 |
Report from Business Process Management Suite Workshop- Essence of BPM -
|
Cat: IT |
|---|---|---|
Kanzo Kobayashi and Kazuyoshi Watanabe |
09323u/18212r |
Title
Report from BPMS Workshop
BPMS研究会報告
Index
- Introduction:
- Staus-quo of IT Coordinators:
- Who makes Request For Proposal (RFP)?:
- Requirements
Engineering:
- Busienss
Analysis Body Of Knowledge (BABOK):
- BPM
and BPMS:
- Position
of BPM in ITC's Process Guideline:
- Defective
portion of ITC's PGL:
- Synchronization
of Management and IT:
- Image
of Hourglass:
- IT
investment comparison (US vs. Japan):
- Difficulty
of consensus building among organizations:
- Hierarchial
structure of process:
- Integration of BPM, PMBOK, BABOK & Requirements
Engineering:
Why?
-
This lecture was held at Business Innovation
Center Osaka sponsored by Kansai Institute of Information Systems
& Industrial Renovation (KIIS) and ITC Kinkikai on Mar.14, 2009.
Almost 100 or more audience participated, which indicates how
this theme takes an opportunity now in Japan.
-
Mr. Kenichi Hara of NTIS, NEC affiliate company
and Mr. Kazuyoshi Watanabe, chairman of SCC-Japan followed my
lecture and developed the same theme, giving vivid presentation
based on their practices; both are well-known experts of BPM
technology in Japan and are core members of monthly held BPMS
workshop at IICA since last April surrounding Mr. Takaaki Seki,
chairman of ITCA.
-
Followimg is the summary of presentation myself and essence of Mr. K. Watanabe.
- 本講義は、KIISおよびITC近畿会の共催で2009/3/14に大阪産業創生館で開催された。約100名を超える聴衆参加されたことはこのテーマで今日本で時機を得たものであることを示している。
- NTISの原健一氏とSCC日本チェアマンの渡辺和宣氏が、小生の講演に引き続き、彼らの実践に基づく臨場感溢れるプレゼンを行った。両氏共このBPM技術のエキスパートであり、昨年4月以来ITコーディネータ協会の関会長を囲んで毎月開催されたBPMS研究会の中心メンバーである。
- 以下は、小生の講演内容と渡辺和宣氏の講演の骨子である。
Resume
要約
>Top
0. Introduction:
- BPM (Busness Process Management) is defined as to function bridging between Business and IT.
- As BPM attempts to imporve processess continuously, it
should be called as 'process optimization process.'
- This definition should be identical to that of IT Coordinators
in Japan, who are also defined to aim bridge between Management
and IT.
- The contents (1-9) was lectured by myself, (10- 13) by K. Watanabe
0. 序章:
- BPM (Busienss Process Management)の定義は、ITとビジネスをつなぐ機能である。
- BPMは、連続的にプロセスの改善を試行するので、「プロセスの最適化を行うプロセス」と言われる。
- この定義は、日本のITコーディネータのそれと同じである。それもまた経営とITの橋渡しを目的としているからである。
- 講演内容は、(1-9) は小生、(10- 13)は渡辺氏が担当
>Top 1. Status-quo of IT Coordinators:
- IT Coordinator (ITC):
- A institution of ITC has been established
since 2001 as a recommend qualification of an expert of both
corporate management and IT technology by METI.
- The accumulated number of ITC's are 8577 as of
Dec.31, 2008, of which 6,406 retains the title.
- The average age of ITC's is 46.7.
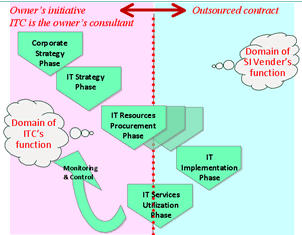 ITC's Process Guideline (PGL) :
ITC's Process Guideline (PGL) :
- Corporate Strategy Phase
- IT Strategy Phase
- IT Procurement Phase
- IT Implementation Phase
- IT Services Utilization Phase
- Monitoring & Control
- PGL phases and ITC's status:
- Owners's initiative, where ITC is the owner's consultant
(left side)
- Outsourced contract to SI vendor (right side)
- IT Services Utilization:
another contract or the owners own opeartion
1.
