.5% /2000
- (Cf: EU 30.9%, NAFTA 23.9%) /2000
- Japan exports parts to East Asian countries, and China assembles them.
2. アジアでも市場統合が進んでいる:
- 欧州の経済統合:政治主導
- 1952: 欧州石炭鉄鋼共同体
- 1999: ユーロ登場
- 欧州議会 (5年毎の直接選挙)
- 欧州連合理事会
- 欧州委員会
- アジアの経済統合:市場主導
- 1967: ASEAN 5ヶ国
- 1999: ASEAN 10ヶ国
- 1997: ASEAN+3
- 域内貿易の増加
- 域内直接投資の増加
- 貿易強度指数:相互依存性増加
- 日本が部品を東アジア諸国に輸出し、中国がそれをアセンブルする構造
>Top 3. What has been the modern capitalism:
- When the modern capitalism was established?
- c1500:
- Prolonged 16C: (1450 - 1640) 190 years
- the age of Geographical Discovery
- development of Venetia and Genova
- c1650: around Thirty Years' War (1618-48)
- c1800: Industrial Revolution and French Revolution
- Backflow of cotton:
- 1700: UK import embargo of cotton from India.
- 1720: UK banned the use of cotton from India.
- c1820: UK overwhelmed India in cotton export.
- 1814: India to UK: 1.3 vs. UK to India: 0.8
- 1821: India to UK: 0.5 vs. UK to India: 19.1
- Relationship of politics and economics
- collusion in Europe and US
- apathy or antagonism in Asia
- Japan lost its unique civilization during modernization.
- Modernization = Westernization?
- Meiji restoration = a kind of cultural revolution?
- Remodernization of Japan:
- 1946: Tokyo Tribunal of War Criminals
- strangulation and funeral of Japanese civilization
- Breakaway from progressivism:
- turning point from mass-production, mass-consumption, and mass-disposal
- Historical awareness:
- Japanese intellectuals lost its foundation.
- Japanese illuminators:
- Yukichi Fukuzawa
- Masao Maruyama: from value of being to that of doing
- Hisao Ohtsuka: model of Western capitalism, depending on Protestantism
- Max Weber: Protestant ethic and spirit of capitalism (1905)
- an issue of 'self-denigrating historical view'
- Any country which doesn't teach its on history?
- Japan has pushed forward progressivism, forgetting its own identity (Y. Murakami)
- Limit of mass production, mass consumption and mass disposal
- press circle lacking in substance due to too much ideological conflict
- Japanese postwar illuminati:
modern ideal type
- Value of doing rather than value of being (M. Maruyama)
- What was western capitalism?
- Relativization of Asia and Japan
3. 近代資本主義と何だったのか:
- 近代資本主義の成立時期:
- 1500頃
長期の16世紀: 190年
大航海時代
- 1650頃
30年戦争
- 1800頃
産業革命、フランス革命
- 綿工業:
- 1700: 英、インド綿輸入禁止
- 1720: 英、インド綿使用禁止
- c1820: 英国がインドを凌駕
- 政治と経済活動の関係:
- 欧米は癒着
- アジアは無関心または敵意
- 近代化の中で失われた日本の文明:
- 近代化=西欧化?
- 明治維新は一つの文化革命か?
- 日本の再近代化
- 1946東京裁判
- 日本の文明の扼殺と葬送
- 進歩主義からの決別
- 大量生産、大量消費、大量廃棄からの曲がり角
- 歴史意識 :
- 日本のインテリはその基盤を喪失
- 日本の啓蒙家
- 福沢諭吉
- 丸山正男
- 大塚久雄
- 自虐的歴史観
- 自国の歴史を教えない国はあるのか?
- 日本は自国のアイデンティティを忘れて進歩主義を邁進 (村上泰亮)
- 大量生産・大量消費・大量廃棄の限界
- イデオロギー対立による論壇の空洞化
- 日本の戦後の啓蒙家:理念型
- である価値からする価値へ (丸山真男)
- 西欧資本主義とは何だったのか?
