 |
Digital Process Innovation |
Cat: ICT |
|---|---|---|
Masahiro Akiyama (秋山雅弘) & Hideki Haragucchi (原口英紀) |
09x17u/18212r |
Title
Digital Process Innovation
デジタルプロセス・イノベーション
Index
- Introduction:
- Japanese monotukuri industry:
- Overseas manufacturing industry:
- Goal of monotukuri industry:
- Digital process innovation:
- Digital enterprise:
- Fundamental knowledge of CAD:
- Present and future of CAD:
- Manufacturing and 3D:
- 3D through the door:
- Innovation for survival:
- Couldn't organize this:
- Unfailing system selection:
- Concept of the digital city:
Why?
-
Monotukuri, or manufacturing is hallmark of Japanese industry. It it is empowered by IT, which will recover its competitiveness in the global market. In particular, 3D CAD would be an essential tool to optimize production process
-
3D is the maximum dimensions which human beings can visualize: shapes expressed in 3D give us tangible images of the target product.
-
Thus, 3D CAD could be an effective tool to visualize manufacturing process and product.
-
ものつくりは日本産業のお家芸である。もしそれがITで武装されれば、グローバル市場での構想力を回復できる。特に、3D CADは、生産プロセスを最適化する上で必須のツールである。
-
3Dは人間が可視化できる最大の次元である。3Dで表現された形は目標とする形について有形のイメージを得ることが可能となる。
-
即ち、3D CADは、ものつくりのプロセスと製品を可視化する効果的なツールとなり得る。
Resume
要約
>Top
0. Introduction:
- This book is written aiming to activate Japanese industry by digital engineer.
- The author has been involved in developing CAD system; first from order-made in-house CAD, then general-purpose packaged CAD, now focused in 3D CAD.
0. 序章:
- 本書は日本の産業をデジタルエンジニアリングによって活性化しようという目論見で書かれた。
- 著者はCADシステムの開発に関与してきた。最初はオーダーメードのインハウスCAD、その後、汎用CADパッケージ、今や3D CADに焦点が当たっている
>Top 1. Japanese monotukuri industry:
- Japan is an island country with insufficient natural resources, but has a long tradition of technology and manufacturing. Particularly during the Tokugawa (17-19C), it has maintained self-supporting economy in national isolation policy using effectively various skills and technique of artisan of agriculture and light industry.
- Hamamatsu city area with 600K population, Shizuoka prefecture:
originated from manufacturing center of textile industry, then developed sipping machinery, leading to birth of Toyota, Suzuki, and Yamaha,
- Long tradition of kimono culture had prevented to import economic British cotton goods since Queen Victorian period.
1. 日本のものつくり:
- 日本は資源に恵まれない島国であるが、技術とものつくりの長い伝統があう。特に、る徳川時代には、鎖国経済の中で、農業や軽工業の様々な技や工芸を巧みに活かして鎖国政策の中での自給自足経済を維持してきた。
- 静岡県浜松市地域 (人口60万):
繊維産業の中心地域として発達し、その後は紡績機械、やがてはトヨタやスズキの誕生につながった。
- 長い着物文化の伝統が、ビクトリア時代からの安い綿製品を阻止してきた。
>Top
2. Overseas manufacturing industry:
- Chinese mold-making industry:
- Chinese small-medium companies are using recently 3D CAD /CAM
- various incentives given by the government as well as cheaper and aggressive labor power, economic price of land and building,
- Perfect name of strength of each industrial center:
- US: marketing
- EU: engineering
- Japan: manufacturing
- US IT industry:
carrier pass of MIT or Stanford students as a risk-taker in the following order:
- to establish a venture business
- to enter a promising venture business
- to enter a successful company
- to enter a major company
- Center of German automobile industry:
- Shuttgart, Land Baden-Wurttemberg: cradle of automobile like Mercedes-Benz, Porsche, Maybach
- Industry-government-academia joint research.