ITコーディネータ(ITC) の現状:
- ITコーディネータ (ITC):
- 資格認定者累計:8577名
- 資格保有者::6,406名 (2008/12/31現在)
- 平均年齢:46.7歳
- 経営とITの融合を推進するITコーディネータ
- ITCプロセスガイドライン(PGL):
- 経営戦略フェーズ
- IT戦略策定フェーズ
- IT資源調達
- IT導入
- ITサービス活用
- モニタリング&コントロール
- PGLフェーズとITCステータス:
- 主体性の領域: 準委任
- 委任性:請負契約:
アウトソース、成果責任あり
- ITサービス活用フェーズ:
別契約、または発注者自身
>Top
2. Who makes Request
For Proposal (RFP)?:
- User companies cannot write Request For Proposal (RFP):
- According to JUAS research (n=635), 23% of user corporations
mostly prepare RFP by themselves, but 53% ask the detailed
RFP to the vender and 24% totally leave RFP in the vender's
hands.
2. 要求仕様書は誰が作成するのか?:
- ユーザ企業はRPFを書けない:
- JUAS調査 (635社): 23%は自社でRFP作成、53%は詳細をベンダ依存、24%はすべてベンダに依頼。
>Top 3. Requirements
Engineering:
- Requirement Development:
- Elicitation: Cf: < elicit, entice, lace; like Detective
Colombo
elicit corporate strategic issues from stakeholders
- Analysis:
analyze business process
- Specification:
make specification of IT system to be implemented
- Verification:
verify utilization and operation of the system
- Requirement Management:
- recurrently confirm and make detailed document
- change of specification is costly: as much as 30-50% of total
cost
- Gap of two cultures:
- Corporate executives tell by business terms, while developers
make coding by computer terms.
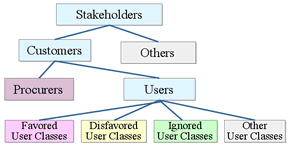 User classes:
User classes:
- Expand then contract technique:
- User:
- favored user classes
- disfavored user classes
- ignored user classes
- other user classes
- Source: BABOK V1.6
3. 要求工学とは:
- まず要求開発
- 経営課題を聞き出し
- elicit
- entice
- lace
- 業務プロセスを分析
- ITシステム要件を仕様化
- 活用・運用まで検証
- 次ぎに要求管理
- 顧客要求
- 二つの文化:
- 経営者は経営者の言葉で、開発社はコンピュータの言葉で語る。
- ステイクホルダとユーザの階層構造
- ユーザ・クラス
対象を広げてから集約
- ユーザ:
- 好意的ユーザ
- 反感的ユーザ
- 無視するユーザ、
- 無関心なユーザ
>Top 4.
Busienss Analysis Body Of Knowledge (BABOK):
- ITC's PGL and BABOK:
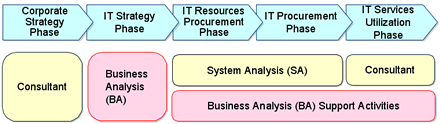
- BA’s main activities:
to make plan for IT system necessary for business process improvement
and information
process, through visualization and communication.
- raise business issues
- identify root causes
- specify vision and scope for the
solution
- make To-be model
- define requirement of system
- Source: Masakazu Kobayashi, ITC, 2009
- Comparision of BABOK and PMBOK:
BABOK
PMBOK
Knowledge base
Busienss Analysis Body of
Knowlege (V1.6 -> 2.0)
Project Management Body of
Knowledge (V4.0)
Organization
Int'l Institute of Biz Analysis
(IIBA)
Project Management Institute
(PMI)
Establishment
2003, Toronto
1969 Pennsylvania
# of members
5,000
265,000
Japan division
IIBA-Japan, Dec. 2008
PMI-Japan, 1998
Qualification
Certified Biz Analysis Professional
(CBAP)
Project Management Professional
(PMP)
# of qualified p.
450
270,000
- Synonym of BA:
- Consultant, Project Manager, Busienss Architect, Product Manager,
Business Analyst, Developer, System Analyst, Qualty Assurance
Analysit
- A rose by any other name would smell as sweet.
