
Cat: SCI
Pub: 2000
#: 0719
Yotaro Hatamura (畑村洋太郎)
07812u/18212r
Titile
Study of Failure
失敗学
Tag
; 2007 problem; Connive; Date & title; Failures about 300; Failures grow; Frequent failures; Hierarchical structure; Home truth; Indemnification; Lifetime 30 years; More failures; Museum of failure; Potential failure =Potential loss; Punitive penalty; Strong main route deteriorates; Thinking plane; ; ;
Why
- A proverb of "Every failure is a stepping stone to success,"
or "Learn from one's mistakes" is a profound lesson.
- Y. Hatamura, Prof. of mechanical engineering of Univ. of Tokyo
emphasizes the importance of lessons from failures; because there are hidden essences of technology which may lead to more creative engineering.
- 「失敗は成功のもと」「失敗から学ぶ」という諺は深淵な教訓を秘めている。
- 畑村東大工学部機械工学の教授は、失敗からの教訓を重視している。そこにはより創造的なエンジニアリングにつながる可能性のある隠れた技術の本質がある。
Résume
Remarks
>Top 0. Introduction:
- Lesson of failures is information conveyed from shadow of the world:
- an negative image:
detour, unnecessary experience, or a kind of taboo or concealment.
- story of 'Home truth' can easily enter listener's mind than success story.
0.
序:
- 失敗の教訓は、陰の世界の情報伝達:
- 負のイメージ:
それは回り道、不必要なもの、忌み嫌われ、隠すべきものと見なされる。
- 「痛い目」の話は成功した話よりずっと聞き手の頭に入る
>Top 1. Historical three major accidents:
- 1940: Falling of the suspension bridge in Tacoma, Washington
- Cause: autonomous vibration by whirl of wind.
- 1952: Falling of the world first passenger plane 'Comet' of UK
- Cause: metal fatigue
- endurable 1 million times by the power of 10, but only 100 times by the power of 20.
- 1942-46: Crash of transport ships named 'Liberty' of US (10,000 tonnage) during voyage in northern sea.
- Cause: cold brittleness
- elasticity of steel is lost at 0 degree C.
- 1985: Case of Seikan Tunnel 53.85km(between Aomori and Hokkaido)
- lesson of tunnel fire disaster
- escape tunnel
- power car for rescue
- smoke scavenger system
1.
歴史上の三大事故の教訓:
- 1940: WA州タコマの吊り橋の崩落:
- 原因: 自動震動
- 1952: 世界初のジェット旅客機コメットの墜落(英国):
- 原因: 金属疲労
- 1942-46:輸送船リバティ (米国)の崩壊
- 原因: 低温脆性
- 1985開通: 青函トンネルのケース:
- トンネル火災事故の教訓
- 避難用トンネル
- 救助用動力車
- 排煙装置
>Top 2. Kinds of failures:
- There is hierarchical structure among failures: the upper failure can be assigned to social causes, while the lower to personal causes.
- There are also two kinds of failures: good ones and bad ones.
- Good failure:
- small cluster of failures from which we can have experiences or lessons.
- Bad failure:
- Neither experiences nor lessons can be obtained, or simple repetition of failures by negligence or miss judgment.
- Hierarchical causes of failure:
-
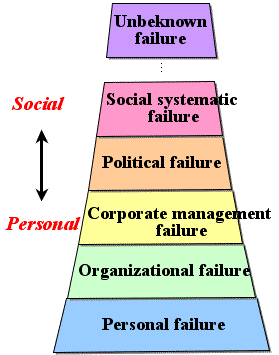
- Kinds of failure :
2.
