Summary |
要約 |
>Top 1. Essence of Mobile Internet Market:
- 'Mobility' and 'Personalization' are two basic requirements of
modern people.
- Mobile Internet is acknowledged in the market like the ubiquitous
telephone service.
- All handheld PC users should have mobile internet function.
- Instant message, instant Web browsing and eCommerce at any situation
are effective to utilize small pieces of disposable times.
- Japanese younger generation will eagerly accept integrated services
of information, communication, audio-visual contents and game applications.
- Another emerging market will be device-unconscious services such
as car, vending machine, POS terminal, positioning service, and
wearable security service.
- Business sphere will be innovated by the integration of voice
and data, wired and mobile, private and public networks.
- But we must keep in mind that mobile internet services should;
- not pursue flat rate tariff,
- keep reasonable cost which may not burden users, targeting
less than 1/10 of the present telephone tariff.
- not pursue realtime video transmission by circuit switching;
only practicable for near on-demand broadcasting services.
- not guarantee data speed; be best-effort service targeting
optimization of average throughput.
|
1. モバイルインターネットの市場の本質:
- MobilityとPersonalizationは、現代人の基本的欲求である。
- 電話で実証されたように、モバイル・インターネットも認識される。
- ノートPCは、すべてモバイル・インターネットのユーザ。
- ユーザの細切れの可処分時間を利用する、即時伝達、即時処理の簡易Web browsingとeCommerceには、潜在需要がある。
- 日本の若者層は、「情報」「通信」「AV」「ゲーム」を統合したアプリケーションを開拓する。
- 自動車、自販機、POS端末、位置情報、Wearableなセキュリティ端末など、通信機を意識させないアプリケーションの拡大
- ビジネスにおける電話とデータ、有線と無線、構内システムと公衆システムの統合がイノベーションをもたらす。
- 但し、以下条件あり。
- ワイヤレスでは定額制、使い放題は無理。
- ユーザに大きな負担とならない通信コスト。現状は電話並。これより一桁下を目標。
- 回線交換型のリアルタイム映像通信は不向き。リアルタイム・オンデマンドではなく、放送型のニア・オンデマンドを併用すべき。
- データスピードの保証は求めるべきにあらず。ベストエフォットベースであるべきで、平均スループットの最大化こそ目標。
|
>Top
2. CDMA Systems between Japan-Euro vs. US:
- IMT2000 is the basic standard recommended by ITU in early 1990's
to use 2GHz frequency zone, aiming data communication of 2Mbps in
fixed environment, 384Kbps in walking level, and 144Kbps at high
speed situation. To achieve this target, Japanese NTTDoCoMo and
European main makers standardized W-CDMA system using bandwidth
of 5MHz.
- In opposition to the above, Lucent, Motorola, Nortel and Qualcomm
of North America and Samsung of Korea (LMNQS Group) proposed cdma2000 system using the same bandwidth of 1.25MHz as the existing CDMA
(called '1X') or using triple bundled bandwidth ('3X').
There had been severe patent contest between the two camps, but
finally both agreed to give cross licenses each other.
- The original idea of LMNQS Group was based on 'processing high
speed data communication using wider bandwidth' and 'focusing mobile
telephone as the main demand', but afterward they reconsidered that
the demand of data communication exceeding 144Kbps would be doubtful
and concluded that it is not economical to use wider bandwidth by
all mobile terminals like W-CDMA system. They stressed smooth upgrade
strategy would be a right answer, pursuing coexistance with the
exisiting CDMA system and use of standard bandwidth of 1X system
as well as 3X system if needed.
- In addition, HDR (High Data Rate) system appeared in the
market by optimizing of burst data of asynchronous Internet access
between 38.4Kbps - 2.4Mbps averaged 600 Kbps, which can use the
existing base station facilities of 1.25MHz channel.
- This system aims to install HDR base station in urban areas,
backed up 144Kbps serviced by MC-1X in other areas. Flexible
investiment to the facilities becomes possible according to
the market situation, which can also utilize split bandwidth
by the same facilities causing minimized operation and maintenance
cost.