- Seven knowledge area of BABOK:
- Enterprise Analysis
- Requirements Planning and Management
- Requirements Elicitation
- Requirements Analysis and Documentation
- Requirements Assessment and Validation
- Requirements Communication
- Fundamentals
4.
BABOKとは:
- RFPの作成分担:
- 23%: RFPのほとんどを自社で作成
- 53%: ベースは自社で、細部は委託先で
- 24%: すべて委託先が担当
- PGLとBABOK: (左図)
BAの主な活動:
可視化とコミュニケーション
を通じて業務プロセス改善
と情報整理に必要なITシステムを企画 する。
- ビジネス上の問題を提起する
- 根本の原因を特定する
- 解決策のビジョンとスコープを特定する
- 将来の状態をモデリングする
- システム要件を定義する
- BAの同義語
- コンサルタント
- プロダクト・マネジャ
- ビジネス・アーキテクト
- プロジェクト・マネジャ
- ビジネス・アナリスト
- デベロッパ
- QAアナリスト
- (バラは何と呼ばれようとも...)
- BABOKの7つの知識領域:
- 要求分析
- 要求の計画と管理
- 要求の引き出し
- 要求分析と文書化
- 要求の評価と検証
- 要求のコミュニケーション
- 基礎能力
>Top
5. BPM and BPMS:
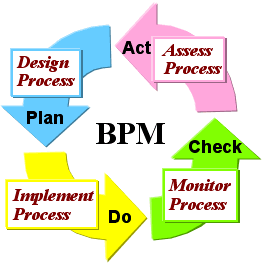 Business
Process Management (BPM) is a methodolory to perform
corporate objective; whose activites are composed of
Design, Modeling, Exection, Monitoring, and Optimization stage.
It can be categorized as the following PDCA cycle:
Business
Process Management (BPM) is a methodolory to perform
corporate objective; whose activites are composed of
Design, Modeling, Exection, Monitoring, and Optimization stage.
It can be categorized as the following PDCA cycle:
- <Plan>:
visualize existing process and design 'to-be'
business process, then
model by trying 'what-if
analysis' on the process:
- <Do>:
execute all steps of the process.
- <Check>:
monitor the process. Business Acitivity Monitoring
(BAM) tool can be used.
- <Act>:
assess and optimize the process identifying
potential bottlenecks or other improvements.
- Business Process Management Suite (BPMS):
- a technology to make IT system to realize both rountine
and nonroutine business processes. It is also a kind of a tool
to realize MDA (Model Driven Architecture) which does not depend
on a particular platform.
- Three layers to attain Service Oriented Architecture (SOA):
- Portal as User Interface layer: Web2.0, RIA,
Flash, etec.
- Process definition: rountine and nonrountine
business flow
- System interface: Enterprise
Application Intergration (EAI), Enterprise Service
Bus (ESB); connecting with hitherto ERP, CRP, and legacy
system.
- BPMS Modeling tool: ARIS, Savvion, etc.
5.
BPMとBPMS:
- BPMとは:
BPM
は企業目標を実現する方法論。その活動はデザイン、モデリング、実行、モニタリング、最適化から成る。以下のPDCAに分類できる。
- <Plan>
既存プロセスの可視化とTo-be業務プロセスの設計、さらに仮説分析試行によるモデリング
- <Do>
プロセスの全ステップの実行
- <Check>
プロセスのモニタリング。BAMツールも活用。
- <Act>
プロセスのボトルネックや改善を特定して、プロセスの評価と最適化
- BPMSとは:
- 定型および非定型業務プロセスを実現するITシステムを作成する技術。特定プラットフォームに依存しないMDAを実現するツール
- SOAを実現するための3層構造
- ユーザ・インタフェース層としてのポータル:Web2.0やRIAなど
- プロセス・デザイン
- システム・インターフェース:EAIやESB
- BPMSモデリングツール:ARIS, Savvionなど
Re: Expansion
of PDCA Cycle:
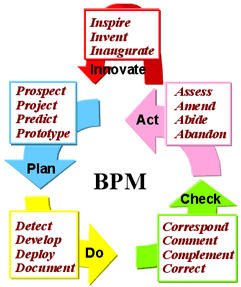 ITC's
PGL describes 'Double Loop Control,' in case to respond risk change
and review the scheme itself of monitoring & control. Mr. Tomohiro
Takanashi, ITC, advocates Strategy-Plan-Do-Learning-Innovation
(SPDLI) Cycle as the double loop control.
