3G & 4G Mobile
Communication Systems
Cat: ICT
PUb: 2002
#: 0203a
Hajime Yamada
02228u/18218r
Title
3G & 4G Mobile Communication Systems
3G/4G
モバイル・コミュニケーション・システム
Lecturer
Hajime
Yamada
山田 肇
Place
IECP Forum
IECP Forum
Time
Feb. 2002
2002年2月
Index
Tag
; ; 4G; ARPU; IPv6; MVSO; Non-3G service; P2P application;; Seamless service; Trade-off; ;
Point
-
his is the essence of the report of Prof. Hajime
Yamada of Glocom, International University of Japan presented
in February 2002. (The schematics are simplified
or abridged.)
-
The original report was jointly made by Glocom
and Accenture; the details can be accessible at:
http://www.glocom.org/tech_reviews
/tech_news/20020213_s1/index.html
-
2002年2月に開催された国際大学GlocomのIECP研究会で発表された山田肇教授によるレポートの骨子である。(表現等は一部簡略化した。)
-
なお、この報告書は、国際大学Glocomとアクセンチュアとの共同研究として、詳細以下ホームページに掲載されている。
http://www.glocom.org/tech_reviews/
tech_news/20020213_s1/index.html
Summary
要約
>Top 1. Generations of mobile telephone:
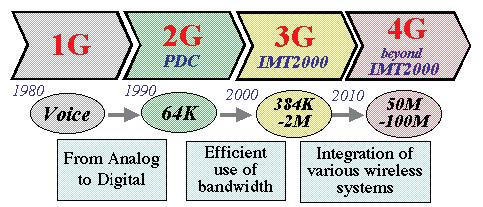
- Mobile telephone has making technological advances almost every
decade. Now the fourth generation (4G) type is in the process of
standardization mainly by International Telecommunication Union
(ITU).
- In Japan, The Council of Information & telecommunication under
Ministry of Public Management discusses about the basic concept
of 4G standardization, aiming to realize "seamless services"
combined with various wireless systems such as mobile telephone
and wireless LAN.
- >Top The basic concept of 4G services will include:
- Drastic improvement of transmission speed (similar to optical
fiber)
- Introduction of software defined radio
- Full introduction of IP technology, including IPv6
- Seamless connection among various communication systems
- Definition:
"4G in a broad sense" includes various wireless services
such as Wireless LAN, Intelligent Transport System (ITS), Bluetooth,
converging "4G in a narrow sense" which is advanced services
of mobile telephone.
1. 携帯電話の世代推移:
- 携帯電話は、ほぼ10年毎に世代が推移しており、既に、次の10年を見据え、国際電気通信連合(ITU) を中心に第4世代(4G)
の規格化が進められている。
- 日本では、情報通信審議会 (総務省) が4Gの基本コンセプト策定にあたっており、携帯電話と無線LAN等の複数無線システムが連携した「シームレスサービス」の実現が志向されている。
- 4Gの基本コンセプト:
- 通信速度の飛躍的向上(光ファイバ並)
- ソフトウェア無線の導入
- システムのオールIP化IPv6の導入
- 複数通信システムとのシームレスな接続
- "広義の4G"は、
無線LAN、ITS、Bluetooth、デジタル放送等多様なシステムと、"狭義の4G" (携帯電話の発展形)
とか機能的に融合する。
>Top 2. Seamless mobile services:
- As Various payservices other than 3G ("Non-3G") may compete
with
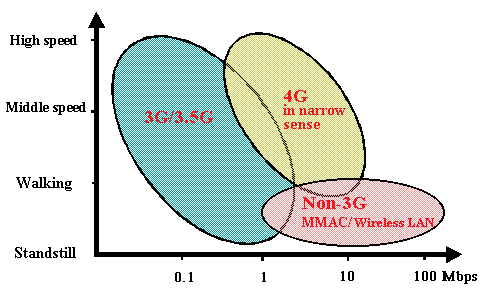 3G service, and new entrants are also participating in the market,
seamless service across the different 3G and Non-3G operators will
be difficult.
3G service, and new entrants are also participating in the market,
seamless service across the different 3G and Non-3G operators will
be difficult.