- Quick designing: from 300 to 15 minutes in average designing of mold.
2. 海外をみると:
- 中国の金型産業:
- 中国の中小企業は最近は3D CAD/CAMを活用
- 政府優遇策、安く熱心な労働力、安価な土地建物
- 各地域の強み:
- 米国:マーケティング
- 欧州:エンジニアリング
- 日本:マニュファクチャリング
- 米国IT産業:
MITやスタンフォードの学生の進路
- 自分のベンチャー会社設立
- 成功しそうなベンチャーへの就職
- 成功した会社への就職
- 大会社への就職
- 独の自動車産業の中心地:
- シュツットガルト:メルセデス、アウディの本社
- 産官学の共同研究
- 金型設計:平均300分から15分へ
>Top 3. Goal of monotukuri industry:
- SMB manufacturing center in Japan:
- Ohtaku of Tokyo and Higashi-Osaka of Osaka
- Higashi-Osaka city:
- Decrease of SMB
of Higashi-Osaka:
from peak 10,033 companies in 1983 to around 8,000 now.
- Tokiwa Seiki Co., Ltd: manufacturer of specialized ferrule and fitting
- Takenaka Seisakusho Co., Ltd.: manufacturer of specialized corrosion free bolt and nat
- Key to success:
- Investment in equipment, particularly in high-technology and IT.
- Technical development capability
- Human resources development
- Survival strategy:
- Digital meister: IT and Process
- IT utilization and production process innovation
- Goal of manufacture:
- QCD: Quality improvement, Cost down, and Quick Delivery
- aiming ultra-manufacturer, ie, digital enterprise'
3. ものつくり産業のゴール:
- 日本の中小企業製造の中心地:
- 大田区、東大阪市
- 東大阪市:
- 徐々に衰退:ピーク時10,033 (1983)社 から8,000社へ
- トキワ精機:特殊継ぎ手部品
- 竹中製作所:錆びない特殊ネジ
- 成功の鍵:
- 設備投資、特にハイテクとIT
- 技術開発能力
- 人材育成
- 生き残り戦略:
- デジタルマイスター:ITとプロセス
- IT活用と生産プロセス改革
- 製造業のゴール:
- QCD:納期、コスト、納期
- 超製造業=デジタルエンタープライズ
>Top 4.
Digital process innovation:
- Digital is discrete, while analog is continuous.
- Merit of digitalization:
- Mass data processing:
If measure 10cm cubic using laser by 0.1mm unit, the data (point group) will be 8M. If each data is expressed 64 byte (xyz axis each 4 byte), the data volume will be 512MB.
- High speed:
wide-band transmission
- Dimension control: visualization and control:
can exceed 2D drawing on paper. Earlier review of 3D shape is available, causing less failure designing. Dynamic simulation is also possible.
- Definition of digital process innovation:
- Premise: use of digital technology as premise
- Object: business flow (process) of manufacturing, distribution and service industry
- Action: not only improvement or optimization of process, but also making innovation
- Goal: to maximize profitability
- Not being a follower, but a challenger to differentiation from competitors.
4.
デジタルプロセスイノベーション:
- デジタルは離散、アナログは連続
- デジタル化のメリット:
- 大量データ処理:
10cm立方体を0.1mm単位で計測するとデータ量 (点群)は、8Mとなる。これをXYZ軸の64バイトで表現すると、データ量は512MB
- 高速処理:
広帯域伝送
- 次元の制御:可視化と制御
2次元の図学を超える。3Dの形状について早期のレビューが可能。設計上の失敗の減少。動的にシミュレーションも可能。
- デジタルプロセスイノベーションの定義:
- 前提:デジタル技術の利用
- 目的:製造・流通・サービスの業務フロー (プロセス)
- 行動:プロセスの改善や最適化のみならず、イノベーションを起こす
- ゴール:収益性拡大
- ライバルへの追従者ではなく差別化追求者
>Top
5. Digital enterprise:
- Resources: Human + Facility + Capital and DIgital information
- PDM: Product Data Management includes CAD
- BOM: Bill of Materials for assemblies
- ERP: connecting management and engineering
- SCM: connecting with external companies
- CIO: practice of digital engineering
- Mindset of 'Change or die'
- Top-down or Bottom-up:
- Bottom-up: change from field site
- Top-down: speedy decision for differentiation
- Merit of 3D CAD:
- User divisions such as manufacturing and analysis appreciate the merit.