ITC's
PGL describes 'Double Loop Control,' in case to respond risk change
and review the scheme itself of monitoring & control. Mr. Tomohiro
Takanashi, ITC, advocates Strategy-Plan-Do-Learning-Innovation
(SPDLI) Cycle as the double loop control.- As an alternative cycle, I'd propose an expanded PDCA cycle to
correspond properly to the original PDCA cycle, which could be
called PDCAI cycle. When Innovation cycle needed, which should
be done after assessment and before the next planning.
- Furthermore, several alliterated words are added to define PDCAI
cycle in more details.
<参考> PDCAサイクルの拡張
- PGLには、リスク変化に対応し、モニタリング&コントロールの仕組みそのものを見直す「ダブルコントロール」が必要であるとしている。高梨智弘氏はこのダブルコントロールとして、SPDLI
(Strategy, Plan, Do, Learning, Innovation) サイクルを提唱
- ここでは、元のPDCAサイクルを拡張した'PDCAI'サイクルを提案したい。Innovationサイクルが必要な場合は、評価の後、次ぎの計画の前に行われるべきである。
- またさらに、PDCAIサイクルを、さらに詳しく定義するために頭韻の用語を追加している。
>Top 6.
Position of BPM in ITC's PGL:
- From corporate management:
- BPR: drastic reviewing of organization and business rule
- Rreflection on distributed specialists who forcuss a part
of processes.
- 1993: "The Reengineering Revolution" by Michael Hammer and
James Champy
- BSC analysis
- Introduction of ISO
- From accountability:
- 1992: COSO framework (Treadway)
- 1995: COBIT
- 2002/7: Sarbanes-Oxley Act: Enron, WorldCom incidents
- 2006: J-SOX in Japan (applicable from 2008/4)
- Management - IT Bridge and 4 piers:
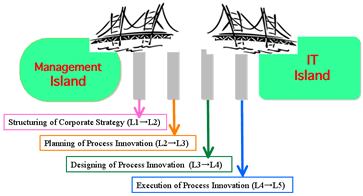
- Who makes the bridge pier from which side?
- Level-1 to Level-3: Business process model defined by SCOR
(Supply Chain Operations Reference-model)
6.
ITC-PGL上でのBABOKの位置付け:
- マネジメントからの要請:
- BPRによる組織やビジネスルールの見直し
- プロセスが分断された分権型専門家組織に対する反省
- 1993:「リエンジニアリング革命」Michael Hammer
- BSC分析手法
- ISOの導入
- アカウンタビリティからの要請:
- 1992:COSO (Treadway委員会) の内部統制フレームワーク
- 1995:COBIT (情報システム監査人) の監査基準
- 2002/7:SOX法 (Sarbanes-Oxley Act) EnronやWorldCom等不正経理事件
- 2006:J-SOX法:金融商品取引法成立(2008/4から適用)
- 経営〜It橋と4本の橋脚:
- 誰がどちら側から橋を架けるのか
- レベル1〜3はSCOR (Supply Chain Operations Reference-model) による業務プロセスモデル
>Top 7. Defective portion
of ITC's Process Guideline:
- ITC's Process Guideline is not enough to bridge management and
IT:
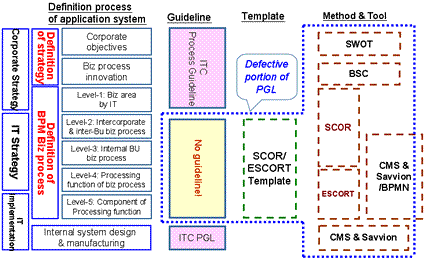
- Source: BPMS Workshop by Masakazu Inoue,
ITC, 2009
7.