失敗の種類:
- 失敗には階層性がある。
- 上位階層ほどより社会的原因、下位階層ほどより個人的原因。未知の失敗原因は別格
- 良い失敗:
- 学ぶべき経験のある小さな失敗群
- 悪い失敗:
- 何も学ぶことができず、単なる不注意や誤判断などから繰り返される失敗
- 個人にとっては意味があっても、多大な被害を被る失敗
- 失敗原因の階層性: (左図)
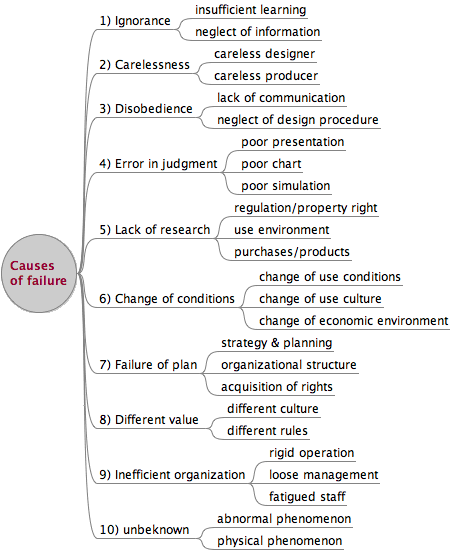
- 失敗の原因:
- 無知:
- 学識不足
- 伝承無視
- 不注意:
- 設計者
- 生産組織
- 手順の不遵守:
- 連絡不足
- 設計手順
- 誤判断:
- ポンチ絵段階
- 計画書段階
- 仮想演習不足
- 調査検討の不足:
- 規制・特許
- 使用環境
- 購入品・製作
- 制約条件の変化:
- 使用条件の変化
- 使用文化の変化
- 企画不良:
- 戦略企画
- 組織構成
- 権利取得
- 価値観相違:
- 異文化
- 規範の違い
- 組織運営不良:
- 運営の硬直化
- 管理の緩み
- 構成員の疲労
- 未知:
- 異常現象の発見
- 物理現象の発見
>Top 3. Frequent causes of failure:
- Hidden relevance between parts:
- Eg.: heat of a particular part aversely affects the other part.
- Design change in transitu:
- miss or leak of arrangement
- Control division is indispensable.
- CE (Chief Engineer): responsible supervisor for a new car (Toyota)
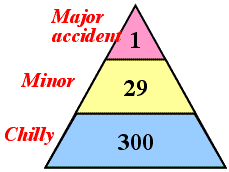
- >Top Failures grow: Law of Heinrich:
frequency of accidents
- major disaster: 1
- small accidents: 29
- chilly experiences: 300
- Failure can be estimated:
- Propagation of failure:
- Cause of failures tends to be hidden:
- 2000: concealment of recall by Mitsubishi Motors.
- Cause of failures tends to be simplified:
- "Extinguish fire in case of earthquake"
- Cause of failure tends to be changed:
- Dispensing miss of drugs
- 1986: Disaster of Chernobuiri nuclear plant:
- Failure tends to be mythified:
- Tragic Warship Yamato
- Failure information tends to be localized:
- Failure information tends to be attenuated:
- Objective failure information is not useful:
- Failure information should be specified:
- Phenomenon
- Background
- Progress
- Cause (probable)
- Management
- Summation
- Explicit knowledge (record, propagation)
- Appointment of young (girl) listener:
- the listener should not criticize thefailure:
3.
よくある失敗の原因:
- 部品間の隠れた関連:
- 例:特定部品の熱が他の部品へ悪影響
- 設計の途中変更:
- 手配漏れ:
- コントロール部門が必須
- トヨタのCE (チーフエンジニア) 新車の責任者
- 失敗は成長する。
ハインリッヒの法則:
- 重大災害: 1
- 軽災害: 29
- ひやりとした体験: 300
- 失敗は予測できる:
- 失敗の伝わり方:
- 失敗原因は隠れたがる:
- 2000: 三菱自動車のリコール隠し
- 失敗原因は単純化される:
- 地震のときは消化せよ
- 失敗原因は変化しやすい:
- 投薬ミス
- 1986:チェルノブイリ原発事故
- 失敗は神話化されやすい:
- 悲劇の戦艦大和
- 失敗情報はローカル化しやすい:
- 失敗情報は減衰しやすい:
- 客観的失敗情報は役立たない:
- 失敗情報は知識化しなければならない
- 事象
- 背景
- 経過
- 原因
- 対処
- 総括
- 知識化(記録、伝達)
- 若い女性を聞き取り役に:
- 失敗を批判しない
>Top 4. Whole understanding:
- 1944: Explosion of Aircraft carrier 'Ohtorii'
- real veteran:
- pseudo veteran:
connives or neglect
problems which seems unable to react.
- Importance of entire understanding:
- understanding causality of a phenomenon.