5. デジタル・エンタープライズ:
- 経営資源:人・モノ・金・デジタル情報
- PDM:
- BOM: アセンブルのための部品表
- ERP: 経営とエンジニアリングをつなぐ
- SCM: 外の企業をつなぐ
- CIO:デジタルエンジニアリングの実践
- 生きるか死ぬか:
- トップダウンかボトムアップか:
- ボトムアップ:現場からの変化
- トップダウン:差別化のための迅速な決定
- 3D CADのメリット:
- 製造や解析のようなユーザ部署がメリットを評価
>Top 6.
Fundamental knowledge of CAD:
- History of general-purpose CAD:
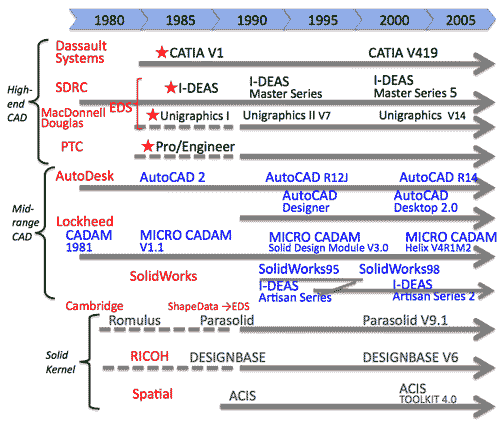
- In-house CAD since 1970s:
can support surface data (wire frame).
- Toyota: CADETT, CAELUM
- Nissan: CAD II, α-CAD
- Mitsubishi: MERIT
- Mazda: GNC
- Yamaha: ESPRi
- Suzuki: SCAD
- 4 Major CAD
- Dassault Systems (Fr): CATIA
- SDRC (US): I-DEAS
- Graphics Solution, then EDS (US): Unigraphics
- Parametric Technology (PTC,; US): Pro/Engineer
- Mid range CAD: (less than $10K)
- Autodesk (US): AutoCAD
- Autodesk (US): Mechanical DeskTop
- Intergraph (US): Solid Edge
- CoCreate Software (Ger): Solid Designer
- Bentley Systems (US): MicroStation
- Dassault Systems SolidWorks (Fr): SolidWorks
- Photoron (Jp): Zuno-Century, using DesignBase
- 2D CAD:
- Lockheed (US): CADAM
- AutoDesk (US): AutoCAD
- HP: ME10
- Hitachi: GMM, HICAD
- NEC: CAE-2D
- Fujitsu: ICAD
- Ashlar: Ashlar Vellum: easy to use
- Features of 3D CAD:
Continuance of proficiency of 2D CAD eliminates big jump of productivity increase.
- assistance of automation of post-process
- less human intermediation
- no requirement of retyping
- simulation is possible
- A company: 30 years history x 1 product x 3 trials = 90
- B venture: 1 year history x 3 product x 30 simulations = 90
- Coordinates of surface model and its perpendicular line can be transferred to CAM.
- Rapid prototyping
- Calculation of surface area, volume and weight, which enables cost estimation of materials, delivery.
- Solid model is surface model plus topology information (called B-reps, boundary representation) , which will lead to product model.
- linked with BOM (Bill of Materials)
6.