ITC-PGLでの欠如箇所:
- ITC PGLとBPMの位置付け:
- <左図> 出典:BPMS研究会、井上正和ITC, 2009
- ITCプロセスのみでは経営とITの橋渡しができない
- <経営戦略フェーズ>
- 戦略定義:
- 経営課題定義
- 業務プロセス改革課題
- <IT戦略策定フェーズ>
- BPM業務プロセス定義:
- L1: IT化業務分野定義
- L2: 企業間、事業間のビジネス課題定義
- L3: 事業内業務プロセス課題
- L4: 業務プロセス処理機能課題
- <IT導入フェーズ>
- L5: 業務処理機能コンポーネント課題
- Level-2からLevel-5のガイドラインが欠如
>Top 8. Synchronization of Management and
IT: (経営とITの同期化)
IT purpose
Management
purpose
KGI
KPI
Contribution by IT
Profitable
IT
儲かるIT
Cost down
Fixed cost
Payroll cost
Process efficiency, offshore
プロセス効率化、オフショア
Other expenses
Inventory reduction, biz transaction, system
cost
在庫削減、事務処理自動化、システムコスト
Variable cost
Raw materials & fuels
Forecast simulation
予測シミュレーション
Infrastructure cost
Communication cost, outsource
通信費、アウトソース
Sales up
Share up
Sales channel
Network sales
ネットワーク販売
M&A
System integration
システム統合
Globali-zation
Network
Global network
グローバルネットワーク
Alliance
Sales channel
販売拠点
Competitive IT
勝てるIT
Branding
Internal
Corporate culture
Intelligence sharing
情報共有
Compliance
Visualized business process
業務プロセス可視か
External
Publicity
Web site, SEO
ウェブサイト, SEO
CSR
Information disclosure
情報開示
Customer satisfaction
QCD
High quality
Quality control system
品質管理
Quick delivery
SCM
サプライチェイン
Agility
Primary response rate
Call center
コールセンタ
Quick response
Business process
業務プロセス
- Contributions by IT systems are related to each business
process.
- Source: BPMS Workshop by Masanori Wada, ITC, 2009.2
>Top 9. Image of Hourglass:
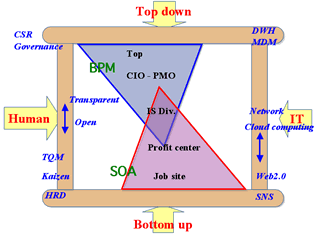 From BPM to SOA:
From BPM to SOA:
- from coarse grain to fine grain
- X-axis:
- Human factor vs. IT factor
- Y-axis:
- Top-down approach vs. Bottom-up approach
- Four corners:
- Human & Top-down:
CSR, Governance
- Human & Bottom-up:
TQM, Kaizen, HRD
- IT & Top-down:
DWH, MDM
- IT & Bottom-up:
Web2.0 & SNS
9.
砂時計のイメージ:
- BPMからSOAへ:
- 粒度を粗から蜜へ
- X軸:人間系対IT系
- Y軸:トップダウン対ボトムアップ
- 4隅:
- 人間系トップダウン:
CSR、ガバナンス
- 人間系ボトムアップ:
TQM、カイゼン、人材育成
- IT系トップダウン:
DWH、マスターデータ管理
- IT系ボトムアップ:
Web2.0、SNS
>Top 10. IT investment comparison (US vs.
Japan):
- Source: Mr. K. Watanabe, ITC, SCC-Japan Chairman, who made the presentation together with me.
 Why
Japanese IT investment is lower in amount and lower ROI than
those of US?
Why
Japanese IT investment is lower in amount and lower ROI than
those of US?
- <US excellent corporations>:
- clear corporate strategy by CEO
- clear business requirements by CIO
- Business process is documented, because of more labor
mobility.
- IT system is properly implemented by Requirements
engineering.