- Virtual experience of failure:
- Traditional craftsmanship:
- Eg: Traditional metallurgy 'Tatara method': sword smith of Japanese swords
4. 全体を理解する:
- 1944: 空母大鳳の爆発:
- 本物のベテラン:
- 偽のベテラン:
自分が対応できない問題は無視し、見て見ぬふり
- 全体を理解することの重要性:
- 仮想失敗体験:
- 伝統製法:
- 伝統的な冶金学"たたら製法": 日本刀の製作
>Top 5. Failure yields creativeness:
- There should be neither 'logical thinking,' nor 'reasonable thinking.' from the beginning.:
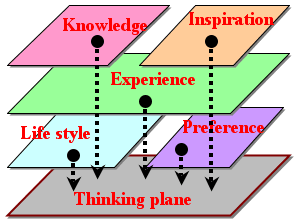
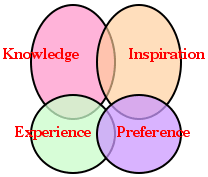
- >Top Thinking plane:
Many seeds of ideas are falling on the thought plane from various planes of knowledge, inspiration, experience, preference, and life style.:
- It is assumed "Isolated discrete hypothesis":
- Such try and error method could be called 'verification of hypothesis.'
- Practices of hypothesis are useful.
- Uncompromising cutoff of seeds of ideas is necessary.
- Idea note:
- Write down random seeds of ideas on a note.
- Make context or scenario among the ideas.
- Make concrete solution for each issue.
- Consider further development of the idea.
- >Top Date of creation and title of the contents are important.
- Front plan and back plans
- Back plans:
- Hesitation memo
- Reason for decision memo
- Conclusion memo
- Self-reflection memo: summary
- Message memo: remarks or warning
5.
失敗が創造を生む:
- 「論理思考」も「筋道思考」も最初からは存在しない。
- 思考平面:
アイデアの種がさまざまな平面 (知識、ひらめき、経験、好み、生き方)から思考平面に落ちてくる。
- 「孤立分散仮説」ともいうべき
- この試行錯誤は「仮説立証」と呼ぶ。
- 仮想研修は有効。
- アイデアの種の大胆の切り捨ては必要。
----------------------------
- Re: 思考平面 (Hermann model風)
- アイデアノート:
- ばらばらの思いつきの種をノートに書く
- 脈絡をつける。
- 個々の問題を解決する。
- さらなる発展を考える。
- 日付と表題は重要
- 表プランと裏プラン
- 裏プラン
- 迷いメモ
- 決定理由メモ
- 結果メモ
- 省察メモ
- 伝承メモ
>Top 6. To seize failures
three-dimesionally:
- Potential failure is potential loss:
- To make use of failure is to raise market value of BS.
- Avoid thought-stopping situation.
- Experience of hydroplaning phenomenon.
- >Top Effectiveness of plea-bargaining of US:
- Pursue of real cause subject to indemnification
- Punitive penalty against conscious neglect.
- In Japan, compensation is around real penalty.
6. 失敗を立体的に捉える:
- 潜在的失敗は、含み損:
- 失敗を活かすことはBSの時価評価を上げる
- 思考停止を避ける
- ハイドロプレーン現象の体験
- 米国の司法取引制度の有効性:
- 免責を条件に真の原因追及
- 未必の故意に対する懲罰的罰則
- 日本では実損害程度の賠償
>Top 7. To avoid fatal failure:
- Maturity of technology and acquisitive attitude:
- Operation strictly depends on the manual.
- Training according to manuals:
- Teach what happens if deviated from the manual.
- Eg: case of JCO criticality accident.
- Eg: 2000: case of hydroxylamine factory of Nisshin-Kako
- >Top Evolution of technology:
- lifetime: about 30 years (almost same as a human activity)
- Change of coherence according to maturity of technology:
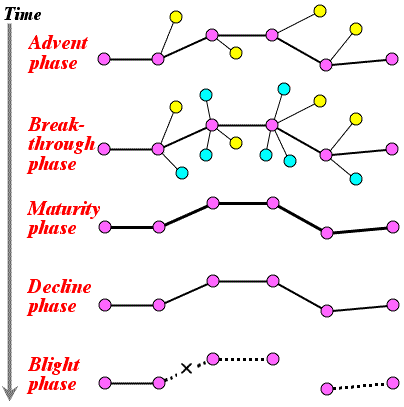
- At the maturity phase, only the main route can survive, truncating alternative routes, and at the decline phase it becomes fragile route, and then ruins.
