For IT Revolution in Japan
Rechallenge toward 21st century
Cat: ECO
Pub: 2001
#0103
Kanzo Kobayashi
01131u/18205r
Title
For IT Revolution in Japan
IT革命の今日の課題
Subtitle
Rechalleng toward 21st century
21世紀に向けての日本の再チャレンジ
Author
Kanzo Kobayashi
小林寛三
Published
Jan. 2001
2001年1月
Index
- IT Revolution is IP revolution
- Japan-US IT imbalance:
- Wideband usage for Internet connection:
- Internet proliferation rate per capita:
- Cyber Korea-21:
- Competitiveness of IT Industry:
- Business Method Patent:
- Emergence of Swap Software:
- Next Generation Type of Web Technology:
- Public Investment to Education:
- Globalization and skills level:
- eGovernment in US:
- Pyramid of Wealth:
- Three success factors of IT Revolution:
Why?
- New 21st century has come!
- It is often criticized by overseas that Japan
has been "too little and too slow" in proceeding IT
revolution. Can Japan to break through this situation toward 21st
century?
- As an inside watcher of current activities and
market atmosphere of the IT industry, I dare to mention several
viewpoints and suggestions for the advancement of IT revolution
in Japan, which include mixed theme of political, economical,
cultural, educational and technical issues. Also it is particularly
important for us not to shrink from challenging these piles of
problems to attain.
- 新たな21世紀がついに到来した。
- IT革命に関しては、日本は、海外からいつも"Too little, too slow"と言われ続けてきたが、21世紀に向けてこの突破は可能なのだろうか?
- IT業界で考える場を与えられた者として、最近のIT革命への今日的な課題を整理する。テーマは、政治・経済・文化・教育・技術と広範囲に亘り、これら課題山積の中で、萎縮せずに意欲的にチャレンジする精神が重要である。
Summary
要約
>Top 1. IT Revolution is IP Revolution:
- This
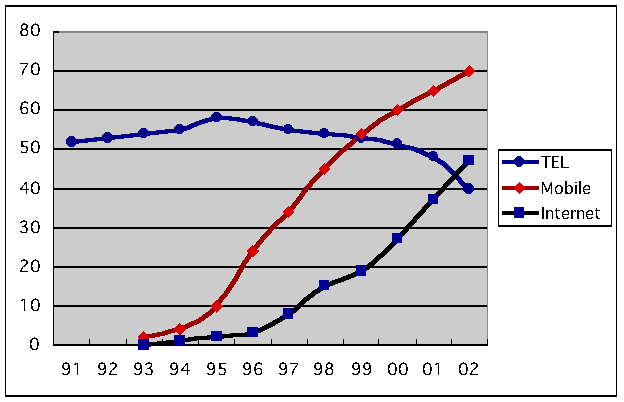 chart shows number of subscribers of telephone, cellular
phone and Internet in Japan.
chart shows number of subscribers of telephone, cellular
phone and Internet in Japan.
The number of cellular phone
subscribers exceeded that of wire telephone for the first time in
1999.
Wire phones have been basic communication medium, used as a basic
figure in telecom industry, but leading role of wired phone is finishing;
cellular phones can expand more than one for each person.
- NTTDoCoMo expects that all movable objects could be possible users
during 2005-2010 in Japan; the total number will be about 360 million,
including 120M for all population, 100M for car navigators, 60M
for bicycles, 50M for mobile PCs, 20M for pets (dogs & cats),
and 10M for motorcycles & ships. All these subscribers will
be mobile Internet users. Such trend suggests that wire telephone
will be soon no more than a niche service.
- The essence of Internet is IP (Internet Protocol, usually referred
as a set of TCP/IP); all information of voices, pictures, movies
are digitized and transmitted in a form of digitized packets (IP
packets). Within several years, all telephones will be in the form
of IP-telephone.Also it is expressed like "Everything on IP"
or "IP over Glass" meaning all IP-packetized information
transmitted on optical fiber. Thus the essence of IT revolution
is IP revolution, that is, expansion of Internet.
1. IT革命の本質はIP革命:
- 左図は、電話、携帯電話、インターネットのユーザ数を示す。
- 昨年1999年に、携帯電話のユーザ数が (有線) 電話のユーザ数を始めて抜いた。
有線電話は、通信の基本的なインフラであり、すべての基礎数字となっていた時代は終了した。携帯電話は1人1台以上の普及が期待できる。
- NTTDoCoMoによれば、日本では、これから2005-2010年にかけて移動するものすべて、即ち、全人口120M人、全ての自動車 (カーナビ) 100M台、自転車
60M台、携帯PC 50M台、ペット (犬猫)20M匹、オートバイ・船等 10M台、合計360M台もの移動通信の需要可能性があるという。
これら移動通信は、すべてモバイル・インターネットの端末として伸びていく。
有線電話もこの流れの中で、もはや主役ではなくなってきている
- インターネットの本質はIP (Internet Protocol) にある。音声も画像も動画もすべてIP化して伝送することになろう。数年もすれば、すべての電話はIP電話となり、まさに、"Everything
on IP"、あるいは、光ファイバ上のIPという意味で、"IP over Glass"となる。正に、IT革命の本質はインターネットの拡大、即ち、IP革命にある。
>Top
2. Japan-US IT imbalance:
- This is Japan-U.S. Comparison of the information investment
ratio. (Sources: Information White Paper 2000)
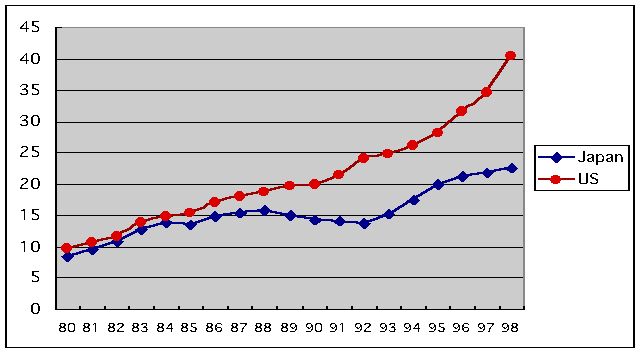
- This ratio shows information-related investment (60% as new investment
and 40% as maintenance and operation fees for existing systems)
against all non-housing investment in private sector.
- This chart is symbolic of 'the lost decade in Japan' after collapse
of bubble economy since 1990.
- 1992 became a typical divining year; showing remarkable increase
in US investment while Japan decreases; if compared to golf match,
US scored a birdie, while Japan hit a boggy shot.
- This imbalance between Japan-US reflects Japanese decade long
serious recession. But also there will be another essential difference;
in US information investment is regarded as rationalization to new
economy, while in Japan such clear motivation blurred because of
potential in-house unemployment status in MIS division mainly committed
to mainframe legacy systems. In US most advanced package software
like ERP were positively induced as a process of BPR (Business Process
Reengineering).
