Summary |
要約 |
>Top
0. Prologue:
- The author defines "The bubble" would be a situation
at an event where the number of venders are more than that of users.
The theme of "RFID" (Radio Frequency
Identification) is really in such a definition.
- Also the theme has various aspects or impacts by different interests
of the observers.
|
0.プロローグ:
- 著者によれば、「バブル」の状態とはどのイベントでもベンダーの数の方がユーザの数より多い場合をいう。RFIDのテーマは正にその場合に当てはまる。
- またこのテーマは、当事者の興味対象によって様々な側面やインパクトがある。
|
>Top
1.The meaning of "Traceability":
- Bar code:
Bar code technology made it possible the individual
recognition of products, which paved the way for convenience
store handling three to four thousand items in a shop by 3 or 4
part-timers.
- Visualization:
Visualization is another key factor of this ID technology. Conventional
retail shop has been a black box, where the owner could not mention
or visualize the items sold and the item on the shelf. The owner
only controlled in terms of sales amount, feeling blurred trend
of decrease of the inventory. Now convenience store can trace any
item sold and the balance of the inventory item by item. Furthermore
such information (SKU, Stock Keeping Unit) is controlled by the
headquarters of the store. Thus POS (Point of Sales) made the shop
'visible' from anywhere. This is the reason why product planning
tend to be done at the retail side rather than maker side.
- SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) is the smallest
unit of an item that may be dispensed from inventory or returned
to a vendor.
- Traceability:
The terrific quality of RFID made it possible to trace each item
attaching ID tag at individual product. Such traceability would
be of great help in case of trace or callback if there were defective
goods such as harmful medicine or lemons. Traceability also enables
to make any product as a lottery.
- Wireless reading:
Reading the information by wireless system is another essence of
RFID, which is much convenient than bar code system. RFID is also
useful for the control of fixed asset. Positioning of each item
will be more useful but may cause privacy problem of the users.
- EPC (Electronic Product Code):
In a factory, such tractability is already used for the process
control by way of detailed cost account and control of supply parts.
This technology is applicable at belt conveyor sushi shop where
use-by hour sushi will be automatically removed off.
- EPC is a unique number that identifies a specific item in
the supply chain. Once the EPC is retrieved from the tag (RFID),
it can be associated with dynamic data such as origin of the
procut or date of the payment.
|
1.トレーサビリティの意味:
- バーコード:
バーコード技術は商品の個体識別を可能にした。これによって3~4人のアルバイトで3~4千点の商品を取り扱うコンビニストアが可能になった。
- 可視化:
可視化はID技術のもう一つのキーファクターである。従来の小売店はブラックボックスであり、その店主は販売品目や在庫の状況を掴めなかった、つまり可視化できなかった。店主は売上金額だけを管理しており、在庫の減少傾向を曖昧に把握するだけであった。今やコンビニエンスストアは売上品目や在庫バランスを品目毎に把握することができる。更に、これらの情報(SKU)
はその店の本社で管理されている。このようにPOSは店をどこからでも可視化できるようになった。このことが商品企画がメーカ側ではなくむしろ小売側で行われるようになった理由である。
- SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) とは、在庫として保管あるいはベンダーに返品する商品の最小単位をいう。
- トレーサビリティ:
RFIDのすごさは、個々の商品にIDタグを付けることで商品毎の追跡が可能になったことである。このようなトレーサビリティは毒性のある薬品や欠陥品のような商品の追跡や回収の場合に極めて有効となる。トレーサビリティはまたすべての商品を宝くじにすることができる。
- 無線読み取り:
RFIDのもう一つの本質は、無線システムによって情報を読み取ることであり、それはバーコードよりもずっと利便性が高い。RFIDはまた固定資産の管理にも有効である。個々の品目の位置情報は有効であるが、ユーザのプライバシィの問題を生じる可能性がある。
- EPC (Electronic Product Code):
工場では、すでにこのようなトレーサビリティが利用されて詳細な原価計算や供給部品管理によるプロセス管理に利用されている。この技術は回転寿司店でも時間期限の経過した寿司を自動的に取り除くことに応用されている。
- EPCとは、サプライチェインにおいて個々の商品を識別する固有番号である。このEPCを、RFIDのタグから読み取ることで、その商品が原産地や精算日のような詳細データと関連させることができる。
|
>Top 2. Social Impact of ID Technology:
- Database & Network
It is more essential for RFID shows to have the feature of database
and network than that of interface. Thus RFID is backed by the giant
database and network system. And RFID brings two kinds of social
impact as follows:
- 1) Visualization:
There are two types of visualization: in ubiquitous and realtime
environment. Such visualization can guarantee integrity of the
information, which can empowers any holder of the integrity.
- Integrity is source of the brand.
- Privacy issue could be a balance of power between a consumer
and a vendor
- 2) Individualization:
ID technology also brings differentiation by recognizing the
item individually. Such individualization causes 'property'
in the item with the release of physical location. And finally
it may separate the physical product and transaction, which
may affect a new business model of rental or rolling transactions.