- >Top Ironically, rationalization leaving only strong main route leads to deteriorates assurance of the mail route itself.
- >Top Re: 2007 problem: loss of experience and know-how by massive retirement of veteran baby boomer generation in Japan.
- Pursue of effectiveness make poorer accumulation of knowledge and experience stored in the organizational tree structure.
7. 致命的失敗をなくす:
- 技術の成熟と利益追求:
- 操業はマニュアル通りに
- マニュアル教育:
- マニュアルからはずれた場合の教育必要
- 例:JCO臨界事故
- 技術の進化:
- 寿命は約30年(人間の活動と同じ)
- 技術の成熟に伴う脈絡の変化:
- 萌芽期
- 発展期
- 成熟期
- 衰退期
- 破滅期
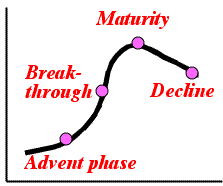
- 成熟期になると選択肢は切り捨てられてメインルートだけが許容され、衰退期にはひ弱なルートとなり、破滅する。
- 皮肉にも、強固なメインルートのみを残す合理化が、メインルートの確実性まで細めることになる。
- 注)2007年問題:
大量のベテラン団塊世代の退職による経験ノウハウの喪失
- 効率化の追求は、組織の樹木構造に蓄えた知識経験をますます貧しいものにする。
>Top 8. Concept of museum of failure:
- Necessary information of failure is about 300.
- 20,000 samples are too much.
- Database of failure:
- Technical background
- Economical background
- Psychological background
- Concept of 'Museum of failure': >https://www.museumoffailure.se/
- Collection of failure information
- Publish of failure information
- Display and education of failure information
- Real experience of failure
- Consultation of failure
- Study of failure
8.
失敗博物館構想:
- 必要な失敗情報はせいぜい300
- 20,000もの失敗情報は不要
- 失敗情報データベース:
- 技術的背景
- 経済的背景
- 心理的背景
- 失敗博物館の構想:
- 失敗情報収集
- 失敗情報発信
- 失敗情報伝達
- 失敗実体験
- 失敗コンサルティング
- 失敗学研究
Comment
- >Top Obviously there are more failures than a success story; which means more lessons than an ecstasy.
- There is an award for invention, but there isn't one for failure: why not establish a kind of award for useful failure?
- The story of Apollo 13 is described as "a successful failure",
or "a
glorious failure."
- 明らかに成功物語より失敗の方が多い。つまり有頂天より教訓の方が多いということである。
- 発明には賞があるが、失敗にはない。有効な失敗には何か賞を設けるべきではないか?
- アポロ13号は"成功した失敗"また"栄光の失敗"と表現されている。
 |
Cat: SCI
|
|
Yotaro Hatamura (畑村洋太郎) |
07812u/18212r |
Titile |
Study of Failure |
失敗学 |
|---|---|---|
Tag |
; 2007 problem; Connive; Date & title; Failures about 300; Failures grow; Frequent failures; Hierarchical structure; Home truth; Indemnification; Lifetime 30 years; More failures; Museum of failure; Potential failure =Potential loss; Punitive penalty; Strong main route deteriorates; Thinking plane; ; ; | |
Why |
|
|
Résume |
Remarks |
>Top 0. Introduction:
|
0. 序:
|
>Top 1. Historical three major accidents:
|
1. 歴史上の三大事故の教訓:
|
>Top 2. Kinds of failures:
|
2. 失敗の種類:
|
>Top 3. Frequent causes of failure:
|
3. よくある失敗の原因:
|
>Top 4. Whole understanding:
|
4. 全体を理解する:
|
>Top 5. Failure yields creativeness:
|
5. 失敗が創造を生む:
|
>Top 6. To seize failures three-dimesionally:
|
6. 失敗を立体的に捉える:
|
>Top 7. To avoid fatal failure:
|
7. 致命的失敗をなくす:
|
>Top 8. Concept of museum of failure:
|
8. 失敗博物館構想:
|
Comment |
|
|