- Thus, the year of 1992 became the starting point of Japan-US imbalance
spreading in updating information systems.
2. 日米IT格差の原点:
- 左図は、情報化投資比率の日米比較である。 (出典:情報化白書2000)
- 即ち、非民間設備投資に対する情報化投資額の割合 (新規情報化投資+既存システムの維持・運用費用の合計。前者の比率は約60%)で、1990からのバブル経済の崩壊に伴う日本の「失われた十年」の影響が大きい。
- 1992年は、米国の情報化投資の伸びに比べて、日本むしろ減速しており、ゴルフに例えれば、いわば米国のバーディーに対し、日本のボギーという結果となってしまった。
- 日米格差は、日本での不況という要因は大きいが、更にそれに加えて、日本の場合、伝統的なメインフレームの技術を中心とする情報システム部門という潜在的な社内失業者を抱えていたため、合理化のための情報化投資が選択できなかった。一方、米国では、ERPパッケージなどBRPの一貫として積極的な情報化投資が行われた結果である。
- この1992年は、今日の日米IT格差が広がった原点とも言える年となった。
>Top
3. Wideband usage for Internet connection:
- This is to show the progress of band usage for Internet.
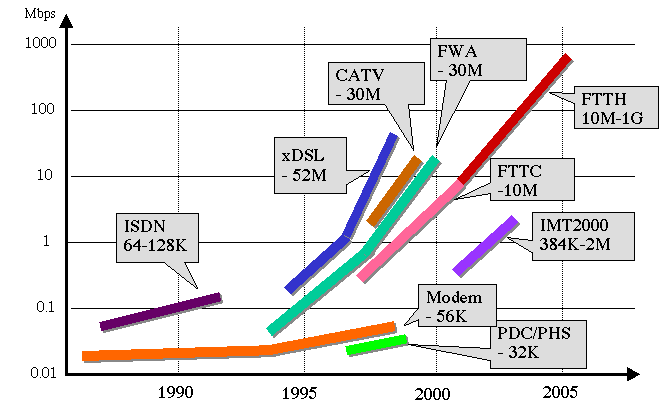
- This chart looks like ski lifts of mountain climbing, but these
should be much steeper, because Y axis is logarithmic scale.
- Comparison with a lift of mountain climbing well express the situation
that we much change lifts to climb a higher place (wider-band usage).
We must throw away a modem used for connection with wired phone
and change into TA (Terminal Adapter) for ISDN.
- Similarly, we much buy or rent different communication devices
each time to utilize xDSL, Cable TV, IMT2000 and finally optical
fiber.
- Internet originally has developed assuming always-on connection
like LAN environment. But no one has actually other options to use
wired telephone line at home. Benefit and convenience by Internet
are guaranteed by using wideband, always-on and cheap rate connection;
without these three factors the fully functioned merit could not
be realized. Information society could attained escaping from such
traditional telephone rate thinking charged by connecting time enforcing
people to minimize communication time and handle information bit
by bit.
- To fulfill the telecom infrastructure will be a synonym to realize
such widerband, always-on and cheap connection of Internet as quickly
as possible. In addition, it becomes soon a general trend for individuals
or corporations to shift to the areas fully equipped with favorable
environment for Internet.
3. インターネットの広帯域利用:
- 左図は、インターネットの広帯域化を示す。
- Y軸は対数目盛になっているので、これを山登りのリフトに例えると、実際にはもっと急峻になる。
- 山登りのリフトに例えたのは、より高い所 (広帯域利用)に登るには、リフトを乗り継がなければならない点も似ているからである。
- 即ち、有線電話線にモデムを接続したインターネット利用の環境は、ISDNに切り替えるためには、モデムを捨ててTA (Terminal
Adapter)を購入する必要がある。
- 同様に、xDSLやCable TVを利用する場合、IMT2000を利用する場合、そして究極の光ファイバを利用する場合、いずれも接続用の通信機器をその都度、購入・レンタルが必要になる。
- インターネットは本来はLANの環境を想定して発達してきたので、常時接続が前提であった。それを家庭で接続する場合は、やむなく有線電話の回線の利用をしてきた。インターネットの良さも便利さも、広帯域+常時接続+安い接続料金、この「広・常・安」が実現しなければ本来の長所が発揮されない。情報化社会の実現は、接続時間を気にして、細切れ情報をちびちび利用するような従来の電話料金の発想では到底実現しない。
- 通信インフラの充実とは、まずこのインターネットの広・常・安を実現することと同義語であると認識して、早期に実現図る必要がある。また、これからは企業も個人も情報インフラの整った地域に移動することが一般的となる時代がやってくる。
>Top
4. Internet proliferation
rate per capita:
- This is Internet proliferation rate per
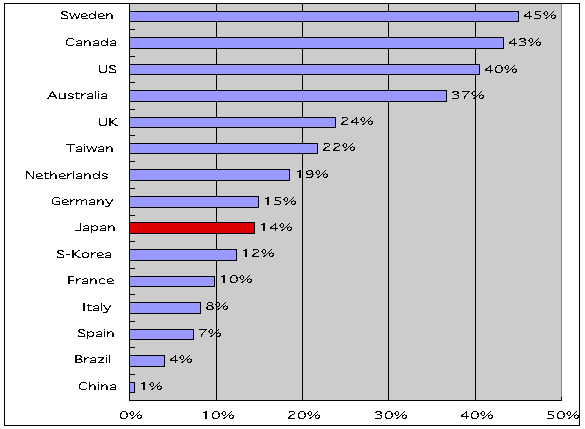 capita in
each country as of the end of 1999. (Source:
Computer Industry Almanac. Inc.)
capita in
each country as of the end of 1999. (Source:
Computer Industry Almanac. Inc.)
- The actual top ranking three are 1) Iceland with population 0.3
million, 2) Finland, population 5M, and 3) Norway, population 4
M, which are omitted here due to too little population.
- Korea (population 46M) shows remarkable growth in using Internet,
whose users has already exceeded 16M, with proliferation ratio about
35%, ranking in world top-class.
- Contents used by Internet is important, but it becomes meaningful
with substantial number of users.
- If this is an Olympic game, Japan should aim to be categorized
in the top rankings, let alone taking a some color of medal.
4. 今日の技術:
- 左図は、1999年末の一人当たりのインターネットユーザ数である。
(出典:Computer Industry Almanac. Inc.)