- <New Non-3G entrants expected>:
- NTT Communications
- NTT-East, NTT-West
- Erricson
- Mobile Internet Service
- WIS
- Speednet, etc.
- <Further development of services>:
- Enhancement of mobility by "handover", enabling
mobile internet at the middle speed.
- Wireless voice communication by VoIP
2. サービスのシームレス化:
- 3G以外の有料通信サービスは、3Gと競合する可能性があり、かつさまざまなプレーヤが新たに参入しつつあるため、仮に技術的な課題がクリアされたとしても、異なる事業者間をまたがるサービス統合は容易ではない。
(ビジネス上はシームレスとはならない。)
- <3G以外の有料通信サービスへの参入:
- NTTコミュニケーションズ
- NTT東西
- エリクソン
- Mobile Internet Service
- WIS
- スピードネット等
- 更なるサービス発展可能性>
- ハンドオーバによりモビリティ向上、中速でのデータ通信が可能
- VoIPによる無線音声電話
>Top 3. Four Key Players:
Key players
Access NW
Voice Ser
Data Ser
NW
device
3G
Existing carrier
DoCoMo
KDDI
J-Phone
○
○
○
○
Mobile Virtual Network Operator
○
○
○
Non-
3G
New entrant
NTT-com
NTT-E/W
WIS
○
○
○
ISP
Nifty
MSN
IIJ
○
○
- The future seamless services will be determined depending on circumstances
of which player(s) will gain the number of customers within the following
four possible candidates of seamless services.
- >Top <3G Players>:
- Both voice and data mobile communication service operators.
- Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MVNO) resell services, borrowing
access network from the existing carriers.
- <Non-3G Players>:
- Data mobile communication service only.
- Internet Service Providers (ISPs) resell data services, borrowing
access network from the new entrant players.
3. 4つのキープレーヤ:
- シームレスサービス実現の鍵を握る以下4プレーヤの内、今後どのプレーヤが顧客を握るかによって、具体的にどのようなシームレスサービスが実現できるのかが決まる。
- <3Gプレーヤ>:
- ボイスサービス、データサービスいずれも行っている。
- 仮想移動体通信事業者(Mobile Virtual Netwrok Operator, MVNO) は、アクセスネットワークを既存キャリアから借りて、サービスを再販する。
- <3G以外のプレーヤ>:
- データサービスに特化したプレーヤである。
- インターネット接続事業者(Internet Service Provider, ISP) は、アクセスネットワークを新規参入プレーヤから借りて、サービスを再販する。
>Top 4. Quadrant scenarios (in 2010):
- Here is the four scenarios in Japanese 3G and Non-3G
 mobile communication
services forecast in 2010; who will be the major player or how the
competition occurs.
mobile communication
services forecast in 2010; who will be the major player or how the
competition occurs.
- Remarks:
- Time frame:
the scenarios foresee the situation around 2010, when 4G mobile
communication services will proliferate in Japan.
- Mass or knitted:
means degree of proliferation in pay mobile communication services.
(Neither includes free communication, nor utilization for devices
and animals.)
- Mass: major pay mobile communication services (more
than one million users)
- Niches: not major pay mobile communication services
(not more than one million users)
- 3G: the user base of 2G shift mostly to 3G according
to the expansion of service are and improvement of mobile terminals.
Several enhanced services In voice are expected such as QoS
and global roaming, etc. In data communication the key applications
will be contents delivery service and further utilization for
business purposes.
- PHS: will not replace 3G services.
- >Top Non-3G: wireless LAN and other wireless services after
3G such as MVNO (Mobile Virtual Network Operators) . Non-3G services
start from urban areas, which might cover nationwide areas.
- Free communication services: various independent network
services promoted by local governments and ISPs.
- 2G and 3G carriers: Three existing mobile common carriers; NTT
DoCoMo, AU, J-Phone.
- New carriers: Local ISP, Electric utility companies, and
other entrants. Existing wired common carriers such as NTT communications,
NTT-East, NTT-West can be entrants in mobile services.
- Wireless communication services: various communication
services using free access network resources by local governments,
grassroots ISPs, and other groups.
