Presentation |
Message |
>Top 0. Prologue:
- Hard power is a typical Merkmal, i.e., characteristics
of industrial society, while so-called soft power is getting
more important in information society. Now Japanese soft power should
be noted: where is the source of such soft power.
- Soft power is comparatively more dependent to personal quality
and motivation than hard power.
- It is worth to checking whether appropriate supportive policies
are promoted by each country, society, and market.
|
0. 序:
- 工業化社会の特徴であるハードパワーに対し、情報化時代における特徴は、ソフトパワーにある。現在、日本のソフトパワーが注目されている、そのソフトパワーはどこにその源泉があるのだろうか。
- ソフトパワーはハードパワーに比べて、個人の資質・意欲に依存する度合いが大きいとは言える。
- そのソフトパワーを発展させるための支援が各々の国・社会・市場で適切に行われているかについても検証する必要がある。
|
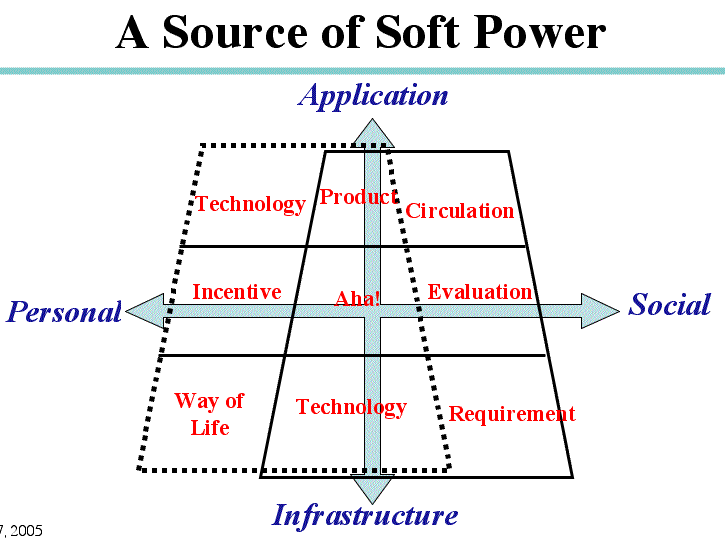 |
>Top 1. A source of soft power:
- Statistic data were selected from "IMD World Competitiveness
Yearbook 2004", which contains index representing a source
of soft power.
- <Above figure>
I'd list up nine factors of a source of soft power as displayed
above.
- X-axis: Left side is plotted out of personal mentality or
situation, right side social environment, and center actions
of making products responding social needs.
- Y-axis: Lower part represents abstract factors of infrastructure,
and upper part concrete appearance of products.
- First layer represents "stage of will" :
A challenger who aims to be a creator must solidify his or her
will.
- Second layer represents "stage of an amateur": The
challenger exerts an effort to make products feeling various
incentives, and being appreciated by colleagues or organization.
The challenger will have firm hopes of future vision.
- Third layer represents "stage of professional":
The challenger now have basic technology to express own style
or idiom. The products will have social evaluation and be able
to distribute in the market. Thus a professional creator comes
into existence.
- Soft power production less depends on traditional infrastructure
such as capital, equipment, or organization unlike hardware production.
But then it depends more on personal will, ability, and efforts.
- However, traditional industrial products also needs factors
of soft power, particularly at the initial stage of designing
or planning; Talented people can undertake these creative jobs
requiring preferable surroundings.
- Silicon Valley in California, world famous for software production
center, has typical such environment preferable for exhibiting soft
power. It is important that there are various social infrastructure,
appropriate evaluation systems with high compensation in the market
mechanism, and also open and affluent community, comfortable climate
and natural environment, etc.
- Even before starting software production, the area of West Coast
was an orchard. Now silicon valley continuously performed to maintain
better education and research environment, incubation of venture
business, stable and fertile community and natural environment.
English environment gives an advantage to collect versatile human
resources from worldwide and to sell products to the global market.