- なお、実際のトップ3の国は、
1) Iceland、人口0.3M、
2) Finland、人口5M、
3) Norway、人口4Mであるが、人口が少ないためにこの図からは漏れている。
- 注目すべきは、韓国の伸びで、すでに16M人 (人口46M)を突破したと見られており、35%程度の普及となり、一気に世界のトップクラス入りとなった。
- インターネットの活用は、中身が重要とは言えまずは普及である。
- 日本もオリンピックと同様に、一気にメダルとは言わぬが、せめて決勝 (トップクラス)入りを目指すことを目標とすべきである。
>Top
5. Cyber Korea-21:
- This is "Cyber Korea-21" reporting system
to the president office in
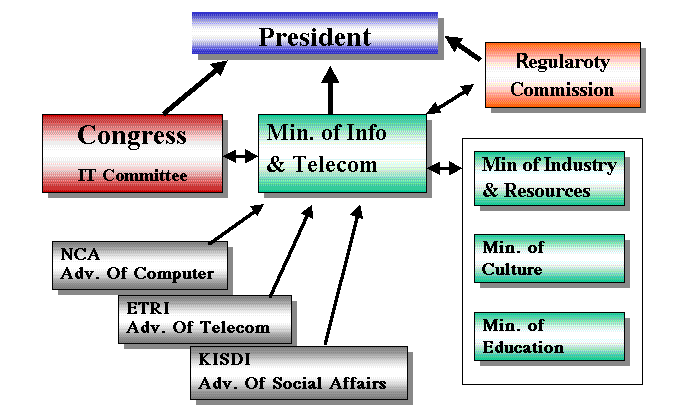 Republic of Korea by the functions of
Ministry of Information and other related organizations.
Republic of Korea by the functions of
Ministry of Information and other related organizations.
- Compare the size of population; Japanese 126 million, while Korean
46M, and GDP; Japanese $4,378 billion, while Korean $407 billion
(1999).
- Korea suffered the IMF economic crisis in 1997, the following
year Kim DaeJung became president and promoted active structural
reform, stressing IT new business with "Cyber Korea" vision.
- Consequently, the users of Internet jumped to 5 times increase;16.4
million as of August 2000 from 3 million in two years. It is surprising
that high speed connected users increased to 2.6 million by ADSL
and Cable TV; bringing Korea to the top ranking Internet user at
a stretch.
- We must mention that Korean statistics in GDP growth rate and
unemployment ratio through 1997 and 1999 respectively; 5%/2.6%→△6.7%/6.8%→10.7%/6.3%.
During the same period Japan also suffered severe economic recession,
but no so much like Korea. It is natural that sharp crisis brings
more strong message to swing from old sense of values; which is
described as "Creative Destruction" meaning to let old
values go and let new ones come. On the contrary Japan seemed to
have rescued the old industry almost finished their roles to survive
spending enormous public fund under the pretext of preserving the
present financial world.
5. 韓国のIT革命の現状:
- 左図は、情報通信部および大統領府 (青瓦台)を中心としるIT政策決定システムである。
- 日本と韓国とは、人口は126M対46M、GDPは、$4,347B対$407B (1999年)である。
- 韓国は、1997年のIMF経済危機、および翌年の金大中大統領就任以来の計画構造改革、"Cyber Korea 21"のビジョンおよびIT起業ブームによって大きく様変わりしてきた。
- その結果、2年前に300万だったインターネット利用者は、2000年8月には1640万人へと5倍以上に急増した。特に、ADSLやCABLE
TV経由といった高速サービスでの利用者が260万人もいる。インターネットの広帯域利用においては韓国は一気にトップクラスの利用国となった。
- 韓国は、97年の経済危機以降、98年、99年とそれぞれGDP伸び率と失業率が、5%/2.6%→ △6.7%/6.8%→ 10.7%/6.3% となっている。この間、日本も厳しき経済環境であったが、韓国ほどの激しい落ち込みは示していない。危機の溝が深ければその分真剣に既存の価値観からの転換を図ろうとする動きが生まれる。「古いものが退場し、新しいものが誕生する」ことが創造的破壊であって、日本の場合は、退場すべき役割を終えた組織の延命を、金融システム維持の名目で、公的資金で救済するという逆のことが行われたのではないか?
> Top
6. Competitiveness of IT Industry:
- This is Competitiveness of IT Industry
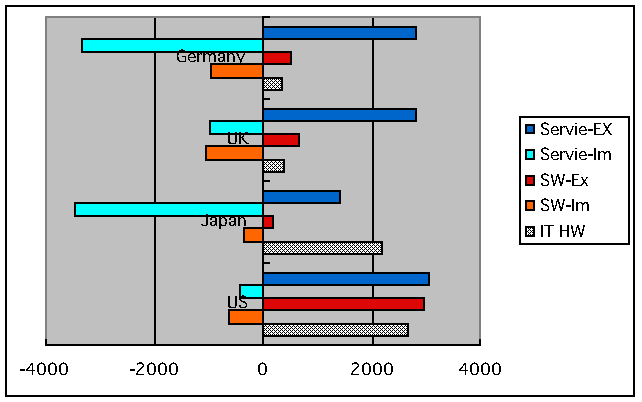 among Germany,
UK, Japan and US. (Source: "Information Technology Outlook
2000"), showing export in the right column and import in
the left. Please note that production of hardware in the right column
is described in 1/100 scale.
among Germany,
UK, Japan and US. (Source: "Information Technology Outlook
2000"), showing export in the right column and import in
the left. Please note that production of hardware in the right column
is described in 1/100 scale.
- The core industry in Information Age will be software and service.
- Japan is superior in peripheral technology such as liquid crystal,
compact-packaged PC notebook, and DVD player. But compared to US
and Europe, Japan is excessively importing software and services.
- Even Japanese word processor named Ichitaro has been swept over
by MS Word.
- Package software such as OS, database, ERP, SCM, CRM are almost
made in US and partly in Europe. These packages are regarded as
defacto standard; it is reality that Japanese software companies
only function as subcontractors in making Japanese version and debugging
of localization as well as installation, operation and maintenance
of the systems.
- Furthermore, there is a handicap in two bytes code using countries
like Japan, China and Korea who must convert the original one-byte
code into double byte within limited time.
6. IT産業の国際競争力:
- 左図は、国別IT産業規模を示す。 (出典:OECD "Information Technology
Outlook 2000")右側が輸出量、左側が輸入量となっており、ハードウェアは1/100表示にしてある。
- 情報化社会での中核的な産業は、これからはソフトウェアとサービス産業である。日本は、液晶や薄型ノートPC実装技術やDVDなどの周辺技術に優れているが、ソフトウェアと関連のサービスに関しては、欧米に比べて大きな入超になっている。日本語のワープロソフト「一太郎」すら、米国のMS
Word に席巻されてしまった。OS、データベース、ERP、SCM、CRMなどのパッケージソフトはほとんどは米国、一部欧州製であり、それらが事実上の標準となっており、日本のソフトウェア産業はそれらの日本語化やバグ取りをした後のシステムの構築・維持・保守という下請け的な役割を演じさせられているのが現実である。
- 特に、2バイトのソフトウェアを利用する日本、中国、韓国の3ケ国は、1バイトで作られたソフトウェアを早急に2バイトに変換しなければならないというハンディキャップがある。
> Top
7. Business Method Patent:
- The essence of IT revolution is IP (Internet Protocol) revolution,
but, as for IP, there is an another aspect; Intellectual Property.
