What is SHARABLE? |
Cat: ECOPub: 2006#:0622a |
|
Shumpei Kumon |
06709u/18214r |
Title
What is SHARABLE?
通識/智本論
Author
Shumpei Kumon
公文俊平
Published
June 2006
2006年6月
Index
- Hypothesis:
- Commodities and Capital:
- Sharables and Chihon:
- Kind of information:
- Attribute of sharables in cyberspace:
- RDF (Resource Description Framework):
- URI, URL, URN:
- Structure of Sharables:
- Contradiction of Information Society:
- Mechanism how to share sharables:
- Data and metadata:
- Third order order:
- "Netpital" in Information society:
- Property born in Information society:
- Substructure and Superstructure:
Why?
- Prof. Shumpei Kumon of Rep. of Glocom, IUJ, tries to expand key
concept of "The Capital" written by Karl Marx to analyze
capitalism, applying to the information age. I'd say that this challenge
could be expressed as The Capital 2.0.
- He proposes that Merchandise (Waren) circulated in the
market corresponds to "Knowledge shared in the network",
which could be named "sharable".
- Similarly, there should be a corresponding term of Capital in the information society; which he proposes "Chihon"
in Japanese, but has note yet proper English term at the moment.
(He murmured "Intel " would be appropriate, reminding interplace corresponds to marketplace.
- Remark:
What about "Netpital" (Net
+ Capital), which reminds would Netizen (Network citizen) instead
of Citizen?
- A dictionary says, "Capital is material wealth used or
available for use in the production of more wealth." Then
a new term corresponding to capital should be "Knowledge
used or available for use in the product of more knowledge"
- 国際大学Glocom代表の公文俊平教授は、カール・マルクスが資本主義分析のために書いた資本論の概念を、情報社会に適用しようと概念を拡張しようとしている。これは、いわば、資本論2.0とも言うべき挑戦と思われる。
- 曰く、市場において流通する商品に相当するものは、ネットワークで通有される知識で、これを「通識」を言えよう。
- 同様に、情報社会における資本に相当する言葉を、日本語では「智本」と言うが、まだ対応する英語の適訳がない。市場 (Marketplace)を智場
(Interplace)と表現した連想で、Intelをつぶやいたが...
- 注)では、シチズンがネチズン(Netizen)を連想させる Netpital (Net + Capital)というのは如何だろうか?
- 辞書によれば、「資本とは富のより多くの生産のために使用されたあるいは使用に供される物質的な富である」であるならば、智本とは、「知識のより多くの生産のために使用されたあるいは使用に供される知識である」と言えよう。
Tag
; Accessibility-Findability-Usability ; Folksonomy; Knowledge neuron; Netpital; Ontology; RMT; Sharable; Spime; The Capital; URI-URL-URN;
Summary
要約
>Top
0. Hypothesis:
- Throughout the human history, main forms of production have changed
as follows. During these processes relative weight of production
of knowledge or information has constantly increased.
- Self production: to consume or use for oneself
- Tribute production: to pay tribute or tax for upper class
- Commodities production: to sell consumers as commercial products.
- Commons production: to produce for community
0.
仮説:
- 人類史の中では、生産の四基本形態の主流は以下の変遷が見られる。知識・情報の生産のウェートは一貫して増加する。
- 自家生産: 自分で消費・使用する
- 貢納生産: 公的生産、年貢・納税等階層の上位に供与する
- 商品生産: 他人に販売する
- 共的生産: 仲間生産
>Top
1. Commodities and Capital:
- Opening paragraph of The Capital Vol-1:
by Karl Mark
"The wealth of those societies in which the capitalist mode
of production prevails, presents itself as "an immense accumulation
of commodities," its unit being a single commodity. Our investigation
must therefore begin with the analysis of a commodity ..."
- Self-replication:
- G - W -G' ; where, Geld (Money) - Ware (Commodity) - mehr(increase)
Geld
- Game of Wealth:
- Here, knowledge or information is an object of ownership, which
is produced and sold as commodity.
1.
商品と資本:
- 資本論の冒頭:
「資本制的生産様式が支配的な社会の富は、個々の商品をその要素とする「巨大な商品集積」の形をとっている。従って。我々の研究は商品の分析から始まる。...」
- 財・サービスの自己増殖:
- G-W-G': 貨幣 - 商品 - 貨幣'
- 富のゲーム:
- そこでは知識・情報も所有権の対象。商品として生産・販売される。
>Top 2. Sharables and Chihon (like Capital in information age):
- The form of knowledge in the information age would be sharable:
- knowledge or information produced by humans or machines to
be shared by the community from the beginning.