|
1. ソフトウェアの源泉:
- 統計データは、IMD World Competitiveness Yearbook 2004から、ソフトパワーの源泉となるような指標を抽出した。
- <左図> ここではまずソフトパワーの源泉を以下の9つの象限に分けて考察してみる。
- X軸左側列に個人的な心情や状況を、またX軸右側列に社会的な場や環境を位置づけ、X軸中央列には、個人が社会の期待に応える形での作品制作の行動を示す。
- Y軸下方には抽象的なインフラ的要素を、Y軸上方には具体的な作品の出現を表す。
- 第一層は、「志の段階」において、クリエータを目指す者は、社会のニーズを背景に各人の生き方として、まずクリエータたらんという意志を固める。
- 第二層「アマチュアの段階」において、教育課程あるいは初期の研修の段階で、組織や仲間の評価の後押しを受けて、インセンティブを感じつつ、努力を重ね、試作を繰り返す。その途中において、自らの将来像に確信を深めていく。
- 第三層は「プロフェッショナルの段階」に到達することは、個人の作風を表現する基本的な技術を持ち、具体的な成果物や作品に対する社会的評価を得て、市場に流通させることができることを意味する。プロとしてのクリエータの誕生である。
- ソフトパワーは、従来のハードウェア (工業製品)に比べて、資本や設備や組織などの要素の比重が少なく、反面、個人的な意欲・能力・努力への依存度の方が大きい
- ただし、従来の工業製品の生産過程においても、デザイナーや研究者や商品企画者などの製品制作の初期の段階では、このソフトパワー的要素が必要であり、やはり個人の資質・能力およびそれを取り巻く環境が重要であることは言うまでもない。
- ソフトウェアの世界的に主要な生産地であるシリコンバレーなど米国西海岸の特徴を見ると、そこには、ソフトパワーが生まれる環境・風土があり、クリエータを醸成・育成するさまざまな社会的な基盤があり、正当な評価を報酬が得られる市場基盤があり、長くその場所に生活したいと思うような豊かなコミュニティとそれを取り巻く気候条件や豊かな自然環境が存在していることが重要である。
- 例えば、以前は果樹園だった米国西海岸のシリコンバレーの土地では、デジタルのフルーツを実らせるためには、長年に亘る教育・研究機関、ベンチャー育成の環境、多様で安定的なコミュニティを建設・維持しそれを包含する自然環境の保護を継続的に行う努力が必要だったのである。また英語の環境は、多様な人材を世界から集め、その作品をグローバルな市場に展開する意味でも非常に有利に働いた。
|
>Top 2. Indices of Soft Power competitiveness:
- Let's consider indices of soft power which are appropriate for
neutral comparison among nations. These indices should satisfy following:
- to be mutually correlative to the soft power.
- to be explicit and objective, and be expressed numerically.
- to be stable for a certain long time.
- to be certain degree of independent among the indices.
- to be an influential policy to the soft power.
- Cf above 3: a faddish phenomenon which is focused to much
may not be a stable index for a long time.
- Cf above 4: double sampling to the same phenomenon should
be avoided.
- Cf above 5: for example, an immigration policy to treat creative
jobs favorably could be an affirmative index.
- By the way, productivity measured by the attained level caused
by efficiency of soft power may cause a big difference compared
to the case of hardware. Hardware causes several % of difference,
but soft power could cause several times. The reason is productivity
of hardware depends on mainly muscle, while that of soft power
on mainly brain; in other words, muscle differs from repetitive
ability, but brain differs from difference of explosion of creativity
and curiosity.
- It is generally difficult to estimate such invisible soft power mostly depending on personal qualification by visible measurement. But we must find out an appropriate indices which
will be able to grasp invisible flow of factors just like invisible
flow of underground water.
- Index of absolute number or growth rate:
- Regarding to index, absolute figure reflects strength of each
country, but in the case of comparison of soft power, index per
capita is more suitable. Because soft power rather depends on
more individual creativity.
- If there were statistic data of growth rate per capita, which
would be better figure to compare grade of creativity. People
who want to challenge in the creative field would act depend on
his immovable resolution or credo rather than based on cool feasibility
like economic activity.
- Environment or atmosphere of the Age may significantly affect
creative activities. History shows that excellent artistic works,
invention and discovery are outnumbered around big social changes
such as war, revolution or end of century. Thus, change of figure
per capita will be a good index of creativity.