- In 1999, battles at "Business Method Patent" suddenly started
in US;
- Amazon.com company filed Burns & Noble.com for a patent infringement
about 'One Click method.'
- Priceline.com company files Microsoft and its affiliate Expedia.com
for a patent infringement about 'Reverse Auction method.'
- In addition, the situation of another case considered as decided
in 1996 judgment has changed; this is a case filed by AT&T for
patent infringement about 'Discount method
of telephone charges' by Excel Communications, but the
district court decided that the patent was invalid in view of such
kind of invention using mathematical calculation could not be patented.
But in October, 1999 the appellate court overturned this deciding
that such invention could be patented, but the patent of this case
was null and void by being obvious knowledge.
- Furthermore, the craze came to Japan; 'International Scientific
Co. Ltd.' insisted that time-based charging using ID and password
as well as sales of contents and shopping mall operation know-how
are patented and may infringe their business model patent.
- As these backgrounds, there is big difference in number of lawyers
between US (920K) and Japan (only 20K), and in cost level of royalty;
15-30% in software (6-7% in medical) in US, while around 1-5% in
Japan.
- Furthermore, US adopts "First-to-invent system", while
Europe and Japan adopt "First-to-file system", and regarding
patent information. US adopts "Publication-after-grant policy"
valid for 17 years after the grant, but amended to 20 years after
the application, while Europe and Japan adopt "Automatic
Publication policy", automatically publicizing 18 months
after the application and valid for 20 years after the application.
- Submarine patent means 17 years validity after the
grand (which was amended later, remaining some transitional measures)
may bring sudden exclusive grant (like surface of a submarine) for
old and matured technology after elongated examination.
- In US Donald Reagan administration (1981-89) changed to Pro-Patent
Policy in 1885, which was succeeded in Bush and Clinton administrations.
In particular 1994 rule of examination deregulated conditions of
eligibility, which caused rush of applications of many business
method patents.
7. ビジネス・モデル特許:
- IT革命の本質は、IP革命であるが、もう一つ本質として、IPはIntellectual Propertyの側面がある。
- ビジネス・モデル特許については、1999年に至って、突然、米国でビジネスモデル特許に関する訴訟合戦が開始された。
- アマゾンドットコム社が、バーンズ&ノーブル社をワンクリックに関する特許侵害で提訴し、
- プライスライン社が、マイクロソフト社とその子会社のエクスペディア社をリバース・オークションに関する特許侵害で提訴した。
- また96年に解決済みと思われていた事件も逆転判決が行われた。AT&T社は、エクセル・コニュニケーション社を電話料金の割引方法に関する特許侵害は、「数学的な算定方式を利用したビジネス・メソッドは発明の対象とならない」として、地裁は特許無効の判決を下していたが、99年10月の控訴審においては、「この種の発明は特許と対象となるが公知により権利は無効」となった。
- なお、日本にも飛び火した。インターナショナル・サイエンティフィック (株)による公告。インターネット上でID/パスワードを使い、時間単位の課金、コンテンツの販売、ショッピングモールの運営は、同社のビジネスモデル特許に抵触するというものである。
- これらの背景としては、日米の弁護士数の圧倒的な差がある。米国92万人対日本2万人である。また、ロイヤリティについては、米国ではソフトウェアでは15-30%
(医療品Hが6-7%)、日本では1-5%が相場である。
- 米国の特許制度は特に、「先発明主義」であるのに対し、欧州・日本は「先願主義」を採用している。また、特許情報に対し、米国は「非公開主義」従来は、特許期間は、特許付与から17年間だったが、そのご出願時点から20年に改正された。それに対し、欧州・日本は「公開主義」
(出願後18ケ月後に公開、存続期間は20年) を採用している。
- サブマリン特許:最近までは、審査期間の如何を問わず、特許付与から17年間とされたため (その改正後も経過措置がある)、古い成熟した技術に対し、突然 (潜水艦が浮上する如く)独占的な特許権が認められるケースをいう。
- また米国では、特に、レーガン政権時代(81-89年) の85年にプロ・パテント政策への転換が行われ、ブッシュ、クリントン政権にも引き継がれた。特に、94年の新審査基準によって、特許適格性が大幅に緩和され、多くにビジネスモデル特許申請の背景となっている。
> Top
8. Emergence of Swap Software:
- Swap Software is a kind of software for P2P (Peer-to-Peer)
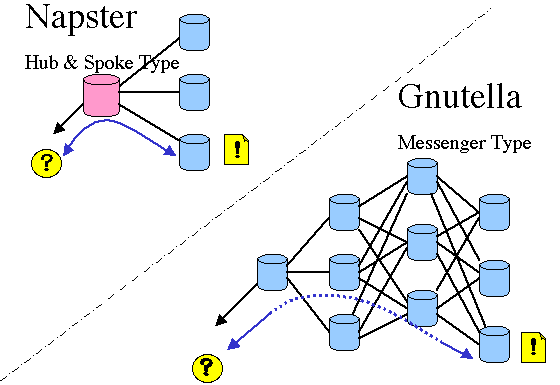 communication. P2P is a communication protocol originally developed
for simple LAN environment connecting equal terminals. ('Peer' means
equal rank or ability.) Client & Server system, however, is
different in function, and high & low relation between server
and client.
communication. P2P is a communication protocol originally developed
for simple LAN environment connecting equal terminals. ('Peer' means
equal rank or ability.) Client & Server system, however, is
different in function, and high & low relation between server
and client.
- A killer application of the P2P appeared, which is "Napster."
- Napster appeared and rapidly proliferated as a utility software
of music files of MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3) format, in order to
search the particular server and download them directly from the
stored database connected to the server. It seems to be a kind of
software exchanging files between libraries.
- It is indicted downloading by this Napster for violation of the
copyright of music.
- 'Gnutella' which was developed by Nullsoft, an AOL affiliate,
as a JAVA application lately appeared; another P2P software enabling
research and download without requiring help of the particular server.
(It is expressed 'Servant' meaning Server plus Client functions.)
The download using this Gnutella' makes it difficult to trace the
participated servers or particular routes for assumed infringement
the copyright.
- Meanwhile, these file sharing technology is expected to be useful
in sharing common knowledge in the field of science, or projects
like looking for a needle in a haystack; 1) human genome search,
2) discovery of huge prime numbers, 3) cooperation to SETI (Search
for Extra Terrestrial Intelligence) project, and 4) data analysis
of elementary particles by CERN by the downloaded program using
capacity of huge number of PCs connected Internet.
- Furthermore, a Irish group of Ireland developed a program named
'FreeNet', which can remove the source of information from
where is is downloaded. This FreeNet is developed intending the
world of free common share of information and obsoleting conservation
of worldwide copyrights.