- Dynamic self-replication may occur:
- K - S - K'; where Knowledge - Sharable - increase of Knowledge
- Game of Knowledge:
- Process of sharing and replication of sharables.
- Right of Share: base of right of sharables.
- Other commodities or services are tend to be object of right
of share.
2.
通識と智本:
- 情報社会の「智」の要素形態は「通識」である。
- 最初からヒトやマシンによる通有を前提として生産される知識・情報
- その自己組織運動体が智本:
- K - S - K'、ここでは Knowledge - Sharable - Knowledgeの増加
- 智のゲーム:
- 通識の通有過程と書き換え過程
- 通識通有の基盤となる権利:通有権?
- そこでは、一般の財・サービスも通有権の対象とされがち
>Top 3. Kind of information:
- Primary information (Environment information):
- Geography, landscape, environment
- Object information
- 'What' information: existence, material information:
- 'When-Where' information: movement
- Secondary information (Document information):
- Sample information: specimen
- Zoo, animal or soldier under surveillance ('findability')
- Expression or record of primary information such as document,
picture, movie
- written record, contract
- various recording media or genre
- memo, contract, newspaper, book
- Web site, blog, email
- new genre produced by mobile (URL in cyberspace)
3.
情報の種類:
- 一次情報: (環境情報)
- 地理・景観情報、環境の形状
- 客体情報:
-
存在: 特性情報、何がある、何である
- 所在: 移動情報、いつ、どこにある
- 二次情情: (ドキュメント情報)
- 標本:客体の情報源
- 動物園、監視カメラ内動物・兵士
- 文書・画像・動画等一次情報の表現・記録
- 文字による記録媒体、契約
- 様々な記録媒体とジャンルをもつ
- メモ、契約者、新聞、書物
- Webサイト、ブログ、電子メール
- モバイルの普及が生む新ジャンル
>Top 4. Attribute of
sharables in cyberspace:
- Accessibility:
- unique URI in the Web, having several inbound links and outbound
links
- inbound links: linked by other sharables or places
- outbound links: attached URI of other sharables
- Findability:
- several key words or tag; possibility to be found
- Usability:
- searched "sharable" is freely shared and used
- For meaningful sharables:
- Shift of basic viewpoint: power shift from producer basis
to user basis
- To be wary of deception of malicious producers of sharable
- To avoid jerk of incapable or narrow-visioned producers
4.
サイバースペース内の通識の属性:
- アクセシビリティ (可接性) :
- Web内の一つのURL、いくつか入リンクと出リンクを持つ
- ファインダビリティ (可見性) :
- いくつかのキーアドやタグを持つ。発見可能性
- ユーザビリティ (可用性):
- 見つかった通識は、それにアクセスして自由に通有、使用できる
- 通識を意味あるものにする上で
- 基本的視点の転換:生産者本位から使用者本位へパワーシフト
- 邪念ある通識生産者に騙されないために
- 無能な、視野の狭い生産者に困らされないために
>Top Knowledge neuron (知のニューロン)
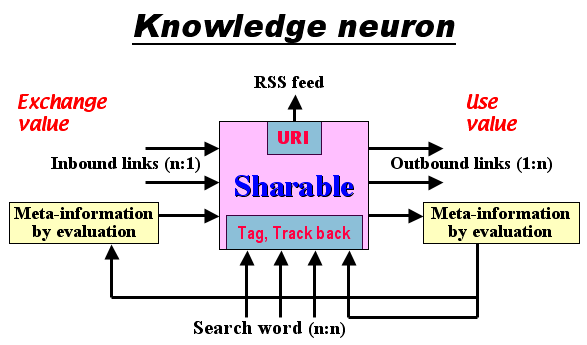
-
Keyword:
- meta-information which mutually links sharables.
- Search engine selects appropriate keyword and connects inbound
link there.
- Tag:
- meta-information which is attached to the sharable constitutes
inbound links.
- can be attached by XML
- Bookmark:
- users of the sharable make inbound link to it.
>Top 5. RDF (Resource
Description Framework):
- Conceptual connection between sharables (URI's):
- Triple structure as basic factor:
- Subject - Verb (predicate) - Object
- Thing (System) - attribute - value
- can be identified by URI
- Triple of Japanese language; but transitive verb is used in
English.
- Concerning an elephant, its nose is long.
- Concerning today, the weather is fine.