- Higher ROI (Profitable IT investment)
- IT investment ratio to sales: about 3%
- <most of Japanese corporations>
- obscure corporate strategy
- vague business requirements (no CIO)
- business process is not managed, because of less labor
mobility (lifetime employment).
- Only users knows the business process
- Lower ROI
- IT investment ratio to sales: 1% or less
- Effect of IT investment: (research by Prof.
Akihiko Shinozaki)
- Highest score effectiveness:
high IT investment as well as high innovation of organization,
process and human resource.
- 2nd highest effectiveness:
low IT investment but high innovation of organization,
process and human resource.
- 2nd lowest effectiveness:
high IT investment but low innovation of organization, process
and human resource.
10.
IT投資日米比較:
- 以下出典は、渡辺和宣氏、ITCでSCCーJapan代表。今回、小生と一緒に以下趣旨での講演を行った。
- 日本のIT投資は米国に比べて、なぜ低く、また低ROIなのか?
- <米国優秀企業>
- 戦略目標が明確 (CEO)
- ビジネス要求が明確 (CIO)
- ビジネスプロセスがドキュメント化
- 高いROI (儲かる)
- IT投資比率 (対売上高)約3%
- <日本の多くの企業>
- 戦略が曖昧
- ビジネス要求が不明確 (CIO不在)
- ビジネスプロセスが管理されていない
- ユーザ担当者だけが把握
- 低いROI
- IT投資比率 (対売上高)1%以下
- IT投資効果 (篠崎彰彦享受の研究)
- IT投資効果:最高
IT投資高く、かつ組織・プロセス・人の改革度も高いケース
- IT投資効果:2位
IT投資低いが、組織・プロセス・人の改革度が高いケース
- IT投資効果:最下位から2番目
IT投資高いが、組織・プロセス・人の改革度が低いケース
>Top 11. Difficulty of consensus building
among organizations:
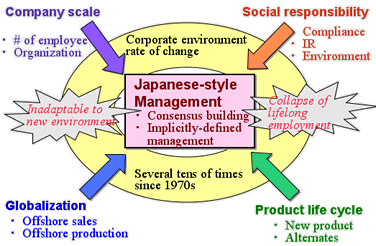 Japanese-style
management has been changed since 1970s due to four-dimensional
changes of environment:
Japanese-style
management has been changed since 1970s due to four-dimensional
changes of environment:
- Growth of company scale
- Globalization
- Increase of social responsibility
- Shorter product life cycle
- Thus, the past management style such as group consensus building
and implicitly-defined management have been changed.
11.
組織間合意形成の困難性:
- 、以下4次元の環境変化により、
日本的経営スタイルは1970年代以降変化
- 企業規模の成長
- グローバル化の進展
- 社会的責任の増大
- 製品ライフサイクルの短命化
- さらに以下の日本的経営の特徴も変化を余儀なくされている。
- 集団的意志決定方式
- 非明示的な管理方式
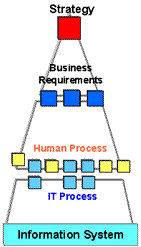
>Top 12. Hierarchial structure of process:
- Processes should be designed hierarchically by top-down approach
from Level-1 through Level-5:
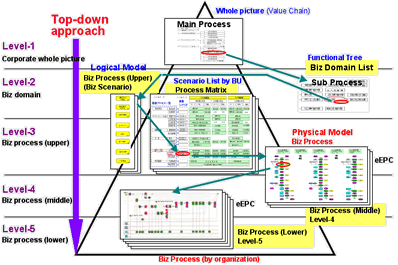
- EPC = Electronic Product Code
- Hierarchical Process Model by Process Reference Model:
- Corporate strategy can be discomposed into business process
by each step of detailing process, which has the following merit:
- Able to concentrate in analysis and design of hierarchical
level of each phase.
- Project management gets easier.
- Less number of man-hour
in case of outsouced consultant.
- High quality by interview using models rather than hearing.
12.