- Thus, cyber space tends to contain various and individual needs
fulfilled by using universal network.
8. スワップ・ソフトの隆盛:
- Swap Softwareとは通信に用語で言えば、P2P(Peer-to-Peer)通 信となる。これは当初は簡易なLANのように対等な端末同士の通信方式のことであった。
(Peerとは、地位 や能力が対等な人の意)
- なお、Client & Server方式は、上下関係がありこれに該当しない。
- そのP2Pのキラーアプリケーションが登場してきた。"Napster"である。始めは、インターネット上に保存されているMP3形式の音楽ファイルをサーバで検索して、ダウンロードするためのソフトとして急速に普及した。いわば図書館相互間のファイル交換のようである。
- このNapsterを使った音楽ファイルの共有が著作権法に違反するとして告訴されている。
- その後登場したGnutellaは、サーバを必要としないP2Pで、検索・ダウンロードが可能なソフトがNullsoft社 (AOLの子会社)によってJava
Applicationとして開発された。("Server+Client=Serventと呼ぶ)これは、関与するサーバやルートが多く、著作権違反で特定の主体を訴訟することは至難と言われる。
- これらファイル共有技術は、科学分野の情報の通有という意味で期待されている。ヒトゲノム計画、巨大な素数の発見、地球外生命を探索するSETIプロジェクト、CERNによる素粒子データ解析など、インターネットの接続されたパソコンがダウンロードしたプログラムによって、干し草の中の針を探すのである。
- 更に、アイルランド人のグループは、"FreeNet"というインターネット上から情報の源泉を取り除いてしまうプログラムを開発した。これは意図的に世界の著作権の保護自体を陳腐化させることでm情報の自由通有される世界を目指している。
- このように、サイバー空間には、普遍的なネットワークとそれを利用する多様で個別で異質なニーズを双方を満たそうとしている。
>Top
9. Next Generation Type of Web Technology:
-
This is a chart of the Next Generation Type
of Web Technology.
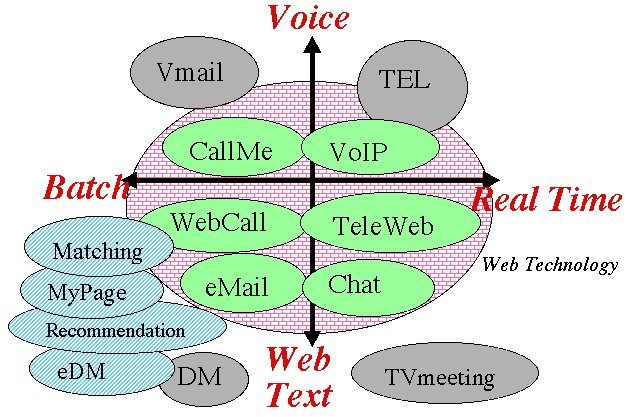
- Vertical axis shows voice communication vs. Web communication
including text.
- Horizontal axis shows realtime process (=respond now) vs. batch
process (=call back later)
- Web technology has enabled versatile communication media and drastically
changed marketing style.
- It was our custom to respond now by telephone and confirm later
by mail.
- Thereafter voice mail, TV phone and TV conference system appeared;
all these media are enhanced by Web technology bringing us various
types of communication services combining realtime and batch processed
services.
- Customer became 'Individual customer' ('Kokyaku', both homonym
in Japanese); It became decisively important how to analyze individual
need and reflect it to more considerate services (Database Marketing,
One-to-one Marketing, etc.)
- Traditional Callcenter transformed into 'Customer Center' or 'Contact
Center', which are equipped various functions for better customer
relationship. Whenever press "Call Me" button on the Web,
you can talk with or question to an operator of callcenter looking
the same Web information via telephone or Void (Voice over IP).
This is a remarkable combined media of realtime communication and
operator's special advice by the customer's choice.
- eCRM (e-Customer Relationship Management) will be a new customer-oriented
services combination of Web, Database and Callcenter.
9. 次世代型WEB技術:
- ここに、次世代型の多様なWeb技術を図示した。
- 縦軸は、音声かあるはWeb (テキストを含む)かの区分。
- 横軸は、情報がリアルタイムに処理 (=今すぐ)か、バッチ処理 (=後で返事)かの区分。
- Web Technologyは、通信の多様性をもたらし、特にマーケティングのあり方を大きく変えている。
- リアルタイムの通信は、まず電話で、詳しくは後から手紙でというのが一般的な方法だった。
- その後、Voice mailやTV電話、TV会議システムなどが導入されたが、Web技術によって、これらが統合化され、リアルタイムとバッチ処理の通
信を組み合わせた多様な通信サービスが登場している。
- 顧客は「個客」となり、いかに個別の情報を把握してきめ細かくサービスをスマートに実施するかが重要になってきた。 (データマイニング、あるいはコンタクトセンタと呼ばれるような機能を取り入れてきた。)
Web上の「Call Me」ボタンを押すことで、同じWeb画面をオペレータと共有しながら、電話やVoIPなどで会話することができるようになった。これはユーザの選択に基づくWebに、リアルタイム性とオペレータの専門性を組み合わせた新しい通
信の形態である。
- eCRM (e-Customer Relationship Management)は、Webとデータベースとコールセンタが連携した新しい顧客サービスのシステムである。
>Top 10. Public Investment to Education:
- Japanese Public Investment
to Education
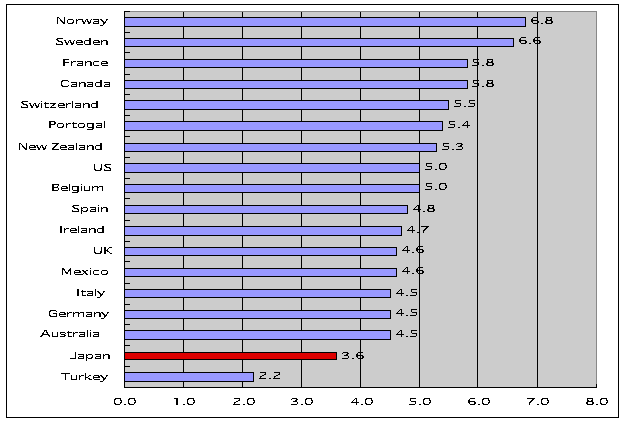 shows as low as 3.6% in GDP, while other advanced
countries around 5% or more.
shows as low as 3.6% in GDP, while other advanced
countries around 5% or more.
- Japanese education has been supported by parents' passion and
hopes expecting better education brings better recruitment, increase
of job post of big corporations, and all middle-class sentiment
during constant high economic growth period, but such trend seems
to approach its limit.
- However, after collapse of bubble economy we feel stagnation or
a kind of blockade in Japanese society; pressure of restructuring,
less children and more elderly people, or trend of avoidance of
science or technology by children.