- Concerning Mr. A, his boss is Mr. B
- Concerning a dog, its affiliation is mammal.
5. RDF (Resource Description Framework):
- 通識 (URI)相互間の概念的なつながりの指定
- 基本要素としての三部構造体:
- 主語~動詞 (述語)~目的語
- 事物 (システム)~属性~値
- すべてURIで指定可能
- 日本語の三層構造文
- 象は~鼻が~長い
- 今日は~天気が~よい
- A氏は (の)~上司が (は)~B氏だ
- イヌは~所属が~哺乳類だ
>Top 6. Schemes such
as URI, URL, URN:
- Reference: RFC3986
- URI, URL, URN:
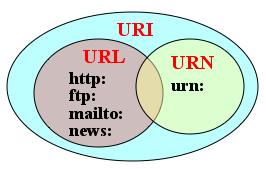 URI= Uniform Resource Identifier; a method of identifying a resource by official schemes on the Web. About 30 kinds of official
URI schemes are registered, including tel: in mobile Web, and javascript: ,
etc.
URI= Uniform Resource Identifier; a method of identifying a resource by official schemes on the Web. About 30 kinds of official
URI schemes are registered, including tel: in mobile Web, and javascript: ,
etc.- URN= Uniform Resource Name;
a method of identifying a resource by universal name,
which is effective even if the resource is shifted or extinct.
There is the only scheme of urn: coupled with following NID (Namespace ID). ISBN code is also
a URN of books.
- URL (Uniform Resource Locator)
- http:// user: pass@ www.7key.jp :80
nw/urluri.html
- Protocol: http://
- User name: user:
- Domain name of Web server: www.7key.jp
- Port Number: :80
- File pass: nw/urluri.html
6. URI, URL, URNというスキーム:
- 参考: RFC3986
- URI, URL, URN:
- URI:
Web上でリソースを識別する手段をいう。
公式のURIスキームは、IANAに30ほど登録済。携帯電話のWeb用のtel: やjavascript: など
- URN:
名前という普遍的な属性でリソースを識別する。リソースが移動・消滅しても有効
urn:という1つのスキームで、それに続くNID (Namespace ID)とセットでURN名前空間を定義する。
書籍のISBNコードもURNである。
- URL: アドレスなど具体的なアクセス手段によってリソースを識別する。
- http:// user: pass@ www.7key.jp :80
nw/urluri.html
- プロトコル: http://
- ユーザ名 (省略可) : user:
- Webサーバのドメイン名: www.7key.jp
- 使用ポート番号 (80なら省略可) : :80
- ファイルのパス名: nw/urluri.html
>Top 7. Structure of
Sharables:
- Centralized control
type:
- Ontology = Taxonomy
+ Rule of Inference:
- Ontoloagy:
- one of technique to structure sharables (URI)
- the meaning each sharable has is not questioned. Understanding
of the truth is not requested. (T.B.Lee)
- It is inferred only by external standard specified by the taxonomy.
- Each ontology is decided from top-down or centralized outside
control.
- If plural ontology coexist, it is correlated by specified equivalence
or difference.
- Taxonomy:
- integral of various triples
- designation of type/class of sharables (URI)
- designation of basic relation between classes, ie, inclusion,
differentia, copulation, equivalence
- Rule of Inference:
- derivation of derived relation between classes
- syllogism
- Grass-root distributed type:
- >Top Folksonomy:
- decentralized bottom-up trials in opposition to top-down ontology.
- Folksonomy type: tag, SB
- Complete centralized is impossible, but complete distributed
is meaningless.
- Opposing two mindsets?:
- Internet:
- Intelligent vs. Stupid
- Bell's head vs. Net heads
- Sharable:
- Liberian's controlled vocabulary vs. Netizen's folksonomy
- Semantic Web vs. SS (Scale Space?)
7.
通識の構造化:
- 集中統制型:
- オントロジー=タクソノミー+推論規則:
- オントロジー:
- 通識 (URI)の構造体化のための一手法
- 各通識それ自体のもつ意味は問わない。真の理解は求めていない。(T.B.Lee)
- あくまでもタクソノミーの指定する外的標準だけを頼りに推論する。
- 各オントロジーの決定は、トップダウンないし外から集権的になされる。
- もし複数のオントロジーが併存していれば、同値・差異関係の指定によって関連される。
- タクソノミー:
- 様々なトライプルの総体
- 通識 (URI)のタイプ/クラスの指定
- クラス間の基本的関係の指定:包含、差異、連結、同値等
- 推定規則:
- クラス間の派生的関係の導出
- 三段論法
- 草の根分散型:
- フォークソノミー:
- トップダウン型のオントロジーに対抗するボトムアップの分権的な試み
- フォークソノミー方式:タグ、SB
- 完全集中は不可能、完全分散は無意味
- 対立する2つのマインドセット:
- インターネット:
- インテリジェント 対 スチュピッド
- ベルヘッズ 対 ネットヘッズ
- 通識の分類:
- 司書の統制語彙 対 智民のフォークソノミー
- セマンティックWeb 対 SS
>Top 8. Contradiction
of Information Society:
- Sharable vs. Private knowledge
- Public interest vs. Private interest
- concerning Disclosure of information (Glasnost)
- economic value of information: inversely proportional to the
number of people who have known.