- Combination of services of1X and HDR are complimentary, and
the chipset is designed for such dual purpose;1X service is
always available even no existent area or capacity saturated
area of the HDR stations.
|
2. CDMA方式で日欧と米国で対立:
- IMT2000は、1990年代初頭にITUによる2GHz帯の利用に関する勧告が基礎になっている。その際、固定環境で2M、歩行レベルで384K、高速移動で144Kbpsのデータ通信を意図していた。これを達成するために、5MHzの帯域幅を利用する W-CDMA方式が日本のNTTDoCoMoと欧州主要メーカとの間で欧州標準として規格化した。
- これに対し、北米のLucent、Motorola, Nortel, Qualcomm, 韓国のSamsungがLMNQS連合が、既存のCDMAと同じ1.25MHZ帯域(これを1Xという)を使用するか、3本束ねて使用する3Xを cdma2000として提唱し、両陣営は激しく対立したが、結局、両陣営はそれぞれのライセンスをたすき掛け方式で使用することを合意した。
- 当初は、LMNQS連合も「高速データ通信は帯域を広げて処理する」、かつ「今後とも電話が需要の中心」という考えだったが、「144Kbps以上のデータ通信の需要は考えにくい」ということで、W-CDMA方式のようにすべての端末を広帯域対応にするのは経済合理性に反すると考えた。また既存のCDMAシステムからのスムーズなアップグレード、即ち1Xと3Xとが同一システム内で共存できるというメリットもあった。
- さらに、インターネットの非対称型で、バーストデータに最適化した高速データ通信専用のHDR (38.4K - 2.4Mbps、平均600K)
が登場し、既存の1.25MHzの基地局設備をそのまま使用できる。
- 即ち、都市部にHDR基地局を設置し、地方はMC-1Xによる144Kbpsサービスでバックアップする。この組合せは市場動向を見ながら漸次柔軟に対応すればよい。また、細切れ状態の周波数帯を、同一システムで統一できるので設備・運用コストが削減できる。
- 1XとHDRは補完関係にあり、チップもデュアルモード化される。HDRの基地局がない、あるいは満杯の場合は1Xサービスとなる
|
>Top
3. Advantages of new technology of Qualcomm:
- gpsOne; tracking 4 GPS satellites with adjustment by terrestrial
signal from the station(gpsOne server)
- BREW(Binary Runtime Environment for Wireless); can operate
in the native mode by terminal CPU, unlike Java via virtual machine.
Qualcomm prepares ASIC chip for BREW, and whose API is planed to
be opened. The present mobile Java (KVM) contains difficulty in
speed and expression capacity in addition to memory efficiency.
- Multiband system:
In Japan various bandwidth (800MHz, 1.5GHz and 2GHz) are allocated.
Single technology has the advantage if it is applicable to any kind
of these bandwidth in the way of cooperation of the infrastructure,
nationwide roaming service and utilization of massive products made
for 800MHz.
- Importance of three 'seamless' viewpoint:
- Timeframely seamless: the current mobile terminal continues
to be useful. Update of the systems can be decided subject to
the market situation.
- Environmentally seamless: usable according to any environment
of fixed, portable or mobile, also functional at public or private
networks.
- Regionally seamless: usable anywhere in nationwide
and cross border.
- HDR (High Data Rate):
This technology was developed how to optimize burst data transmission
peculiar to the Internet in mobile environment, neglecting such
essential conditions for telephony as avoidance of time delay and
instant power failure. Therefore, separate channel using 1.25MHz
bandwidth is prepared to use only data transmission of 1-2Mbps.
To secure stability of communication, it is the key issue how to
control power level because receiving terminal varies distance from
the base station.
- Viewpoint of GoS (Grade of Service):
HDR system has no power control in download channel, instead
it controls data speed accordingly keeping uploading power capacity
as much as possible. In more specific, transmission data speed
is changeable according to the C/I (Carrier/Interference) ratio
of the terminal sampled every 1.67 msec, by the way of changing
modulation method, packet size (5 stages from 1024 to 4096 bits),
error rate (3 stages from 1/4 to 1/2) and sending speed per
packet (5 stages from 26.67 to 1.67 msec). After all the speed
becomes changeable from 38.4K to 2.4Mbps (average 600Kbps),
which gives higher speed service in favorable situation or lower
one in unfavorable situation.
- Use of the existing base station:
Download channel of HDR adopts TDMA system dynamically allocating
1.67 time slot to each terminal. Data communication is allowed
to reconnect and resend in case of discontinuation by cellular
crossing. The adjacent cells use the same frequency processed
by code modulation of CDMA technology. The existing facilities
and devices of the base stations are mostly commonly used for
voice and data communication. HDR base station looks like a
function of router from the viewpoint of IP network in the backbone
network.