- Consequently, this is a technology
of mappingthe real products world into the
virtual network world performing the above two functions.
- Application:
- Efficiency: Inventory optimization, Quality control,
Cost management
- Security management: Food, Hospital, Antitheft
- Marketing: Disclose of information, Track record
of positioning.
- Recycle: Consumer durables
- New Business: Rolling transactions.
|
2.ID技術の社会的なインパクト:
- データベースとネットワーク:
RFIDは、そのインターフェイスよりもデータベースやネットワークの特徴の方がより本質的である。RFIDはその背後の巨大なデータベースとネットワーク・システムで支えられているのである。
RFIDは、以下のような2つの社会的なインパクトをもたらす。
- 1) 可視化:
可視化には2つある。ユビキタスとリアルタイム環境での可視化である。この可視化によって情報の正統性 (integrity)
を保証することができ、正統性の保持者はパワーを持つことができる。
- 正統性はブランドの源泉である。
- プライバシィ問題は消費者とベンダー間のパワーバランスと考えられる。
- 2) 個別化:
ID技術は、また商品を個別に認識することで差異を作り出す。この個別化によって、商品は物理的な所在から解放された「所有」が可能となる。究極は物理的な物と商取引とが分離し
(商物分離)、レンタルや転々流通など新たなビジネスモデルに影響を与える。
- 結局、これは、上記の2つの機能を使うことで、リアルなモノ世界をバーチャルなネットワーク世界にマッピングする技術である。
- 応用分野:
- 効率化:在庫最適化、品質管理、原価管理
- 安全管理: 食品、病院、盗難防止
- マーケティング:情報開示、位置情報履歴
- リサイクル:耐久消費財
- 新ビジネス:転々流通
|
>Top 3. Viability of
RFID:
- New Supply Chain by EPC (Electronic Product Code):
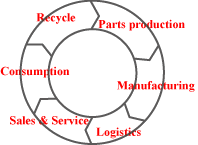 Conventional
linear supply chain should be revised to cyclic supply chain by
introducing EPC technology, which aims to create new value creation
for customers. The decisive change is that the linear supply chain
is managed by the viewpoint of supplier, while the cyclic one by
that of customer. Conventional
linear supply chain should be revised to cyclic supply chain by
introducing EPC technology, which aims to create new value creation
for customers. The decisive change is that the linear supply chain
is managed by the viewpoint of supplier, while the cyclic one by
that of customer.
- Terminology of traceability:
- Trace back
- Trace forward, or tracking
- There are two groups who expect the possibility
of RFID:
- 1) Network-centric group:
This group emphases the connection between real world and virtual
world. That is, we can recognize and trace each RFID-attached
product from anywhere via network and database. Most of visionaries
belong to this group.
- 2) Process-management-centric
group:
(maybe pragmatist)
RFID itself has affluent function, including all necessary information
to manage each product. Big "kaizen" will
be possibly by this traceability If we apply this technology
to cost accounting, we can change the conventional production
indirect cost into direct cost. Most of pragmatists belong to
this group, who may realize this technology earlier than the
first group. (Eg: business models, or home information appliances)
- Traceability is a technology to recover connection:
It has been a feature of modern society that no one knows the name
of producers and that of consumers regarding to the particular product.
Such transaction between anonymous people has been a base of the
modern market mechanism. Even a chance customer can buy a product
at the fixed price.
- But this anonymity makes it impossible to trace the particular
product if it was once sold. Tracing or recalling the product
is impossible.
- Regarding to the particular products such as medicine or food,
if it was turned out to be harmful or needed to be additionally
guided after the sale, traceability would be indispensable.
- Possible enclosure by corporate group:
In order to avoid enclosure or division by corporate group who use
this RFID technology, we should prepare 'open platform' of the ID
technology to secure interoperability: EPC code as a successor of
JAN (Japanese Article Number) code.
- All parties and systems related to business transaction should
share network based on open platform; such as supplier, consumer,
government, products monitoring site, word-of-mouth (WOM) communication
or reputation site, tracking application, recycle application,
products record application, as well as various industrial and
corporate network.
- The key is 'interoperability.'