|
2. ソフトパワー競争力の指標:
- このソフトパワーを各国の間で客観的に比較するための指標を考察する。これらの指標の条件としては
- ソフトパワーとの相関関係が強いこと
- 明示的かつ客観的に数値化可能であること
- 長期間安定的な指標であること
- 指標間のある程度の独立性が認められること
- ソフトパワーに影響を与える政策であること
などが必要となる。
- 3. については、ある分野の流行の頂点にある現象にスポットライトを当てすぎると長期的な指標として安定性を欠く。
- 4. は同じ現象を2回サンプリングすることにならないかの配慮からである。
- 5. についていえば、例えば、クリエイティブな職種を移民政策上優遇することは指標になり得る。
- なお、ソフトパワーの生産性は、効率によって達成した成果のレベルからも、ハードウェアの場合に比べ、大きな差が生じる。
おそらく後者が%のレベルであるとすると、前者は倍数のレベルの差があると考えられる。その理由は筋力と頭脳の差であり、あるいは規則的な繰り返しに対し、創造力と好奇心の爆発の差に起因するからである。
- このように個人の資質に大きく依存する見えないソフトパワーを如何に普遍的な見える尺度で測定することは非常に難しいが、底流に関連する要因の流れ
(いわば見えざる地下水の流量) を把握できるような指標を採用したい。
- 絶対値の指標か増加率の指標か:
- 採用する指数については、国家単位の経済指標の場合、その絶対額が国力を反映しているが、ソフトパワーの場合の比較は、一人当たりの数値を使用した。ソフトパワーは個人のクリエイティブに依存する度合いが高いからである。
- また「一人当たりの数値の伸び率」の統計があれば、さらにクリエイティブの度合いをより鮮明に表現する数値になり得る。クリエイティブな分野に挑戦しようとする人々は、経済活動のように冷静にフィージビリティを計算した上で挑戦ではなく、情熱、閃きなど個人の堅い信念や信条に基づいて行動を起こすことが多いと思われるからである。
- 時代の環境や雰囲気は、クリエイティブな活動に大きく影響すると推定する。歴史的に見ても、すぐれた芸術作品、発明・発見は、戦争や革命や世紀末などの大きな社会的な変動の前後により多く出現している.
これらは、一人当たりの数値の変化率がクリエティビティの良い指標になり得ることを示している例と言える。
|
>Top 3. Indices of IMD:
- Following items were cited from "Economic performance",
"Government efficiency", “Business efficiency", "Infrastructure”of
IMD Word competitiveness Yearbook 2004. But a few data are lacking.
- >Top 1. <Way of Life>:
- How versatile life styles people can select?
- "GDP per capita" (US$ per capita):
Culture as the upper structure of economy and society.
- "Unemployment rate", % of labor force:
The higher unemployment rate may enforce to shift to emerging
industry.
- "Urban population", % of total population:
There is an aspect that 'the atmosphere of city makes people
freer.'
- "Population under 15 years", % of total population:
New culture will be usually promoted by younger generation.
- "University education":
University will be the epitome of future society.
- "Foreign high-skilled people":
New culture will be incubated getting global provocation.
|
3.
IMDの指標:
- 以下の項目は、IMD World Competitiveness Yearbook 2004の"Economic
performance", "Government efficiency", “Business
efficiency", “Infrastructure”より関連の統計資料を引用した。但し、一部のデータはなし。
- 1. <ライフスタイル>:
- いかに多様なライフスタイル、人生設計が可能か
- GDP、一人当たり、US$:
経済・社会の上部構造としての文化
- 失業率, 労働人口比%:
失業率の高さは、むしろ新産業へのシフトの指標の面あり。
- 都市人口、人口比%:
「都市の空気は人々を自由にする」面あり
- 若者人口 (15歳未満), 人口比%:
新たな文化は、若者からまず先に発信地になる。
- 大学教育:
大学は未来社会の縮図的な面あり。
- 外国人技術者:
グローバルな刺激の中から新たな文化が生まれる
|
- >Top 2. <Will>:
- How the society allows highly motivated or positive actions?
- Quality of Life:
aiming better quality of life based on the present quality of
life.
- Energy consumption:
Total final energy consumption per capita. Energy consumption
is the result of various activities.
- Individual consumption:
Private final consumption expenditure per capita", US$
After the basic clothes, food, and habitation, sound culture consumption
increases.
- Quality of air transportation":
Liberalization of movement of people depends on development of
traffic means.
|
- 2. <意志>:
- いかに意欲的・積極的な行動が可能な社会か?
- 生活の質:
現在の生活の質を基に、更なる生活の質の向上を目指す。
- エネルギー消費:
エネルギー消費は、諸活動の活性化の基盤
- 個人消費率:一人当たり
衣食住から更なる文化的な消費へ
- 航空輸送の質:”
交通手段の発達による移動の自由度
|
- >Top 3. <Requirement>:
- How the cultural activities arouses global interest? Is such global
exchange easier?
- Tourism receipts:
Actualization of cultural exchange by the increase of tourists.
- Direct investment flows inward:, % of GDP
Interest level to Japan by the amount of foreign investment to
Japan.
- Trade to GDP ratio:
(Export + Import)/(2 x GDP). Typical one of indices of globalization
of Japan.
- Attitudes toward globalization:
Consciousness or attitude toward globalization.
- Number of designated World Heritage:
- Number of global conferences or fora:
|
- 3. <要望>:
- 文化活動は国際的な関心を集めているか、グローバルな交流が可能か?