- possible abuse by getting private knowledge
- possible loss of public interest by leaving private knowledge
undistributed.
- Insider and outsider could not be clearly divided.
8.
情報社会の基本矛盾:
- 通識対私識
- 公益対私益
- 情報公開を巡って
- 情報の経済価値:知る人の数に反比例
- 私識を入手して悪用する可能性
- 私識のままにおくことで公益が損なわれる可能性
- インサイダーとアウトサイダーの境界の不分明
>Top 9. Mechanism how
to share sharables:
- Once sharable is produced, it is put somewhere.
- People or machines that want to know discovers and pull it.
- And they discover other people who want it, and push it (personalization)
- In this world, the concept of 'send' or 'receive' information
will become obsolete.
- Information is broadcast to unspecified number.
- Push economy vs. Pull economy
- "When push comes to pull" Aspen Institute
9.
通識の通有の仕組み:
- 通識は、生産されるとどこかに置かれる。
- それを欲しい存在 (人や機械)が発見してプルする。
- それを欲する相手を発見してプッシュする(パーソナライゼーション)
- この世界では、発信/受信は古い言葉になる。
- 情報は不特定多数にブロードキャストされる
- プッシュ経済対プル経済
- 「プッシュがプルになる時」アスペン研究所
>Top 10. Data and Metadata:
- The same data could be original data or metadata depending on
the perspective.
- Eg: Books in Amazon.com: includes information about the book,
such as book review, popularity, quotation.
- Index or particular terms can be retrieved
- Eg: " >Top spime"
(space+time) of Bruce Sterling: historical things became metadata.
- Note:
With such six of RFID, GPS, Search engine, CAD, Rapidly prototype,
3D printers, and Recycling, one could track the entire existence
of an object, from before it was made, through its manufacture,
its ownership history, until its recycling.
10. データとメタデータ:
- 同じデータが、見方によって元データにもメタデータにもなる。
- 例: アマゾンの本: 書誌情報、書評・評判情報、引用情報を含む
- 索引や特定の語句の検索も可能
- 例: ブルース・スターリングのいうspime
:メターデータにもなった歴史的事物等
- 注)
RFID, GPS, Search engine, CAD, Rapidly prototype, 3D printers,
およびRecyclingの6つによって、オブジェクトは作られる以前から、生産途中、所有している間、そしてリサイクル過程に至るまで完璧に追跡可能となる。
>Top 11. Third order
order:
- First floor: Arrangement of things
- arrangement of book in a library, commodities arrangement
in display showcase
- Second floor: Taxonomy of things
- order of information to keep arrangement
- Third floor: Taxonomy of taxonomy
- order of metadata which select or discover various types of
taxonomy.
- backbone of information order in the age of ambiguity of data
and metadata.
11.
三階の秩序:
- 一階:事物の配列
- 図書館の本の並び方、陳列棚の商品
- 二階:事物のタクソノミー
- 様々な配列を指定する情報秩序
- 三階:タクソノミーのタクソノミー
- 様々なタクソノミーを選択・発案するためのメタデータの秩序
- データとメタデータの区別が曖昧になる時代の情報秩序の柱
>Top 12. "Netpital"
(Net + Capital) in Information society:
- Remark: "Netpital " is tentative translation, which represents
a kind of currency in Information society.
- Mechanism of self-organization:
- wired sharables
- meta-sharable, which becomes also sharable.
- collaboration by open source
- distribution by peer-to-peer
- C&C (Communication & Collaboration) Network as background:
- Change of function of IT and groupware
- From social software to SNS
- From distributed & collaborative network to supporting tool
of group empowerment through C&C
- Netpitalization and aggregation of sharables and tendency
to grow meta-XXX
12.