|
3.RFIDの可能性:
- EPCの導入による新たなサプライチェイン: <左図>
従来の線形のサプライチェインはEPCを導入することで循環型のサプライチェインに改善すべきである。これは顧客に対する新たな価値創造を目指す。決定的な創意は線形のサプライチェインが供給者の視点で管理されていたのに対し、循環型は顧客の視点で管理されていることである。
- トレーサビリティの用法:
- トレースバック (遡及)
- トレースフォワード (追跡)、またはトラック
- RFIDに期待をかける2つのグループ:
- ネット重視派:
このグループはリアル世界とバーチャル世界との間の連結を強調する。即ち、RFIDを装着した個別商品をネットワークとデータベースを通じてどこからでも認識・追跡可能である。多くの夢想家はこのグループ。
- プロセス管理重視派:
RFID自身には、個別商品を管理するためのすべての必要な情報など豊富な機能があること。このトレーサビリティによって大きな改善が可能となる。もしこの技術を原価計算に応用すれば、生産間接費を直接費に変えることができる。多くの現実派はこのグループで、おそらく第一グループより早くこの技術を実現しそう。
(ビジネスモデルや情報家電など)
- トレーサビリティはつながりを回復する技術:
誰も特定の商品について生産者や消費者の名前を知らないのが近代社会の特徴であった。このような匿名の人々による取引は近代の市場メカニズムの基礎であった。一元の客であっても商品を定価で買うことができるのである。
- しかしこの匿名性は一度販売した特定商品を追跡することは不可能になる。商品の追跡やリコールは不可能なのである。
- 薬や食品のような特定商品は、もし販売御に毒性がわかったり、追加の指導が必要になった場合、トレーサビリティが不可避になる。
- 企業グループによる囲い込みの可能性:
RFID技術を利用する企業グループによる囲い込みや分断化を防ぐために、我々はID技術の相互運用性の確保のためにオープン・プラットフォームを準備すべきである。EPCコードは、JANコード
(バーコードの日本標準)の後継となるべき。
- ビジネス取引に関係するすべての当事者やシステムはオープンなプラットフォームに基づくネットワークを共有すべきである。これらの当事者には、生産者、消費者、行政、商品モニターサイト、口コミ・評判サイト、追跡アプリケーション、リサイクル・アプリケーション、商品履歴アプリケーション、および様々な業界・企業のネットワーク。
- 相互運用性が鍵
|
>Top 4. New Social Model
by information sharing:
- To make 'merit of information sharing' to a business-society
model:
Regarding to disclosure of information of product record, there
are two types of models; Whose information will be most credible?
- 1) Dependence without information:
This model is to gain creditability of customers by making open
of the vendor's all information.
- 2) Dependence with information:
This model is to gain credibility of customers by establishing
brand image, without discloser of the vendor's information.
- Two aspects of 'privacy':
- People shows that allergic response to centralized control
(asymmetric control) to such case as the residents basic information
system, recently deployed in Japan.
- But people tend to show openness to credible people, particularly
in case of mobile phone.
- People feel anxiety of their private information being censored,
monitored, or misused unknowingly by unknown people.
- The way of solution should lay stress on not only (1) solution
by technology or design, and (2) solution by law or institution,
but also (3) solution by business model.
- Store Imagination 2009 Policy:
The law of Protecting Personal Information will be enforced in Apr.
2005. Followings are the key guideline in the privacy issue:
- Compliance with METI's guideline
- Never correspond person to commodity in a store.
- Never have personal information database
- Prepare service to nullify RFID when customers leave the store.
- Possibility of Japanese success model:
Because of:
- Very sensitive logistics, such as convenience store
- Development of palm-top commerce, such as mobile phone
- Strong demand for more convenient, safer, and securer services.
|
4.情報共有による新たな社会モデル:
- 情報共有をビジネス・社会モデルに:
商品履歴情報開示を巡る2つのモデル。誰の情報が一番信用できるか。
- 1) 知らしめず依らしめる:
このモデルはベンダー情報をすべて開示することで顧客の信頼を得る。
- 2) 知らしめて信頼を得る:
このモデルは、ベンダーの情報を開示せずに、ブランドイメージを確立することで顧客の信頼を得る。
- プライバシーを巡る二面性:
- 住基ネットに見られるような集中管理 (情報非対称) へのアレルギー
- 一方で、携帯電話のように信頼できる相手には開放的態度
- 知らない間に、知らない人にプライベート情報が監視、モニター、利用されることの不安
- 解決の方法は、(1) 技術的解決や、(2) 法的制度的解決に加えて、(3) ビジネスモデルによる解決をもっと重視すべき
- ストア・イマジネーション・2009ポリシー:
2005年4月より個人情報保護法が施行される。以下はプライバシーに関する重要なガイドである。
- 経産省のガイドラインへの対応
- ストア内では、人のモノの紐つけは行わない
- 個人情報データベースは持たない
- ストア退出時にはICタグを利用不能にするサービスを用意する
- 日本的な成功事例の可能性:
その理由は
- きめ細かいロジスティックス
(例:コンビニ)
- 手のひらコマース
(例:モバイル)
- 便利・安全・安心に対する強いニーズ
|
 Conventional
linear supply chain should be revised to cyclic supply chain by
introducing EPC technology, which aims to create new value creation
for customers. The decisive change is that the linear supply chain
is managed by the viewpoint of supplier, while the cyclic one by
that of customer.
Conventional
linear supply chain should be revised to cyclic supply chain by
introducing EPC technology, which aims to create new value creation
for customers. The decisive change is that the linear supply chain
is managed by the viewpoint of supplier, while the cyclic one by
that of customer.