プロセス階層構造:
- プロセスはトップダウンによりレベル1からレベル5まで階層的に設計される (左図):
- プロセス参照モデルのプロセス階層モデル (左図)
: <事業戦略の反映>
- レベル-0:
- 事業戦略
- <事業部>
- 顧客要求納期順守、
製品在庫の削減
- レベル-1:
- 戦略課題
- <営業、向上>
- 見込生産から受注生産へ
- レベル-2:
- 業務要求・業務課題
- <特定営業、向上>
- 製品受領組立生産、
精度の高い納期解答
- レベル-3:
- 業務プロセス・プロセス改革要求
- <業務プロセス上位>
- 逐次計画、組立計画追加、
在庫引当納期解答
- レベル-4:
- 改革と標準化が反映した業務プロセス
- <業務プロセス中位>
- 組立日程計画、引合・受注時に納期回答
- レベル-5:
- 業務プロセス・情報システム
- <業務プロセス下位>
- 能力負荷調整シミュレーションシステムによる納期解答(ATP=Available To Promise)
- レベル-6:
- 情報システム・コンポーネント
- <業務プロセス支援機能>
- シミュレーション・パラメータ設定、利用可能在庫計算、引当
- 戦略は段階的詳細化によって業務プロセスに落とし込める
- フェーズに沿った階層レベルの分析・設計に集中できる
- プロジェクトマネジメントが容易
- 外部コンサルタント工数が少なくて済む
- ヒアリングではなくモデル利用のインタービューによる高い品質
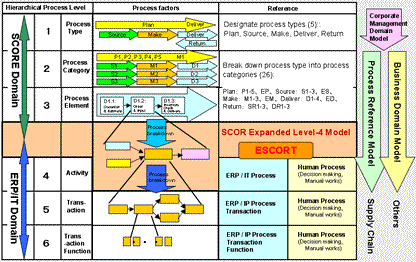
>Top 13. Integration
of BPM, PMBOK, BABOK & Requirements
Engineering:
- Strategy, Process, Requirements, Project Management should
be integrated:
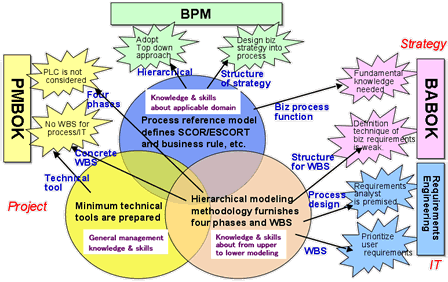
- GUTSY-4: Hierarchical Four Modeling Methodology
- ESCORT: Process Reference Model
- PLC = Project Life Cycle
- Concept of Process Innovation, including IT Strategy:
- Confirm corporate plan and business strategy:
- market analysis, SWOT, KGI, KPI
- Resolve to-be model of management function:
- corporate management
- purchase
- accounting
- management information
- production management
- sales & marketing
- Clarify requirements for IT system:
- requirements for various IT systems
- Establish long-term information strategy:
- fit & gap between as-is and to-be models
- roadmap of IT strategy
13. BPM,
PMBOK, BABOKおよび要求工学の統合
- 階層的4モデリング方法論 (GUTSY-4)とプロセス参照モデル (ESCORT)による戦略、プロセス、要求、プロジェクトマネジメントを統合する。
- プロセス改革構想
- 確認:経営計画・事業戦略
- 市場環境分析
- SWOT
- 分解:あるべき経営機能
- 経営管理
- 購買
- 会計・財務
- 経営情報
- 生産管理
- 営業・マーケティング
- 明確化:システムへの要求
- 情報システム支援要求
- 構想:長期的情報戦略
- フィット&ギャップ
- IT戦略ロードマップ
Ref
- >Top Six major movements in the evolution of SCM. (Wiki, 2009/3, etc.)
- Creation Era:
Concept of SCM was of great importance since early 20C by the
creation of assembly line.
- Integration Era:
highlighted by EDI systems in 1960s and developed by ERP systems
through 1990s.
- Globalization Era:
Since1980s, creating more value-added
and reducing costs through global sourcing.
- Specialization Era (Phase-1):Outsource manufacturing & distribution.
In 1990s abandoned vertical integration, sold off non-core
operations and outsourced. Multiple OEMs and vendor-managed
inventory (VMI)
- Specialization Era (Phase-2): SCM as a service
Specialization within in SCM with the inception of transportation
brokerages, warehouse management, and non asset based carriers,
etc.