情報社会の智本:
- 注)智本=Netpital は仮の訳である。
- 自己組織の仕組み:
- 通識のネットワーク化
- 通識のメタ化 (メタ通識も通識化する)
- オープンソースによる共働生産
- P2Pによる流通
- 背景にあるC&Cネットワーク:
- Communication & Collaborationネットワーク
- ITやグループウェアの役割変化
- ソーシャル・ソフトウェアからSNSへ
- 通識の「智本化」のアグリげーションやメタ化とも関連
>Top 13. Property born
in Information Society:
- Position property: also a function of technology
- more popular site
- upper position of portal site
- frequently used key word
- catchy domain name
- Cyber property:
- software
- Game property: game items, character, data
- >Top RMT=
Real Money Trading
- Cyber pen in China, earning RMT by game.
13.
情報社会に生まれる財:
- 位置財: 技術の関数でもある
- 人気の高いサイト
- 検索結果の上位の場所
- 多く使われるキーワード
- 覚えやすいドメイン名
- サイバー財:
- ソフトウェア
- ゲーム財:ゲームのアイテム、キャラ、データ
- RMT=Real
Money Trading
- 中国のサイバータコ部屋
- 各種のデータ:マイニング結果も
>Top 14. Substructure
and Superstructure:
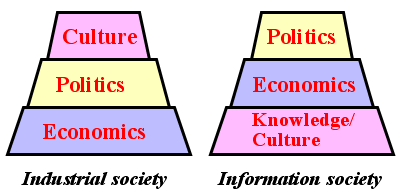 Industrial
society:
Industrial
society:
Economics is substructure, supporting upper politics and culture
systems- But, in the Information society, information and culture will
be substructure, supporting upper economics and politics.
- Question:
This is a reversal or addition of further substructure under economics.
14.
下部構造と上部構造:
- 産業社会では、経済が下部構造で、上部の政治・法・文化システムを支える。
- 情報社会では、情報・文化が下部構造となり、上部構造の経済・政治を支える。
- 疑問:
これは逆転なのか、経済よりもさらに下の構造ができたのか?
Comment
- We need to create various new concepts and terminology appropriate
to the information society; some will be diverted or expanded from
the present ones, but some must be totally created, just as then
economists created lots at the time of emerging industrial society.
- Who will succeed the analysis of the information society as Karl Marx who wrote the essence of the
capitalism.
- 情報社会に適切な概念と用語を作り出す必要がある。その一部は現行のものの転用や拡張がされるだろうが、一部は全く新たに作らなければならない。あたかも当時の経済学者達が勃興しつつある産業社会の時期に多くを作り出したように。
- 資本主義の本質を描いたカール・マルクスのように、情報社会の分析を誰が記すのだろうか?
Title |
What is SHARABLE? |
通識/智本論 |
|---|---|---|
Author |
Shumpei Kumon | 公文俊平 |
Published |
June 2006 |
2006年6月 |
Index |
|
|
Why? |
|
|
Tag |
; Accessibility-Findability-Usability ; Folksonomy; Knowledge neuron; Netpital; Ontology; RMT; Sharable; Spime; The Capital; URI-URL-URN; |
|
Summary |
要約 |
>Top 0. Hypothesis:
|
0. 仮説:
|
>Top 1. Commodities and Capital:
|
1. 商品と資本:
|
>Top 2. Sharables and Chihon (like Capital in information age):
|
2. 通識と智本:
|
>Top 3. Kind of information:
|
3. 情報の種類:
|
>Top 4. Attribute of sharables in cyberspace:
|
4. サイバースペース内の通識の属性:
|
>Top Knowledge neuron (知のニューロン)
|
|
>Top 5. RDF (Resource Description Framework):
|
5. RDF (Resource Description Framework):
|
>Top 6. Schemes such as URI, URL, URN:
|
6. URI, URL, URNというスキーム:
|
>Top 7. Structure of Sharables:
|
7. 通識の構造化:
|
>Top 8. Contradiction of Information Society:
|
8. 情報社会の基本矛盾:
|
>Top 9. Mechanism how to share sharables:
|
9. 通識の通有の仕組み:
|
>Top 10. Data and Metadata:
|
10. データとメタデータ:
|
>Top 11. Third order order:
|
11. 三階の秩序:
|
>Top 12. "Netpital" (Net + Capital) in Information society:
|
12. 情報社会の智本:
|
>Top 13. Property born in Information Society:
|
13. 情報社会に生まれる財:
|
>Top 14. Substructure and Superstructure:
|
14. 下部構造と上部構造:
|
Comment |
|
|