- Regarding to English literacy, Japan ranks bottom among Asian
countries, which is worrying about communication literacy in Internet,
because 80% of its contents are in English. It must strengthen English
and computer literacy at the earlier stage of school.
- Expenses for education should be regarded as an investment for
the next generation and for the next society.
10. 教育の公的負担:
- 教育への公的投資という意味では、日本は、他の先進国が対GDP比率5%程度以上あるのに対し、日本は3.6%であり、際だって低い。
- 日本の教育は、高度成長期の経済規模の拡大、大企業のポスト拡大など一億総中流意識を反映して、子供は「頑張る」ことをインセンティブを感じ、親による熱心な教育熱に支えられてきたが、もはや限界にきているのではないか?
- しかし、バブル経済崩壊後の日本社会の閉塞感、リストラ圧力、少子高齢化の中で、学歴重視の風潮の中で、子供の「理科離れ」「工学部離れ」が顕著になってきた。
- また、英語力など国際的な比較においても日本はアジア諸国の中でも低位にあり、インターネットのコンテンツの80%以上が英語であるといわれる状況を鑑みると心配である。語学教育と情報教育は初等教育段階でもっと強化すべきであると思う。
- 教育は次世代を育成するという意味では、社会に対する投資として認識する必要があろう。
>Top 11. Globalization and skills level:
- This is a challenging chart of Globalization and skills labels.
- IT Technology brought us a
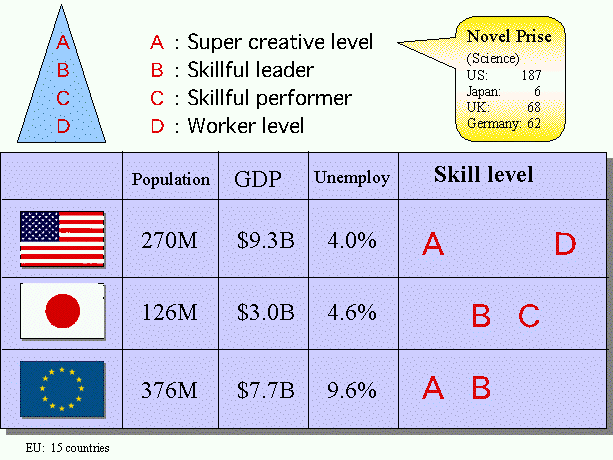 new era irrelevant to old regime, customs
and vested rights. People can interchange across the border and transact
globally. Information, in particular can circulated transcending time
and space difference; all these brought us more opportunities for
new challenges.
new era irrelevant to old regime, customs
and vested rights. People can interchange across the border and transact
globally. Information, in particular can circulated transcending time
and space difference; all these brought us more opportunities for
new challenges.
- Internet Age requires following three kinds of literacy:
- Information Literacy
- English Literacy
- Global Literacy
- In particular, Global Literacy requires following elements are needed:
- Ability of dialog in N:N debate
- Rich expression
- Clear point of argument
- Affluent content
- Imagination to understand a viewpoint of the partner.
11. グローバル化とスキルベレル:
- グローバル化とスキルレベルについてのイメージ図である。
- IT技術の進展に伴い、旧来の制度・習慣・既得権にとらわれない時代が到来した。また人々が国境を越え交流し、グローバル市場は増大している。特に情報は時間・空間を超越して流通
するようになり、総じて新たな挑戦の機会が増大した。インターネット時代には3つのリテラシィが要求される。
- Information Literacy
- English Literacy (日本は1998年のTOEFLで、アジア最下位だった。)
- それにGlobal Literacyである。
- 特に、Global Literacyについては、以下の5要素が必要となる。
- 対話能力、N対Nでの議論能力
- 豊かな表現力
- 明快な論旨
- 豊富な内容
- 相手の立場を理解する想像力
>Top 12. eGovernment in US:
- This is the idea of eGovernment in US (Federal Government).
- The concept of
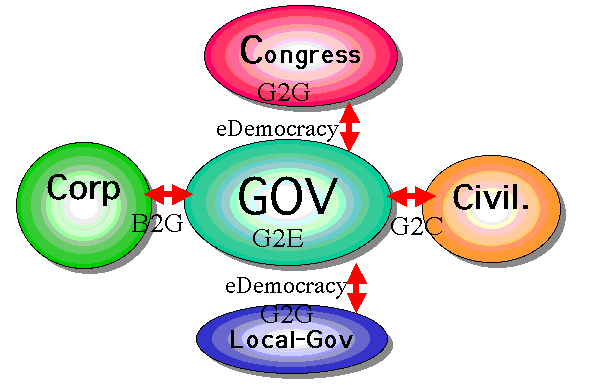 eGovernment in US has been realized in steady registrations.
Followings are the main policies for eGovernment;
eGovernment in US has been realized in steady registrations.
Followings are the main policies for eGovernment;
- NPR (National Partnership for Reinvestment Government), 1993
- GPRA (Government Performance & Result Act), 1993
- CIO at each office.....IT Management Reform Act, 1996
- Reduce of paperwork.....Government Paperwork Elimination Act,
1998
- Official announcement of eGovernment.....Memorandum for eGovernment,
1999
- Electronic Signatures in Global & Nation Commerce Act, 2000
- The above legislations aim:
- G2C (Government-to-Customer) Public Access
- G2C (Government-to-Customer) Transaction
- G2G (Government-to-Government) Procurement
- G2E (Government-to-Employee) Intranet
- G2G (Government-to-Government) Extranet
- eDemocracy
- All these steps show how serious eGovernment is promoted.
- The base of the above is 'Disclosure of Official Information Act'.
In Japan, such disclosure act becomes always controversial about the
extent of such disclosure. In principle all information should be
disclosed, and exceptions if any should be finally judged by judicature
where the administration is responsible for full accountability of
reasons of the nondisclosure.
12. 電子政府:
- 米国連邦電子政府の構想図 (Federal eGovernment)である。
- 米国での電子政府の構想は1993以来、着実な法制化をおこなってきた。主要な政策としては、
- NPR (National Partnership for Reinvestimen Governmnet) 1993
- GPRA (Government Performance & Result Act of 1993)
- 各省庁にCIO設置;IT Management Reform Act, 1996
- ペーパーワーク削減:Government Paperwork Elimination Act, 1998)
- 電子政府構想の発表:Memorandum for eGovernment, 1999
- 電子書名法:Electronic Signatures in Global & Nation Commerce Act,
2000
- そしてその機能としては、
- 情報公開・提供の電子化:G2C Public Access
- 行政手続きの電子化:G2C Transaction
- 政府調達の電子化:B2G Procurement
- 政府内業務の電子化:G2E Intranet
- 政府間業務の電子化:G2G Extranet
- 民主政治プロセスの電子化:eDemocracy
- 電子化を通じて、如何に着実にユーザサービスに徹しとしているかが感じられる。
その基礎になるのは情報公開制度である。日本では、いつもどこまで情報公開するのかが議論となるが、すべてを情報公開することを原則とし、それでない扱いをする場合は、その最終判断を第三者 (裁判等) に委ねるとともに、行政側が非公開の理由についての説明責任をもつことが必要である。
>Top 13. "Pyramid of Wealth":
- This is the design printed on the reverse of US one dollar
 note,
as referred in his bestseller book "Pyramid of Wealth"
written by Pro. Lester Thorow of MIT. This design is adopted by
President Roosevelt of US in 1931 just after the Great Depression
with the aim of encouraging people under the recession.
note,
as referred in his bestseller book "Pyramid of Wealth"
written by Pro. Lester Thorow of MIT. This design is adopted by
President Roosevelt of US in 1931 just after the Great Depression
with the aim of encouraging people under the recession.