- アジアおよび日本の相対化
>Top 4.
The rise of middle class changes Asia:
- Enforced free trade by Europe: Asia were not sovereign states.
- 16C-17C: Asia had been the center of world trade system.
- 17C-18C: China and Japan continued isolation policy.
- 1820-1950: Asia (including Japan) had shown the lowest economic growth in this period.
- 1869: Suez canal was opened. Scheduled service by steel-hulled liners. Completion of colony bank, colony company and colony network.
- Post WWII:
- Two ways for development: socialism and development dictatorship
- US hegemony project: top-down promotion of capitalism.
- Asia in 21C: US -lead liberalism must be changed.
- 1997-98: East Asian monetary crisis: beginning of the end of US-lead liberalism (Model of Pax Americana and Japanese economic growth)
- 1985: Plaza Accord and higher yen had promoted Japanese investment in ASEAN.
- Electronics industry in Singapore and Malaysia
- Automobile industry in Thailand
- 2006: AFTA (ASEAN Free Trade Area)
- Change of US: from manufacture to finance
- 2002: ASEAN +3 (CJK) framework
- 2008: Chiang Mai Initiative: financial cooperation in ASEAN+3
- China and India were immune to the financial crisis due to their internal regulation.
- BPO: Business Process Outsourcing:
- Manufacture in China, and IT in India
- Asian market: from export factory to consumer market
- expansion of middle class: middle management, white color, and blue color
- China: more than 200M - 300M (10-15%) (2004):
- explosive consumer market of car, real estate, cosmetics, etc.
- India:150M (annual income more than $3000):
- consuming car and real estate; cosmetics and health food
- Rise of middle class:
Total 500M
- 1950s-60s: Japan
- 1970s-80s: Four Tigers (NIES) : S-Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Singapore
- 1985- : Thai, Malaysia, Philippines, Indonesia
- Resonance of Americanization, Japanization and Sinicization:
- Dual track policy by Thaksin of Thai: Promotion of IT and agriculture-SMB
- Elite culture vs. Popular culture:
- Japan could be one of Asian models
- Cool Japan: Japanese cuisine, anime, game, Japanese products
- Japanese traditional craftsmanship
4.
中産階級の台頭がアジアを変える:
- 欧州によって強制された自由貿易:
アジアは主権国家ではなかった。
- 16C-17C: アジアは世界貿易システムの中心
- 1820-1950: 日本を含むアジアは世界でも最低の経済成長地域
- 1869: スエズ運河開始。鋼鉄船による定期航路。植民地銀行、植民地会社、植民地ネットワークの完成
- 第二次大戦後:
- 開発への2つの道:社会主義と開発独裁
- 米国ヘゲモニープロジェクト:上からの資本主義育成
- 21Cのアジア:米国主導の自由主義は変わらざるを得ない
- 1997-98: 東アジア金融危機:米国主導の自由主義の終わりの始まり (アメリカの平和と日本の経済成長)
- 1985: プラザ合意と円高は、日本のASEAN向け投資を促進
- シンガポール、マレーシアにおけるエレクトロニクス産業
- タイにおける自動車産業
- 2006: AFTA:ASEAN自由貿易圏
- 2002: ASEAN+3 (日中韓)フレームワーク
- 2008: チェンマイ合意:ASEAN+3による金融協力
- 中印は、国内規制ゆえに金融危機を免れた
- BPO: Business Process Outsourcing
- 中国の製造業、印度のIT
- アジア市場:輸出工場から消費市場
- 中国:2-3億人 (10-15%) (2004)
- 爆発的な消費者市場:車、不動産、化粧品など (1960-70年代の日本と同様)
- 印度:1.5億人 (年収$3000以上)
- 自動車・不動産、化粧品、健康食品
- 中間層の拡大:合計5億人
- 1950-60年代:日本
- 1970-80年代:NIES
- アメリカ化、日本化、中国化の共鳴
- 二元化政策 (タクシン首相): IT化と農村・中小企業振興
- エリート文化と大衆文化:日本はアジアの一つのモデル
- Cool Japan: 日本食、アニメ、ゲーム、日本製品
- 匠、伝統技術
>Top
5. China and India:
- Similarity and dissimilarity of China and India:
- Sung China in 11-12C: experienced Renaissance, providing newly discovered products
- Compass, black gunpowder, and printing technology (woodcut)
- chinaware, silk
- trade surplus
- Zheng He of Ming: marine expanding policy until 1434
- India: multiplicity of climate, ethnics, religion and language
- Hindu, Islam, Buddhist, Christian, Jewish, Sikh, Jainist, Zoroastrian, etc.