- Dual mode of HDR and 1XMC:
The Chipset is made for dual mode of HDR and MC1X, which is
commonly used for voice and data communication, and is usable
nationwide from the beginning as 1X service of 144Kbps in non-HDR
service areas.
|
3. Qualcommの新技術とアドバンテージ:
- gpsOne:
GPS衛星信号(衛星4個)とcdmaOneネットワーク信号(gpsOne server)を併用。
- BREW(Binary Runtime Environment for Wireless)
JavaのようにVirtual machineを介さずに、直接端末機のCPUにnativeでアクセス。Qualcomm社ASICを活用。このAPIをオープンにする構想あり。現在の携帯用Java(KVM)は、スピード、表現力に難点あり、かつ使用メモリーも多い。
- マルチバンドシステム:
日本での異なった周波数帯(800MHz, 1.5GHz, 2GHz)のオペレーションを同一技術にすることのメリット大きい。インフラ設備の共用。全国ローミング、量産効果(世界ではまだ800MHzが主力)。
- 3つのシームレス:
- 時間的シームレス:これまでの端末は同じように使用できる。システムの更新は市場動向を見ながら行える。
- 環境的シームレス:固定、ポータブル、モバイルそれぞれの環境で同じように使える。公衆網にも自営網にも対応できる。
- 地域的シームレス:広域で使える。国境を越えて使える。
- HDR (High Data Rate):
インターネット型のバーストデータを効率的に移動体環境で伝送できるかという課題について、電話型の遅延や瞬断を許さないという条件を切り捨てることが前提に開発した。それゆれ、電話チャネルとは別に、同じ1.25MHz帯域幅のチャネルを1-2Mbpsのデータ専用で使う構想。通信の安定性を確保するためには、基地局からの距離が常に変動する端末における受信電力の制御が課題である。
- GoS (Grade of Service)の考え方:
HDRの下り回線においては電力制御は行わず、送信電力は最大値に設定したまま、代わりにデータスピードを制御する。具体的には、変調方式、パケット長(1024-4096bitの5段階、誤り訂正率(1/4
- 1/2の3段階)、1パケットの送信時間(26.67 - 1.67 msecの5段階)をその瞬間(1.67msec)毎の端末機の対搬送波干渉率(C/I)に従った変化させ、送信データスピードは、38.4Kから2.4Mまで変化する。(平均600Kbps) 即ち、状況の良い所にいるユーザには高速で、そうでないユーザには低速でサービスするという考えである。
- 既存の基地局の利用:
HDRの下り回線は、1.67msecのタイムスロットを各端末に機動的に割り当てるTDM方式を採用。データ通信の場合はセル間の移動でリンクが切れてもつなぎ直しすればよい。隣接セルにも同一周波数を使い、符合識別で処理するというCDMA技術は堅持しており、既存のCDMAの基地局の設備、および音声データ共用の端末機もほとんどの部品が共通に使用できる。バックボーンネットワークである既存のIP網から見れば、HDR基地局はルータに見える。
- HDR端末のチップはMC1Xとのデュアルモードが基本。これにより、音声とデータの共用。HDRインフラ未整備地域では、1Xによる144Kbpsでサポートされるので、早期に全国での使用が可能。
|
>Top
4. World Mobile Market Forecast in 2004:
- There are three groups of systems:
- Group-I (second & half generation): advocate of conventional TDMA system.
Enhancing the conventional TDMA (GSM/IS-136) by updated GPRS and
EDGE, and trying to maintain this 2.5G system as long as possible,
not expecting too much about higher data communication needs.
- Group-II (third generation): advocate of W-CDMA system
Promoting W-CDMA system as the ideal method for the time being.
They believe the system should level up drastically from 2G, 3G
then 4G.
- Group-III (third generation): advocate of cdmaOne and cdmaOne2000 system
Keeping compatibility of 2G and 3G based on cdmaOne technology,
and trying to deploy HDR system for higher data communication.
- Worldwide market forecast in 2004 (by the lecturer):
- 70% of the world market satisfy the present voice and lower data
communication, while only 30% requires higher data communication.
- The market share of voice + lower data is estimated: GSM 60%,
cdmaOne series 30%, W-CDMA 10%.
- At the moment,
- GSM system is prevailing in voice.
- How much grow the need for higher data communication?