CADの基礎知識:
- 汎用CADの歴史:
(左図)
- インハウスCAD
各自動車会社の独自ソフト
- Toyota: CADETT, CAELUM
- Nissan: CAD II, α-CAD
- Mitsubishi: MERIT
- Mazda: GNC
- Yamaha: ESPRi
- Suzuki: SCAD
- 4大汎用CAD ★印
- CATIA
- I-DEAS
- Unigraphics
- Pro/Engineer
- ミッドレンジCAD
低価格(100万円以下)
- AutoCAD
- Mechanical DesignTop
- Solid Edge
- SolidDesigner
- MicroStation
- SolidWorks
- 頭脳Century
- 2D CAD:
- CADAM
- AutoCAD
- ME10
- GMM, HICAD
- CAE-2D
- Ashlar Vellum
- 3D CADの特徴:
2D CADに慣れ親しんだことが、むしろ大きな生産性向上を阻害
- 後工程の自動化支援
- 人間の介在の最小化
- 再入力が不要
- シミュレーションが可能
- サーフェイスモデルの座標とその垂線がCAMへ連繋
- Rapid prototyping
- 表面積と体積と重量計算によって、材料や流通コスト計算が可能
- ソリッドモデルは、サーフェイスモデルの連結情報 (トポロジー)を付加→B-reps
そしてプロダクトモデルへ
- BOMと連結
>Top 7. Present and future of CAD:
- Advent of mid-range 3D CAD in c1995
- Price; around ¥1M (PC base)
- Penetration in the market:
- Around 1998-1999: year of jump
- 2000: solid modeling kernel was developed
- Design element: a batch of design procedure with parameter and constraint
- Top-down designing by 3D CAD:
- able to attach memo or comment anywhere on the model
- Major players in CAD maker (as of 2001):
- Dassault systems (Fr): sales $1.3B with market share 17% in 2000
- EDS (US)
- PLM (Product Lifecycle Management)
- data sharing with CAE tools
- PDM (Product Data Management) tool:
- Meta-project function such as:
- document management,
- change management,
- product configuration management,
- workflow management
- Age of collaboration:
- EDS: Visualization pipeline: small sized viewing data
- jt-format of EAI (Engineering Animation)
- use of 'e-Vis': tool library for collaboration
- 'DesginKnet': occasional transfer of each change data of design into 3D format data
7. CADの現状と今後:
- ミッドレンジ3D CADの登場:1995年頃
- 価格:約100万円
- 普及:
- 1998-1999頃:急激な普及の年
- 2000: ソリッド・モデリング・カーネル開発
- デザインエレメント:パラメータや拘束条件を一緒にした設計手順のまとまり
- 3D CADによるトップダウン設計
- モデルの任意の場所にメモ記入可能
- 主なCADメーカ:
- Dassaut systems , 仏:売上$1.3B、シェア17%
- EDS、米国
- PLM:
- CAEツールとのデータ共有
- PDM (Product Data Managment) tool:
- Meta-project functionとして
- 文書管理
- 変更管理
- 製品構成管理
- ワークフロー管理
- 協業の時代:
- EDS: Visualization pipeline: 小容量で可視化データとして
- jt形式 (EAI社)
- e-Visの利用:協業のためのツール群
- DesignKnet: 設計変更内容を3D形状データに随時反映
>Top 8. Manufacturing and 3D:.
- 3D CAD has developed drastically since two decades; typically in the proliferation of general-purpose 3D CAD and in the development of solid technology.
- 3D CAD can express 3D design in wireframe, surface and solid models.
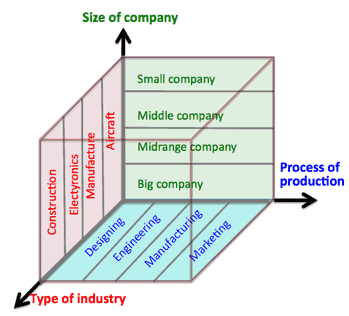 Proliferation of 3D CAD:
Proliferation of 3D CAD:
- Type of industry:
- Aircraft industry
- Automobile
- Electronics
- Construction
- Apparel
- Size of company
- Bib company
- Midrange company
- Middle company
- Small company
- Process of production
- Design by CAD
- Engineering: simulation by CAE
- Manufacturing by CAM
- Marketing
- Advertisement
- Testing by CAT
- Combined use of high-end CAD and midrange CAD is effective.