- China: more secular polytheism
- Chain of marine waters: East China Sea, South China Sea, Bengal Bay, Arabia-West Indian Ocean, Red Sea, East Mediterranean Sea, and West Mediterranean Sea
- Marine Silk Road: Arabian dhow and Chinese junk
- Network of overseas Chinese and Indian:
- Trade in Asia:
- Traffic origin from Japan: 53% in 1990 to 38% in 2002
- Trade share of great China: 43% in 1990 to 54% in 2002
- Overseas Chinese:
30M
- Commercial emigrant: mostly Southeast Asia in 19-20C
- Coolie: mostly North America and Australia for mining and railway construction
- Temporary expatriate: 1900-1950 through diplomatic support
- Mixed breed: US, Canada, Australia
- Overseas Indian: 16M
- former British colony: until 1910s; Caribbean, Mauritius, Fiji; and former French colony West Indies
- emigrant: 1950-70 to UK, US, Canada
- guest labors: 1970s, Arabic countries; 1980s, ASEAN
- IT specialist: recently US and EU
- Former expatriates who are now cosmopolitans are becoming promoters of business and innovation in global economy.
- Education-minded expatriates:
- Jewish, Chinese and Indian expatriates are all education-minded.
- Value of knowledge and information depends on human network.
- Universities in India:
- IISc: Indian Institute of Science (1909)
- IIT: Indian Institute of Technology (modeled on MIT)
- IIM: Indian Institute of Management (modeled on HBS)
- Computer-related colleges: more than 1600, creating 120K engineers annually.
- Chinese shift to a route of reform and liberalization: 1978
- inducing overseas Chinese capital, then Japan, Korea and US-European capitals
- 1992: visit and speech of Deng Xiaoping when he visited the south.
- Staggering development.
- Chairman Jiang Zemin and Premier Zhu Rongji: progressed since 1998.
- Chairman Hu Jintao and Premier Wen JIabao combination: 2005.3
- Joined WTO in 2001 (143th member)
- Four key points to understand modern China:
- Country of competition; among various rivals
- Bad debt, national companies and financial system are in serious situation; thus high growth and foreign capital inflow are essential.