4. 四象限のシナリオ (2010年):
- 2010年までに、日本において、第3世代のモバイルサービス(3G) およびそれ以外の無線通信サービス(Non-3G)
から第4世代のモバイルサービス(4G) がどのように実現されるかについて、4通りのシナリオを描いた。
- 注:
- タイムフレーム:
日本で4Gの実用化が見込まれる2010年前後を想定
- マス/ニッチ:
有料通信サービスの普及度合いを示す。
(無料通信サービス・モノ・動物等の利用は含まず。)
- マス: メジャーな有料無線通信サービス (1億人以上)
- ニッチ: マイナーな有料無線通信サービス(1億人未満)
- 3G: 2Gのユーザベースは、エリア拡大と端末変更に伴い、ほぼ3Gに移行する。音声通話では、QoSや国際ローミング等の差別化が行われる。データ通信では、コンテンツ配信、ビジネス利用の拡大が鍵。
- PHS: 3Gにとって代わることはない。
- 非3G:
無線LAN およびMVNO等の3G以上の無線通信サービス。都市部中心のサービスだが、状況次第では、全国的なカバーエリアを達成する可能性あり。
- フリー通信サービス:
地方政府および地方ISPなどによる自主的なネットワークサービス
- 2Gおよび3G キャリア:
NTT DoCoMo、AU、J-Phoneの3社
- ニューキャリア:
ローカルISP、電力会社、その他新規キャリア。なお、NTTコニュニケーションズ、NTT東西も新規無線キャリアになり得る。
- 無料通信:
地方自治体、草の根ISP等の組織や個人による「通信リソースの無償開放」によるボランタリーネットワーク上の通信。
>Top 5. Market forecast of each scenario:
- Market forecast (unit: \ trillion = about $10
billion):
- <Left-top> "Never
Ending Story" scenario:
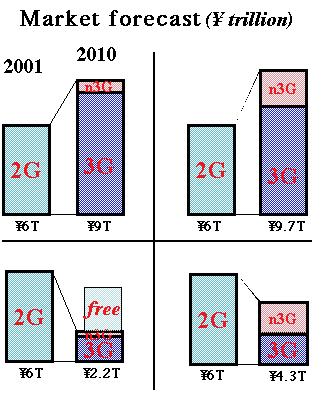
- Strong needs for 3G services will continue, and the mass users
will be 3G. Pay mobile communication services other than 3G
will be used only in urban areas.
- >Top Most of 2G users will shift to 3G services. Moderate increase
of number of users are expected, and ARPU (Average Revenue Per
User) in data communication will be maintained, while in voice
will show gradual downtrend.
- Non-3G services covering similar size of PHS users will keep
limited influence.
- <Right-bottom> "Dawn
of the New Age" scenario:
- Majority users will shift to non-3G pay services which will
attain nationwide covering areas, and existing 3G users will
sharply decrease accordingly.
- In voice services, though limited users will utilize QoS and
global roaming services, mass users will shift to mobile IP
phone service which will have similar function of the present
mobile telephone.
- <Right-top> "Struggle
for Supremacy" scenario:
- 3G and Non-3G pay services will have segmented market share
according to different needs of mass users.
- 3G market will come to maturity, and the number of new users
will reach the ceiling.
- New growth will mostly occur in non-3G pay mobile services.
ARPU in data services will also decline.
- <Left-bottom> "The
End of Myth" scenario:
- Voluntary networks using redundant bandwidth of wired communication
via wireless base stations will emerge as grassroots ISP services,
etc. Mass users will shift to such free mobile environment.
- 3G mobile service industry will decline, reducing their revenue,
though heavy users remains, paying relatively expensive ARPU.
- >Top New demand of free data communication using P2P applications will also emerge.