- Particularly, simulation by CAE and testing by CAT can decrease numbers of trial production and its cost.
- CAT or CAI (Computer Aided Inspection): Comparison of CAD data and measurement of product by noncontact scanner.
- Trial production model is usually different from design model due to shrinkage by cooling and spring back by press working.
8. ものつくりと三次元:
- 3D CADは、過去20年の間に大きく進化した。特に、汎用三次元CADの普及と、ソリッド技術の進展。
- 3D CADは、三次元形状では曲線 (ワイヤフレーム)、曲面 (サーフェイス)、そしてソリッドで表現
- 3D CADの普及方向 <左図>
- 業種
- 規模
- 工程
- CADによる設計
- CAEによるシミュレーション
- CAMによる製造
- マーケティング
- 広告
- CATによる試験
- ハイエンドCADとミッドレンジCADとの組み合わせ利用が効果的
- 試作モデルは普通は設計モデルと異なる。冷却による収縮、プレス加工によるスプリングバック
>Top 9. 3D through the door:
- Merit of 3D:
PDM (Product Data Management)
for PLM (product life cycle management).
- Grasp of shape:
enable to share the designed image
- Presentation:
Virtual-Reality like advertisement
- Processing:
Time to market, rapid prototyping
- Product analysis:
Strength design, fluid analysis, ray trace simulation
- Manufacturing analysis:
Manufacturing simulation
- Automatic drawing:
coexistence with paper information
- Automatic form making: BOM, cost estimate, weight calculation
- Testing:
CAT and CAI (Computer Aided Inspection) using CCD camera and laser range finder
- Use of 3D technology enables efficient and effective process innovation.
9. 三次元化の扉の向こう:
- 三次元のメリット:製品ライフサイクルのためのPDM
- 形状把握:
デザインイメージの共有
- プレゼン:
VR的な広告
- 加工:
Time to market、高速造形
- 製品解析 :
強度設計、流体分析、光線追跡simulation
- 生産解析:
Manufacturing simulation
- 自動図面化
- 自動帳票化
- 検査:
CAT、CAI
- 三次元技術の利用によって効率的・効果的なプロセスイノベーションが可能となる。
>Top 10. Innovation for survival:
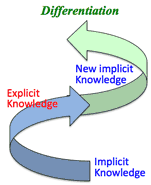 Manufacturing process:
Manufacturing process:
- Designing: CAD Design
- Analysis & simulation: CAE Engineering
- Model design & fabrication: CAM Manufacturing
- Test & experiment: CAT Testing
- Production
- Spiral effect:
- to conduce explicit knowledge from implicit knowledge
- to find new implicit knowledge
- to make differentiation
10. 生き残りのための変革:
- ものつくりのプロセス
- デザイン・設計:CAD Desgin
- 解析・シミュレーション:CAE Engineering
- 型設計・加工:CAM Manufacturing
- 検査・事件:CAT Testing
- 生産
- スパイラル効果:
- 暗黙知の形式知化
- 新たな暗黙知の形成
- 差別化
>Top 11. Couldn't organize this:
- Assentation society - Japan
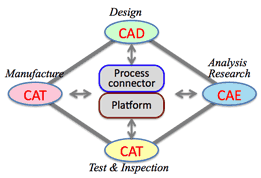 Digital Diamond: Process combination using CAD, CAE, CAM, and CAT:
Digital Diamond: Process combination using CAD, CAE, CAM, and CAT:
- Design model:
Transfer the design model made by CAD to the central platform.
- Analysis model:
Make analysis data for simulation by CAE, calculating the data using by solver.