- The point is how to cultivate so-called killer application at
the reasonable cost, that is:
- Visual and high audio email service
- Enhancement of contents service
- Full-scale of eCommerce
|
4. 世界市場予測 (2004年) :
- 世界の3つの流れ:
- 第一グループ (第2.5世代):
旧守TDMA派
TDMA(GSM/IS-136)をGPRSとEDGEで補強し、長期間に亘って、この2.5世代を維持し、高速インターネットの市場重視せず。
- 第二グループ (第3世代):
W-CDMA派
W-CDMAを当面の理想として推進。第2世代→第3世代→第4世代とシステムが全面的に変更されていくという考え。
- 第三グループ (第3世代):
cdmaOne2000派
cdmaOneをベースに、第2世代と第3世代とのcompatibility堅持。高速インターネットに対しては、専用のHDRを導入。
- 2004年の世界市場の独自予測
(講演者による):
- 世界市場の70%は、音声+低速データで満足。高速データのニーズは30%。
- 音声+低速データ市場のシェアは、GSM 60%, cdmaOne系列30%, W-CDMA 10%と推定。
- 高速データ市場のシェアは、HDR(1X)で70%、W-CDMAは30%と推定。
- 現状では、
- 音声は、まだGSMがまだ当分主流
- 高速データの需要がどの程度急成長するか?
- ポイントは、いかに安い価格体系で、キラーアプリケーションを開発できるかにかかっている。即ち、
- 音声、画像を添付した本格的なメールサービス
- コンテンツの高度化
- より本格的なeコマース
|
>Top
5. Features of Japanese Market:
- Gadget* Paradise:
Japan is expected to be an epicenter of new market trend. Japanese
government allocated to the carriers for free of charge 48MHz bandwidth
in 800MHz zone, 24MHz in 1.5GHz zone, and 60MHz in 2GHz zone without
applying open tender. If the mobile tariff is cheaper, new demand
for data communication can be aroused. But such applications are
not practical as video telephone or mobile movie based on circuit
switch base, rather burst data communication will be promising.
Users are eager to use split disposable time by mobile environment.
In Japan there are exceptionally rich homogeneous youth market,
who are ready break new emerging market.
- *Note: Gadget means a small specialized mechanical
or electronic device; a contrivance, easily recognized by loitering
about in Akihabara area, Tokyo.
- *Note: It is controversial whether iMode users should
be counted as Internet users from the viewpoint of utilization
, computer literacy (edit and reuse of information) or consciousness
as a netzen, not from the system architecture. (Cf: Digital
Divide by Mr. T. Kimura)
- Prospect of Mobile Internet in Japan:
- First stage: higher speed Internet application for Japanese
youth, such as color still picture, movie graphic, high quality
voice and audio by 8Kbps.
- Diversified mobile equipment: PDA, Notebook PC, Modem adapter
for desktop PC
- Diffusion of B2C and B2B application by mobile Internet.
|
5. 日本市場の特質:
- ガジェット(Gadget *)天国:
日本が市場開拓の震源地となる可能性は大きい。日本では800MHz帯で片道48MHz、1.5GHz帯で片道24MHz, 2GHz帯で片道60MHzが、幸い、入札によらないで割り当てられている。利用料金を安く設定すれば、新たなデータ通信需要が喚起される。但し、ビデオ電話、携帯映画のような回線交換型のアプリケーションは現実的でない。むしろバースト型の高速データ通信の需要である。ユーザが携帯端末で利用するのでは「ぶつ切りの可処分時間」の利用である。日本には、世界で例外的な「画一的かつ富裕な若者市場」*がある。
- *注)Gadeget:気の利いた小物、目新しい道具。A small specialized mechanical or
electronic device; a contrivance.
- *注)iModeがインターネットユーザとして加算すべきかについては異論がある。システムとしての同一性だけではない、利用状況、コンピュータリテラシィ(加工編集、情報発信等)や、ネチズンとしての意識の面で彼我間には天地の差があるように思える。(Cf:
デジタル・デバイド)
- モバイル・インターネット市場展望:
- 第一段階:日本で若者向けの「ぶつ切り」高速インターネット・アプリケーションの開花
(カラー静止画、動きのあるグラフィック、8Kbpsの音声、音楽等)
- 多様な移動通信端末の普及:PDA、ノートPC、デスクトップPC用のモデムアダプタの普及
- ワイヤレス・イントラネットを中核としたB2C, B2Bによるモバイルビジネスの普及
|
>Top
6. Various Mobile Systems:
- The existing specification (2G):
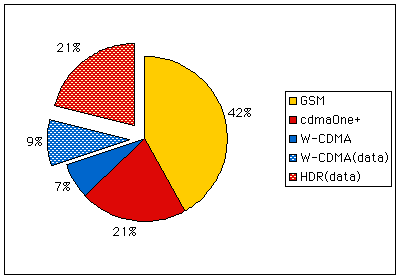
- GSM (Global System for Mobile communications):
GSM is digital mobile telephone system used in 142 countries as
of end of 1999. The speed is 9.6Kbps based on circuit switch.