5. 各シナリオの市場規模予測:
- <左上>Never Ending Story
(果てしない物語) シナリオ:
- 3Gに対するニーズが強く、ほぼすべてのユーザが3Gを利用する一方で、3G以外の有料通信サービスは、都市部を中心とした限定的な普及に留まる。
- 2Gの顧客ベースはほぼ3Gに移行。現在の携帯電話の総ユーザが緩やかに増加し、月額平均収入(Average Revenue
Per User, ARPU)はデータ通信は現状維持、音声通信は緩やかに低下。
- 3G以外は、小規模ながら現在のPHS程度のユーザを確保。
- <右下>Dawn of the New Age
( 新時代の夜明け) シナリオ:
- ほとんどのユーザは全国的なカバーエリアを達成した3G以外の有料通信サービスに乗り換え、3Gは激減し、限定的な普及に留まる。
- 音声通信については、3GがQoS、国際ローミング等で一部ユーザが利用するが、3G以外の音声サービスとして、携帯電話と同等の機能のモバイルIPフォンが登場しマスユーザが利用。
- <右上>Struggle for Superemacy ( 覇権争い) シナリオ:
- 3Gおよび3G以外の有料通信サービスは、マスユーザの異なるニーズを満たし棲み分ける。
- 3G業界は成熟し、新規加入ユーザは頭打ち。
- 期待された伸びは、3G以外の有料通信サービスに奪われ、データARPUも減少傾向。
- <左下>The End of Myth
( 神話の終焉) シナリオ:
- 固定通信の余剰帯域を無線LANの基地局等を介して、相互開放する動きが広がり、草の根ISPなど主体に、ボランタリーなネットワークが形成され、マスユーザは無料の移動通信手段を利用する。
- 3G業界は衰退期。収益は大幅に減少。残ったユーザはヘビーユーザでARPUは比較的高水準である。
- P2Pアプリケーションを利用した通信費無料のデータ通信需要が旺盛。
>Top 6. Comparison of 3G and Non-3G services:
- Following chart shows trade off relationship between 3G and Non-3G
services
-
Features
3G services
Non-3G services
Transmission
High-cost, quality guaranteed, high mobility
Low-cost, best effort, low mobility
Service are
Nationwide, exhaustive
Local, scattered
Brand image
Major brand
Minor brand
Device
Low-cost, small mobile phone
High-cost, PC/PDA
Contents
Small capacity, mobile-specific
Large capacity, Internet-based
User Interface
Simple, mobile phone-based
Complicated, PC/PDA-based
6. 3Gと3G以外の通信サービスの比較:
- 3G以外の有料通信サービスが、いかにユーザニーズのトレードオフとなっているかを以下比較する
-
サービスの特性
3G通信サービス
3G以外の通信サービス
通信サービス
高コスト、通信品質保証、高モビリティ
低コスト、ベストエフォート、低モビリティ
サービス エリア
全国的、網羅的
地域的、離散的
ブランド
メジャーブランド
マイナーブランド
デバイス
低コスト、携帯電話
高コスト、PC/PDA
コンテンツ
小容量、モバイル特有規格
大容量、インターネット準拠
ユーザインターフェース
単純、携帯電話ベース
複雑、PC/PDAベース
Comment
- This is a Roadmap of development of wireless communications in
Japan.
- The above scenario contains various interest of each party, but
the early deployment of the next gereration mobile infrastrucure
is more important for Japan.
- これは日本における無線通信の発展のロードマップである。
- 各シナリオには、それぞれ関係する人々の利害が含まれる。重要なのは、次世代の通信インフラを早く達成することである。
3G & 4G Mobile
Communication Systems
|
Cat: ICTPUb: 2002#: 0203a |
|
Hajime Yamada |
02228u/18218r |
Title |
3G & 4G Mobile Communication Systems |
3G/4G モバイル・コミュニケーション・システム |
|---|---|---|
Lecturer |
Hajime Yamada | 山田 肇 |
Place |
IECP Forum | IECP Forum |
Time |
Feb. 2002 |
2002年2月 |
Index |
||
Tag |
; ; 4G; ARPU; IPv6; MVSO; Non-3G service; P2P application;; Seamless service; Trade-off; ; | |
Point |
|
|
Summary |
要約 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 1. Generations of mobile telephone:
|
1. 携帯電話の世代推移:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 2. Seamless mobile services:
|
2. サービスのシームレス化:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 3. Four Key Players:
|
3. 4つのキープレーヤ:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 4. Quadrant scenarios (in 2010):
|
4. 四象限のシナリオ (2010年):
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 5. Market forecast of each scenario:
|
5. 各シナリオの市場規模予測:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
>Top 6. Comparison of 3G and Non-3G services:
|
6. 3Gと3G以外の通信サービスの比較:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Comment |
|
|