- Complimentary position of China and Japan; technological transfer and shift of production base from Japan to China
- Combination of Japanese team play and Chinese individualism
- NEP (New Economic Policy) in India:
- Reform and liberalization policy since 1991
- IT revolution: 11 times in 8 years; 20% of total export (1996 -2003)
- Narasimha Rao government: 1991-
- Manmohan Singh: 2004.5-
- Indian PFI (Private Financial Initiative):
- Most of projects made by BOT (Build-Operation-Transfer)
5. 中国とインド:
- 中国と印度の共通点と相違点:
- 11-12Cの宋代:ルネサンスを経験、欧州の新発見をもたらした。
- 羅針盤、黒色火薬、活版印刷 (木版)
- 陶器、絹
- 貿易黒字
- 鄭和:海の拡張政策、1434made
- 印度:気候、民族、宗教、言語の多様性
- ヒンズー教、イスラム教、仏教、キリスト教、ユダヤ教、シーク教、ジャイナ教、ゾロアスター教など
- 中国:もっと現世的多神教
- 海域の連鎖:東シナ海、南シナ海、ベンガル湾、アラビア=西インド洋、紅海、東地中海、西地中海
- 海のシルクロード:アラビアのダウ船、中国のチャンク
- 華僑と印僑のネットワーク:
- アジアでの貿易
- 日本からの物流:53% (1990) から38% (2002)
- 大中華圏の貿易シェア:43% (1990)から54% (2002)
- 華僑:30M人
- 商業移民:主に19-20Cに東南アジアへ
- クーリー:主に北米・豪州へ鉱山や鉄道建設
- 一時的な移民:1900-1950に外交的支援を得て
- 欧亜混血児;華裔:米国、カナダ、豪州
- 印僑:16M人
- 1910年代まで;旧英植民地のカリブ海、モーリシャス、フィージー、旧仏植民地の西インド諸島など
- 1950-70: 英国、米国、カナダへの移民
- 出稼ぎ労働者:1970年代アラブ諸国、1980年代ASEAN諸国
- IT専門家:最近米欧へ
- 以前の移民たちは現在はコスモポリタン化して、グローバル経済の中でビジネスやイノベーションの推進者となっている。
- 教育熱心な移民:
- 知識や情報の価値は人的ネットワークに依存
- ユダヤ人、華僑、印僑は教育熱心
- IISc (インド科学大学院大学)
- IIT (インド工科大学)
- IIM (インド経営大学)
- コンピュータ関連大学:1600校、毎年12万人エンジニア輩出
- 中国の改革開放路線への転換:1978
- まず華僑資本、次に日韓、米欧資本導入
- 1992:トウ小平の南巡講話
- 雁行型発展
- 江沢民主席と朱熔基首相コンビ:1998年以降
- WTO加盟(2001、143番目)
- インドの新経済政策:
- 1991より改革開放路線
- IT革命:8年間に11倍;輸出の20% (1996-2003)
- ナラシマ・ラオ政権:1991-
- マンモハン・シン政権:2004.5-
- 多くのプロジェクトがBOT方式で推進
 Comparison of fundamentals of BRICs:
Comparison of fundamentals of BRICs:
- Source: CIA
>Top 6.
Changing ASEAN:
- Southeast Asia ethnicity:
- the center of marine network
- cross region of Chinese and Indian culture
- a multiple of spiritual culture and climate
- Hinayana Buddhism:
- Ayutthaya Kingdom (14C) and Malacca Kingdom (15C)
- spices and condiment
- Triangular trade:
- struggle for hegemony: Portuguese, Spain, Netherlands, UK
- continued 300 years (15-17C)
- Indian cotton, spices and European silver
- the Spice Islands: clove, nutmeg, pepper, fragrant wood
- finance and credit transaction
- Indian hundis, Islamic contract, and Chinese silver
- Free trade project by UK:
- 1841: Opium War-I (1942 Nanjiang Treaty)
- 1856 Opium War-II (Arrow War) (1860 Convention of Peking)
- origin of coolie
- Development dictatorship:
- Sukarno (1945-67) and Suharto (1967-98) (Indonesia)
- Lee Kwan Yew (Singapore, 1959-90)
- Mahathir bin Mohamad (Malaysia, 1981-2003)
- Japanese contribution:
- the Plaza Accord (1985)
- staggering development in 1980s -90s:
- Washington consensus:
- Market fundamentalism guided by Washington, IMF and World Bank
- from Current Account Convertibility to Capital Account Convertibility
- New leaders of ASEAN
6.