- However, the design shows the Pyramid of Wealth is still under
construction. American resolution is described in Latin saying:
And the basement of the Pyramid is inscribed with 1776 in Roman
figures.
- ANNUIT COEPTIS
...........He [God] has favored our undertakings.
- NOVUS ORDO SECLORUM
...........a new order of the ages is born.
 By the way, US coin has following seal to emphasize 'unity among
diversity.'
By the way, US coin has following seal to emphasize 'unity among
diversity.'
- E PLURIBUS UNUM......... one out of many.
-
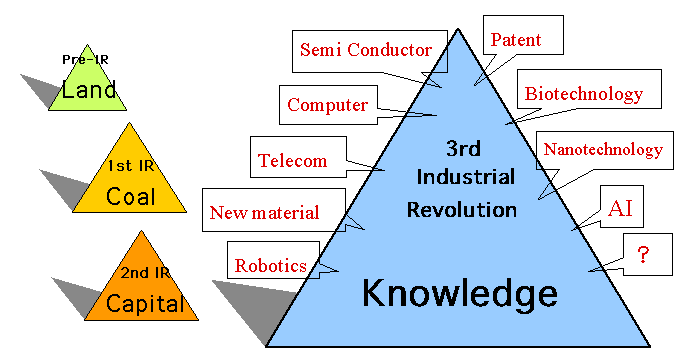
- The source of wealth before the Industrial Revolution
was 'Land', therefore, the battles for getting land were
repeated.
- After the First Industrial Revolution occurred
in Britain in 18th century, coal energy became the
source of this wealth. Coal production of Britain shared 85% in
the world, which led to the invention of steam engine.
- 20th century brought the Second Industrial Revolution,
featured with the development of automobile, steel, chemical and
aircraft industries together with various media like telephone,
radio, TV. Concentration of 'Capital' was the source of
this Second Industrial Revolution, which is typically concentrated
in US.
- >Now we are on the edge into the Third Industrial
Revolution, which is said Information Society.
- US of 1990s began with serious reflection of decline
of US industry in 1980s; but US still holds weak points in steady kaizen improvement, minimization of defectiveness, effective
vocational training, and increase of saving rate, etc. US Economic
growth in 1990s was 2.7% showing a little deterioration compared
with the averaged 3.2% in 1970s. Difference between wealth and
poverty spreads, which caused 'Digital Divide.'
- However, Japan shows averaged 0.4% throughout
1990s, and even negative growth in 1998-99 in particular. As a
result, nine US banks are ranked within worldwide best 10 banks,
while there was only one was nominated in the early 1990s.
In big industry ranking, 20 US corporations are nominated within
the worldwide best 25 corporations.
- Prof. Thurow, the author, describes; "As
we complete the third industrial revolution in the early 21st
century, the art of building a wealth pyramid will be just as
different from that in the twentieth century as today's real pyramid-building
would be from that thousands of years ago"
13."富のピラミッド":
- 左図は米国1ドル紙幣の裏面の図柄である。MITのレスター・ソロー教授の"富のピラミッド"の中に記述がある。
- この図案は、世界大恐慌の直後の1931年に当時のルーズベルト大統領が米国国民を、不況のどん底から鼓舞する目的で採用した。
- 曰く、米国にとっての富のピラミッドの建築はまだ完成していない。その企ては神の加護を受けて成功させようという決意が、ラテン語の表現に見られる。ピラミッドの土台にはローマ数字で
1776と刻まれている。
- ANNUIT COEPTIS
.....神は我らの企てに与し賜へり
- NOVUS ORDO SECLORUM
.....世紀の新秩序生まれる
- ちなみに米国のコインには、多様性の中の統一を強調する刻印がある。
- E PLIRIBUS UNUM........多くの中の一つ
- 産業革命以前の富の源泉は"土地" であっった。それ故、土地を巡る戦いが繰り返された"一所懸命"の時代であった。
- 18世紀英国に端を発した第一次産業革命は、石炭エネルギーがこの富の源泉となった。英国の石炭生産が世界の85%を占めており、蒸気機関の発明につながった。
- 20世紀は、第二次産業革命で位置づけられる。自動車、鉄鋼、化学産業、そして航空機産業が、生まれ電話・ラジオ・TVへとメディアも発展してきた。共通
する富の源泉は、米国を中心とする資本集中が富の源泉であった。
- そして我々は、新たな第三次産業革命と言われる情報化社会を迎えようとしている。
- 1990年代の米国は、80年代の米国産業衰退に対する深刻な反省から始まった。今でも、米国は、技術の着実な改良、不良品率の最小化、職業訓練の充実、貯蓄率の向上などでの弱点を抱えている。米国の経済成長率は、70年代の平均3.2%に比べ、90年代は2.7%
と若干低下している。貧富の差も拡大し、Digital Divideが指摘されている。
- にもかかわらず日本は、90年代を通じて0.4%成長でしかなく、特に98-99年度はマイナス成長となった。この結果、90年代初期に、世界のベスト10の銀行に米国は1行もなかったが、現在は9行がベスト10となった。世界25の大企業中に、98年には米国企業は20社を数える。
- サロー教授の表現では "21世紀の初めに第三次産業革命が達成されるのであれば、富のピラミッドの作り方は、20世紀の富のピラミッドの作り方が数千年前の実際のピラミッドの作り方と異なったように、別の作り方となろう。"
>Top 14. Three success factors of IT Revolution:
- I would suggest the following three elements to perform IT Revolution
in Japan toward 21st century. In Japanese tradition expression, it
can be said as 'Topological Advantage' , 'Members' Consensus',
and 'Providential Support':
14.IT革命成就の3要素:
- 21世紀を、目前に控え、日本のIT革命を成就するための条件を、日本的な3要素の発想でIT革命成就の3要素を考えると、「地の利」「人の和」そして「天の時」は以下のようになる。
1). Topological Advantage:
- It is
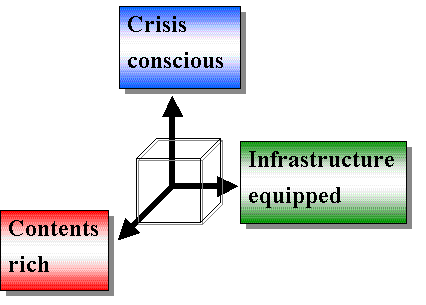 strategically important to confirm advantageous infrastructure
from the viewpoint of geopolitics. In Internet Age, it is equivalent
to environment for Internet connection.
strategically important to confirm advantageous infrastructure
from the viewpoint of geopolitics. In Internet Age, it is equivalent
to environment for Internet connection.