- 観光収入:
観光客の増加による文化交流の活発化
- 対内直接投資額:
外国投資家による日本への関心度
- 貿易依存度:
日本の国際化の指標の一つ
- グローバルへの姿勢:
グローバル化に対する意識・姿勢
- 世界遺産登録数
- 国際会議開催数
|
- >Top 4. <Incentive>:
- Will the market support cultivation or development of soft powers?
- Stock market capitalization: % of GDP
Function and scale of stock market
- Export of commercial services: % of GDP
Global competitiveness of commercial services.
- Venture capital:
Activeness of venture capital.
- Foreign investors:
Degree of deregulation of foreign investment to Japan.
- Effective personal income tax rate: % of an income
Activeness of individual earnings.
|
- 4. <インセンティブ>:
- 市場は、ソフトパワーの育成・発展を支援しているか?
- 株式市場資本総額:
市場の役割・規模
- 商業サービス輸出比率:
商業サービスの国際競争力
- ベンチャー・キャピタル:
ベンチャー・キャピタルの活発度
- 外国人投資比率:”
外国人投資への自由度
- 個人所得税比率:
個人所得の活発度
|
- >Top 5. <Aha! - inspiration>:
- Is the environment appropriate to generate creative ideas?
- Health infrastructure:
Infrastructure building for health and insurance
- Ecological footprint:
Area units per person, ha of biologically productive space.
- Female positions:
% of total legislator, ratio of senior officials and managers;
which is grade of social participation by women.
- Flexibility and adaptability:
how much people will challenge to new frontiers.
- Brain drain:
or global mobility of human resources.
|
- 5. <ひらめき>:
- クリエイティブなアイデアを生み出しやすい環境はあるか?
- 保健政策:
健康・保健のインフラ整備
- 緑化比率:
環境・アメニティの状況
- 女性の地位:
女性の社会的参加度
- 柔軟性と適応力:
新たな分野への挑戦可能性
- 頭脳流出:
頭脳・人材の流動性
|
- >Top 6. <Evaluation>:
Are there proper opportunities to receive academic, artistic, or
cultural evaluations?
- Number of Nobel winners:
Nobel prize winners in physics, chemistry, physiology, and economics;
per capita, since 1950 per million people
- Basic research:
How active basic research, which might contribute long-term economic
development.
- Number of patents in force:
per 100,000 inhabitants
- Productivity in services:
contributing ratio to GDP; per person employed in services; US$
- Number of Olympic medallists:
- Number of movies awarded in global film festivals:
- Number of International Mathematical Olympiad medallists:
|
- 6. <評価>:
優れた学問芸術文化の評価を得る機会はあるか?
- ノーベル賞受賞者数:”
物理・化学・生理医学・経済学分野でのノーベル賞受賞者
- 基礎研究:
基礎研究の活発度
- 有効特許数:
現在有効な特許案件数
- サービスの生産性:
サービス分野によるGDP寄与率
- オリンピックメダル獲得数:
- 国際映画受賞作品数:
- 数学オリンピック受賞者:
|
- >Top 7. <Technology>:
- Are there social infrastructure prepared for gaining technology?
- Number of Computers:
per 1000 people.
- Diffusion rate of broadband:
Number of broadband subscribers per 1000 people.
- Mobile telephone subscribers:
Number of subscribers per 1000 inhabitants.
- Total expenditure on R&D per capita:
US$ per capita.
- Qualified engineers:
availability in labor market.
|
- 7. <技術>:
- 技術獲得のための社会的な基盤が整っているか?
- コンピュータ普及台数:
- ブロードバンド普及率:”
- 携帯電話利用者数:
- R&D支出:
- エンジニア数:
必要なエンジニアの確保
|
- >Top 8. <Product>:
- Are the products published, displayed, and distributed?
- Public service:
Is this independent from political interference?
- Number of art galleries:
- Number of museums:
- Number of publications:
|
- 8. <作品>:
- 作品は活発に公表・展示・出版されているか?
- 公的サービス:”
非政治的な公的サービスの充実度
- 美術館数:
- 博物館数:
- 図書出版数:
|
- >Top 9. <Circulation>:
- Do the distribution systems function well for products ?
- High-tech export:
% of manufactured exports.
- Patent and copyright protection:
Is this adequately enforced?
- Number of days to start a business:
Rapid preparation for procedure of business creation.
- Number of screening of movies:
- Number of TV channels in the capital:
- Amount of music CD:
|
- 9. <流通>:
- 作品の流通システムは活発化しているか?