ASEANも変わり始めた:
- 多彩な東南アジア:
- 海上ネットワークの中心
- 中印の文化の交差地域
- 多様な精神文化と気候
- 小乗仏教
- アユタヤ王国 (14C)、マラッカ王国 (15C)
- 香辛料
- 三角貿易:
- インド木綿、香辛料、欧州の銀
- 覇権争い:ポルトガル、スペイン、オランダ、英国
- 300年間継続 (15-17C)
- 香料諸島:クローブ、ナツメグ、コショウ、香木
- 金融・信用取引
- インドのフンディ (信用状)、イスラムの契約、中国の銀
- 英国による自由貿易プロジェクト:
- 1841: 第一次アヘン戦争 (1942 南京条約)
- 1856: 第二次アヘン戦争 (1956 北京条約)
- 開発独裁:
- スカルノ (1945-67)、スハルト (1967-90)
- リー・クァンユー (1959-90)
- マハティール (1981-2003)
- 日本の貢献:
- プラザ合意:1985
- 跛行的発展:1980-90年代
- ワシントンコンセンサス:
- ワシントン、IMF、世界銀行による市場原理主義
- 経常取引の自由化から資本取引の自由化
- ASEANのニューリーダー達
>Top 7. Japan - an unique civilization sphere:
- Coordinate axis of the West and the East was defined by Europe.
- Industrious Revolution in Japan vs. Industrial Revolution in the West.
- Japanese style revolution by Heita Kawakatsu
- Japan had imported lots of goods from Asia in exchange for exporting tons of cupper and silver, attaining Japanese style industrial revolution in 15-16C.
- The first region (margin of continent; the West and Japan), the second region (Eurasian continent) by Tadao Umesao
- Why only Japan except Europe succeeded to accomplish its industrial revolution?
- Three factors of success of modern capitalism:
- Military power
- State initiative commerce
- Nation state backed by religion
- Break with progressivism:
Yasusuke Murakami
- Ideology of progressivism seems youthful but haste and arrogant.
- But such progressivism had succeeded in changing socioeconomic system of almost all countries.
- This progressivism may cause natural destruction and ecological confusion.
- Modern people had lost god, then ethic and are peril of internal collapse and losing external nature where they live. (Takeshi Umehara)
- Japanese imperial regime: authoritative, but virtually has no power
- this is the reason for long existence of this regime.
- polycentric structure of powers: a kind of council system
- Japanese power system; system of irresponsibility (Masao Maruyama)
- Japanese s1amurai class are elite but owns no land.
- Nonviolence power by court noble:
- ghost; perform incantation; mental rather than physical attack.
- look friend by enemy's eye and enemy by friend's one. (JIen)
- Value of truth - good - beauty:
- Value of truth: scientific revolution since 17C
- Value of good: battle of ideologies in 20C
- Value of beauty: battle against environmental pollution; which is equal to value of the earth, the planet of water.
- Absence of absolutes; transience:
- Japanese culture based on polytheism
- no war in Heian period (350 years) and in Edo period (250 years)
- Civilization seeking after beauty:
7. 独自の文明圏としての日本:
- 西洋と東洋という座標軸は欧州によって定義
- 勤勉革命 (日本)と産業革命 (西洋)
- 日本型産業革命 (川勝平太)
- 日本は、15-16Cに大量の銅・銀を輸出し、アジアの物産を輸入して日本型産業革命を達成
- 第一地域 (大陸の辺縁:西洋と日本)、第二地域 (ユーラシア大陸):(梅棹忠夫)
- なぜ欧州以外では日本だけが産業革命を達成できたのか?