- Fabrication model:
Transfer the simulated 3D data to CAT, making NC data.
- Test & inspection model:
Transfer the data got by contact or noncontact measuring to CAT, and compare the data between design model and physical model.
11. ここができていない:
- 付和雷同社会ー日本
- デジタルダイアモンド:
<左図>
CAD, CAE, CAM, CATによるプロセス連繋
- 設計モデル:
CADで作られた設計モデルは中央のプラットフォームに転送
- 解析モデル:
CAEによるシミュレーションのための解析データを作成し、ソルバーを使ってデータを解析
- 加工モデル:
シミュレートしたデータをCATに転送しNCデータを作成
- 検査モデル:
接触・非接触測定によって得られたデータをCATに転送し、設計モデルと物理モデルとを比較
>Top 12. Unfailing system selection:
 Plenty of option software surrounding 3D CAD:
Plenty of option software surrounding 3D CAD:
- Conversion between 2D and 3D
- Explanation modeler
- PDM (product data management)
- CG
- CAM
- CAE
- CAT
- ROBOT
- Form
- SheetMetal
- Reverse engineering
- Collaboration in a digital enterprise:
- VEM: Value Engineering Management
- then collaborate with PDM, CRM, and SCM
- finally all data are integrated in ERP.
12. 失敗しないシステム選定:
- 豊富な3D CAD周辺のオプションソフト群
- 2D/3D変換
- 拡張モデラー
- PDM
- CG
- CAM
- CAT
- ROBOT
- 帳票
- SheetMetal
- リバースエンジニアリング
- デジタル企業における協業:
- VEM: Value Engineering Management
- さらにPDM, CRM, SCM連携
- すべてのデータはERPへ
>Top 13. Concept of the digital city:
- Digital city:
- Make city planning data using 3D CAD.
- Integrated management of information of land, building, and other public services
- Effective social infrastructure by using all construction data of public sectors
- Designing and recovery simulation of natural disaster
13. デジタル・シティ:
- デジタル・シティ
- 3D CADによる都市計画の立体モデル化
- 土地、建物等公共サービス情報の一元管理
- すべての公共機関の全建設データ活用による効率的な社会インフラ構築
- 自然災害による防災計画のデザインと復興シミュレーション
Comment
- 3D CAD could be a killer application not only as a company, but also as whole city.
- 3D and 2D are different as chalk and cheese.
- 3D CADは一企業にとってでなく、全シティにとってキラーアプリケーションとなろう。
- 3Dは2Dと比べて、雲泥の差である。
Title |
Digital Process Innovation |
デジタルプロセス・イノベーション |
|---|---|---|
Index |
|
|
Why? |
|
|
Resume |
要約 |
>Top 0. Introduction:
|
0. 序章:
|
>Top 1. Japanese monotukuri industry:
|
1. 日本のものつくり:
|
>Top 2. Overseas manufacturing industry:
|
2. 海外をみると:
|
>Top 3. Goal of monotukuri industry:
|
3. ものつくり産業のゴール:
|
>Top 4. Digital process innovation:
|
4. デジタルプロセスイノベーション:
|
>Top 5. Digital enterprise:
|
5. デジタル・エンタープライズ:
|
>Top 6. Fundamental knowledge of CAD:
|
6. CADの基礎知識:
|
>Top 7. Present and future of CAD:
|
7. CADの現状と今後:
|
>Top 8. Manufacturing and 3D:.
|
8. ものつくりと三次元:
|
>Top 9. 3D through the door:
|
9. 三次元化の扉の向こう:
|
>Top 10. Innovation for survival:
|
10. 生き残りのための変革:
|
>Top 11. Couldn't organize this:
|
11. ここができていない:
|
>Top 12. Unfailing system selection:
|
12. 失敗しないシステム選定:
|
>Top 13. Concept of the digital city:
|
13. デジタル・シティ:
|
Comment |
|
|