- ハイテク輸出比率:
- 著作権保護:
著作権保護の有効性
- ビジネス開始速度
ビジネス創設のスピード
- 上映映画本数:
- 首都でのTVチャネル数:
- 音楽CD販売額:
|
>Top 4.
Aha! - index of inspiration:
- Flash of inspiration:
The most important thing of a creator is a moment when an image
swells up and a flash of inspiration appears. Furthermore, It is
decisively important how often to make and to elongate it.
- To maintain the mechanism of such inspiration, various accidental
situations and occasions have been studied. It is at least effective
to prepare intentionally appropriate amenity to support creators
to produce more ideas.
- When and where it upsprings?:
- The Peripatetic school, 4C BC:
Park or promenade suitable for wandering and thinking
- Old Chinese proverb:
On a horse, on a pillow, and in a toilet; interpreted as comfortable
traffic, relaxed bedroom and clean rest room.
- Archimedes discovered the law of buoyancy:
He shouted "Eureka! (I found it!)" when he
discovered Archimedes' principle while taking a bath. Such heuristic
discovery was made is a bathroom.
- Descartes (17C):
Descartes is also said that he got an idea of Analytics thinking
whole day long before a fireplace during tiresome Thirty Years'
War (1618-48). Fireplace in tranquility is a key word.
|
4.
ひらめきの指標 - Aha! :
- ひらめきの瞬間:
イメージが膨らみ、アイデアの発見をひらめいた時が、クリエータにとっては一番重要な瞬間である。さらに、この瞬間をいかに頻繁にそして長く持続できるが決定的に重要となる。
- このクリエータのひらめきのメカニズムを持続させることについては、古来さまざまな偶然的な場面や機会が検討されてきたが、少なくとも、意図的にそれにふさわしい環境を予め準備することで、クリエータによるアイデアを支援することできる。
- いつ・どこでひらめくか?:
例えば、
- 前4Cの逍遙学派:散歩に適した公園や並木道など
- 三上 (馬上・枕上・厠上):現代的に言えば、快適な交通手段、快適な寝室、清潔なトイレ。
- アルキメデスの浮力の原理を発見:
「ユレイカ!(Eureka)」と叫んだ、まさにheuristicな発見は、入浴中に起こったという。
- デカルトもまた、17Cの退屈な三十年戦争中に、終日暖炉の前での思索によって解析学の着想を得たという。静かな環境での暖炉というのもキーワードである。
|
- >Top Personal animation with idea?:
Appearance of inspiration would occur in a different dimension of
convenience; it would be preferable to have extraordinary space,
with surprising and fresh feeling and scene, as well as natural
swing or sway like 1/f wind of wave, also moderate stimulation to
our five senses with open environment。
- Inspiration seems to mostly depend on personal qualification
and ability, if it is true, it is important to have;
- positive attitude of evaluating free and unique idea or possibility,
- tolerance to admit exception or surprising,
- multiple solution, acceptance to argument or objection, and
- place and atmosphere with positive and open mind.
|
- アイデアの個人的な活発化:
ひらめきが起こることは、利便性とは別の次元と思われる。むしろ非日常性な空間、意外性に富む新鮮な感覚と情景、1/f的な風や波などの自然のゆらぎ、五感を適度に刺激する開放感な環境などが好ましいといえよう。
- ひらめきは個人的な資質・能力への依存度が大きいので、1) 自由でユニークな発想や可能性に対する積極的な評価、2) 例外や意外性を認める寛容度、3)
多様な解答とそれに対する異論・反論への許容、4) ポジティブでオープンな場や雰囲気が重要である。
|
>Top 5. Soft power Olympic:
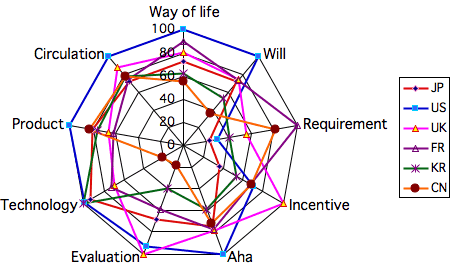
|
5.
ソフトパワー・オリンピック:
- メダル:
- 金メダルl:米国
- 銀メダル:英国
- 銅メダル:フランス
- 米、英、仏はソフトパワーでも伝統的な強み。
- 日本は健闘、韓国は日本を追い上げている。
- 中国の指標は巨大な人口で薄まるものの、一部の指標では意外が強みを発揮
|
- Medals:
- Gold medal: US
- Silver medal: UK
- Bronze medal: France
- US, UK, and France show traditional soft powers.
- Japan also makes a good showing. Korea is rapidly catching up
Japan.
- China's indices are diluted by her big population, but shows surprising
strength in some indices.
|
|