- 近代資本主義成立の3要素:
- 軍事力
- 国家主導の商業
- 宗教を背景とした国民国家
- 進歩主義との決別:村上泰亮
- 進歩主義イデオロギーは若々しいが性急で傲慢
- しかしこの進歩主義はほとんどすべての国々の社会経済システムの変革に成功した。
- この進歩主義が自然破壊や生態系の混乱を生じる
- 近代人は神、そして道徳を失い、内面的崩壊の危機に晒されており、棲む外部自然界を失おうとしている (梅原猛)
- 日本の天皇制:権威はあるが、実質的に権力はない
- これが長期間存続している理由
- 権力の多元化構造
- 日本の権力システム:無責任の体系 (丸山真男)
- 日本の武士階級はエリートだが、土地を所有しない。
- 公家の非暴力パワー:
- 怨霊:加持祈祷:肉体ではなく精神への攻撃
- 味方を敵の眼で見て、敵を味方の眼で見る (慈円)
- 真・善・美の価値観:
- 真の価値:17C以来の科学革命
- 善の価値:20Cのイデオロギーの闘い
- 美の価値:環境汚染への闘い;地球の価値と等価
- 無常観:
- 多神教に基づく日本文化
- 戦争のない時代:平安時代350年、江戸時代250年
- 美の文明
>Top 8. Beyond the modern capitalism:
- Central city of the world:
- Venetia, Genova, Amsterdam, London, New York, then Beijing?
- Fermand Braudel: described long-term cycles of capitalist economy; Cities follow subsequently as centers of the cycle:
- Venice and Genoa in 13-15C
- Antwerp in 16C; Amsterdam 16-18C
- London in 18-19C
- Globalization:
- concurrent process of Americanization and localization
- big surge of export from China to US: actually increase of export from US offshore companies or US/China J/V.
- Profit of US companies from financial services: more than 30%, or 50% including those of affiliates
- Change of the situation that from the world needs US to US needs the world.
- Historically, Europe had been more ideological and US more pragmatic, but now the situation was reversed: US is getting more ideological.
- US $ as the key currency.
- Grope of 21C system:
- What kind of system appears after the fall of US and US dollar.
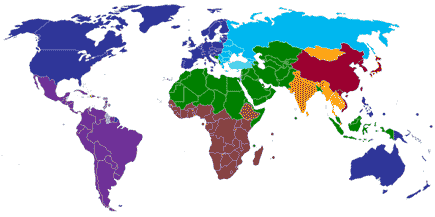 Clash of civilizations (1993, 96) by Samuel Hunchington; cultural fault lines where the clash of civilizations will occur (Wiki)
Clash of civilizations (1993, 96) by Samuel Hunchington; cultural fault lines where the clash of civilizations will occur (Wiki) - Is a core state of each civilization the former empire?
- What would be EU? EU is different from core state or empire as described by Hunchington. EU consists of complicated hybrid organizations of national and international.
- Reorient phenomenon:
- Further development of ASEAN (10) +CJK (3) forum; concept of EAC (East Asian Community)
- shift to networked system without the single center function.
- ACU (Asia Currency Unit) : pooled operation of 10% (about $200B) of foreign currency reserves of member countries.
- Philosophy and consensus of post-modern concept
8. 近代資本主義を超えて:
- 世界の中心都市:
- ベニス、ジェノバ、アムステルダム、ロンドン、ニューヨーク、そして北京か
- F.ブローデル:資本主義経済の長期サイクルを描写。中心都市が次々と現れる。
- ベニスとジェノバ (13-14C)
- アントワープ (16C)、アムステルダム (16-18C)
- ロンドン (18-19C)
- グロバリゼーション:
- アメリカナイゼーションとローカリゼーションの同時進行プロセス
- 中国から米国への輸出急増:実態は、中国内の米国企業または米中合弁企業からの輸出
- 米国企業の収益の内、金融業は30%以上、事業会社の金融収益を入れると50%以上
- 世界が米国を必要の状況から、米国が世界を必要とする状況へ
- 歴史的は、欧州はよりイデオロギー的で、米国はプラグマティックであった。今やそれは逆転
- 基軸通貨としての米国ドル
- 21Cシステムへの模索:
- 米国および米国ドルの凋落の後にどのようなシステムが現れるのか?
- 文明の衝突 (1993, 96) S. ハンチントン
- 各文明のコア・ステイトは、かつての帝国なのか?