- The attached system GPRS (General Packet Radio Service)
is based on packet switch, with the speed of 115..2Kpbs.
- And the enhanced system EDGE (Enhanced Data rate for
GSM Evolution), with the speed of 384Kbps.
- PDC (Personal Digital Cellular) is developed and standardized
in Japan as digital mobile telephone system, using 800MHz and 1.5GHz
band zone based on TDMA system.
- cdmaOne: mobile telephone system used in US and Japan. IS-95A system services at 14.4Kbps, and IS-95B 80Kbps.
- Representative specification of IMT-2000 (International Mobile Telecommunications 2000):
- DS-CDMA (Direct Spread-Code Division Multiple Access) (W-CDMA)
Standardization organization is 3GPP (Third Generation Partnership
Project)
Promoted by European makers like Swedish Erickson and Norwegian
Nokia. In Japan, NTTDoCoMo and J-Phone groups adopted this system.
Spreading ciphered and coded signals in the bandwidth of 5MHz or
10MHz. NTTDoCoMo starts its commercial service of 384Kbps in Japan
this spring, then enhance maximum 2Mbps service after 2002 if 15MHz
bandwidth becomes available.
- MC-CDMA (Multi Carrier-Code Division Multiple Access) (cdma2000)
Standardization organization is 3GPP2 (Third Generation Partnership
Project-2)
Promoted by US makers like Qualcomm and Lucent Technologies. In
Japan KDDI adopted this system.
- MC-CDMA/1X services at 153Kbps, while enhanced MC-CDMA/3X services at maximum 2.4Mbps.
- HDR (High Data Rate) system using standard bandwidth
called 1X(1.25MHz) developed by Qualcomm, based on packet
exchange system only used for data communication.
- Enhanced triple bandwidth service called 3X(3.75MHz)
.
- iXTREME developed by Motorola, giving maximum speed
at 5.184Mbps.
|
6. <参考>:モバイルの各方式:
- 既存(2G)の規格:
- GSM (Global System for Mobile communications):
GSMは、現在、世界142ヶ国/99末で普及しているデジタル携帯電話システム。通信速度は9.6Kbpsの回線交換。
- またこのGSMに追加したパケット交換方式のGPRS (General Packet Radio Service),
115..2Kpbs、
- およびその強化版のEDGE (Enhanced Data rate for GSM Evolution)、384Kbps
がある。
- PDC (Personal Digital Cellular) 日本で標準化したデジタル携帯電話の方式。800MHzと1.5GHzを利用。通信方式はTDMA方式。
- cdmaOne:米国と日本が採用している携帯電話システム。この内、IS-95Aは14.4Kbps、IS-95Bは80Kbps。
- IMT-2000(International Mobile Telecommunications 2000) の代表的な規格:
- DS-CDMA (Direct Spread-Code Division Multiple Access) (W-CDMA)
標準化団体:3GPP (Third Generation Partnership Project)
エリクソン、ノキアなど欧州メーカが推進。日本では、NTTDoCoMoとJフォンの2グループが採用。
伝送信号を暗号化して、5MHz、10MHz等の各周波数帯域に拡散して無線伝送する方式。NTTDoCoMoは、まず384kbpsの商用サービスを開始し、その後15MHz帯域が使用できる2002以降に最大2Mbpsサービス開始予定。
- MC-CDMA (Multi Carrier-Code Division Multiple Access) (cdma2000)
標準化団体:3GPP2 (Third Generation Partnership Project-2)
クアルコム、ルーセントテクノロジーなど米国メーカが推進。日本ではKDDIが採用。
- MC-CDMA/1Xは最大153Kbps、MC-CDMA/3Xは最大2.4Mbps。
- 1X(上下1.25MHz)を使用したにクアルコムが開発したデータ専用のパケット交換方式HDR (High Data Rate) 最大2.4Mbps、
- さらに、3本束ねた、3Xサービス(3.75MHz) がある。
- モトローラ開発のiXTREME、最大5.184Mbpsがある。
|