- SCM 2.0:
Like Web2.0, SCM2.0 follows this notion into supply chain operations:
combination of processes, methodologies, tools and delivery
options due to the effects of global competition, rapid price
fluctuation, short product life cycles, expanded specialization,
near/far and off shoring, and talent scarcity.
- Supply chain business process integration:
Shared information between supply chain partners can only be fully
leveraged through process integration. The key supply chain processes
are:
- CRM
- Customer service management
- Demand management
- Internal & external collaboration
- Lead time reduction initiatives
- Tighter feedback from customer and market demand
- Customer level forecasting
- Order fulfillment
- Manufacturing flow management
- Supplier relationship management
- Product development and commercialization
- Returns management
- Theories of SCM:
- Resource-based view (RBV)
- Transaction Cost Analysis (TCA)
- Knowledge-based view (KBV)
- Strategic Choice Theory (SCT)
- Agency theory (AT)
- Institutional theory (InT)
- Systems Theory (ST)
- Network Perspective (NP)
- Components of SCM:
more management components or increasing the level of each
component can increase the level of integration of business process
link:
- Planning and control
- Work structure
- Organization structure
- Product flow facility structure
- Information flow facility structure
- Management methods
- Power and leadership structure
- Risk and reward structure
- Culture and attitude
- <出典:Wiki, 2009/3等 >
- SCMの6つの動き
- 創生期:
- 統合期
- グローバリゼーション期
- アウトソース期
- SCM as a Servie
- SCM 2.0
- サプライチェインとビジネスプロセスの統合:
特に、以下のプロセスがキー
- CRM
- カスタマーサービス管理
- 需要管理
- 内部外部協同
- リードタイム短縮
- 需要への即対応
- 顧客レベル予想
- 注文充足
- 生産フロー管理
- 供給者関係管理
- 生産開発と商用化
- 返品管
- SCMの理論分野:
- Resource-based view (RBV)
- Transaction Cost Analysis (TCA)
- Knowledge-based view (KBV)
- Strategic Choice Theory (SCT)
- Agency theory (AT)
- Institutional theory (InT)
- Systems Theory (ST)
- Network Perspective (NP)
- SCMの要素:
さらに管理コンポーネントとの統合要素
- 計画とコントロール
- ワーク構造
- 組織構造
- 生産フロー設備構造
- 情報フロー設備構造
- 管理方法
- 権限リーダーシップ構造
- リスク・報償構造
- 文化風土
Title |
Report from BPMS Workshop |
BPMS研究会報告 |
|---|---|---|
Index |
|
|
Why? |
|
|
Resume |
要約 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 0. Introduction:
|
0. 序章:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 1. Status-quo of IT Coordinators:
|
1. ITコーディネータ(ITC) の現状:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 2. Who makes Request For Proposal (RFP)?:
|
2. 要求仕様書は誰が作成するのか?:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 3. Requirements Engineering:
|
3. 要求工学とは:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 4. Busienss Analysis Body Of Knowledge (BABOK):
|
4. BABOKとは:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 5. BPM and BPMS:
|
5. BPMとBPMS:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Re: Expansion of PDCA Cycle:
|
<参考> PDCAサイクルの拡張
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 6. Position of BPM in ITC's PGL:
|
6. ITC-PGL上でのBABOKの位置付け:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 7. Defective portion of ITC's Process Guideline:
|
7. ITC-PGLでの欠如箇所:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 8. Synchronization of Management and IT: (経営とITの同期化)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 9. Image of Hourglass:
|
9. 砂時計のイメージ:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 10. IT investment comparison (US vs. Japan):
|
10. IT投資日米比較:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 11. Difficulty of consensus building among organizations:
|
11. 組織間合意形成の困難性:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 12. Hierarchial structure of process:
|
12. プロセス階層構造:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 13. Integration of BPM, PMBOK, BABOK & Requirements Engineering:
|
13. BPM, PMBOK, BABOKおよび要求工学の統合
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ref |
|
|