- EUはどうなるのか?EUはハンチントンが描いたコア・ステイトや帝国とも異なる。EUはナショナルおよびインターナショナルなの複雑なハイブリッド組織から成る。
- リオリエント現象:
- ASEAN + 3のさらなる発展
- 中心のないネットワーク型システムへの以降
- ACU (アジア通貨単位):各国の外貨準備高の10% (約$200B)の共同運用
- ポストモダン構想の哲学と合意
>Top 9. The era of Pax Asiana:
- History of modern capitalism:
- period of war
- 1870-1913: Pax Britannica US as the hegemony since 1871 (Franco-Prussian War)
- Japan:
- No war period of 250 years of Edo period and 350 years of Heian period in Japan; probably due to delicate balance of religious and secular powers
- requiem mechanism; to prevent impulsion of hate and violence
- Peace is a state of no war:
- Modern European civilization has been based on doctrine of dualism: good and evil
- the final solution is war or revolution until the advent of nuclear deterrence.
- Asian peace concept is different:
- ahinsa: Buddhist doctrine of nonviolence
- Gandhi's nonviolence
- Lao zi and Zhuan zi idea: inaction and nature
- Japanese-style harmonization: root of Pax Japonica
- Recurrence to nature:
- human population growth
- energy consumption
- environmental destruction
- extinction of species
- polytheism rather than monotheism
- monotheism has been favorable agricultural revolution conquering nature.
- symbiosis
- anicca or transience strategy rather than survival strategy (Tetsuo Yamaori)
- Poem of Ryokan:
- Maple leaves fall down, showing both its upper and under side.
- return to the nature if and when alive or dead.
9. パクス・アシアーナの時代:
- 近代資本主義の歴史:
- 戦争の時代
- 1970-1913:パクス・ブリタニカ (1871の普仏戦争後)
- 日本:
- 江戸時代250年、平安時代350年の平和;おそらくは宗教と政治の微妙なバランス
- 鎮魂のメカニズム:憎悪と暴力の衝動の阻止
- 平和とは戦争のない状態:
- 近代英欧文明は善悪の二元論に基づく
- 最終解決は核抑止力の登場までは戦争か革命か
- 自然への回帰:
- 人口増加
- エネルギー消費
- 環境破壊
- 種の絶滅
- 一神教より多神教へ
- 一神教は自然を征服する農業革命に有利だった。
- 共生
- 生き残り戦略より無常戦略へ
- 良寛の句:
- 裏を見せ表をみせて散るもみじ
- 生きていても死んだ後も自然への回帰
Comment
- This is story of rebirth or resurgence of Asia.
- Pax Asiana has been a life work of the author.
- 本書はアジア復活の物語である。
- パクス・アシアーナは著者のライフワークである。
Title |
The Century of Pa Asiana |
アジアは近代資本主義を超える |
|---|---|---|
Index |
||
Why? |
|
|
Resume |
要約 |
>Top 0. Introduction:
|
0. 序章:
|
>Top 1. What is happening in Asia now?:
|
1. 今、アジアで何が起こっているのか:
|
>Top 2. Market integration is in process in Asia:
|
2. アジアでも市場統合が進んでいる:
|
>Top 3. What has been the modern capitalism:
|
3. 近代資本主義と何だったのか:
|
>Top 4. The rise of middle class changes Asia:
|
4. 中産階級の台頭がアジアを変える:
|
>Top 5. China and India:
|
5. 中国とインド:
|
|
|
>Top 6. Changing ASEAN:
|
6. ASEANも変わり始めた:
|
>Top 7. Japan - an unique civilization sphere:
|
7. 独自の文明圏としての日本:
|
>Top 8. Beyond the modern capitalism:
|
8. 近代資本主義を超えて:
|
>Top 9. The era of Pax Asiana:
|
9. パクス・アシアーナの時代:
|
Comment |
|
|