- During the Second Industrial Revolution required favorable environment
for telecommunication as well as traffic and port facilities. Similarly
the Third Industrial Revolution requires widerband, always-on connection
at economical cost in Internet environment.
- In addition, communication are of similar importance of local
connection as global connection. Architecture of Internet started
from LAN (Local Area Network), and local traffic needs prevail more
than remote communication; thus the viewpoint of 'Glocal' (Global
as well as Local) will be a key concept in Internet architecture.
- English Literacy will be another element which can be another
infrastructure in broad meaning. It is pointed out about 80% of
Internet content is published in English; bringing more globalized
technology and market, where bilingual expression will be must.
It is another advantage of bilingual expression which needs more
objective and logical way of thinking.
1). 地の利:
- これは、拠って立つべきポジション、有利なインフラストラクチャを築くことは、地政学上の要であった。今風に言えば、インターネット接続環境となる。過去の産業革命においても、交通、港と並んで通信の整備が重要であった。と同様に、第三次産業革命においても広帯域、常時接続、安価な定額料金の実現は必須である。今までの道路も電力も電話もまさにこの通信インフラを充実させるために基礎になる。また、通信はグローバルな視点と同時に、ローカルな接続をも重視する。インターネットがLANの接続から始まったように、通信インフラもローカルな接続ほど、より緊密となるような内なる情報化、即ち、分散協調的な"グローカル"な視点が重要である。
- 英語力も、情報化社会には広義のインフラとなる。世界のインターネットの情報の80%は英語によって情報発信されている。技術も市場も人々の交流もグローバル化してきている。表現方法も当然、バイリンガルになってくる。それに、バイリンガルな表現は、同時に客観性と論理的な発想という面で非常に役に立つ。
2). Members' Consensus:
- This means a large number of participation. It is information
contents which flow in Information infrastructure. Interactiveness
is such a typical feature of Internet enabling anyone to publish
easily his or her opinion. Until the invention of printing machine
in 15th century ordinary people could not possess a book. In 20th
century people began to have newspaper. Today's color television
started in 1960s, taking more than a decade to proliferate TV set
in each home.
- Now, more than 20 million people are using Internet in Japan,
and increasing more. Progress of media produces more message. There
is no defacto standard in the style of contents, which are always
diversified and personalized. When people acknowledge the benefit
of publishing via interactive media like Internet, everyone could
be Picasso, NY Times or CNN in Internet Age.
2). 人の和:
- これは、大勢の参加を意味する。情報インフラの中を流れるのは、情報コンテンツである。インターネットの最大の特徴は、インターラクティブ、即ち、誰もが容易に情報発信することができることにある。15世紀の活版印刷術の発明までは、誰もが本を所有することはできなかった。20世紀になってようやく人々は新聞を手にすることができた。今日のカラーTVの放送は1960年代になってから始まり、TV受像機が各家庭に普及するには更に10年以上を必要とした。今や、日本ではインターネットの利用者人口は2000万人を突破して、更に普及の勢いがある。メディアの進歩はより多くのメッセージを生み出す。コンテンツにデファクト・スタンダードはあり得ない。コンテンツは常に多様であり、個性的であった。それが安価な双方向メディアであるインターネットと結びつくとき、誰もがピカソ、誰もがNY
Times、誰もがCNNになれる可能性がある。
3). Providential Support:
- We should action NOW. Japan achieved miracle success in manufacturing
technology, organization and logistics, and tasted collapse of bubble
economy and unexpected restructuring. It is a good timing for IT
revolution to ripen. It is the creative destruction which throws
the old things and brings the new one; we need to be more conscious
about changing the present stagnating situation. With stronger consciousness,
we could open the door for future.
3). 天の時:
- 時は今...である。物作りの技術や組織・流通において、日本は奇跡の成功を遂げた。バブル経済の崩壊という敗戦も味わい、リストラクチャリングという現実も目の当たりにした。これほど革命が熟する条件が揃う時機はない。古いものが退場し、新しいものが誕生するのが「創造的破壊」であり、現在の閉塞状況を変えなければという危機感が必要である。その意識が強ければその分、未来の扉を力強く切り開くことができる。
Comment
- This is a presentation material prepared for explaining key factors
in IT industry in 2001
- これは2001年度のIT産業の主要点を説明するためのプレゼン資料である。
For IT Revolution in JapanRechallenge toward 21st century
|
Cat: ECOPub: 2001#0103 |
|
Kanzo Kobayashi |
01131u/18205r |
Title |
For IT Revolution in Japan |
IT革命の今日の課題 |
|---|---|---|
Subtitle |
Rechalleng toward 21st century | 21世紀に向けての日本の再チャレンジ |
Author |
Kanzo Kobayashi | 小林寛三 |
Published |
Jan. 2001 |
2001年1月 |
Index |
|
|
Why? |
|
|
Summary |
要約 |
>Top 1. IT Revolution is IP Revolution:
|
1. IT革命の本質はIP革命:
|
>Top 2. Japan-US IT imbalance:
|
2. 日米IT格差の原点:
|
>Top 3. Wideband usage for Internet connection:
|
3. インターネットの広帯域利用:
|
>Top 4. Internet proliferation rate per capita:
|
4. 今日の技術:
|
>Top 5. Cyber Korea-21:
|
5. 韓国のIT革命の現状:
|
> Top 6. Competitiveness of IT Industry:
|
6. IT産業の国際競争力:
|
> Top 7. Business Method Patent:
|
7. ビジネス・モデル特許:
|
> Top 8. Emergence of Swap Software:
|
8. スワップ・ソフトの隆盛:
|
>Top 9. Next Generation Type of Web Technology:
|
9. 次世代型WEB技術:
|
>Top 10. Public Investment to Education:
|
10. 教育の公的負担:
|
>Top 11. Globalization and skills level:
|
11. グローバル化とスキルベレル:
|
>Top 12. eGovernment in US:
|
12. 電子政府:
|
>Top 13. "Pyramid of Wealth":
|
13."富のピラミッド":
|
>Top 14. Three success factors of IT Revolution:
|
14.IT革命成就の3要素:
|
1). Topological Advantage:
|
1). 地の利:
|
2). Members' Consensus:
|
2). 人の和:
|
3). Providential Support:
|
3). 天の時:
|
Comment |
|
|